Introduction
Enhancing the performance of fan systems is essential for boosting energy efficiency and ensuring operational reliability across a range of applications. By exploring the fundamental principles of fan operation, engineers can identify strategies that not only optimize airflow but also address common performance challenges. The pressing question remains: how can organizations effectively implement these best practices to guarantee that their fan systems function at peak efficiency while minimizing downtime and costs?
To tackle this issue, it’s crucial to understand the underlying mechanics of fan systems. This knowledge empowers engineers to devise solutions that enhance performance and reliability. By adopting a systematic approach, organizations can streamline operations and achieve significant cost savings.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into actionable insights and proven strategies that can transform fan system performance. Stay tuned as we uncover the path to operational excellence.
Understand Fan System Fundamentals
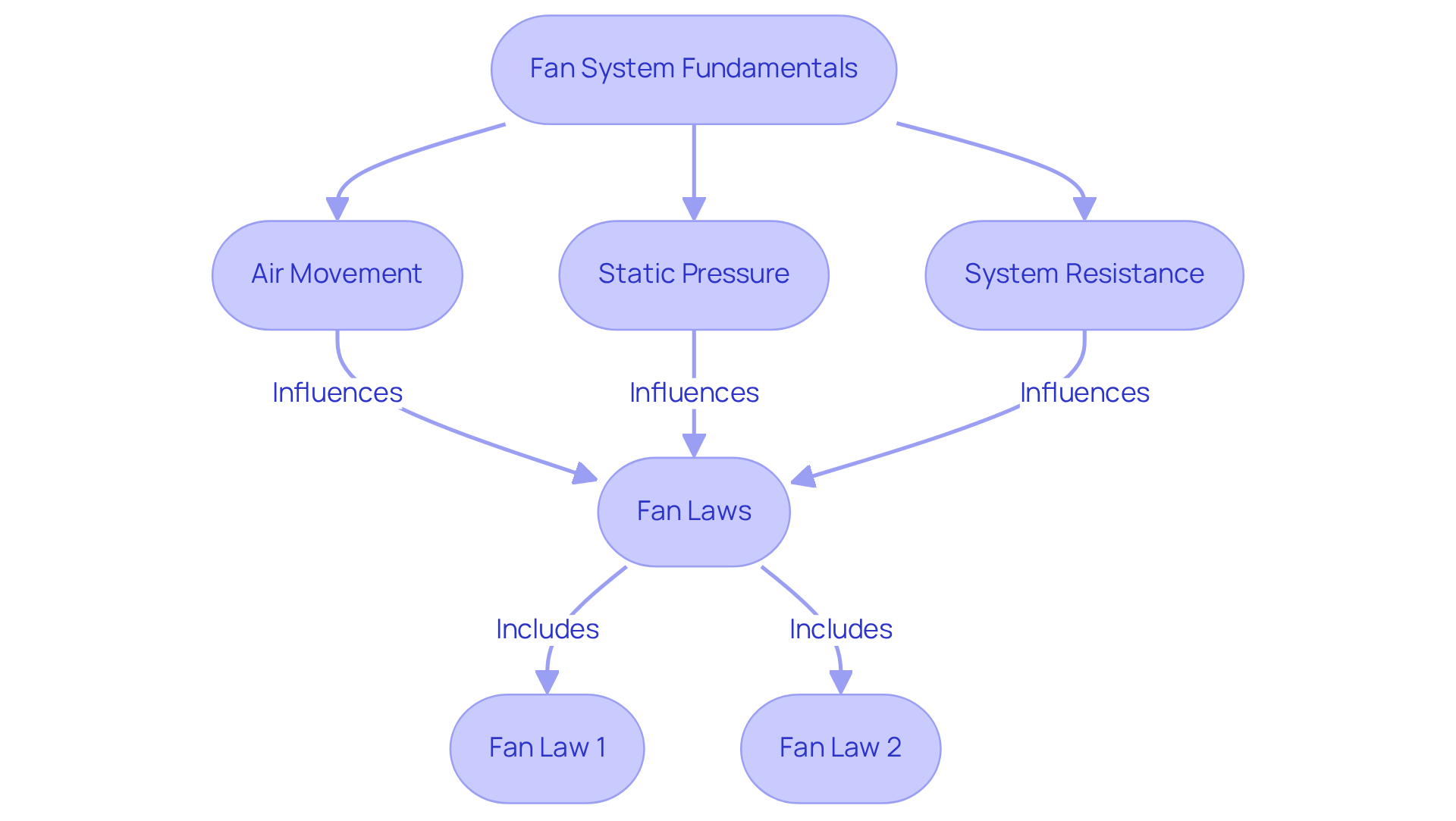
To improve fan system performance, it is essential to understand the fundamental principles governing fan operation, particularly within the context of Gagner-Toomey Associates’ extensive range of cooling solutions. Fans are engineered to circulate air, and their efficiency hinges on several factors, including air movement, static pressure, and system resistance. Mastery of fan laws is crucial, particularly the relationship between air movement and pressure. For instance, increasing the fan speed by 10% results in a corresponding 10% increase in airflow. However, the relationship between airflow and static pressure is more intricate; a 10% increase in airflow can lead to a 21% rise in static pressure, as illustrated by Fan Law 2.
Understanding fan curves, which depict characteristics at various operating points, is vital. These curves aid engineers in selecting the ideal fan for specific applications, ensuring both effectiveness and energy efficiency. Real-world applications of these principles underscore their significance. By applying Fan Law 1, a redesign of belt drive exhaust fans improved output from 15,000 CFM to 16,515 CFM by adjusting the propeller speed from 1000 RPM to 1101 RPM. Grasping these dynamics not only facilitates the selection of the appropriate fan but also plays a crucial role in improving fan system performance in the electronics sector.
Identify and Mitigate Performance Issues
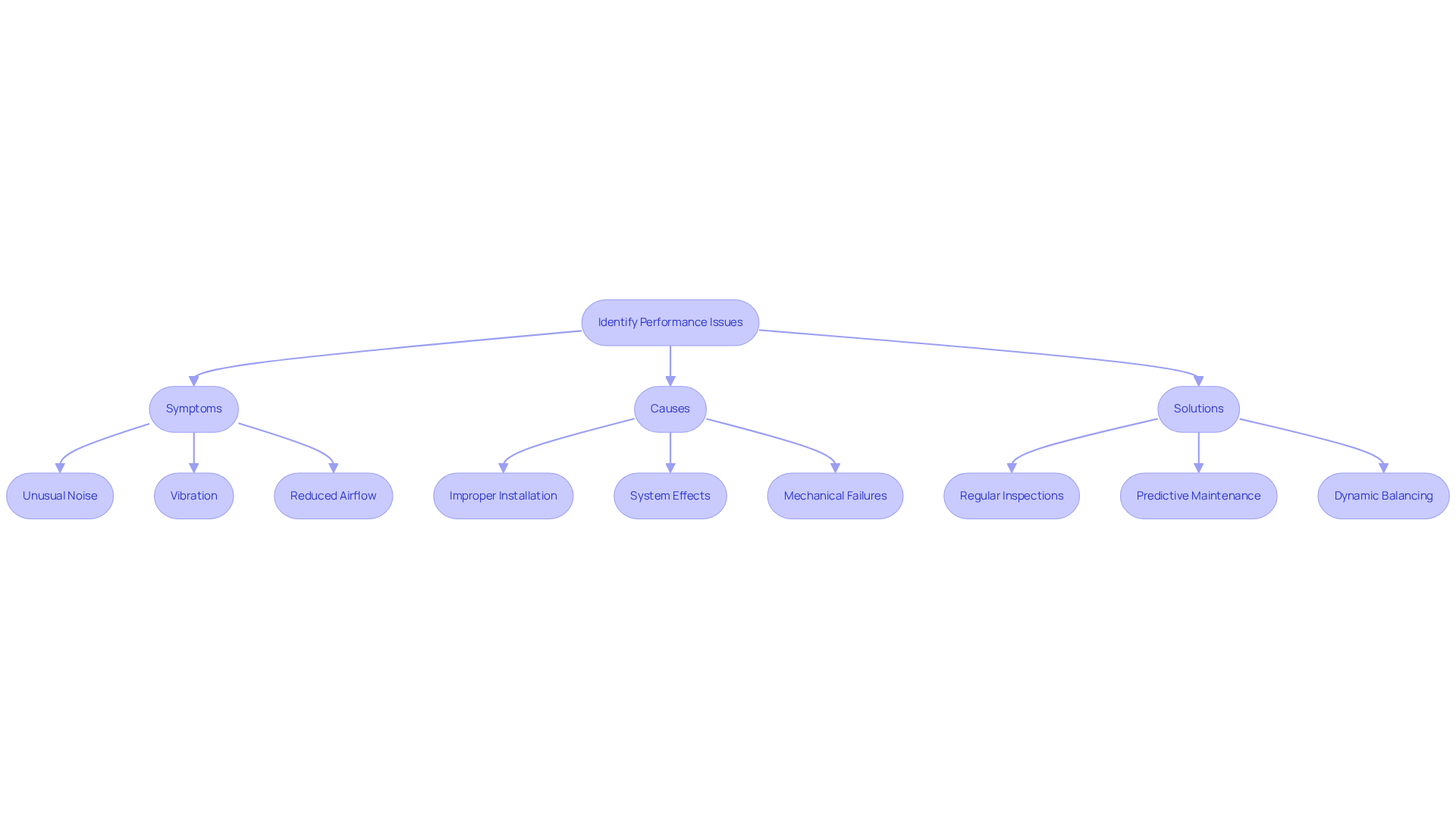
Performance issues in fan systems can stem from various sources, such as improper installation, system effects, and mechanical failures. These inefficiencies often manifest through unusual noise, vibration, and reduced airflow, signaling the need for immediate attention.
To address these challenges, regular inspections and evaluations are crucial. For instance, measuring static pressure at different points in the system can effectively identify blockages or leaks. Furthermore, ensuring that the fan is appropriately sized for the application is vital; oversizing or undersizing can lead to significant operational problems.
Implementing predictive maintenance strategies, including vibration analysis and thermal imaging, allows for the early detection of potential failures, preventing costly downtime. Additionally, inspecting for electrical issues is essential, as defective wiring or connections can cause overheating and disrupt fan operation.
Regular dynamic balancing is also recommended to mitigate excessive vibration, a leading cause of premature fan failure. By proactively addressing these factors, engineers can significantly contribute to improving fan system performance and longevity.
Optimize Fan Design and Components
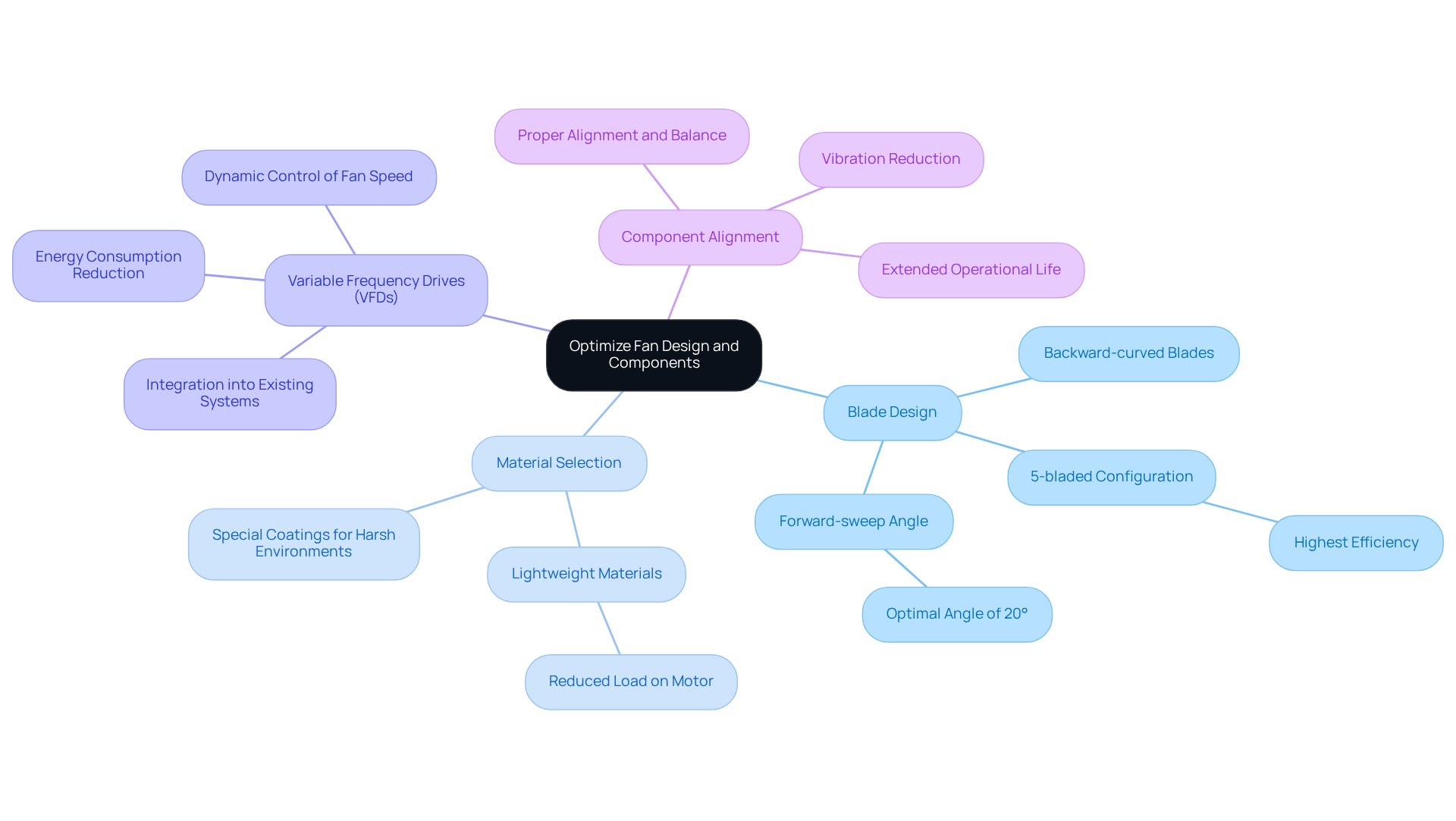
To enhance fan functionality, engineers must consider several critical design elements, including blade shape, material choice, and motor effectiveness, all aimed at improving fan system performance. Gagner-Toomey Associates offers an extensive range of DC input Tube Axial fans and Centrifugal Blowers, with sizes ranging from 15mm to 910mm, all optimized for performance and efficiency.
Key Considerations:
- Blade Design: Backward-curved blades significantly improve airflow while minimizing noise levels.
- Material Selection: Lightweight materials for fan blades reduce the load on the motor, thereby enhancing efficiency.
- Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): Implementing VFDs enables dynamic control of fan speed, which is essential for improving fan system performance by aligning airflow with demand and lowering energy consumption.
- Component Alignment: Proper alignment and balance of fan components reduce vibration and wear, extending operational life and decreasing maintenance costs.
Moreover, many models offer IP protection upon request, further enhancing their adaptability for various applications. With Gagner-Toomey’s innovative thermal management solutions, engineers can achieve superior cooling capabilities tailored to their specific requirements.
Implement Maintenance and Operational Best Practices
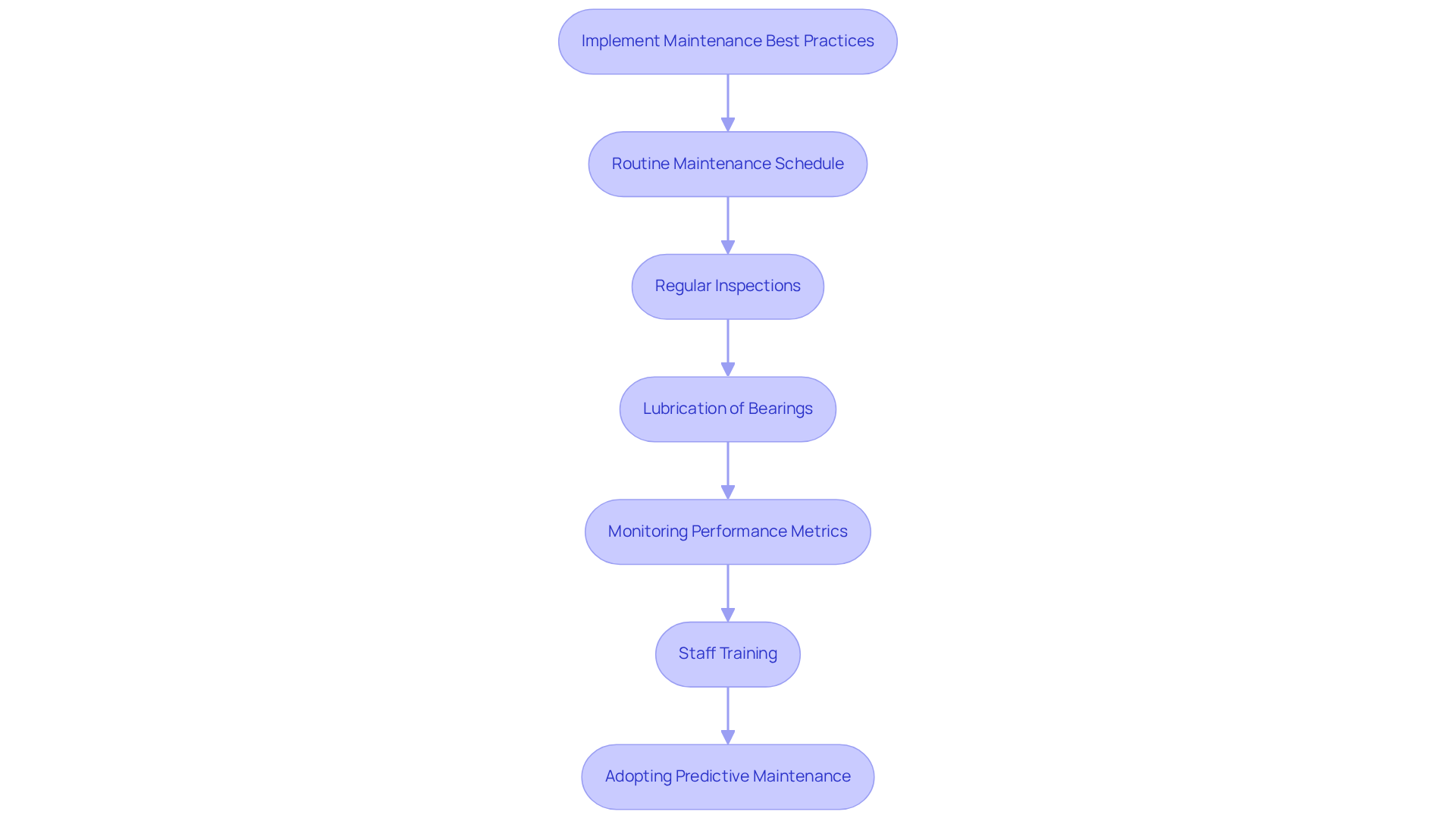
To achieve optimal fan operation, organizations must implement a structured routine maintenance schedule focused on improving fan system performance, which encompasses cleaning, lubrication, and thorough inspection of all components. Regular inspections for dust buildup on blades are essential; consistent maintenance is crucial for improving fan system performance by as much as 30%.
Ensuring that bearings are adequately lubricated is vital to prevent overheating and mechanical failures, which account for over 90% of motor failures due to defects in the stator, rotor, and bearings. Monitoring system performance metrics, such as airflow and static pressure, is essential for improving fan system performance by enabling early identification of deviations from expected performance, thus allowing for timely interventions.
Training staff on operational best practices, including maintaining clear access around fan inlets and outlets, can significantly boost overall efficiency. Furthermore, adopting a predictive maintenance program can contribute to improving fan system performance by proactively addressing potential issues before they escalate, ensuring continuous operation and minimizing costly downtime.
A compelling case study illustrates this point: a company operating in a hazardous location saw a significant reduction in fan-related incidents after implementing a regular maintenance and inspection schedule. This underscores the importance of these practices in maintaining safety and reliability. As noted by industry professionals, “The primary advantages of preventive maintenance come down to reliability. As you keep each asset in good repair, it’s less likely to break down.
Conclusion
Improving fan system performance is not just a goal; it’s a necessity that requires a deep understanding of fan operation principles and the implementation of effective strategies. By mastering the fundamental laws of airflow and pressure, engineers can make informed decisions that significantly enhance efficiency across various applications. This foundational knowledge is crucial for optimizing fan systems, ensuring they consistently operate at peak performance levels.
Key strategies include:
- Identifying and mitigating performance issues through regular inspections and predictive maintenance.
- Optimizing fan design and components for enhanced functionality.
- Establishing a routine maintenance schedule to prevent operational failures.
Each of these approaches plays a vital role in maximizing airflow, reducing energy consumption, and extending the lifespan of fan systems.
The significance of these best practices cannot be overstated. By adopting a proactive approach to fan system management, organizations not only enhance performance but also ensure safety and reliability in their operations. Embracing these strategies leads to improved efficiency, reduced downtime, and substantial cost savings. Therefore, it is imperative for engineers and facility managers to implement these insights to achieve optimal fan system performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the fundamental principles governing fan operation?
The fundamental principles governing fan operation include air movement, static pressure, and system resistance. Understanding these principles is essential for improving fan system performance.
How does fan speed affect airflow?
According to Fan Law 1, increasing the fan speed by 10% results in a corresponding 10% increase in airflow.
What is the relationship between airflow and static pressure?
The relationship between airflow and static pressure is more complex. For example, a 10% increase in airflow can lead to a 21% rise in static pressure, as described by Fan Law 2.
Why are fan curves important?
Fan curves are important because they depict the characteristics of fans at various operating points. They help engineers select the ideal fan for specific applications, ensuring effectiveness and energy efficiency.
Can you provide an example of applying fan laws in a real-world scenario?
An example includes a redesign of belt drive exhaust fans, where applying Fan Law 1 improved output from 15,000 CFM to 16,515 CFM by adjusting the propeller speed from 1000 RPM to 1101 RPM.
How does understanding fan dynamics benefit the electronics sector?
Grasping the dynamics of fan operation facilitates the selection of the appropriate fan, which plays a crucial role in improving fan system performance in the electronics sector.

