Introduction
In today’s world, understanding the complexities of fan speed control is crucial, especially as energy efficiency and performance optimization take center stage. This article explores the mechanisms behind fan speed controllers, focusing on techniques such as voltage control and pulse width modulation (PWM) that can significantly boost operational efficiency. Yet, a pressing question arises: how can engineers effectively choose and implement these methods to cater to the diverse demands of modern cooling systems? The insights provided here will illuminate the path to mastering fan speed regulation, ensuring optimal performance across various applications.
Explore the Principles of Fan Speed Control
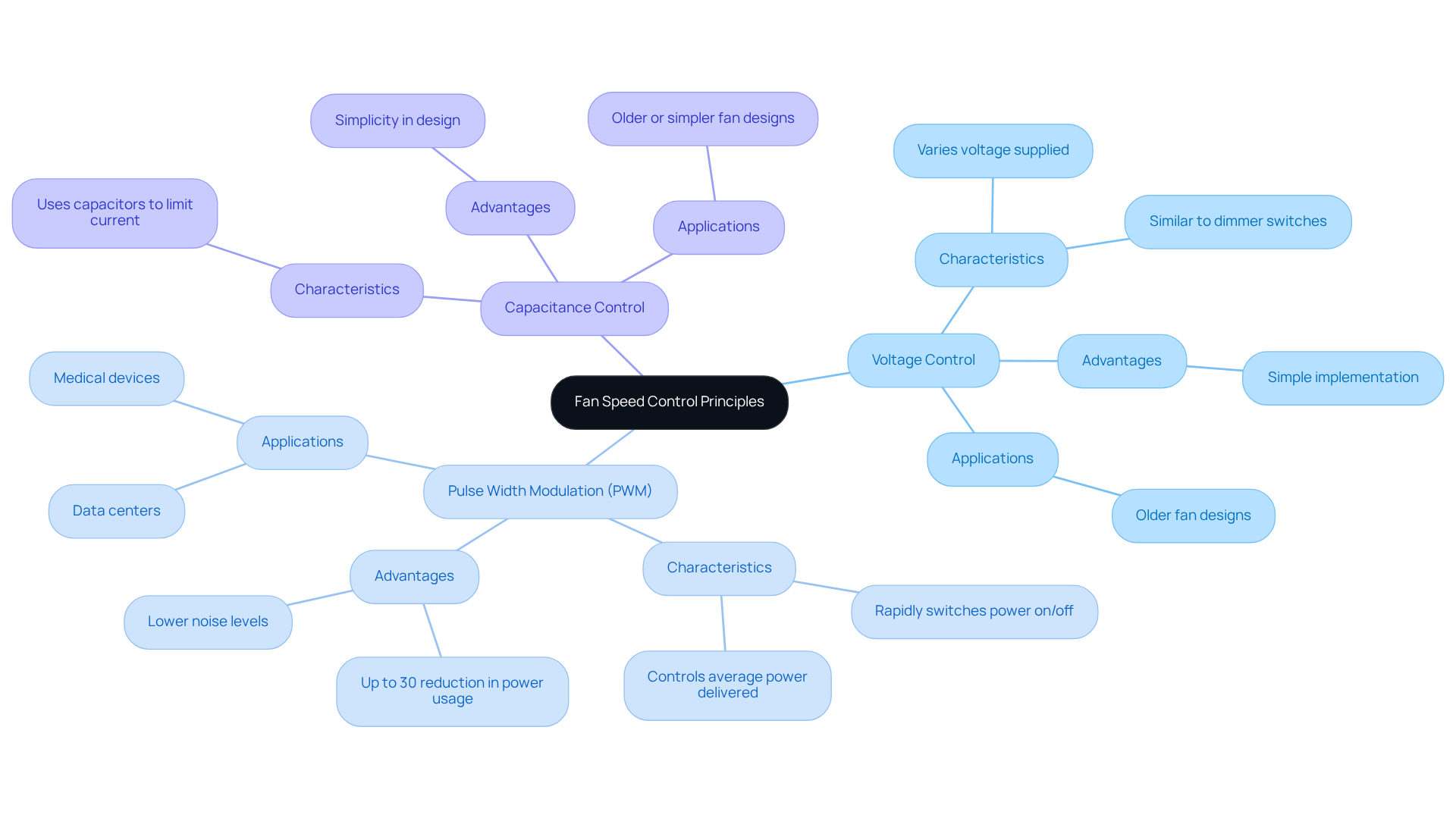
The operation of fan speed regulation is based on how a fan speed controller works by manipulating electrical signals to adjust the speed of the fan motor. Understanding how a fan speed controller works is crucial for optimizing performance and energy efficiency. Here are the most common techniques:
-
Voltage Control: This method varies the voltage supplied to the fan, similar to how a dimmer switch operates for lights. However, it can lead to inefficiencies, as it may not provide smooth speed regulation and can generate excess heat.
-
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM): PWM technology rapidly switches the power on and off to the fan, effectively controlling the average power delivered. This approach is highly effective, demonstrating up to a 30% reduction in power usage compared to conventional voltage management techniques. Additionally, PWM significantly lowers noise levels, making it ideal for noise-sensitive environments such as data centers and medical devices. For instance, ‘Gagner-Toomey Associates’ selection of DC input fans and blowers, available in sizes from 15 to 280mm, are optimized for performance and low noise, making them suitable for diverse applications.
-
Capacitance Control: Some fan controllers utilize capacitors to limit the current flowing to the fan, thereby controlling its speed. While this method is often found in older or simpler fan designs, it may not match the efficiency and performance of PWM.
Grasping these principles is vital for understanding how a fan speed controller works in selecting the appropriate fan management approach for specific applications, ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency. Practical applications of PWM technology have shown significant energy savings, with smart fan controllers achieving a 40% reduction in energy costs in manufacturing environments. This underscores the importance of adopting advanced control methods to enhance operational efficiency and sustainability.
Identify Different Types of Fans and Their Applications
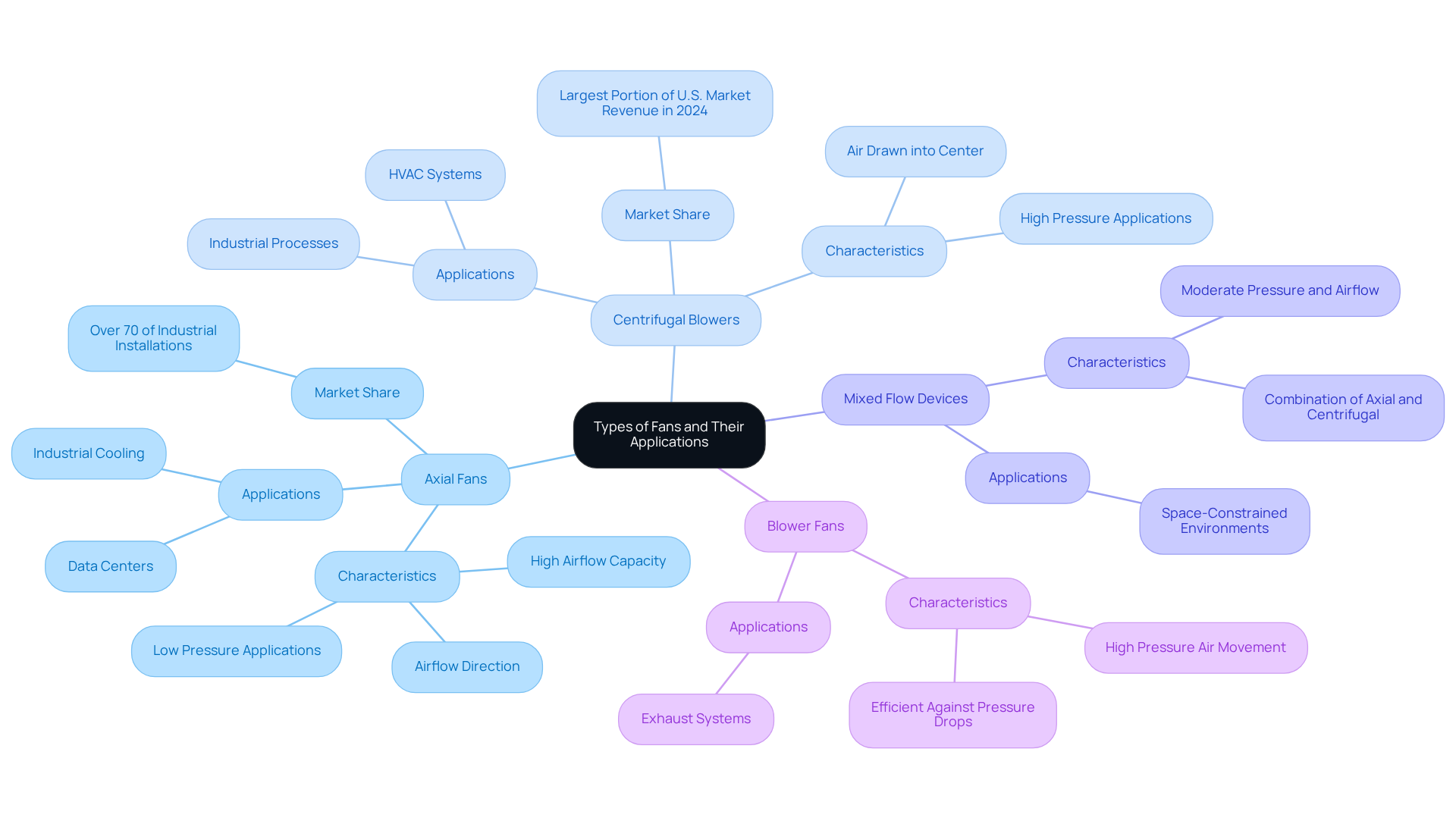
In the realm of cooling systems, various fan types serve distinct purposes, each tailored to specific applications:
-
Axial Fans: These fans operate by moving air parallel to their axis of rotation, making them highly effective in cooling applications. Their design allows for high airflow capacity, making them ideal for scenarios that require low pressure and high volume, such as in data centers and industrial cooling. Significantly, axial blowers represent over 70% of industrial installations for cooling, emphasizing their dominance in the sector.
-
Centrifugal Blowers: In contrast to axial types, centrifugal blowers draw air into the center and expel it at a right angle. This design is particularly suited for high-pressure applications, commonly found in HVAC systems and industrial processes. Their ability to maintain consistent airflow under varying conditions makes them essential in environments where air pressure is critical. The centrifugal blowers segment represented the largest portion of the U.S. industrial ventilation market revenue in 2024.
-
Mixed Flow Devices: These devices combine the features of both axial and centrifugal designs, offering versatility for moderate pressure and airflow requirements. They are frequently employed in scenarios where space is restricted but efficient airflow is still essential.
-
Blower Fans: Designed primarily for ventilation, blower fans move air at high pressure and are frequently used in exhaust systems. Their ability to manage high resistance renders them appropriate for uses necessitating efficient air movement against substantial pressure drops.
For engineers, understanding how a fan speed controller works and the characteristics and applications of these fan types is crucial. By selecting the appropriate fan, they can optimize performance and efficiency in various cooling systems, aligning with the growing demand for effective thermal management solutions across industries. The U.S. Industrial Fans Market is projected to be worth USD 1.73 billion by 2034, with a CAGR of 4.1% from 2026 to 2034, indicating a robust growth trajectory in the sector. Additionally, the EU cooling devices market is anticipated to expand at a CAGR of 11.0% from 2025 to 2035, further highlighting the rising demand for efficient cooling solutions.
Implement Effective Fan Control Techniques
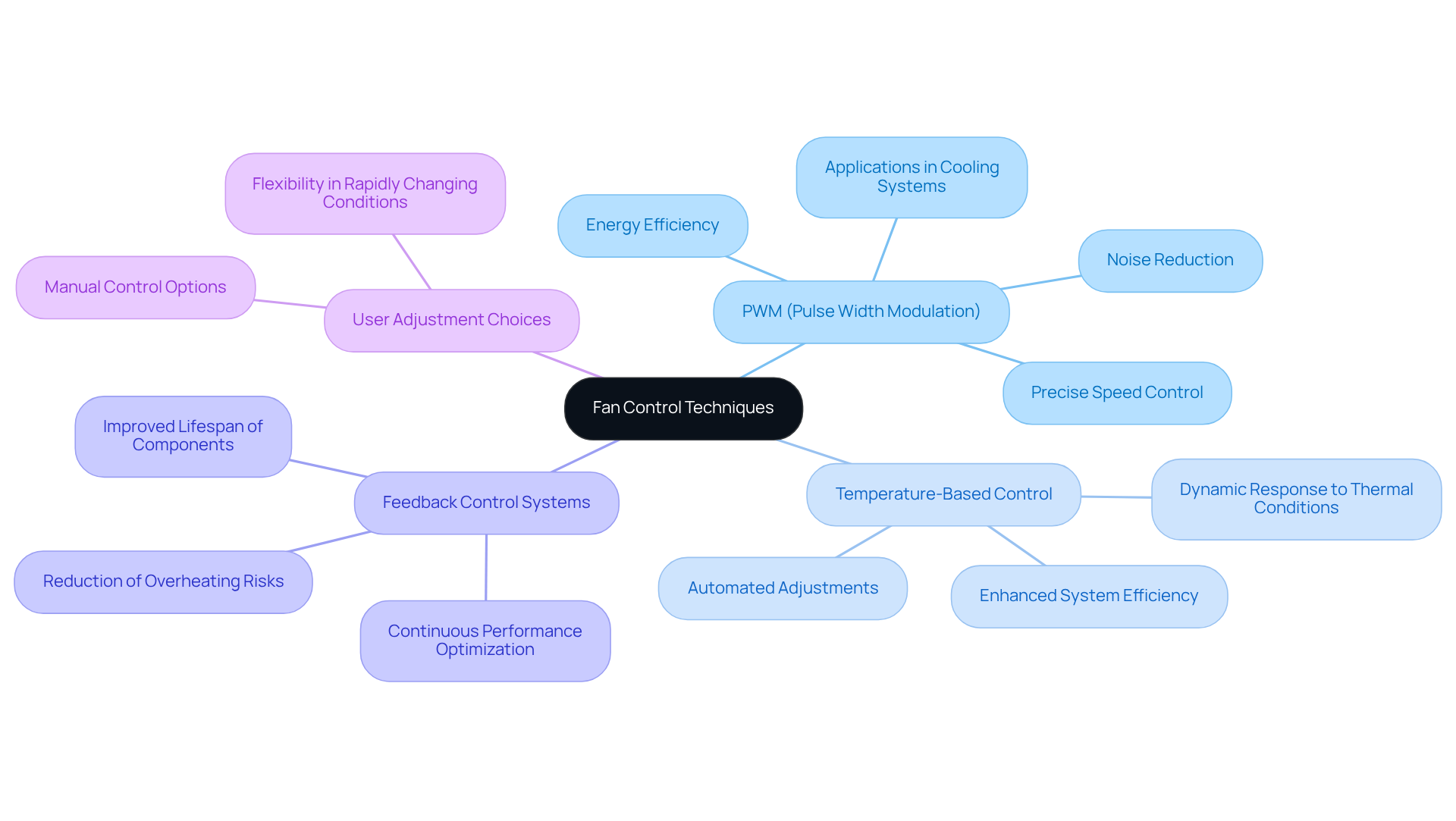
To effectively control fan speed, consider the following techniques:
-
Use of PWM: Implementing Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) allows for precise control over fan speed, significantly reducing energy consumption and noise levels. This method is particularly effective in computer cooling systems, where maintaining optimal temperatures is crucial. PWM units can achieve noise levels as low as 20 dBA, in contrast to conventional models that often exceed 30 dBA, making them ideal for noise-sensitive environments. Furthermore, PWM technology can reduce power consumption by as much as 30%, leading to lower energy costs.
-
Temperature-Based Control: Integrating temperature sensors enables automated fan speed adjustments based on real-time thermal conditions. This dynamic response enhances system efficiency and illustrates how a fan speed controller works, as PWM devices can adjust their speeds from 30% to 100% of their rated capacity, ensuring that cooling is applied only when necessary. Such systems have been shown to decrease Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) in data centers, highlighting their effectiveness in energy conservation.
-
Feedback Control Systems: Utilizing feedback loops helps maintain optimal performance by continuously adjusting fan speeds in response to changing environmental conditions. For instance, understanding how a fan speed controller works, PWM fans dynamically adjust speed in response to temperature fluctuations, ensuring critical components operate within safe limits and reducing performance degradation. This approach not only improves cooling efficiency but also prolongs the lifespan of electronic components by preventing overheating, which can lead to significant operational savings.
-
User Adjustment Choices: For situations that necessitate user involvement, offering manual adjustment options like knobs or switches enables swift modifications based on urgent requirements. This flexibility can be particularly beneficial in environments where conditions fluctuate rapidly, ensuring that engineers can respond effectively to varying thermal demands.
By applying these techniques, engineers can ensure that their fan systems operate efficiently, leading to reduced energy costs and improved overall performance.
Summarize Key Concepts in Fan Speed Control
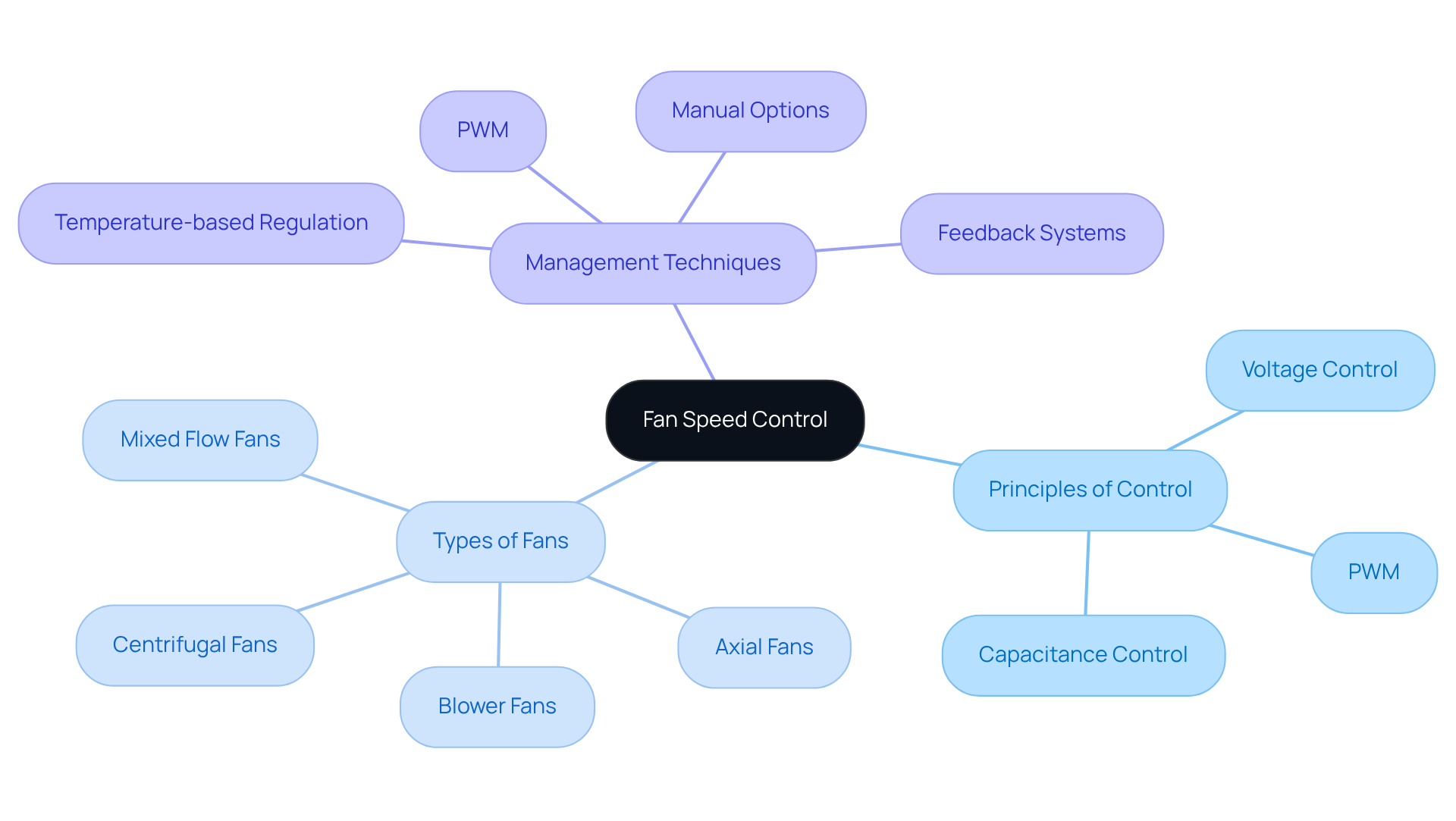
In summary, knowing how a fan speed controller works is crucial for enhancing performance across various applications. Understanding the following key concepts is essential:
- Principles of Control: Grasping voltage control, PWM, and capacitance control is vital for selecting the appropriate method for fan management.
- Types of Fans: Familiarity with axial, centrifugal, mixed flow, and blower fans is necessary to choose the right fan for specific applications.
- Management Techniques: To improve efficiency and performance, it is essential to understand how a fan speed controller works by implementing PWM, temperature-based regulation, feedback systems, and manual options.
By mastering these concepts, engineers can design and implement fan systems that meet the demands of modern electronic applications, ensuring both reliability and efficiency. The variable fan speed controller market is projected to reach approximately USD 2.5 billion by 2033, reflecting a CAGR of 8.9% from 2025 to 2033. This underscores the growing importance of effective fan control within the industry. As highlighted by Honeywell International Inc., the increasing demand for energy-efficient HVAC systems further emphasizes the relevance of these principles in today’s engineering landscape.
Conclusion
Understanding the mechanics behind fan speed controllers is crucial for optimizing performance and energy efficiency across various applications. By examining methods of fan speed regulation – such as voltage control, Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), and capacitance control – engineers can make informed decisions that enhance cooling systems and reduce energy costs. The significance of these technologies is paramount, as they play a vital role in achieving effective thermal management in modern engineering.
This article explores various techniques for fan speed control, emphasizing the advantages of PWM technology. Not only does PWM minimize energy consumption, but it also significantly reduces noise levels. Furthermore, selecting the appropriate fan type – axial, centrifugal, mixed flow, or blower fans – based on specific operational needs is essential. Implementing effective management techniques, including temperature-based control and feedback systems, ensures that cooling systems operate at peak efficiency.
As industries increasingly prioritize energy efficiency and sustainability, the insights shared here serve as a critical resource for engineers and decision-makers. Embracing advanced fan control methods is not merely a technical requirement; it is a strategic move towards enhancing operational efficiency and minimizing environmental impact. By leveraging these principles, stakeholders can contribute to a more sustainable future while meeting the demands of modern electronic applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of a fan speed controller?
A fan speed controller manipulates electrical signals to adjust the speed of the fan motor, optimizing performance and energy efficiency.
What is the voltage control method in fan speed regulation?
Voltage control varies the voltage supplied to the fan, similar to a dimmer switch for lights, but it can lead to inefficiencies and excess heat due to less smooth speed regulation.
How does Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) work for fan speed control?
PWM rapidly switches the power on and off to the fan, controlling the average power delivered. This method can reduce power usage by up to 30% compared to voltage management and significantly lowers noise levels.
What are the benefits of using PWM technology in fan controllers?
PWM technology provides energy savings, reduces noise levels, and is particularly suitable for noise-sensitive environments like data centers and medical devices.
What is capacitance control in fan speed regulation?
Capacitance control uses capacitors to limit the current flowing to the fan, controlling its speed, but it is often found in older or simpler designs and may not be as efficient as PWM.
Why is understanding fan speed control principles important?
Understanding these principles helps in selecting the appropriate fan management approach for specific applications, ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency.
What are the practical applications of PWM technology in terms of energy savings?
Practical applications of PWM technology have shown energy savings of up to 40% in manufacturing environments, highlighting the importance of advanced control methods for operational efficiency and sustainability.

