Introduction
Understanding the nuances of IP68 and IP69K ratings is crucial for manufacturers aiming to develop reliable electronic devices that can endure harsh environments. These ratings not only indicate a product’s resistance to dust and water but also dictate its suitability for various applications, ranging from outdoor electronics to food processing machinery.
However, achieving compliance with these stringent standards poses a significant challenge. How can engineers ensure their products meet the rigorous testing and material requirements necessary for certification? This article explores four critical checkpoints that will guide manufacturers through the complexities of IP68/IP69K compliance, ensuring their devices perform optimally in demanding conditions.
Define IP68 and IP69K Ratings
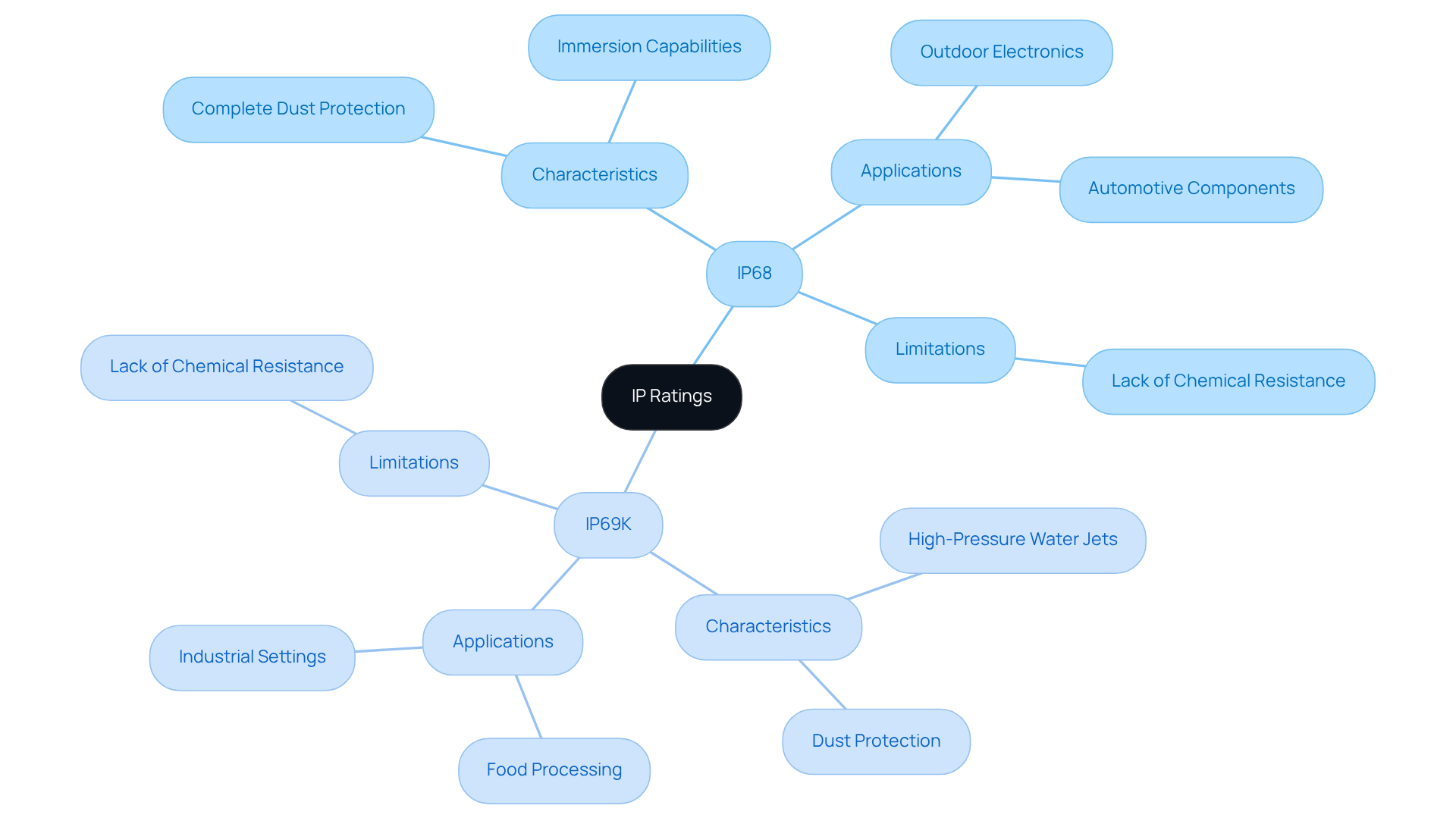
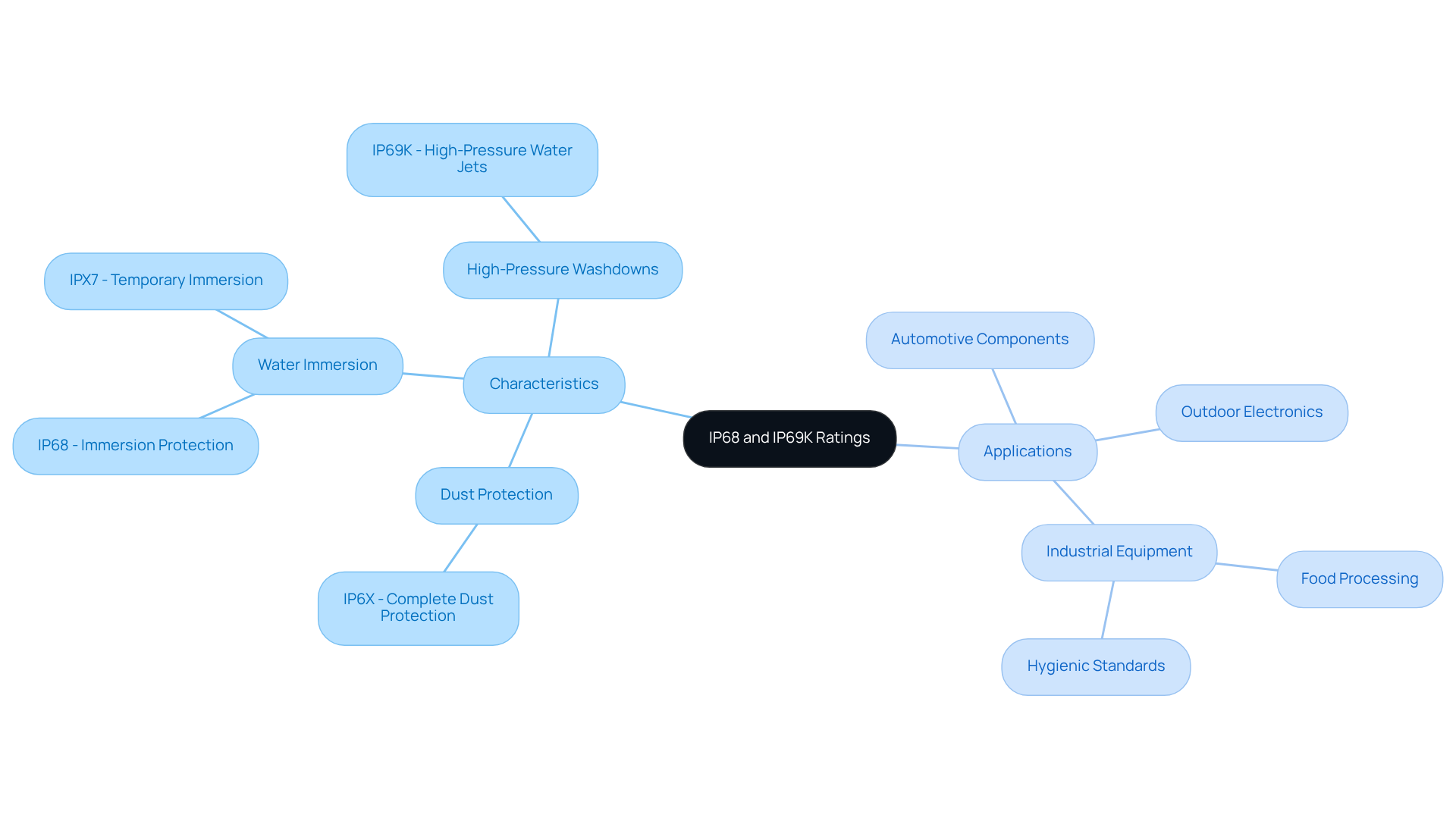
The IP68/IP69K rating signifies complete dust protection and the ability to endure continuous immersion in water beyond one meter for a specified duration. This makes it suitable for environments requiring immersion protection without high-pressure cleaning. Such a rating is crucial for devices exposed to wet conditions, ensuring they remain operational under challenging circumstances.
Conversely, the IP68/IP69K rating denotes protection against dust and high-pressure, high-temperature water jets, offering robust defense against water jets up to 1450 psi. This rating is ideal for settings that demand stringent cleaning protocols, such as food processing and industrial applications.
The primary distinction between these ratings lies in their intended use:
- IP68 focuses on immersion capabilities.
- The IP68/IP69K rating is tailored for high-pressure washdowns.
This difference is vital for engineers when selecting enclosures for specific applications, as it directly impacts the durability and functionality of electronic devices.
Common applications for IP68/IP69K include outdoor electronics, automotive components, and industrial equipment, where reliable performance in wet conditions is essential. In contrast, the highest protection rating is often found in environments that require rigorous hygiene standards, ensuring that equipment can withstand extreme cleaning processes without compromising integrity.
Understanding the limitations of IP classifications, such as their lack of chemical resistance, is crucial for making informed enclosure selections.
Verify Testing Standards for IP68/IP69K Compliance
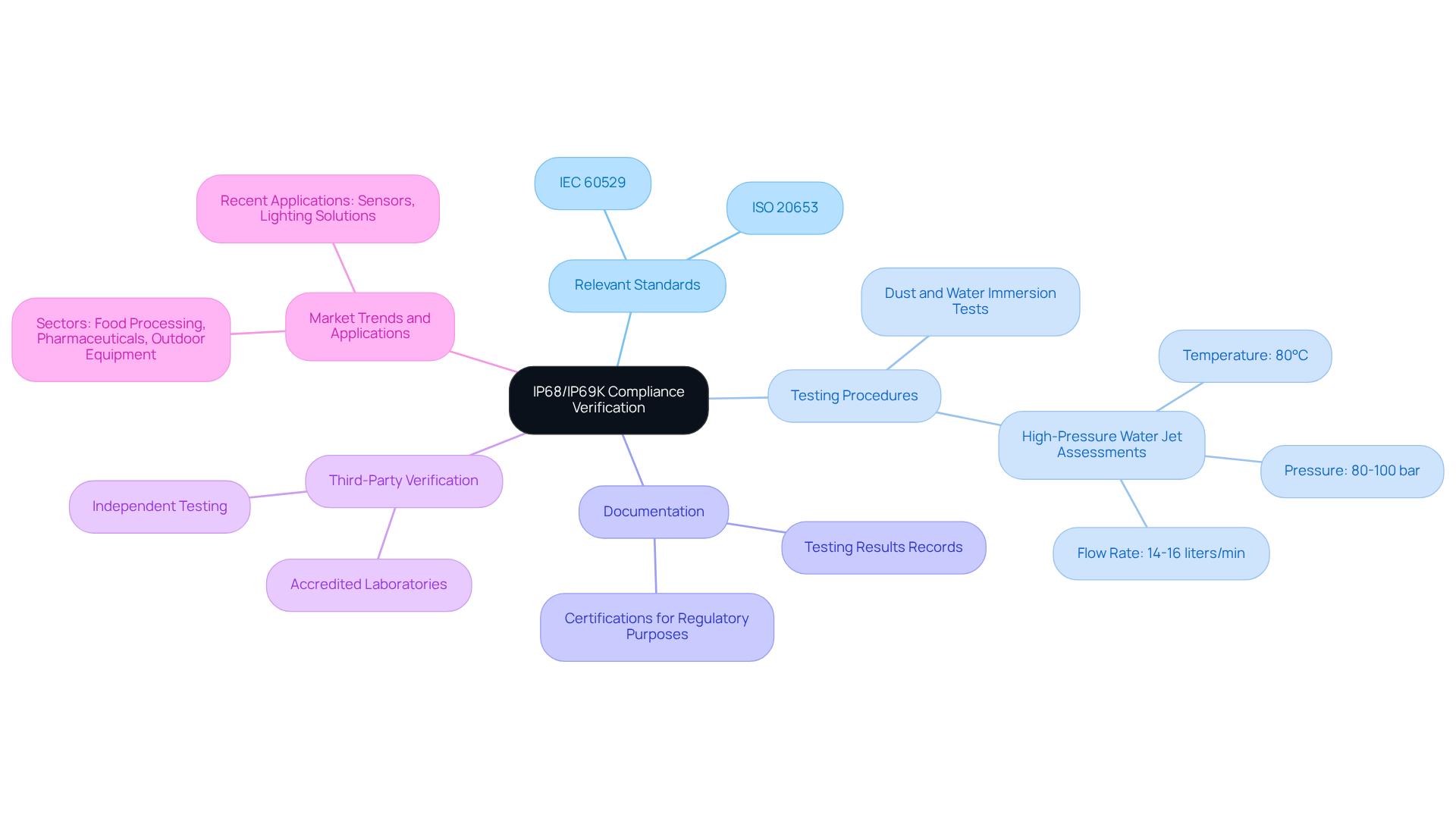
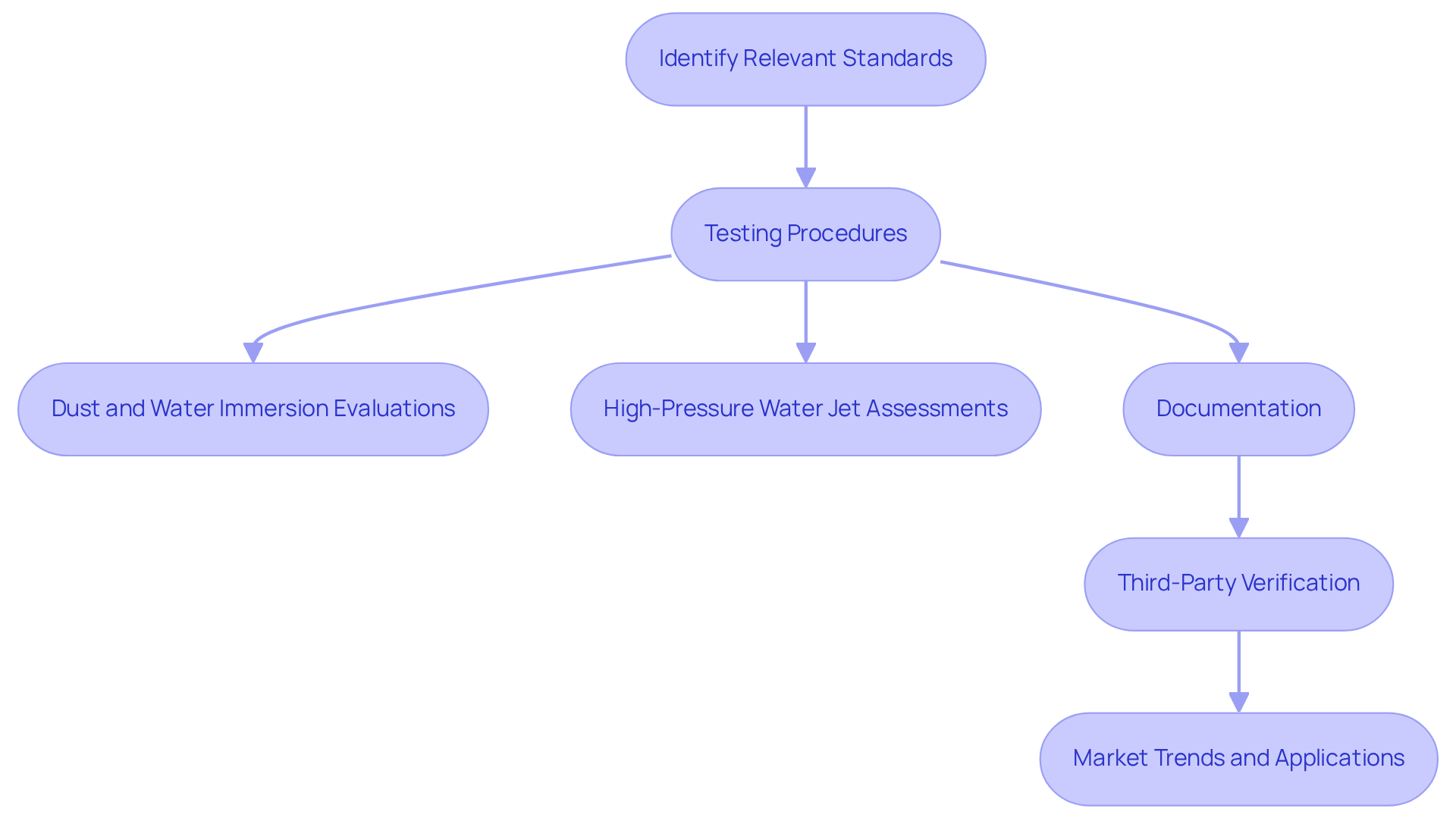
Identify Relevant Standards: Compliance with IEC 60529 for IP68/IP69K and ISO 20653 is essential, as these standards outline the necessary testing conditions for ingress protection classifications regarding IP68/IP69K. Gagner-Toomey Associates’ innovative solenoid and rotary boost pumps are meticulously designed to meet these rigorous standards, ensuring reliability across various applications.
Testing Procedures: To verify their ratings, products must undergo stringent testing. The first rating involves comprehensive dust and water immersion evaluations, while the second rating requires high-pressure water jet assessments at temperatures reaching 80°C, with pressures ranging from 80 to 100 bar and a flow rate of 14 to 16 liters per minute. Gagner-Toomey Associates guarantees that their solenoid pumps, compliant with automotive standards, are rigorously tested to withstand these specific environmental conditions.
Documentation: Maintaining thorough records of testing results and certifications is crucial. This documentation serves as proof of compliance and is vital for regulatory purposes and customer assurance, especially for products certified under IATF 16969 standards.
Third-Party Verification: Engaging accredited laboratories for independent testing significantly enhances the credibility of compliance claims. Third-party verification not only validates the testing process but also fosters trust with customers by ensuring that Gagner-Toomey Associates’ products meet the highest standards of quality and performance.
Market Trends and Applications: The demand for devices with the IP68/IP69K rating is on the rise, particularly in sectors such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and outdoor equipment. Producers like Gagner-Toomey Associates are increasingly focused on achieving IP68/IP69K standards to satisfy stringent hygiene and durability criteria. Recent applications include advanced sensors and lighting solutions designed for harsh environments, underscoring the versatility and importance of these classifications in modern electronics.
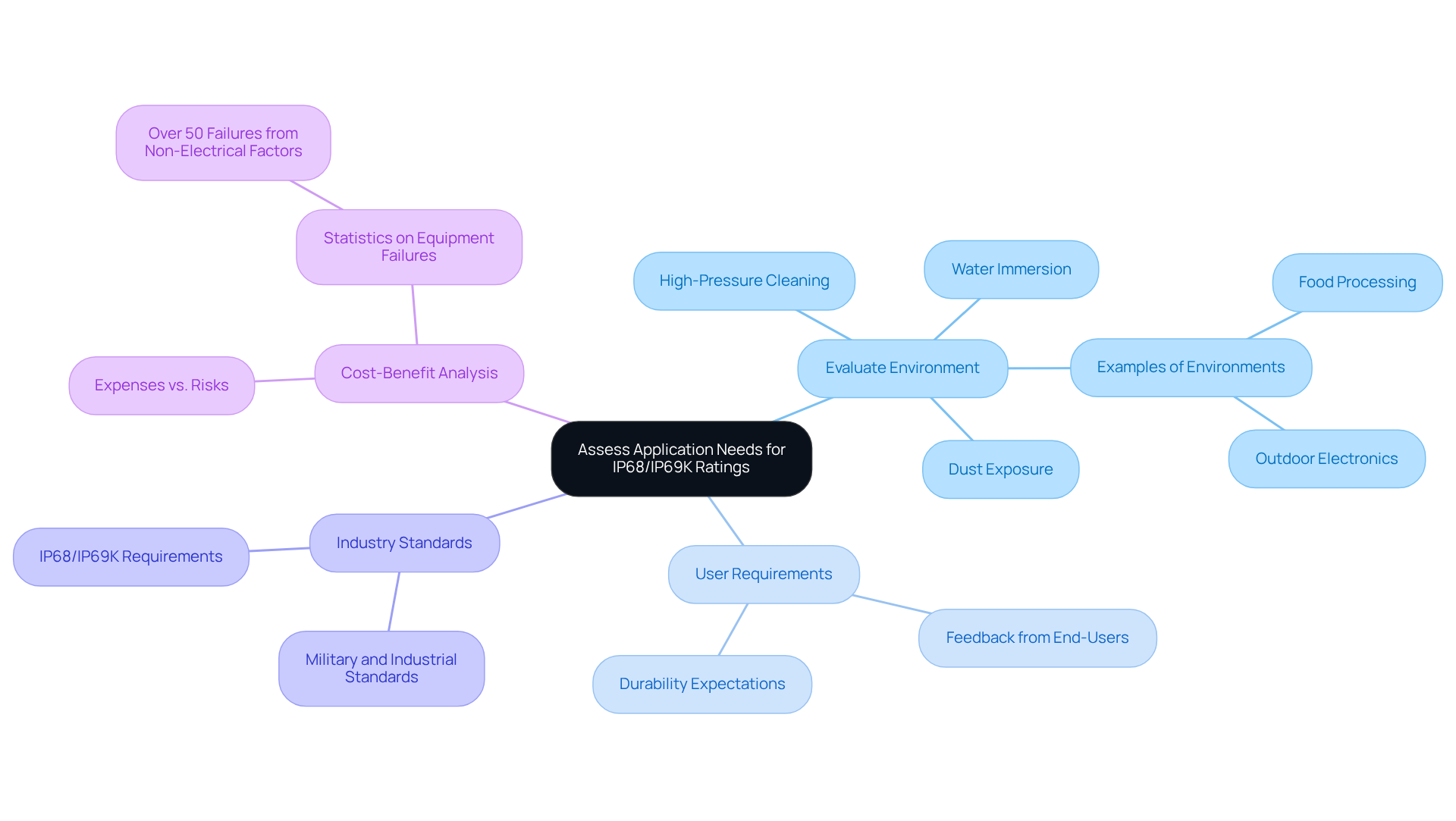
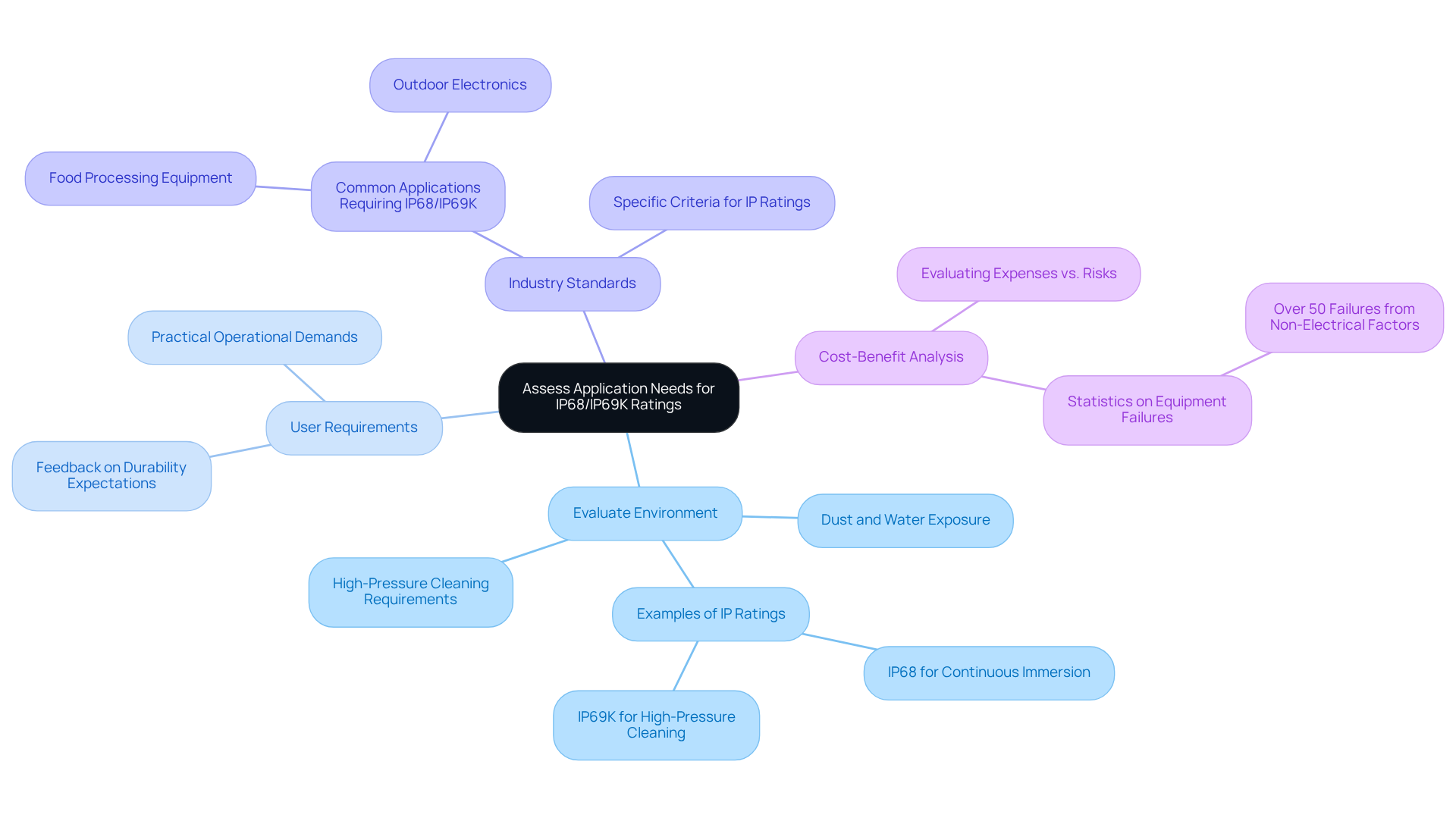
Assess Application Needs for IP68/IP69K Ratings
Evaluate Environment
Assess whether the product will encounter dust, water immersion, or high-pressure cleaning. For instance, devices used in food processing often require IP68/IP69K ratings to withstand rigorous cleaning procedures. In contrast, outdoor electronics may only need an IP67 rating for brief submersion.
User Requirements
Gather feedback from end-users about their expectations for durability and protection. Understanding user requirements can guide the selection of appropriate IP classifications, ensuring that devices meet practical operational demands.
Industry Standards
Investigate industry-specific criteria that may dictate certain IP classifications. For example, outdoor applications typically require at least an IP68/IP69K rating to endure exposure to rain and dust, while military and industrial applications might necessitate IP68/IP69K for prolonged submersion.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Conduct a cost-benefit analysis to evaluate the expenses associated with achieving higher IP levels against the risks of product failure in challenging environments. Notably, statistics reveal that over 50% of equipment failures in outdoor and industrial settings arise from non-electrical factors. This underscores the importance of selecting the right IP rating to mitigate potential risks.
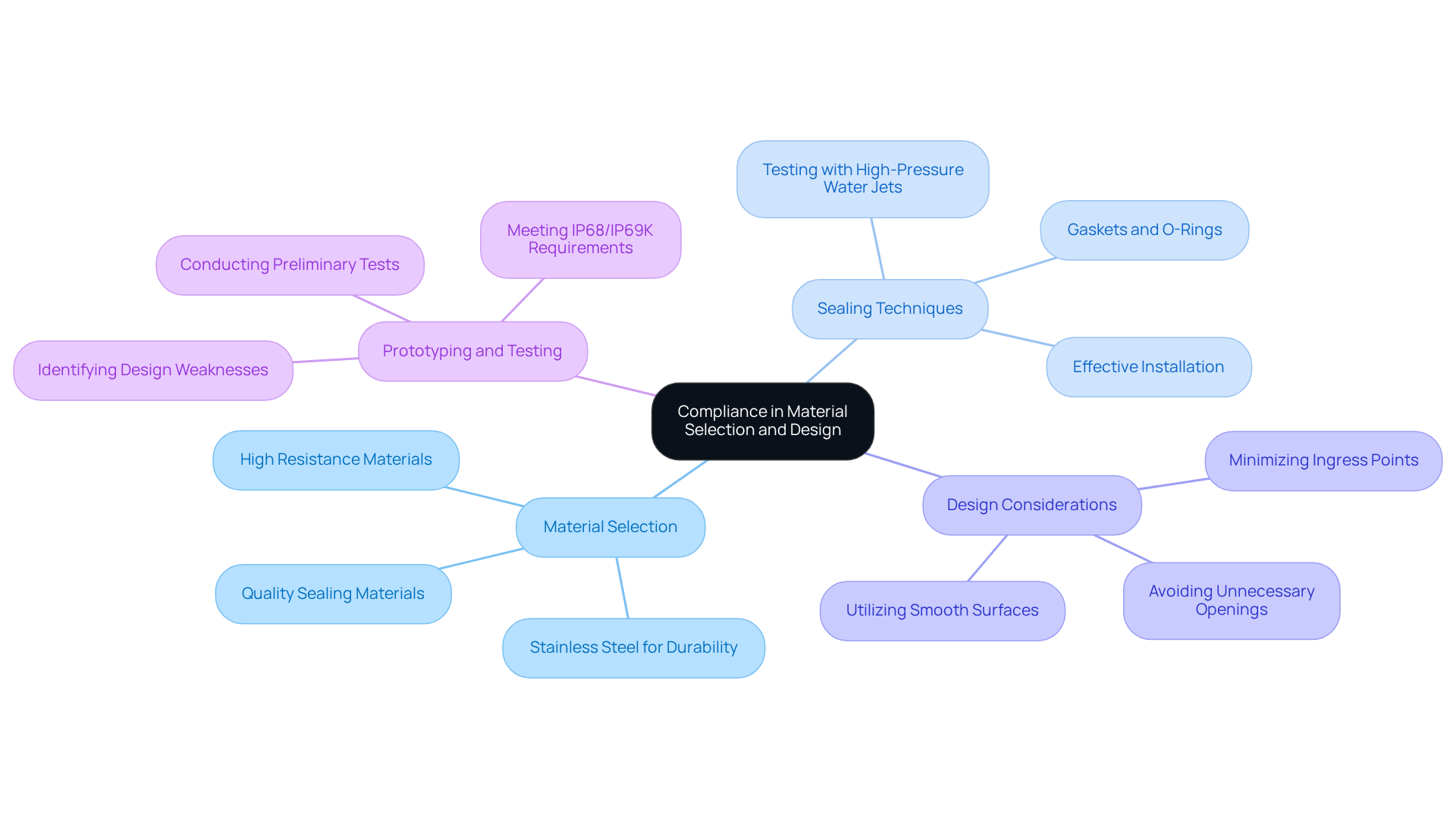
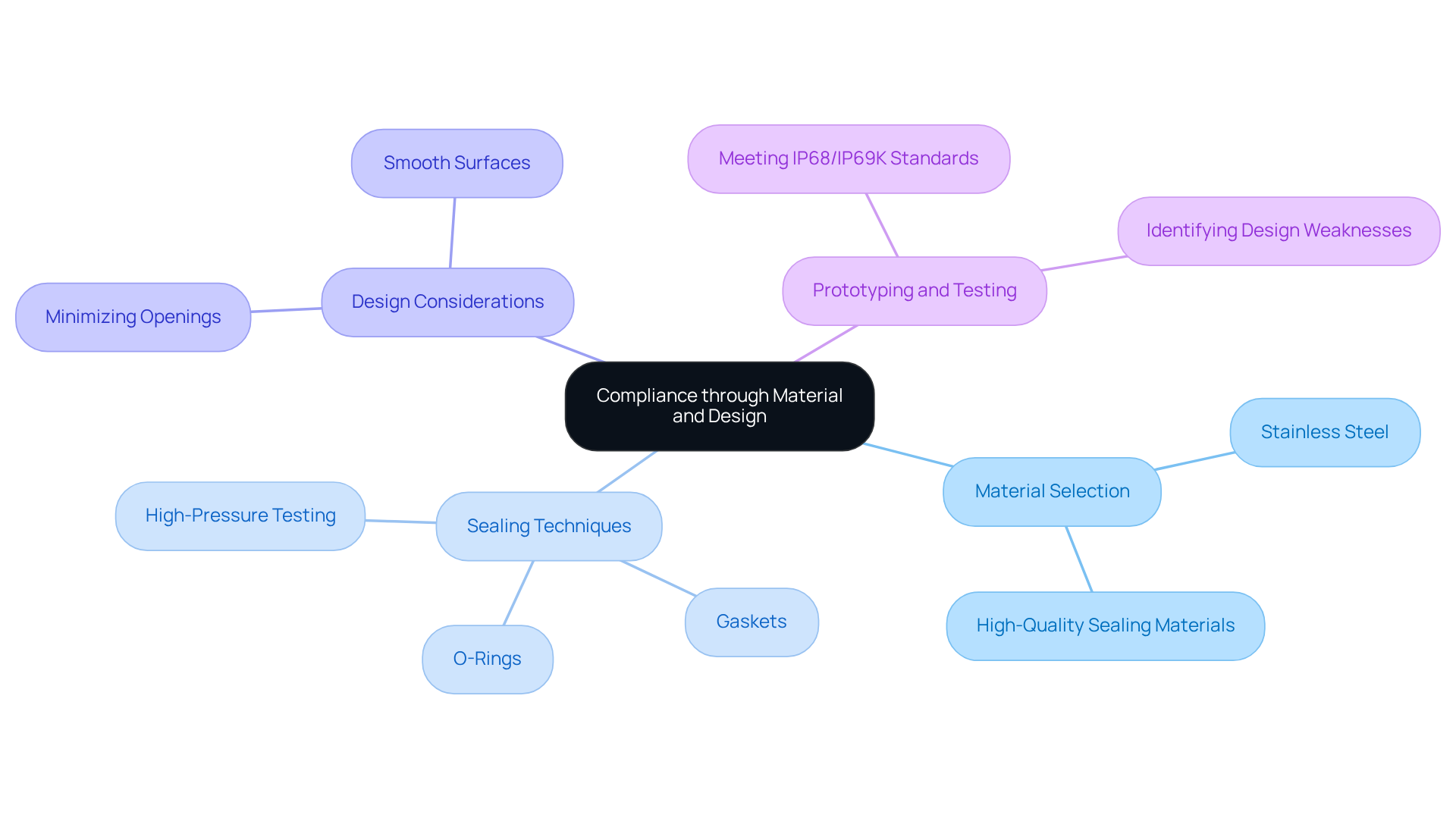
Select Suitable Materials and Design for Compliance
Material Selection: Selecting the right materials is essential for ensuring robust resistance to dust and water. Stainless steel, for instance, is an excellent choice for meeting high protection standards. As Andrew J. Robbins emphasizes, using higher-quality sealing materials is vital for ensuring devices can withstand environmental challenges, particularly in demanding scenarios.
Sealing Techniques: Effective sealing methods, such as gaskets and O-rings, are crucial for preventing ingress. These components must be meticulously chosen and installed to guarantee their effectiveness across various conditions. In high-pressure environments, testing with high-pressure water jets at temperatures reaching 80°C, as specified in the ISO 20653 standard, is particularly important.
Design Considerations: A well-thought-out design can significantly reduce potential ingress points. Utilizing smooth surfaces and avoiding unnecessary openings are proactive strategies that can prevent moisture and dust ingress, which are major contributors to equipment failures.
Prototyping and Testing: Developing prototypes and conducting preliminary tests is critical for identifying potential design weaknesses before final production. This step is essential for ensuring that the product meets the stringent requirements of the IP68/IP69K ratings, ultimately enhancing reliability and performance in real-world applications.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of IP68 and IP69K ratings is essential for engineers and manufacturers operating in environments where devices face extreme conditions. These ratings provide a framework for evaluating the durability and functionality of electronic equipment, ensuring they can withstand dust and water exposure effectively. By focusing on four key checkpoints:
- Defining the ratings
- Verifying compliance standards
- Assessing application needs
- Selecting suitable materials and design
companies can position their products for success in demanding industries.
The importance of rigorous testing standards and documentation cannot be overstated. It is crucial to understand user requirements and industry standards. The distinction between IP68’s immersion capabilities and IP69K’s resistance to high-pressure washdowns reinforces the need for precise selection based on environmental demands. Furthermore, the role of material choice and effective sealing techniques emerges as a critical factor in achieving compliance.
Ultimately, ensuring IP68/IP69K compliance transcends mere regulatory requirements; it is a vital component of product reliability and customer trust. As industries increasingly prioritize durability and hygiene, manufacturers must commit to thorough testing and meticulous design processes. By adhering to these essential checkpoints, organizations can not only meet compliance standards but also enhance the longevity and performance of their electronic devices in the field.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do IP68 and IP69K ratings signify?
IP68/IP69K ratings signify complete dust protection and the ability to endure continuous immersion in water beyond one meter for a specified duration, as well as protection against high-pressure, high-temperature water jets.
In what environments are IP68/IP69K rated devices suitable?
These devices are suitable for environments requiring immersion protection without high-pressure cleaning and for settings that demand stringent cleaning protocols, such as food processing and industrial applications.
What is the primary difference between IP68 and IP69K ratings?
The primary difference is that IP68 focuses on immersion capabilities, while the IP68/IP69K rating is tailored for high-pressure washdowns.
Why is the distinction between IP68 and IP69K important for engineers?
The distinction is important because it impacts the durability and functionality of electronic devices, guiding engineers in selecting appropriate enclosures for specific applications.
What are common applications for devices with IP68/IP69K ratings?
Common applications include outdoor electronics, automotive components, and industrial equipment, where reliable performance in wet conditions is essential.
What should be considered regarding the limitations of IP classifications?
It is crucial to understand that IP classifications do not account for chemical resistance, which is important for making informed enclosure selections.

