Overview
This article presents a systematic approach to diagnosing and rectifying fan noises through four essential steps:
- Identifying common noise types
- Diagnosing their sources
- Implementing effective solutions
- Establishing preventive maintenance practices
It underscores the importance of understanding the nature of fan noises—such as whirring, clicking, and grinding—as this knowledge enables engineers to accurately pinpoint issues and apply the appropriate fixes. Consequently, this not only enhances performance but also prolongs the lifespan of cooling systems.
Introduction
In the realm of cooling systems, fan noise transcends mere annoyance; it serves as a critical indicator of underlying mechanical issues that, if neglected, can precipitate significant operational challenges. The spectrum of sounds—from the steady whirring of a properly functioning fan to the alarming grinding of worn bearings—demands attention. Understanding these auditory cues is essential for engineers committed to maintaining optimal performance.
This article explores the prevalent types of fan noises, offers a systematic approach for diagnosing their origins, and delineates effective solutions to mitigate these disturbances. By prioritizing noise control and implementing preventive maintenance practices, organizations can enhance the efficiency of their cooling systems while fostering a more pleasant working environment.
Identify Common Types of Fan Noises
Recognizing typical varieties of fan noises is essential for diagnosing potential issues in cooling systems. The primary sounds you may encounter include:
- Whirring: This steady sound often indicates normal operation. However, if it becomes louder, it may signal misalignment or other mechanical issues.
- Clicking: Typically caused by loose blades or debris, clicking sounds can be intermittent and may worsen as the fan speed increases, suggesting a need for maintenance.
- Grinding: A grinding sound usually indicates worn bearings or a failing motor, signaling that the fan may be nearing the end of its operational life and requires immediate attention.
- Buzzing: This sound can stem from electrical interference or a failing motor. It may also occur if the fan is incorrectly installed, which can influence performance and lead to fan noises.
Rattling, frequently the result of loose screws or components, can be especially disruptive and may lead to additional mechanical issues if not addressed swiftly. Comprehending these fan noises enables engineers to identify fan-related problems efficiently. Research indicates that a significant portion of operational difficulties in electronics is linked to high-risk zones associated with fan noises, highlighting the necessity for effective sound control studies. For instance, statistics reveal that a major gap in typical operational challenges is concentrated in these high-risk areas.
Furthermore, a case study on fan design optimization demonstrated that structural modifications in blade design can enhance aerodynamic efficiency while significantly reducing sound levels. By prioritizing sound management, engineers can improve device performance and foster a more enjoyable working environment. Moreover, as Gagner-Toomey Associates notes, research suggests that the return on investment for enhanced cooling systems can be realized in approximately 8.58 years, highlighting the financial benefits of addressing fan sound concerns. This underscores the broader impact of efficient sound management strategies within the electronics sector.
Diagnose the Source of the Noise
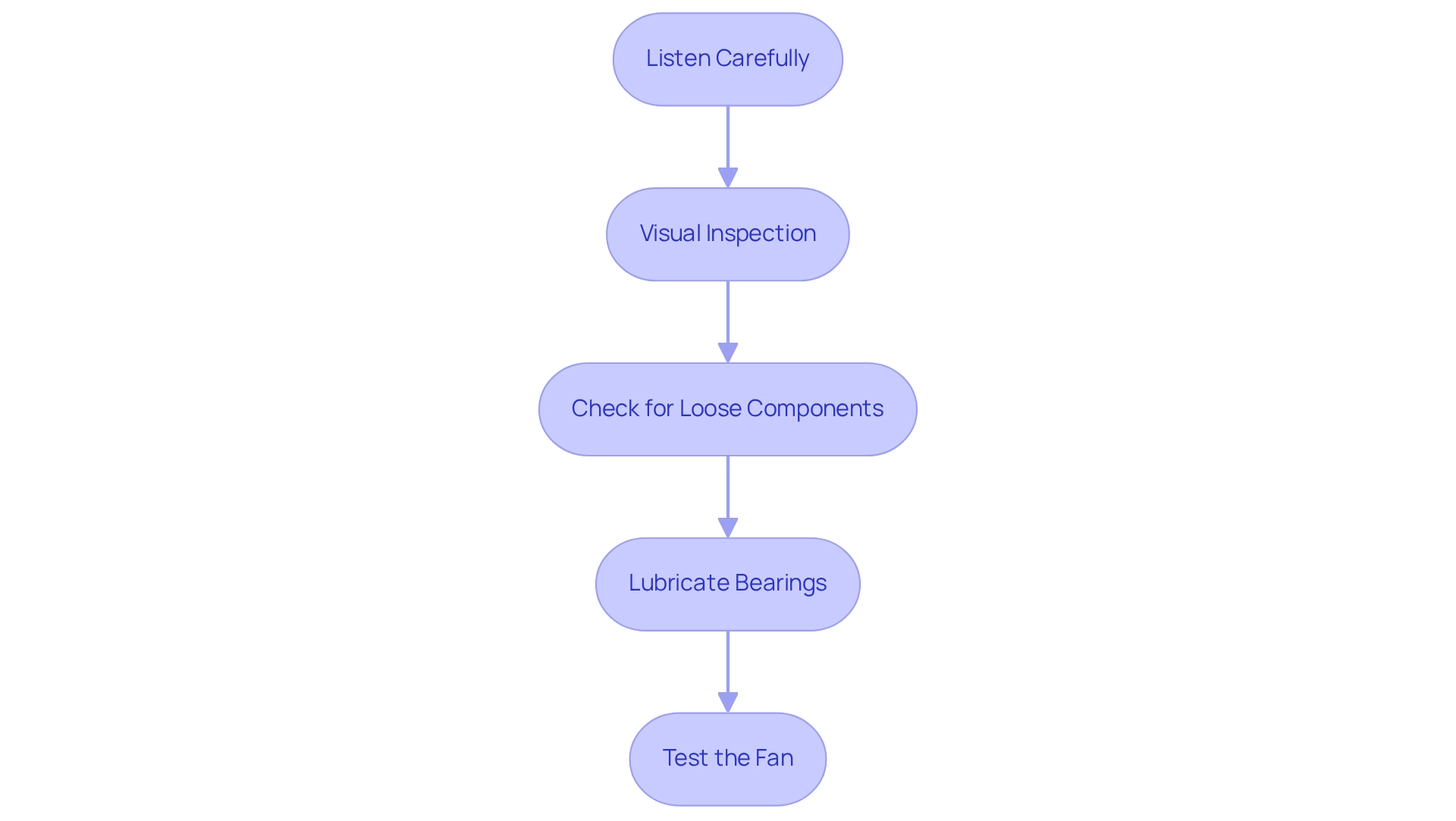
To effectively diagnose the source of fan noise, engineers should adhere to the following systematic steps:
- Listen Carefully: Begin by observing the fan during operation. Pay attention to the nature of the sound produced and the specific moments it occurs, such as at startup, during regular operation, or at shutdown.
- Visual Inspection: Power down the fan and conduct a thorough visual inspection. Look for any loose screws, damaged edges, or debris that could obstruct the fan’s movement.
- Check for Loose Components: Ensure all screws and bolts in the fan assembly are tightened. Verify that the fan blades are firmly connected to the motor to avoid vibrations that can result in sound.
- Lubricate Bearings: If the fan has bearings, apply a small amount of lubricant to reduce friction and sound. This step can often resolve grinding noises that may arise during operation.
- Test the Fan: After making the necessary adjustments, reactivate the fan to determine if the sound continues. If the sound persists, further inquiry may be necessary, including examining the motor or electrical connections.
By following these steps, engineers can effectively diagnose and address issues related to fan noises, ensuring optimal performance in their applications. As highlighted in a recent experimental study carried out in a small-scale low-speed aeroacoustic fan test rig, systematic troubleshooting methods are crucial for identifying and addressing sound-related issues effectively. Additionally, as Maria Isabel Rodrigues reminds us, “These quotes remind us of the passion, innovation, and dedication that drive the field of engineering forward.” This passion is essential when tackling challenges such as fan sound diagnosis, where innovative solutions can lead to significant enhancements in performance.
Implement Solutions to Fix Fan Noises
To efficiently address concerns about fan noises, implement the following solutions:
- Tighten Loose Screws: Ensure all screws on the fan components and housing are secure. This straightforward action can significantly reduce rattling and clicking sounds, which are types of fan noises.
- Balance the Fans: Balancing the fans is essential as unbalanced fan components can lead to excessive noise. Utilize a balancing kit to adjust the blades, thereby minimizing wobbling and the resulting fan noises.
- Clean the Fan: Accumulated dust and debris on the blades and motor can create disturbances. Regular cleaning with a soft cloth or compressed air is essential for optimal performance.
- Lubricate Moving Parts: Lubricating moving parts can help reduce fan noises by applying lubricant to motor bearings and other moving components to diminish friction and sound. Always use a lubricant recommended by the manufacturer for the best results.
- Replace Worn Components: If noise persists after these adjustments, it may be necessary to replace worn components, such as bearings or the motor itself.
In a recent case study on sound reduction strategies for telecommunications servers, the integration of advanced technologies resulted in a significant decrease in fan noises, demonstrating the effectiveness of systematic approaches to fan maintenance. This process spanned approximately six weeks, highlighting the time commitment required for effective sound reduction. Current studies on optimal design techniques for traction motor units further emphasize the importance of these solutions in enhancing operational environments. As Jack Killeen noted, ‘The directivity analysis provided in Section 5.2.3 presents two key findings,’ underscoring the necessity for continuous improvement in fan design and maintenance practices.
Establish Preventive Maintenance Practices
To effectively maintain fans and mitigate fan noises, it is crucial to implement preventive maintenance practices that ensure operational efficiency and longevity.
Regular cleaning of fan blades and housing every few months is important to eliminate dust accumulation, which can lead to increased fan noises and reduced efficiency. Poor maintenance strategies can reduce a company’s production capacity by as much as 20%, making regular cleaning essential for optimal performance.
- Inspect Components: Conduct periodic inspections of screws, blades, and electrical connections for signs of wear. Promptly replacing any damaged components is vital to maintain optimal performance. According to the case study titled “Benefits of Preventive Maintenance Programs,” 38% of maintenance assets are managed by preventive maintenance programs, underscoring the importance of routine inspections.
Lubricate the fan bearings at least once a year to ensure smooth operation and reduce fan noises. This simple step can significantly extend the lifespan of the fan, contributing to overall efficiency.
Monitor performance by staying vigilant for any changes in fan noises. Immediate investigation of unusual sounds can prevent further damage and costly repairs. Preventive maintenance minimizes unexpected equipment failures, which can lead to costly emergency labor callouts.
- Professional Servicing: Schedule professional maintenance every few years to ensure all components are functioning optimally. This proactive approach can address potential issues before they escalate, thereby reducing emergency labor callouts and enhancing overall reliability. As noted by the Professional Facility Management Institute, 50 percent of facility managers anticipated having open positions within their organizations in 2023, highlighting the critical need for skilled personnel in maintenance roles.
Implementing these practices not only minimizes unexpected equipment failures but also extends the life of your fans, contributing to a more efficient and quieter operational environment.
Conclusion
Recognizing and addressing fan noise is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and longevity of cooling systems. This article outlines common types of fan noises—whirring, clicking, grinding, buzzing, and rattling—each serving as a vital clue to potential mechanical issues. By diagnosing these sounds through careful listening, visual inspections, and systematic troubleshooting, engineers can pinpoint root causes and take action to resolve them.
Implementing effective solutions—such as tightening screws, balancing blades, cleaning components, lubricating moving parts, and replacing worn elements—can significantly reduce noise and enhance operational performance. Moreover, establishing a routine preventive maintenance program is essential. Regular cleaning, inspections, lubrication, and professional servicing not only mitigate noise but also prevent unexpected equipment failures, ultimately fostering a more pleasant working environment.
In summary, prioritizing fan noise management through proactive diagnosis and maintenance is essential for optimizing cooling system performance. By embracing these practices, organizations can enhance efficiency, prolong equipment lifespan, and create a more comfortable atmosphere for all. The investment in addressing fan noise issues reaps significant benefits, underscoring the importance of incorporating effective noise control strategies within engineering practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is it important to recognize different types of fan noises in cooling systems?
Recognizing typical varieties of fan noises is essential for diagnosing potential issues in cooling systems, enabling engineers to identify fan-related problems efficiently.
What does a whirring sound from a fan indicate?
A whirring sound often indicates normal operation; however, if it becomes louder, it may signal misalignment or other mechanical issues.
What causes clicking sounds in a fan, and what do they signify?
Clicking sounds are typically caused by loose blades or debris. They can be intermittent and may worsen as the fan speed increases, suggesting a need for maintenance.
What does a grinding noise from a fan usually mean?
A grinding sound usually indicates worn bearings or a failing motor, signaling that the fan may be nearing the end of its operational life and requires immediate attention.
What could cause a buzzing sound in a fan?
A buzzing sound can stem from electrical interference or a failing motor. It may also occur if the fan is incorrectly installed, which can influence performance and lead to fan noises.
What does rattling in a fan indicate, and why is it a concern?
Rattling is frequently the result of loose screws or components, which can be especially disruptive and may lead to additional mechanical issues if not addressed swiftly.
How does sound management impact the performance of cooling systems?
Prioritizing sound management can improve device performance and foster a more enjoyable working environment, as structural modifications in fan design can enhance aerodynamic efficiency while reducing sound levels.
What financial benefits are associated with addressing fan sound concerns?
Research suggests that the return on investment for enhanced cooling systems can be realized in approximately 8.58 years, highlighting the financial benefits of addressing fan sound concerns.

