Introduction
The landscape of motor technology is evolving. Electronically Commutated (EC) motors are emerging as a formidable alternative to traditional Alternating Current (AC) motors. This shift is largely driven by the quest for energy efficiency and operational flexibility, particularly in applications like HVAC systems, where performance and sustainability are paramount.
As engineers weigh the benefits of each motor type, a pressing question arises: can the advanced capabilities of EC motors truly outshine the reliability and simplicity of AC motors? This inquiry is especially relevant in a world increasingly focused on energy conservation.
In considering this transition, it is essential to evaluate the specific advantages that EC motors offer, such as improved efficiency and adaptability, against the established reliability of AC motors. The decision ultimately hinges on the unique requirements of each application, making it crucial for engineers to stay informed about these advancements.
Understand EC Motors and AC Motors
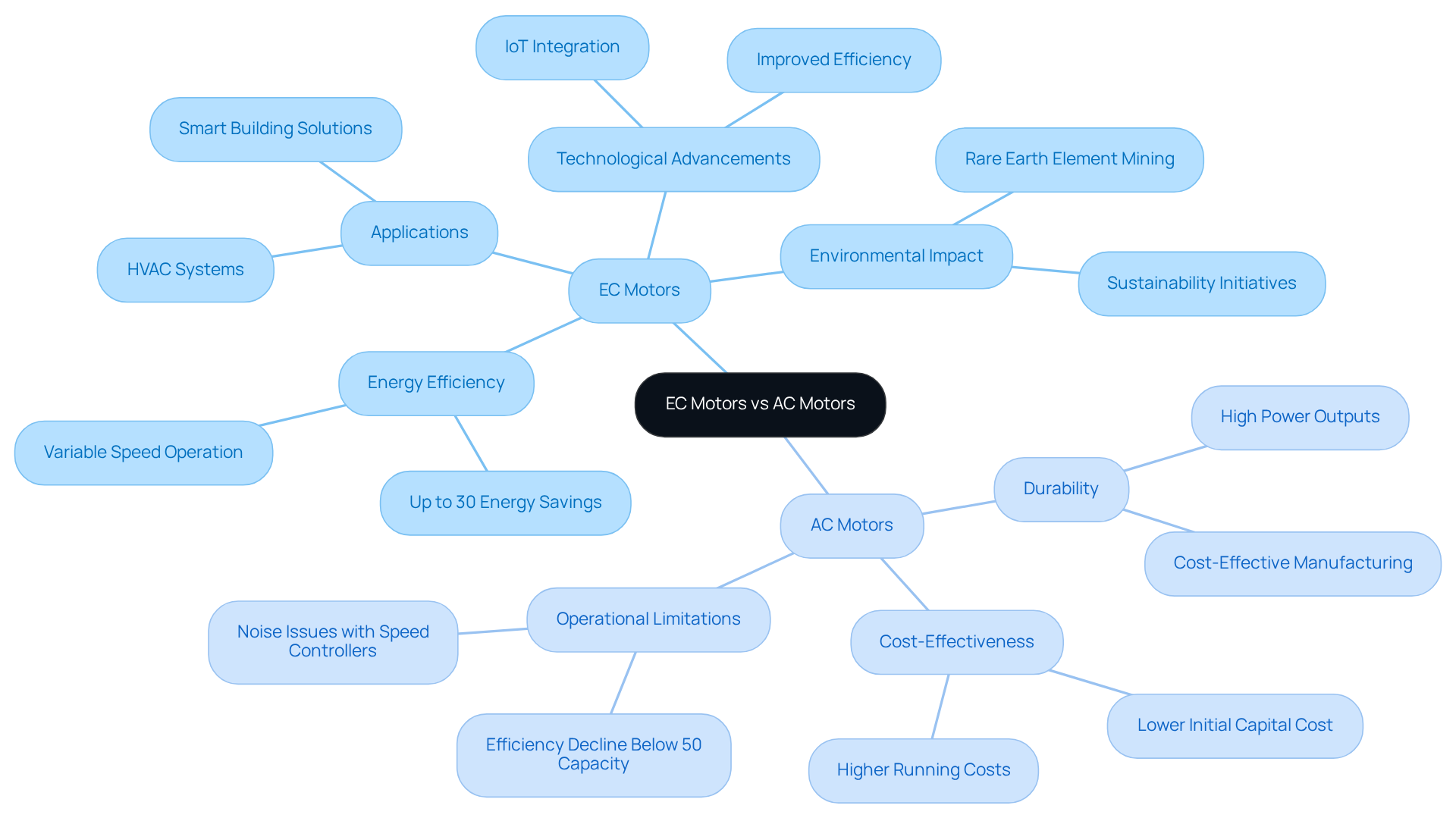
When comparing ec motor vs ac motor, Electronically Commutated (EC) devices represent a significant advancement in energy efficiency, utilizing sophisticated electronic circuitry to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). This transformation allows for precise control of velocity and torque, making EC technology particularly advantageous in HVAC systems where high efficiency and low noise are critical.
EC devices excel in applications requiring variable speed operation, achieving energy savings of up to 30% compared to traditional systems. However, it is essential to recognize that EC devices are not suitable for high-temperature applications due to the risk of demagnetization of their permanent magnets. In contrast, traditional AC machines operate directly on alternating current, highlighting the differences in design when considering EC motor vs AC motor, which features a simpler configuration with a stator and rotor. While AC machines are known for their durability and cost-effectiveness, the comparison of ec motor vs ac motor shows that AC machines often lack the efficiency of EC devices, especially in variable load situations.
The operational effectiveness of AC devices can decline significantly when operating below 50% of their full capacity. In contrast, EC units maintain performance across a broader range of speeds, making them increasingly popular in modern HVAC applications where energy efficiency is paramount. For instance, the HVAC electronically commutated device market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.5% from 2021 to 2028, reflecting the rising demand for energy-efficient solutions in building systems.
Recent advancements in EC engine technology include the integration of IoT capabilities, which enhance their functionality in smart building applications. Engineers have noted that the improved efficiency and reduced maintenance needs of EC devices make them vital for low-carbon HVAC strategies. As Woods Air Movement highlights, EC technologies are gaining traction in sustainability initiatives. As the sector transitions towards sustainability, their acceptance is expected to rise, driven by regulatory pressures and an increasing emphasis on conservation.
Moreover, the environmental impact of rare earth element extraction, crucial for producing permanent magnets in electric machines, presents significant challenges. This necessitates a balanced strategy for their production and utilization, ensuring that the benefits of EC technology are realized without compromising environmental integrity.
Compare Energy Efficiency of EC Motors and AC Motors
EC devices stand out for their remarkable power conservation, often achieving performance levels exceeding 90%, especially under reduced loads. For instance, when comparing EC motor vs AC motor, operating an EC fan at 80% speed can save nearly 50% power compared to similarly sized AC units. In contrast, when discussing EC motor vs AC motor, AC machines typically operate at performance levels ranging from 70% to 88%, influenced by design and load conditions. The significant disparity in power consumption between EC motor vs AC motor makes EC devices particularly attractive for applications where cost is a major concern, such as HVAC systems that require continuous operation.
Furthermore, integrating EC drives into HVAC applications not only enhances efficiency but also reduces maintenance needs. EC fans combine a drive, controller, and impeller into a single unit, resulting in lower operational costs and improved return on investment. Case studies indicate that employing EC devices can lead to energy savings of nearly 50% when operating at optimal rates, underscoring their effectiveness in modern engineering solutions.
Evaluate Performance Metrics: Speed Control and Operational Characteristics
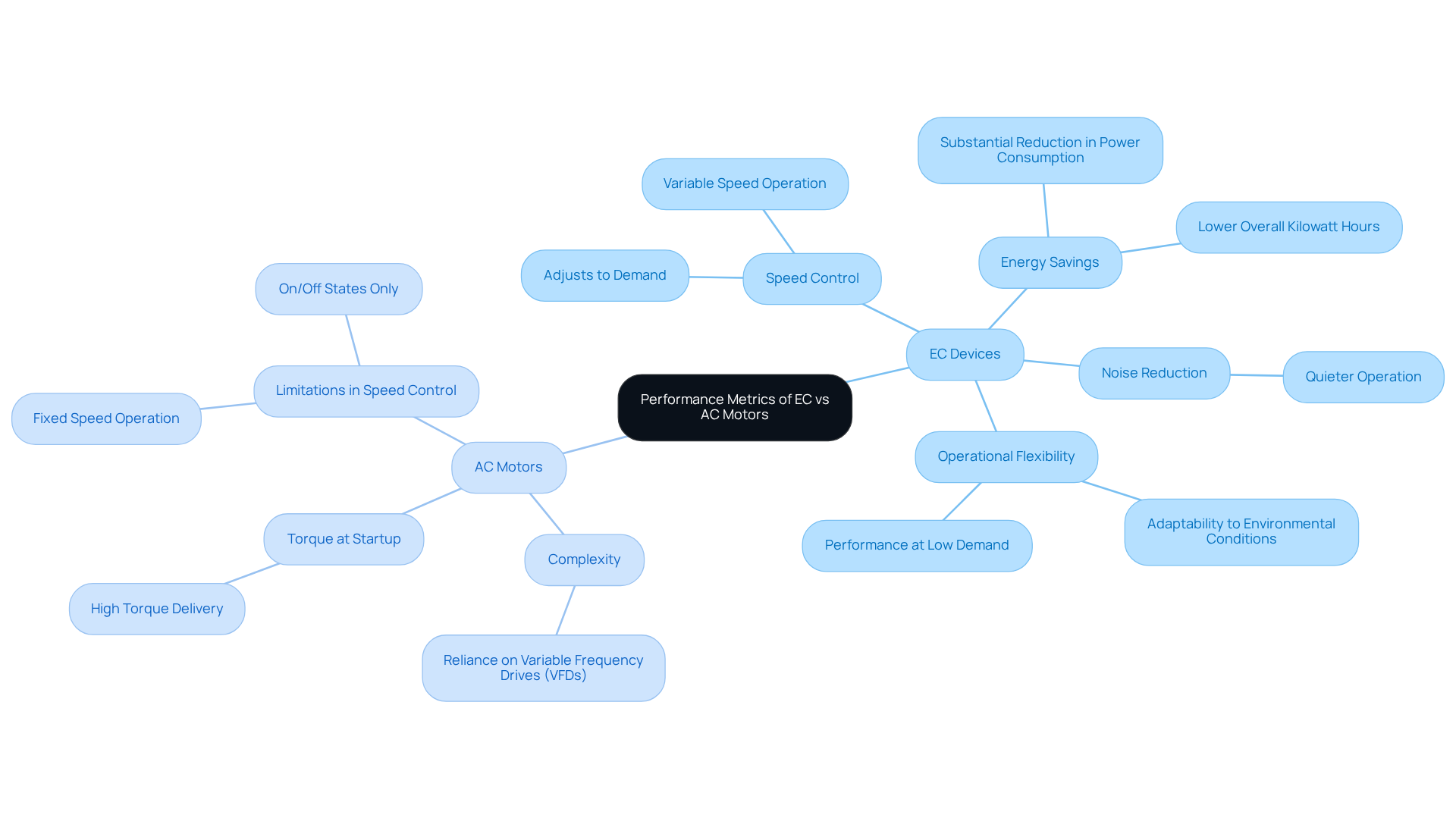
EC devices stand out due to their exceptional control over pace, enabling variable operation without the need for external controllers. This capability is particularly beneficial in applications that require precise airflow or temperature regulation. Operating effectively at reduced rates, EC devices not only maintain performance but also significantly reduce noise levels.
In the discussion of EC motor vs AC motor, it is observed that AC machines typically rely on variable frequency drives (VFDs) for speed adjustments, which adds complexity and cost to the system. While AC units can deliver high torque at startup, the comparison of EC motor vs AC motor reveals that their rotational control lacks the adaptability of EC units, making them less suitable for applications that demand precise adjustments.
Consider the case studies: during periods of low demand, such as cooler mornings, EC devices can adjust their speed to match the required airflow. This capability leads to a substantial decrease in power consumption compared to conventional induction types, which operate only at full speed or are turned off.
This operational flexibility not only enhances system efficiency but also results in significant energy savings. Consequently, EC devices have become the preferred choice among engineers in the HVAC sector.
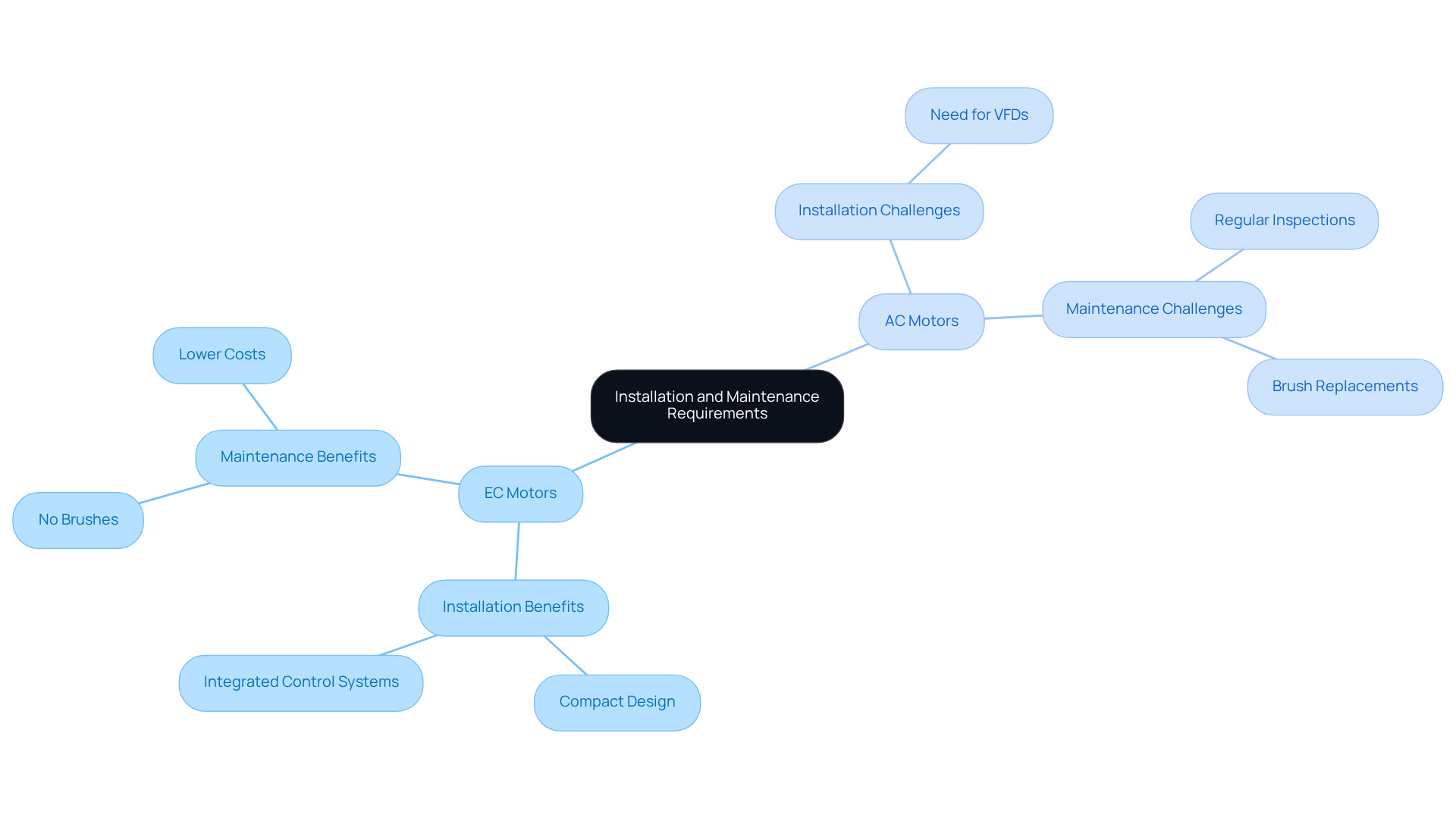
Assess Installation and Maintenance Requirements
EC devices streamline the installation process due to their compact design and integrated control systems, eliminating the need for additional components like variable frequency drives (VFDs). This simplicity not only reduces installation time but also minimizes the complexity often associated with AC devices, which typically require VFDs for effective speed control.
Maintenance requirements further distinguish the differences between EC motor vs AC motor. EC units are designed without brushes, significantly reducing wear and tear and extending their operational lifespans. In contrast, AC devices necessitate regular inspections and potential brush replacements, leading to increased downtime and higher operational costs. For instance, when comparing EC motor vs AC motor, maintenance expenses for EC devices are generally lower, as they require less frequent servicing. This reduction in maintenance needs translates into substantial long-term savings, positioning EC devices as a more cost-effective choice for various applications.
According to maintenance experts, “The decreased upkeep needs of EC devices not only reduce expenses but also enhance operational efficiency, enabling more reliable performance in challenging environments.” Furthermore, case studies reveal that in the analysis of EC motor vs AC motor, while AC motors may incur higher maintenance costs due to their requirement for regular inspections and brush replacements, EC motors consistently demonstrate lower total ownership costs over time.
Conclusion
Electronically Commutated (EC) motors stand out as a superior alternative to traditional Alternating Current (AC) motors, especially in applications where energy efficiency and precise control are critical. The benefits of EC technology – such as substantial energy savings and lower maintenance needs – underscore its increasing significance in modern engineering, particularly within HVAC systems.
Key comparisons reveal that EC motors consistently outperform AC motors in several essential aspects. They achieve higher efficiency levels, particularly under variable load conditions, and their capacity to maintain performance at lower speeds distinguishes them from their AC counterparts. Furthermore, the straightforward installation process and reduced maintenance requirements of EC motors enhance their attractiveness, making them a cost-effective choice over time.
As the industry shifts its focus toward sustainability and energy conservation, the adoption of EC motors is poised to gain momentum. Engineers and decision-makers should weigh the long-term advantages of integrating EC technology into their systems – not only for enhanced operational efficiency but also for a diminished environmental impact. By embracing these advancements, we can pave the way for a more sustainable future in engineering and technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are EC motors and how do they differ from AC motors?
Electronically Commutated (EC) motors utilize electronic circuitry to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC), allowing for precise control of velocity and torque. In contrast, AC motors operate directly on alternating current and have a simpler configuration with a stator and rotor.
What advantages do EC motors offer in terms of energy efficiency?
EC motors can achieve energy savings of up to 30% compared to traditional systems, particularly in applications requiring variable speed operation.
Are there any limitations to using EC motors?
Yes, EC motors are not suitable for high-temperature applications due to the risk of demagnetization of their permanent magnets.
How do AC motors perform at lower capacities?
The operational effectiveness of AC motors can decline significantly when operating below 50% of their full capacity, whereas EC motors maintain performance across a broader range of speeds.
What is the projected growth for the HVAC electronically commutated device market?
The HVAC electronically commutated device market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.5% from 2021 to 2028.
How are advancements in EC technology impacting smart building applications?
Recent advancements include the integration of IoT capabilities, which enhance the functionality of EC motors in smart building applications.
Why are EC motors considered vital for low-carbon HVAC strategies?
Engineers have noted that EC motors improve efficiency and reduce maintenance needs, making them essential for sustainability initiatives and low-carbon strategies.
What environmental challenges are associated with EC motor production?
The extraction of rare earth elements, crucial for producing permanent magnets in electric machines, presents significant environmental challenges, necessitating a balanced strategy for their production and utilization.