Overview
To effectively power your 24V fan, it is essential to grasp its voltage and current requirements. This understanding ensures that the power source aligns with these specifications, preventing damage and optimizing performance. The article underscores the significance of selecting the appropriate power source—whether USB or AC—while offering detailed steps for connection and troubleshooting common issues. This comprehensive approach guarantees the reliable operation of the fan.
Introduction
In the world of electronics, effectively powering a 24V fan is crucial for achieving optimal performance and longevity. Understanding voltage and current ratings, alongside selecting the appropriate power source, are essential nuances that can significantly influence functionality. This article explores the critical aspects of fan power requirements, providing practical guidance on connecting and troubleshooting common issues that may arise.
Whether you choose a convenient USB setup or a more robust AC power source, mastering these fundamentals ensures that fans operate efficiently, accommodating a range of applications in both home and industrial settings.
Understand the Power Requirements of Your 24V Fan
To efficiently operate your fan, understanding the of your is paramount. Start by reviewing the fan’s specifications, typically found on its label or in the user manual. Key aspects to consider include the use of a 24V fan.
- Voltage Rating: Ensure that the 24V fan is rated for . Utilizing a higher voltage can result in irreversible damage.
- Current Rating: This is usually expressed in Amperes (A). For instance, if your fan has a rating of 0.5A, confirm that your at least this amount.
- Power Calculation: Use the formula: Power (Watts) = Voltage (Volts) x Current (Amps). For a 24V fan that consumes 0.5A, the energy requirement is 12 Watts, making it crucial to understand these specifications for selecting the appropriate energy source to avoid potential harm to your fan.
Recent assessments indicate that future-proofing configurations with not only reduces costs but also enhances versatility across various applications. For example, industry data suggests that employing capable of adapting to changing loads can improve efficiency by as much as 20%.
offers a comprehensive range of DC input devices and blowers optimized for performance and efficiency, making them suitable for diverse applications in electronics, automotive, and industrial sectors. Experts underscore the importance of grasping energy needs, particularly as the average typically ranges from 0.2A to 1.0A, depending on the fan’s size and application.
Practical examples of energy calculations can further illustrate this: a 24V fan rated at 0.75A would require a supply capable of providing 18 Watts (24V x 0.75A). Cautions to consider include ensuring that the supply’s output aligns with the 24V fan’s specifications to prevent overheating or malfunction. By ensuring that your energy source meets the fan’s requirements, you can optimize performance and reliability.
Moreover, case studies, such as those related to Ingersoll Rand’s R-Series Rotary Screw Air Compressors, highlight the critical role of , emphasizing the necessity for a thorough evaluation of in fan applications.
Choose Between USB and AC Power Sources
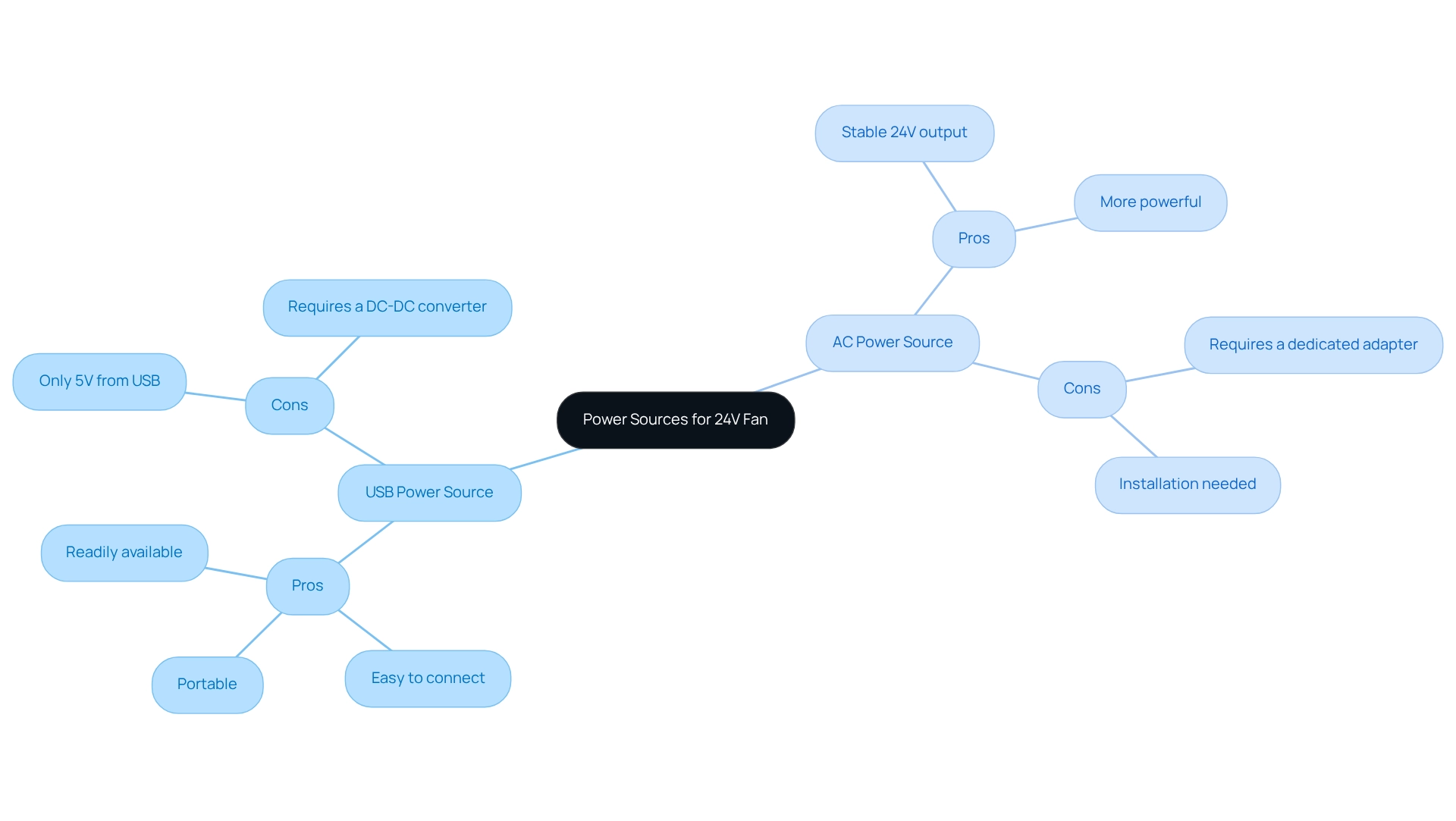
When using a , you can choose between USB and for powering it. Understanding the distinctions between these options is crucial for making an informed decision.
:
- Pros: This option is portable, easy to connect, and often readily available. It is ideal for small supporters or temporary arrangements.
- Cons: However, standard USB ports typically provide only 5V, necessitating a DC-DC converter to step up to 24V. It is essential to ensure that the converter can handle the of the 24V fan.
:
- Pros: In contrast, an AC power source provides a stable 24V output directly, making it suitable for permanent installations. This option is generally more powerful and can accommodate larger 24V fans.
- Cons: On the downside, it requires a dedicated energy adapter, which may occupy more space and necessitate proper installation.
When selecting your energy source, consider your application requirements carefully. Factors such as portability, , and installation difficulty should guide your choice, ensuring optimal performance for your specific needs.
Connect and Power Your Fan: Step-by-Step Instructions
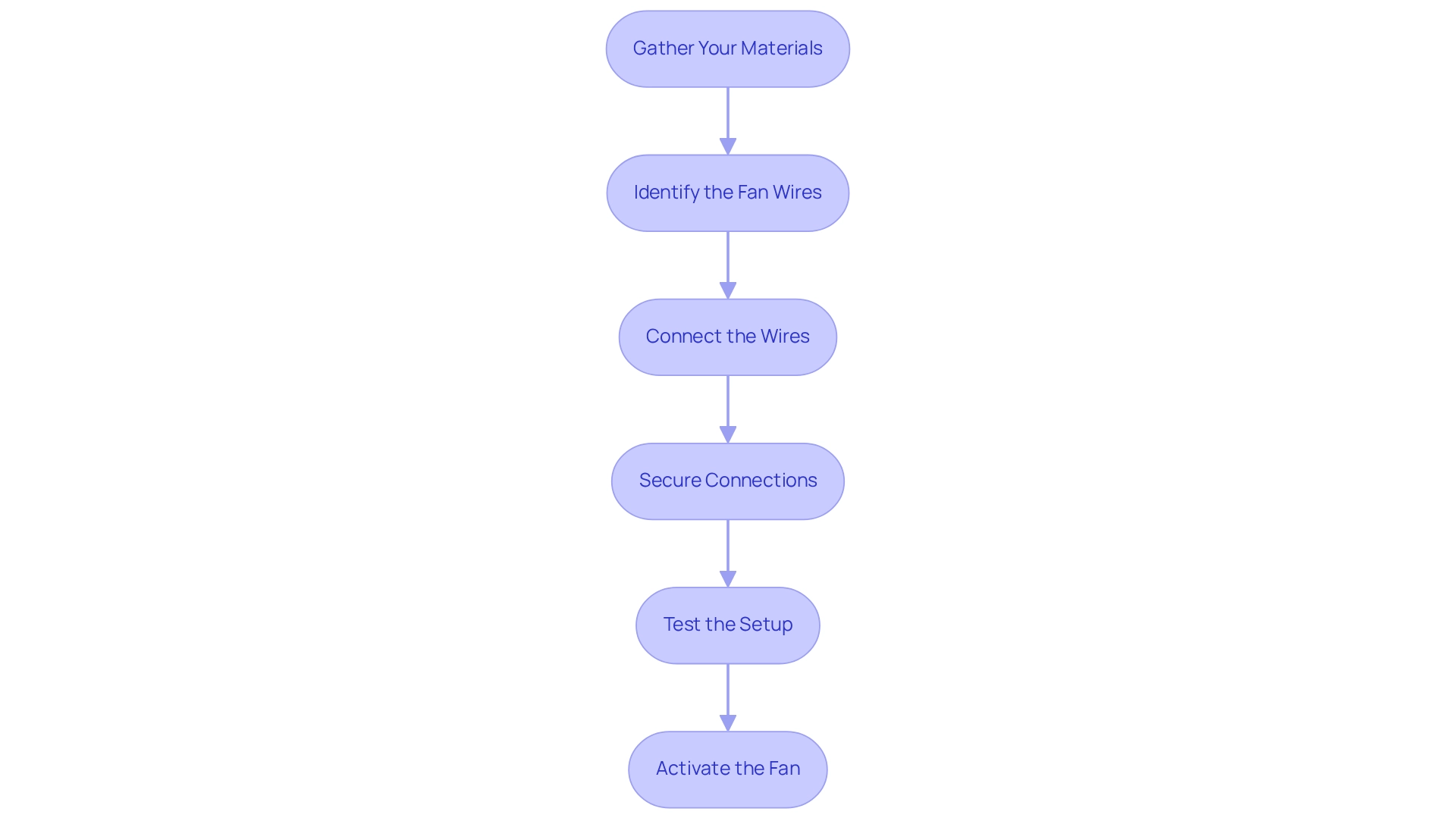
To effectively connect and power , follow these essential steps:
- : Begin by collecting the necessary components: a , a (either a USB with a converter or an AC adapter), connecting wires, a soldering iron (if required), and a multimeter for testing.
- Identify the Fan Wires: Typically, your fan will feature two wires: a positive wire, often red, and a negative wire, usually black. Always refer to the fan’s documentation to confirm this configuration.
- : If you are utilizing an AC adapter, connect the positive wire from the fan to the positive output of the adapter and the negative wire to the negative output. Alternatively, if you are using a USB converter, connect the fan’s positive wire to the output of the converter and the negative wire to the ground.
- : It is crucial to ensure that all connections are secure. For a permanent setup, use soldering; for a temporary solution, connectors are appropriate.
- : Prior to powering on the fan, employ a multimeter to verify the voltage at the fan’s terminals, ensuring it receives the required 24V. Once confirmed, activate the 24V fan and monitor its operation. By meticulously following these steps, you can successfully connect and operate it.
Troubleshoot Common Issues When Powering Your Fan
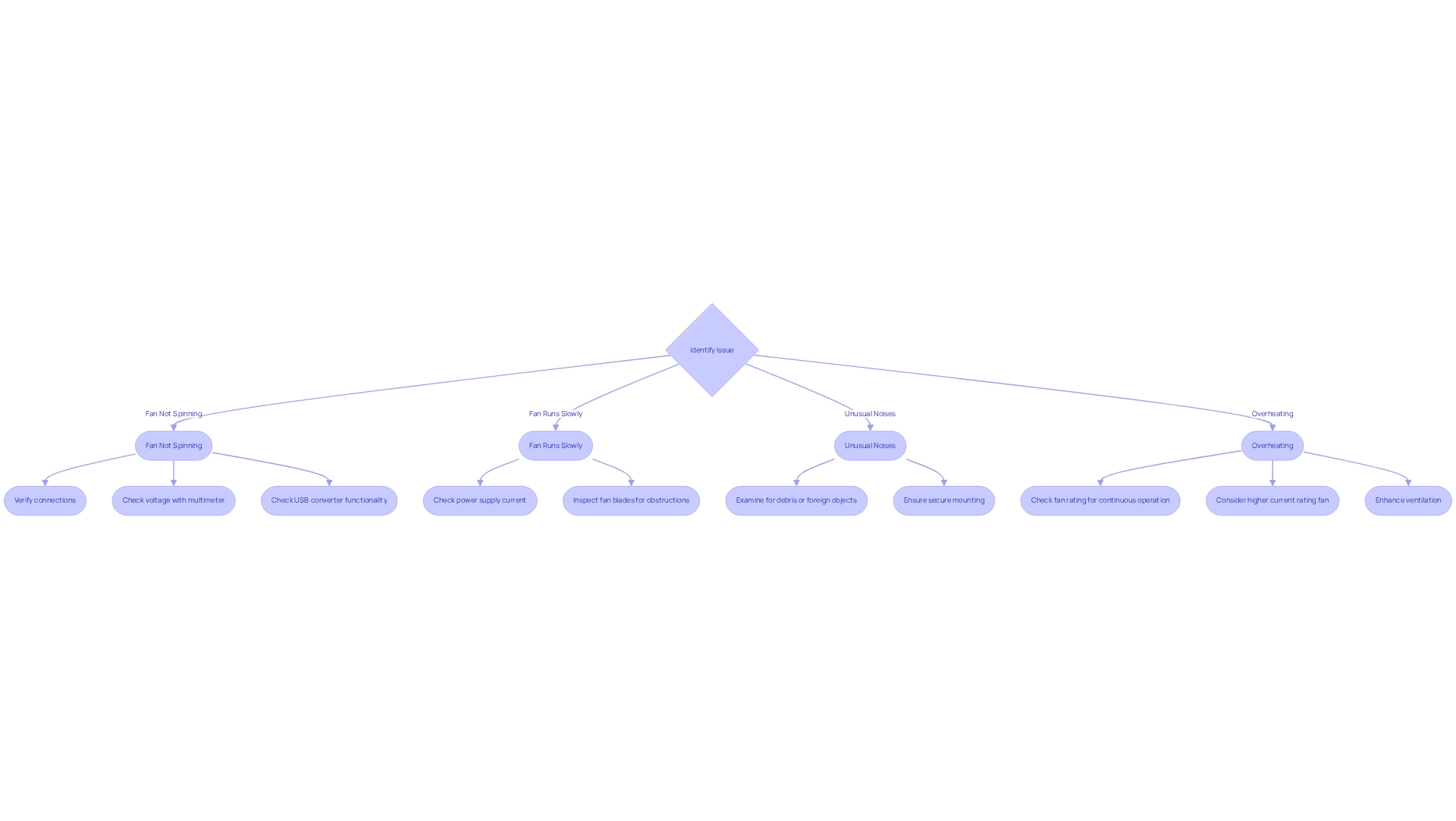
If you encounter issues while operating your , consider the following troubleshooting tips:
-
Fan Not Spinning:
- Verify all connections to ensure they are secure and correctly wired.
- Utilize a multimeter to confirm that the fan is receiving the necessary 24V.
- If employing a USB converter, ensure it functions correctly and can handle the required current.
-
- Confirm that the meets the fan’s current requirements. An underpowered supply may prevent the fan from operating at full speed.
- Inspect for any obstructions in the fan blades that could impede movement.
-
:
- Examine the fan for debris or foreign objects that may be generating noise.
- Ensure the fan is mounted securely and not vibrating against other surfaces.
-
Overheating:
- Verify that the fan is rated for continuous operation at the supplied voltage. If overheating occurs, consider using a fan with a higher current rating or enhancing ventilation around the 24V fan.
By adhering to these troubleshooting steps, you can effectively address common issues and ensure your fan operates smoothly.
Conclusion
Understanding how to effectively power a 24V fan is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. The key takeaways from this article emphasize the importance of grasping the fan’s power requirements, including voltage and current ratings, as well as the selection of an appropriate power source. Whether opting for a USB or AC power setup, each choice presents its advantages and considerations that must align with the intended application.
Connecting and powering the fan involves a straightforward process, where careful attention to wire connections and testing with a multimeter ensures the fan receives the correct voltage. Additionally, troubleshooting common issues such as slow operation or unusual noises can help maintain the fan’s efficiency and reliability.
In conclusion, mastering these fundamentals not only enhances the functionality of a 24V fan but also safeguards against potential damage caused by improper power supply choices. By applying the insights shared in this article, users can confidently navigate the complexities of fan power requirements, leading to improved performance in both home and industrial settings.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is it important to understand the energy requirements of a 24V fan?
Understanding the energy requirements is crucial to ensure the fan operates efficiently and to avoid potential damage. This includes knowing the voltage and current ratings needed for proper functionality.
What should I check regarding the voltage rating of my 24V fan?
Ensure that the fan is rated for 24V DC. Using a higher voltage can cause irreversible damage to the fan.
How is the current rating of a fan expressed, and why is it important?
The current rating is usually expressed in Amperes (A). It is important because your energy source must be able to deliver at least this amount to operate the fan effectively.
How do I calculate the power requirement for a 24V fan?
Use the formula: Power (Watts) = Voltage (Volts) x Current (Amps). For example, a 24V fan consuming 0.5A requires 12 Watts of power.
What is the typical current rating range for 24V fans?
The average current rating for a 24V fan typically ranges from 0.2A to 1.0A, depending on the fan’s size and application.
What are the potential consequences of not aligning the energy supply with the fan’s specifications?
If the energy supply does not align with the fan’s specifications, it can lead to overheating or malfunction of the fan.
How can future-proofing configurations with replaceable energy sources benefit fan operations?
Future-proofing with adaptable supply units can reduce costs and enhance versatility across various applications, potentially improving efficiency by up to 20%.
Can you provide an example of energy calculations for a 24V fan?
For a 24V fan rated at 0.75A, the required power supply would be 18 Watts (calculated as 24V x 0.75A).
What kind of devices does Gagner-Toomey Associates offer related to 24V fans?
Gagner-Toomey Associates offers a range of DC input devices and blowers optimized for performance and efficiency suitable for electronics, automotive, and industrial applications.
What is emphasized in case studies regarding the energy management of fans?
Case studies, such as those related to Ingersoll Rand’s R-Series Rotary Screw Air Compressors, highlight the importance of effective energy management and thorough evaluation of energy specifications in fan applications.

