Overview
To source quality heat pipes for sale, it is essential to adopt a structured approach. This process involves:
- Researching reputable manufacturers
- Evaluating product specifications
- Requesting samples
- Checking reviews
- Exploring tailored solutions
By following these steps, one can ensure a thorough assessment of potential suppliers. The importance of assessing thermal performance, compatibility, and supplier reliability cannot be overstated; these criteria are pivotal for ensuring optimal product functionality and customer satisfaction. This article outlines these specific criteria for selection, guiding readers toward making informed decisions in their procurement process.
Introduction
Understanding the intricacies of heat pipes is essential for professionals engaged in thermal management solutions, particularly within the fast-paced electronics industry. This guide provides a definitive pathway to sourcing quality heat pipes, emphasizing critical selection criteria and effective strategies for navigating the marketplace. Given the multitude of manufacturers and specifications to consider, the question arises: how can one ensure the selection of the optimal option that satisfies both performance and budgetary requirements?
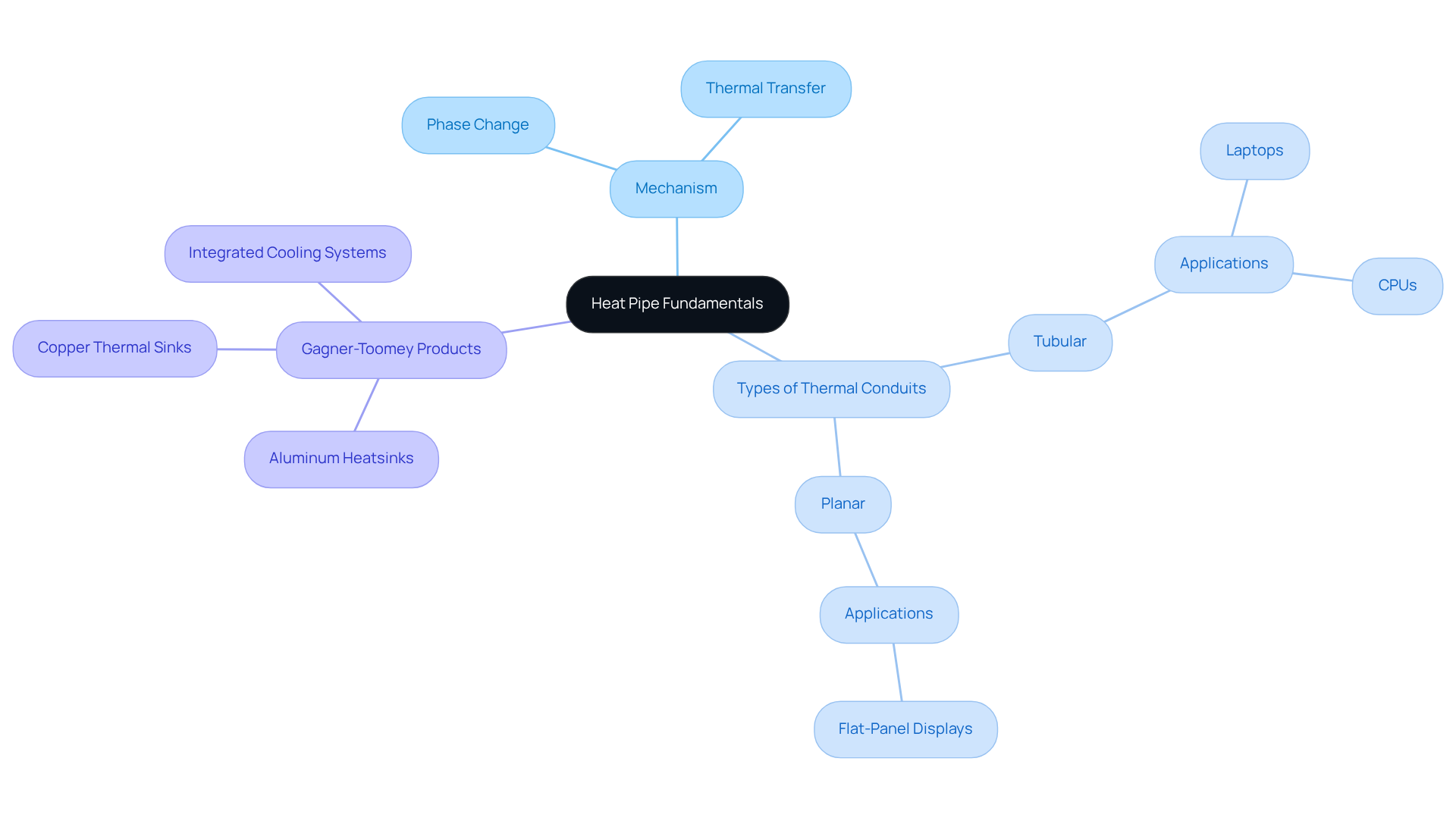
Understand Heat Pipe Fundamentals
Thermal pipes represent advanced temperature control devices that harness the principles of phase change to facilitate efficient energy transfer. These systems consist of a sealed vessel containing a working fluid, typically water, which evaporates at the heat source and condenses at the cooler end. This mechanism allows for rapid thermal transfer with minimal temperature loss.
Understanding the different types of thermal conduits, such as tubular and planar designs, along with their , is crucial. For instance, tubular thermal conduits are commonly employed in laptops and CPUs, while planar thermal conductors are widely used in flat-panel displays.
Gagner-Toomey Associates stands as the world’s largest supplier of thermal management solutions for electronics cooling, offering a diverse range of innovative cooling options, including:
- Extruded aluminum heatsinks
- Copper-based thermal sinks
- Integrated cooling systems
Familiarizing yourself with these fundamentals and exploring Gagner-Toomey’s extensive product offerings, which include various sizes and types of air-movers, will aid in selecting the optimal thermal solution tailored to your specific needs.
Evaluate Key Selection Criteria
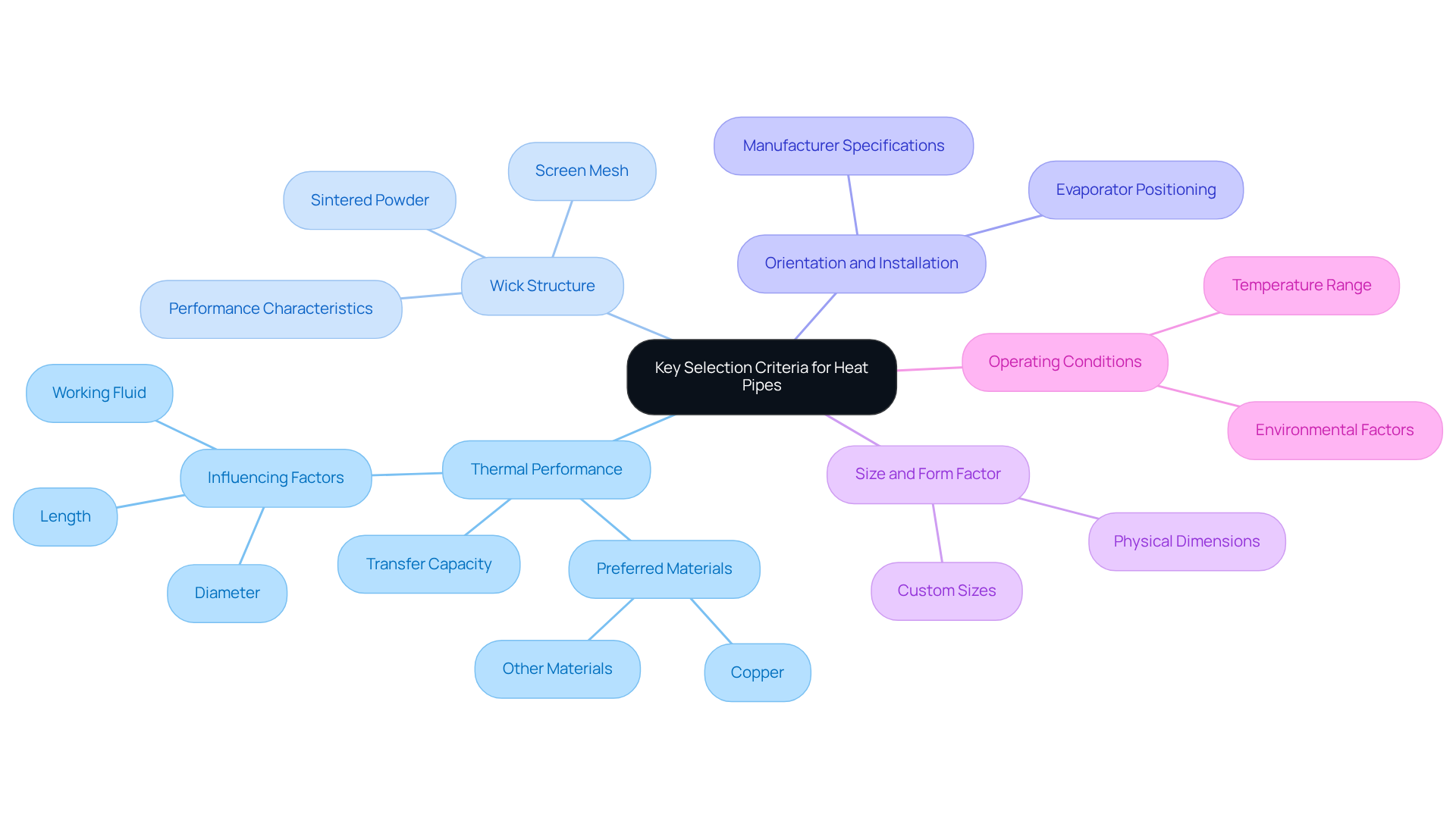
When sourcing heat pipes, it is essential to consider the following key selection criteria:
- Thermal Performance: Evaluate the transfer capacity of thermal energy, which is influenced by the diameter, length, and the working fluid utilized. Materials with superior thermal conductivity, such as copper, are preferred for optimal results.
- Wick Structure: The design of the wick significantly impacts the within the heat channel. Common wick structures, including sintered powder and screen mesh, each provide distinct performance characteristics.
- Orientation and Installation: Heat conduits operate most efficiently when positioned correctly, typically with the evaporator located below the condenser. It is crucial to ensure that the installation adheres to the manufacturer’s specifications to maximize efficiency.
- Size and Form Factor: Assess the physical dimensions of the thermal conductor to confirm compatibility within the design constraints of your application. Custom sizes may be necessary for specialized configurations of heat pipes for sale.
- Operating Conditions: Consider the temperature range and environmental factors that the thermal conduit will encounter, as these elements can significantly influence the selection of working fluid and materials.
Source Quality Heat Pipes
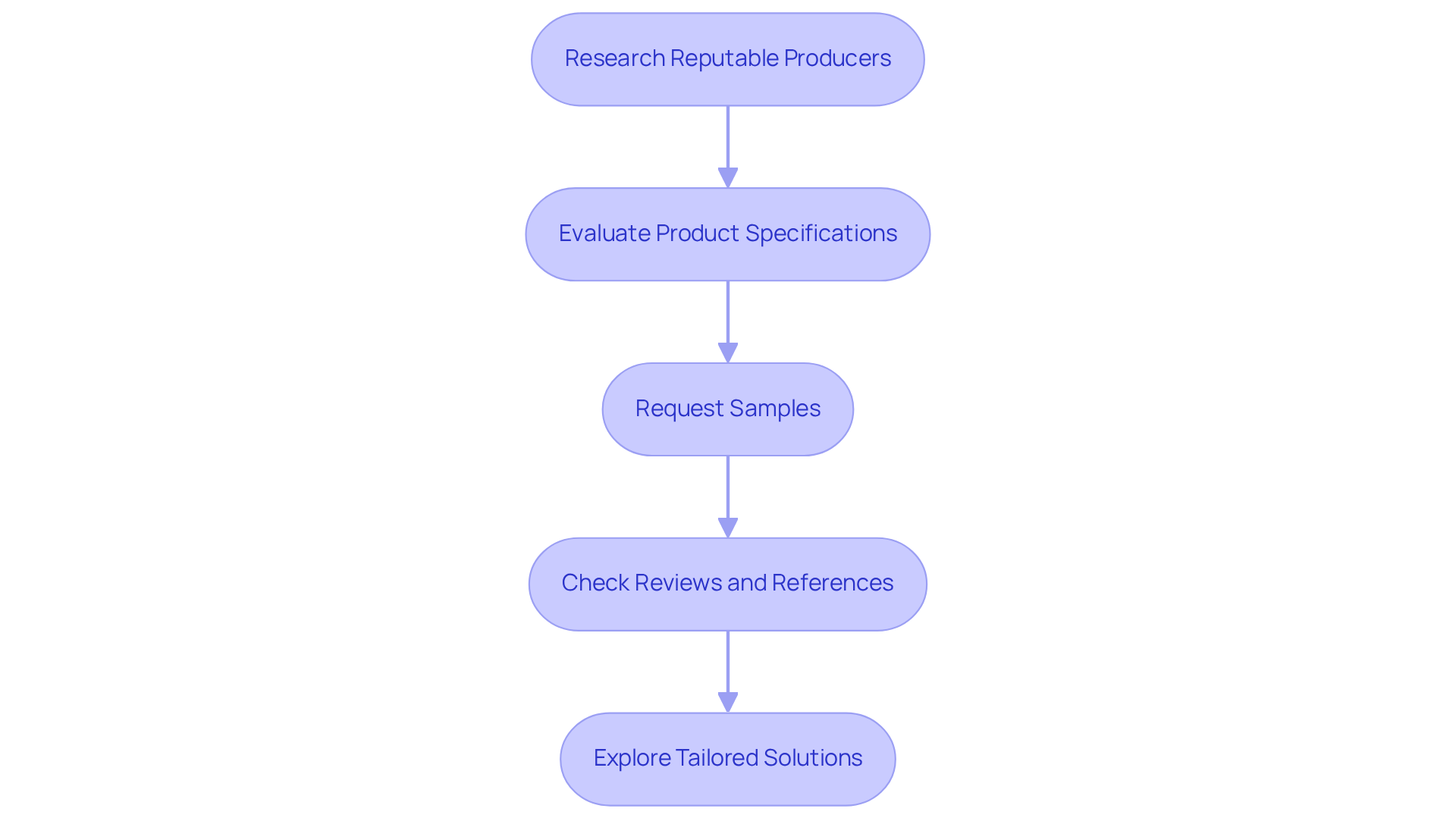
To source quality heat pipes, follow these essential steps:
- Research reputable producers by compiling a list of well-known manufacturers recognized for producing high-quality heat pipes for sale. Utilize resources such as industry directories and trade shows, which can serve as in your search.
- Evaluate Product Specifications: Carefully review the technical specifications provided by manufacturers. Focus particularly on factors such as thermal efficiency, materials used, and compliance with industry standards to ensure optimal performance.
- Request Samples: Before committing to a large order, request samples to assess the quality and functionality of the thermal tubes in your specific application. Testing these samples under real-world conditions can yield critical insights into their performance.
- Check Reviews and References: Investigate customer feedback and case studies that highlight the performance of the thermal conduits in similar applications. Additionally, reach out to other engineers or companies for recommendations to further inform your decision.
- Explore Tailored Solutions: If standard products do not meet your requirements, inquire about customized thermal transfer solutions. Many manufacturers offer design services that allow for product tailoring to specific needs.
Troubleshoot Common Selection Challenges
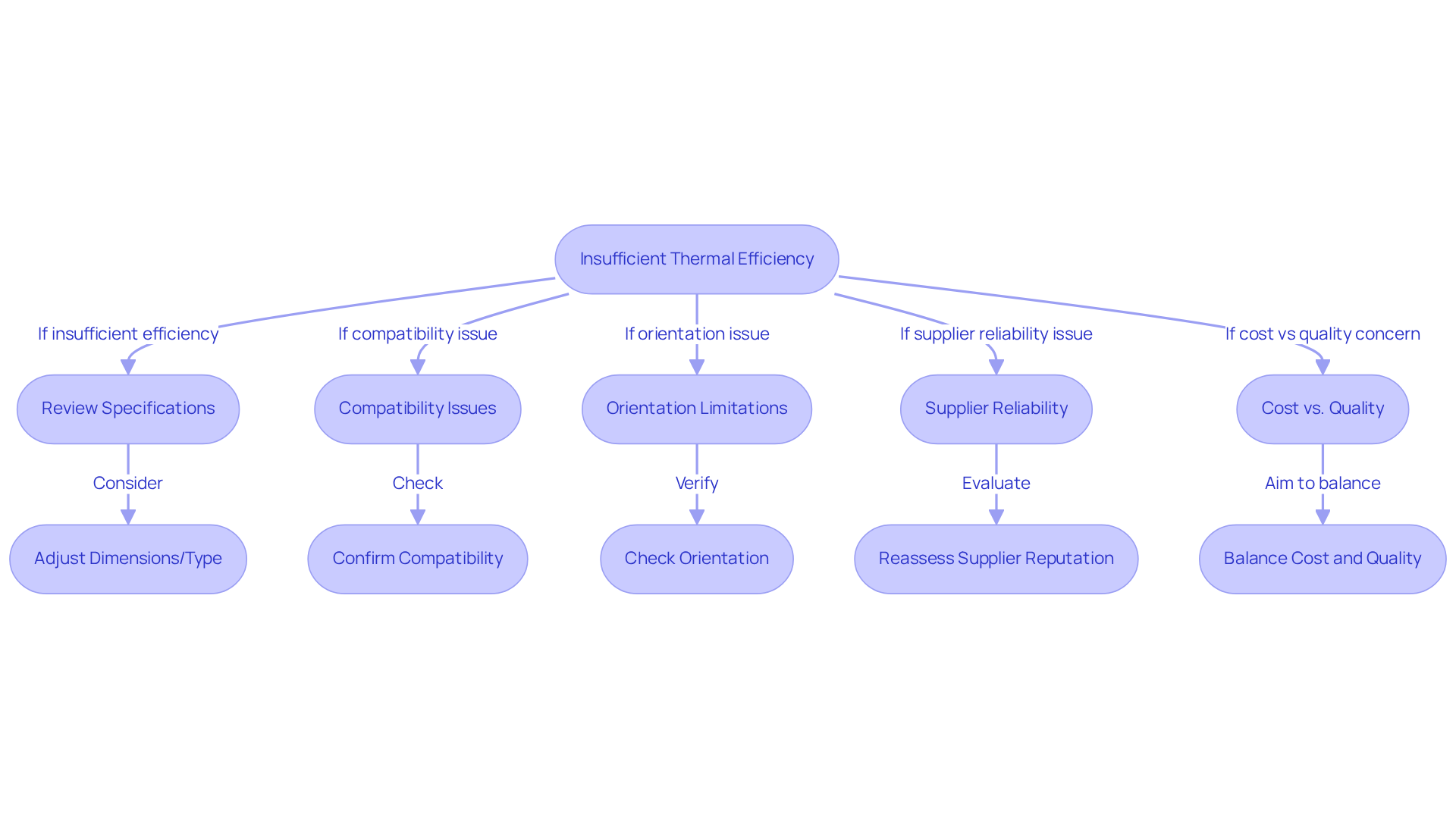
When selecting thermal conduits, various challenges may arise. Below are common issues along with effective troubleshooting strategies:
- Insufficient Thermal Efficiency: Should the thermal conductor fail to meet performance expectations, it is essential to review the specifications in relation to your application requirements. Consider adjusting the dimensions or type of thermal conduit to enhance efficiency.
- Compatibility Issues: Confirm that the selected thermal conduit is compatible with the working fluid and materials within your system. Incompatibility can result in system failures or diminished efficiency.
- Orientation Limitations: If the thermal transfer device does not operate as expected, check its orientation. Optimal performance of heat conduits often relies on gravity; improper installation can significantly hinder functionality.
- Supplier Reliability: In instances of quality concerns, reassess the reputation of your supplier. It may be prudent to source from manufacturers known for their reliability and rigorous quality assurance protocols.
- Cost vs. Quality: Striking a balance between cost and quality can be a daunting task. While the allure of cheaper options is strong, investing in can yield long-term savings by minimizing failures and reducing maintenance requirements.
Conclusion
Sourcing quality heat pipes is a critical process that hinges on understanding their fundamental principles and selecting the right products for specific applications. Grasping the mechanics of thermal conduits, including their types and functionalities, empowers informed decisions that enhance performance and efficiency in thermal management systems.
The article outlines essential steps for sourcing heat pipes, emphasizing the importance of researching reputable manufacturers, evaluating product specifications, and rigorously testing samples before purchase. It also highlights the necessity of troubleshooting common selection challenges, such as thermal efficiency and compatibility, ensuring optimal operation of heat conduits across various applications.
In a landscape where thermal management is increasingly vital, dedicating time to understand and implement these strategies can lead to significant improvements in system performance. By prioritizing quality and reliability in sourcing heat pipes, engineers and designers not only enhance their projects but also contribute to the advancement of technology in thermal management solutions. Investing in high-quality components today ensures long-term success and efficiency in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are thermal pipes and how do they work?
Thermal pipes are advanced temperature control devices that use phase change principles for efficient energy transfer. They consist of a sealed vessel containing a working fluid, typically water, which evaporates at the heat source and condenses at the cooler end, allowing for rapid thermal transfer with minimal temperature loss.
What are the different types of thermal conduits?
The main types of thermal conduits are tubular and planar designs. Tubular thermal conduits are commonly used in laptops and CPUs, while planar thermal conductors are widely utilized in flat-panel displays.
Who is Gagner-Toomey Associates and what do they offer?
Gagner-Toomey Associates is the world’s largest supplier of thermal management solutions for electronics cooling. They offer a diverse range of innovative cooling options, including extruded aluminum heatsinks, copper-based thermal sinks, and integrated cooling systems.
How can understanding thermal pipe fundamentals help in selecting cooling solutions?
Familiarizing yourself with thermal pipe fundamentals and exploring Gagner-Toomey’s extensive product offerings, including various sizes and types of air-movers, will aid in selecting the optimal thermal solution tailored to specific needs.

