Overview
A miniature blower serves as a compact device engineered to produce focused airflow, primarily for cooling and ventilation in electronic applications. With sizes ranging from 15mm to 280mm, these blowers often deliver airflow capabilities exceeding 1,500 liters per minute. This article underscores their pivotal features, including:
- A lightweight design
- Energy-efficient motors
- Versatile applications across sectors such as aerospace and healthcare
These attributes emphasize the critical role miniature blowers play in maintaining the optimal performance and reliability of modern electronic devices.
Introduction
Miniature blowers, often overlooked, play a pivotal role in the efficiency of modern electronics. These compact devices are meticulously designed to deliver powerful airflow in constrained spaces, making them essential for cooling and ventilation across a wide range of applications, from laptops to medical equipment. As the demand for smaller, more efficient electronic devices continues to escalate, the challenge emerges: how can engineers effectively integrate these blowers into designs without compromising performance? Navigating the complexities of airflow management and device compatibility is crucial to harnessing the full potential of miniature blowers.
Define Miniature Blower: Key Characteristics and Functions
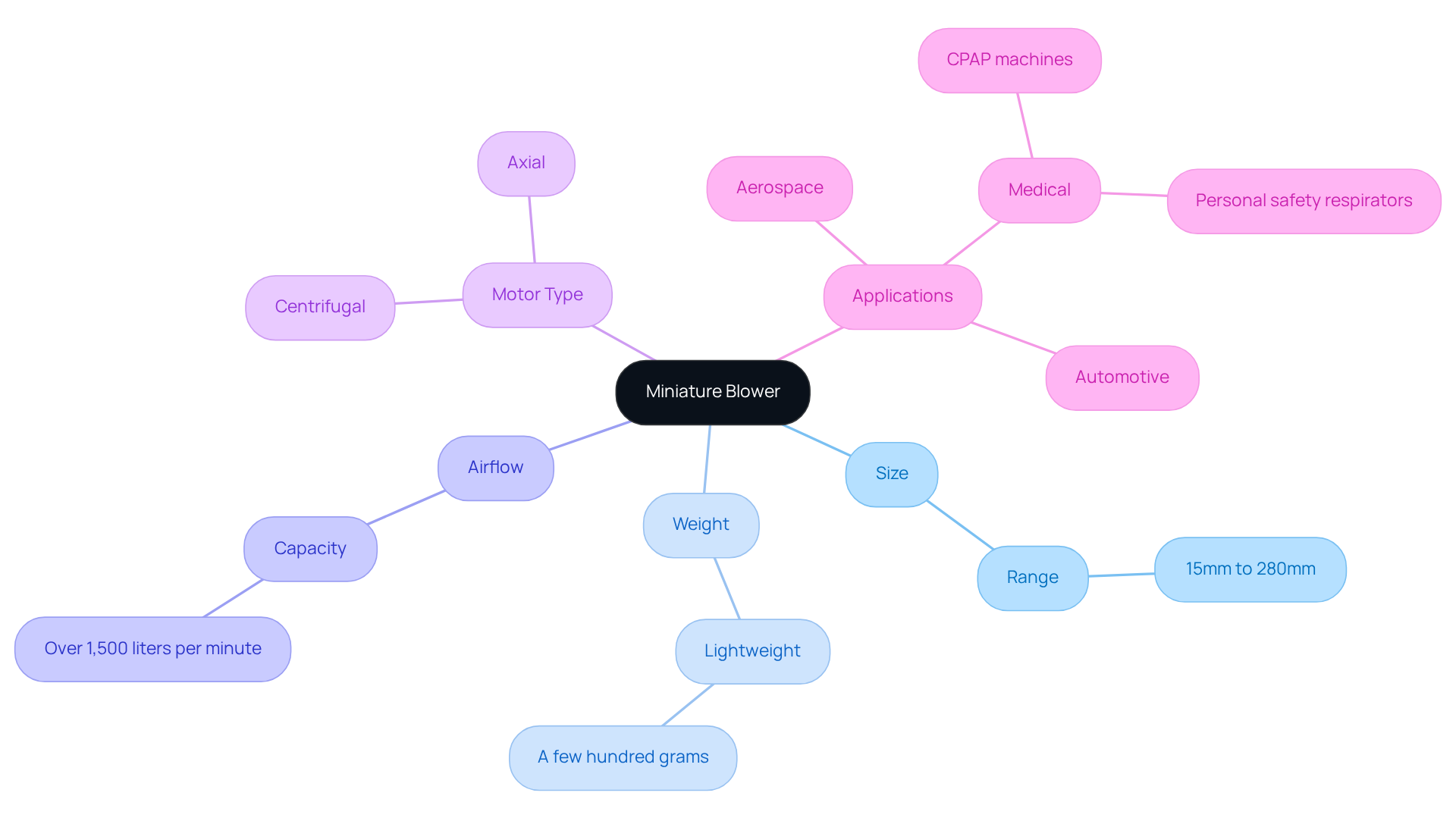
A miniature blower serves as a compact instrument designed to generate a focused flow of air, primarily for cooling and ventilation in electronic applications. These devices are typically lightweight, with sizes ranging from 15mm to 280mm, and can weigh as little as a few hundred grams, making them ideal for space-constrained environments. Despite their diminutive size, they deliver remarkable airflow, often surpassing 1,500 liters per minute, which is essential for maintaining optimal temperatures in electronic devices.
Miniature fans operate using electric motors, commonly configured as centrifugal or axial. They feature electronically commutated motors equipped with hall sensors, which enhance torque and control at reduced speeds, making them suitable for high-pressure applications with low rotor inertia and energy consumption. This design is particularly advantageous in preventing overheating, thereby ensuring efficient operation and prolonging the lifespan of electronic components. Most models also offer IP protection upon request, further enhancing their applicability across diverse environments.
The practical applications of small fans are extensive, spanning sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and medical equipment. In healthcare, for instance, they are crucial components of equipment like CPAP machines and personal safety respirators, where reliable airflow is vital for patient care. Engineers emphasize the importance of these fans, noting that they are fundamental in ensuring optimal performance and durability of devices. As one engineer stated, understanding their unique characteristics is critical for effective design and utilization in electronics.
In summary, the miniature blower plays an indispensable role in modern electronics, merging compactness with robust performance to meet the cooling demands of increasingly sophisticated technologies.
Explore the Role of Miniature Blowers in Electronics Applications
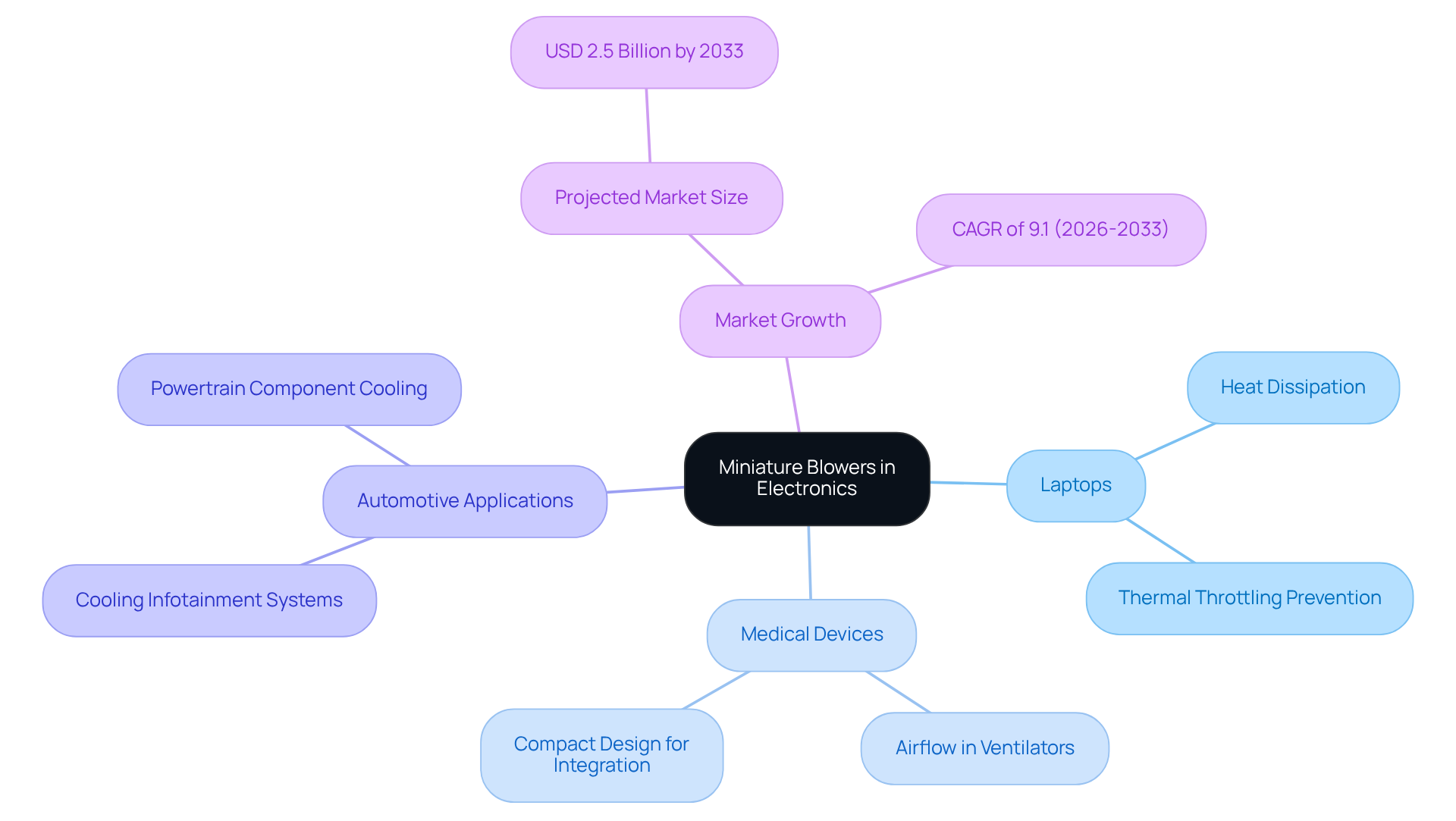
Miniature blowers play a crucial role in a diverse range of electronics applications, especially in cooling systems for laptops, medical devices, and consumer electronics. In laptops, these fans efficiently dissipate heat generated by processors, which is vital for maintaining optimal performance and preventing thermal throttling—an essential factor in enhancing user experience.
The micro fans market is projected to experience significant growth, reaching USD 2.5 billion by 2033, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.1% from 2026 to 2033. This trend underscores the persistent demand for cooling solutions, particularly the miniature blower, which is compact and efficient.
In the medical sector, miniature blowers are indispensable for ensuring sufficient airflow in portable ventilators and other critical equipment, where reliability and compactness are paramount. Their diminutive size allows for seamless integration into confined spaces, making them ideal for contemporary electronic designs that emphasize space efficiency.
Furthermore, small fans are increasingly employed in automotive applications, where they serve to cool infotainment systems and powertrain components. For instance, Nidec Corporation has developed ultra-compact micro fans specifically designed for advanced cooling applications, showcasing their versatility across multiple sectors.
However, as the adoption of these technologies rises, manufacturers and end-users must also navigate integration challenges and compatibility issues.
Trace the Evolution of Miniature Blowers: From Concept to Modern Applications
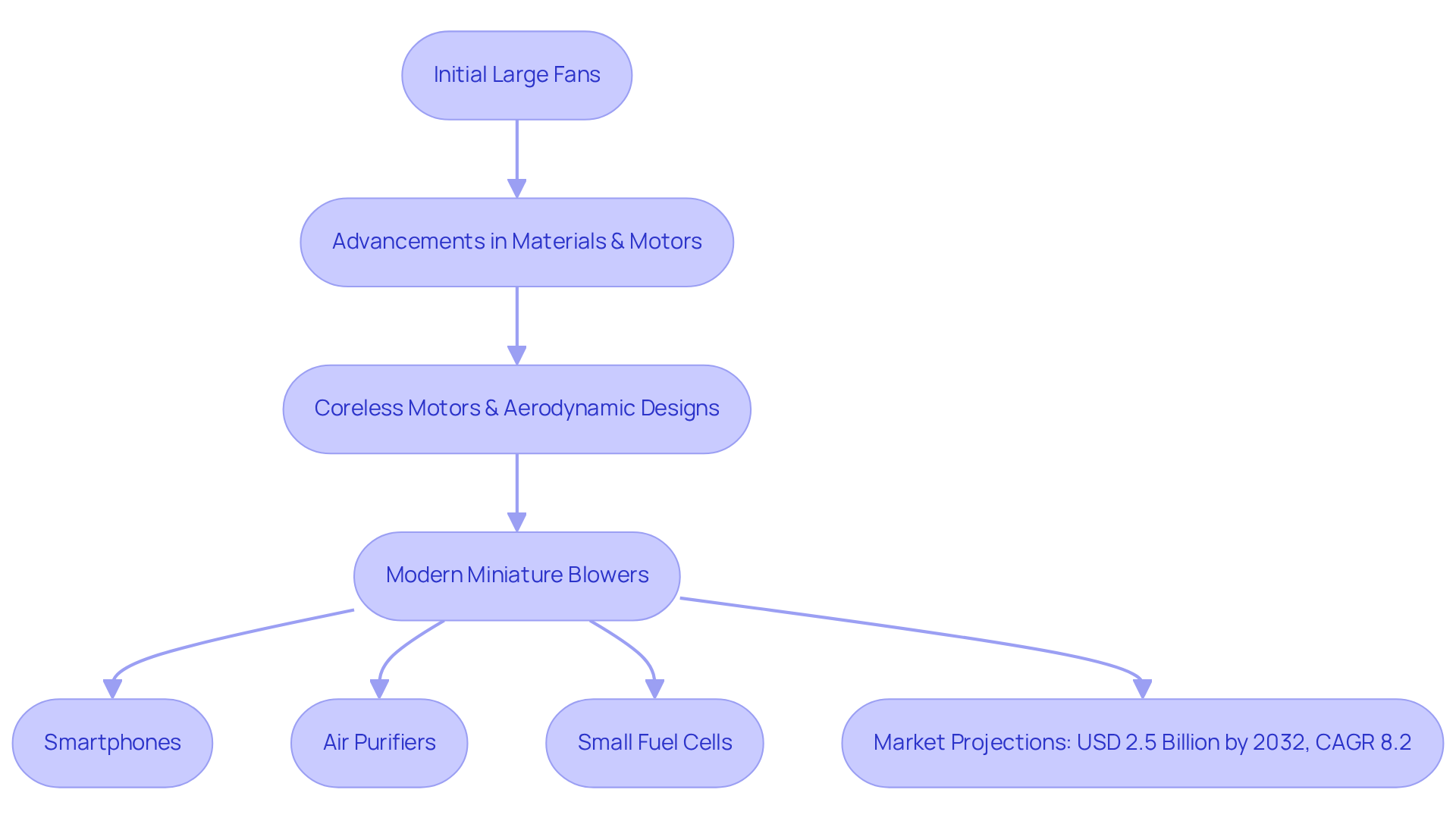
The development of small fans has exhibited remarkable progress since their inception. Initially, these devices were large and cumbersome, primarily serving industrial applications. However, advancements in materials and motor technology have revolutionized their design into compact and efficient solutions. The introduction of coreless motors and enhanced aerodynamic designs has facilitated the creation of smaller fans that deliver greater airflow rates while consuming less energy.
Today, miniature blowers are essential components in modern electronics, reflecting the industry’s shift toward miniaturization and energy efficiency. This evolution not only enables manufacturers to design smaller devices but also enhances their power and reliability, making them crucial in various applications, including:
- Smartphones
- Air purifiers
- Small fuel cells
The mini air device market is projected to reach USD 2.5 billion by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.2%, underscoring the growing demand for these technologies. Nevertheless, the market encounters challenges such as intense competition and low product differentiation, which manufacturers must navigate to sustain their competitive advantage. As the Asia Pacific region continues to bolster its electronics manufacturing sector, the significance of small fans in driving innovation and efficiency in product development becomes increasingly evident.
Identify Integration Challenges: Best Practices for Using Miniature Blowers in Design
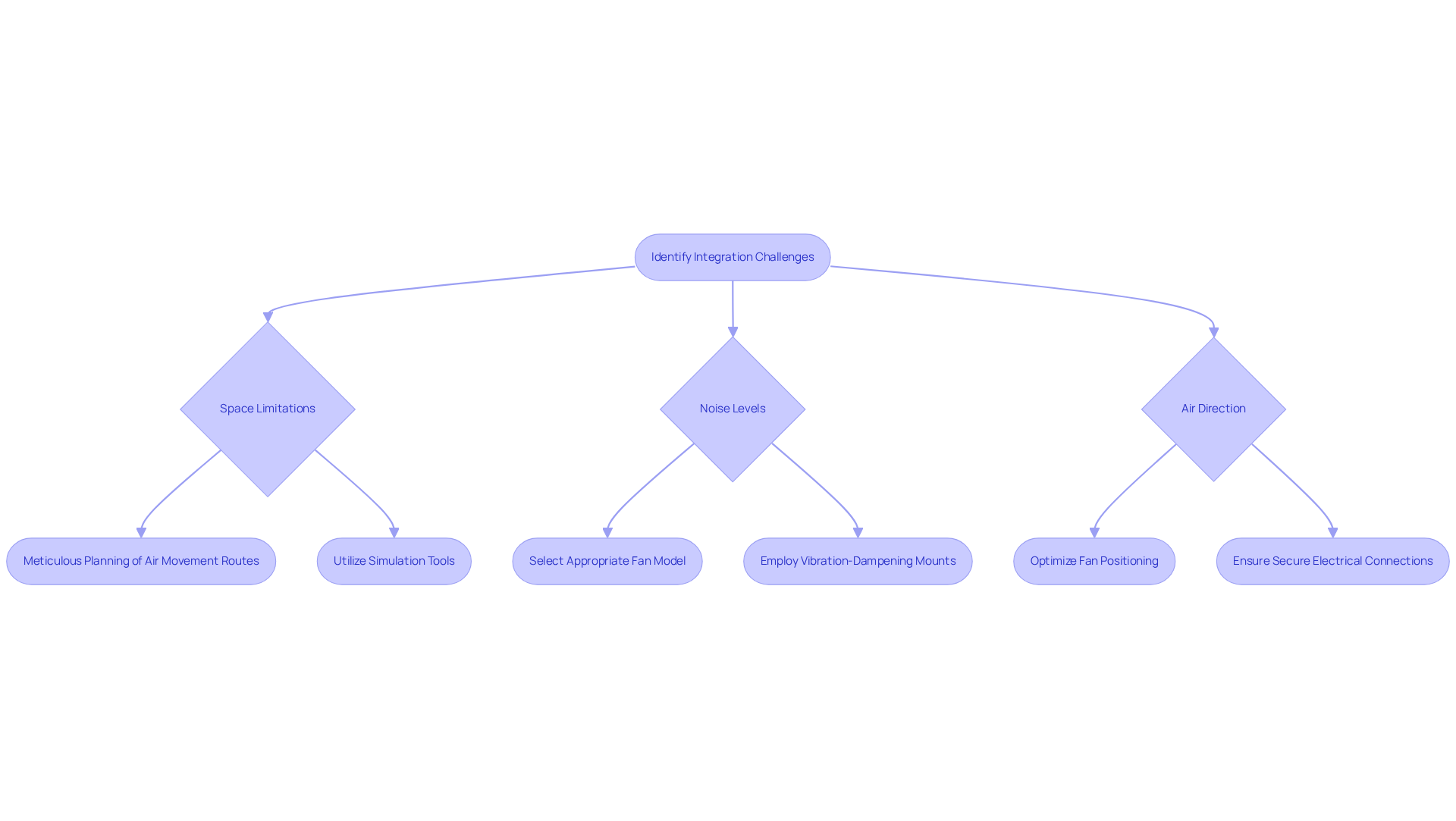
Incorporating small fans into electronic designs presents several challenges, including space limitations, noise levels, and air direction. Engineers must prioritize meticulous planning of air movement routes and thoughtfully consider the fan’s positioning within the device to optimize performance.
Utilizing simulation tools can effectively predict air movement patterns, aiding in informed design decisions. Selecting the appropriate fan model based on air movement capacity, noise level, and power consumption is essential; energy-efficient fans can reduce energy consumption by up to 30%.
Moreover, insufficient airflow contributes to approximately 30% of overheating incidents in devices, underscoring the importance of proper fan integration. Best practices also entail ensuring secure electrical connections to mitigate overheating risks and employing vibration-dampening mounts to minimize noise, as many small fan models operate quietly, making them ideal for sensitive environments.
Additionally, the use of compact fans can yield environmental benefits, such as preventing over 3 million metric tons of packaging materials from being wasted. By proactively addressing these challenges, designers can significantly enhance the effectiveness of their applications involving miniature blowers.
Conclusion
Miniature blowers serve as critical components in the electronics sector, merging compact design with robust airflow capabilities to meet the cooling and ventilation demands of various devices. Their capacity to provide substantial airflow within minimal space renders them essential in modern technology, facilitating the creation of smaller, more efficient electronic devices.
This article underscores the pivotal features of miniature blowers, including their lightweight construction, high airflow rates, and energy-efficient motor designs. Furthermore, it delves into their wide-ranging applications across industries such as healthcare, automotive, and consumer electronics, emphasizing their vital role in sustaining optimal device performance and averting overheating. The transformation of these blowers from cumbersome industrial components to advanced, energy-efficient solutions exemplifies the continuous technological advancements that cater to the needs of contemporary electronics.
In conclusion, the importance of miniature blowers transcends their technical specifications; they embody a crucial element of innovation in electronics design. As technology progresses, it will be imperative for engineers and designers to adopt best practices for integrating these blowers. By tackling integration challenges and capitalizing on the advantages of miniature blowers, stakeholders can bolster the reliability and efficiency of electronic devices, ultimately fostering a more sustainable future in technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a miniature blower?
A miniature blower is a compact device designed to generate a focused flow of air, primarily used for cooling and ventilation in electronic applications.
What are the typical sizes and weights of miniature blowers?
Miniature blowers typically range in size from 15mm to 280mm and can weigh as little as a few hundred grams, making them suitable for space-constrained environments.
How much airflow can miniature blowers deliver?
Despite their small size, miniature blowers can deliver remarkable airflow, often exceeding 1,500 liters per minute, which is essential for maintaining optimal temperatures in electronic devices.
What types of motors do miniature blowers use?
Miniature blowers operate using electric motors, commonly configured as centrifugal or axial. They often feature electronically commutated motors equipped with hall sensors.
What advantages do hall sensors provide in miniature blowers?
Hall sensors enhance torque and control at reduced speeds, making miniature blowers suitable for high-pressure applications with low rotor inertia and energy consumption, which helps prevent overheating.
In what industries are miniature blowers commonly used?
Miniature blowers are used in various sectors, including aerospace, automotive, and medical equipment.
How are miniature blowers utilized in healthcare?
In healthcare, miniature blowers are crucial components of equipment such as CPAP machines and personal safety respirators, where reliable airflow is vital for patient care.
What is the significance of understanding the characteristics of miniature blowers?
Understanding the unique characteristics of miniature blowers is critical for effective design and utilization in electronics, ensuring optimal performance and durability of devices.
What is the overall role of miniature blowers in modern electronics?
Miniature blowers play an indispensable role in modern electronics by merging compactness with robust performance to meet the cooling demands of increasingly sophisticated technologies.

