Introduction
In electronics engineering, managing fan noise levels transcends mere technical challenge; it is a pivotal aspect of user experience. As devices grow more compact and powerful, the demand for quieter cooling solutions escalates, presenting engineers with both an opportunity and a dilemma. How can they effectively balance optimal cooling performance with the necessity for silence in increasingly noise-sensitive environments? This article delves into essential strategies that engineers can adopt to master fan noise control, ensuring that innovation does not compromise tranquility.
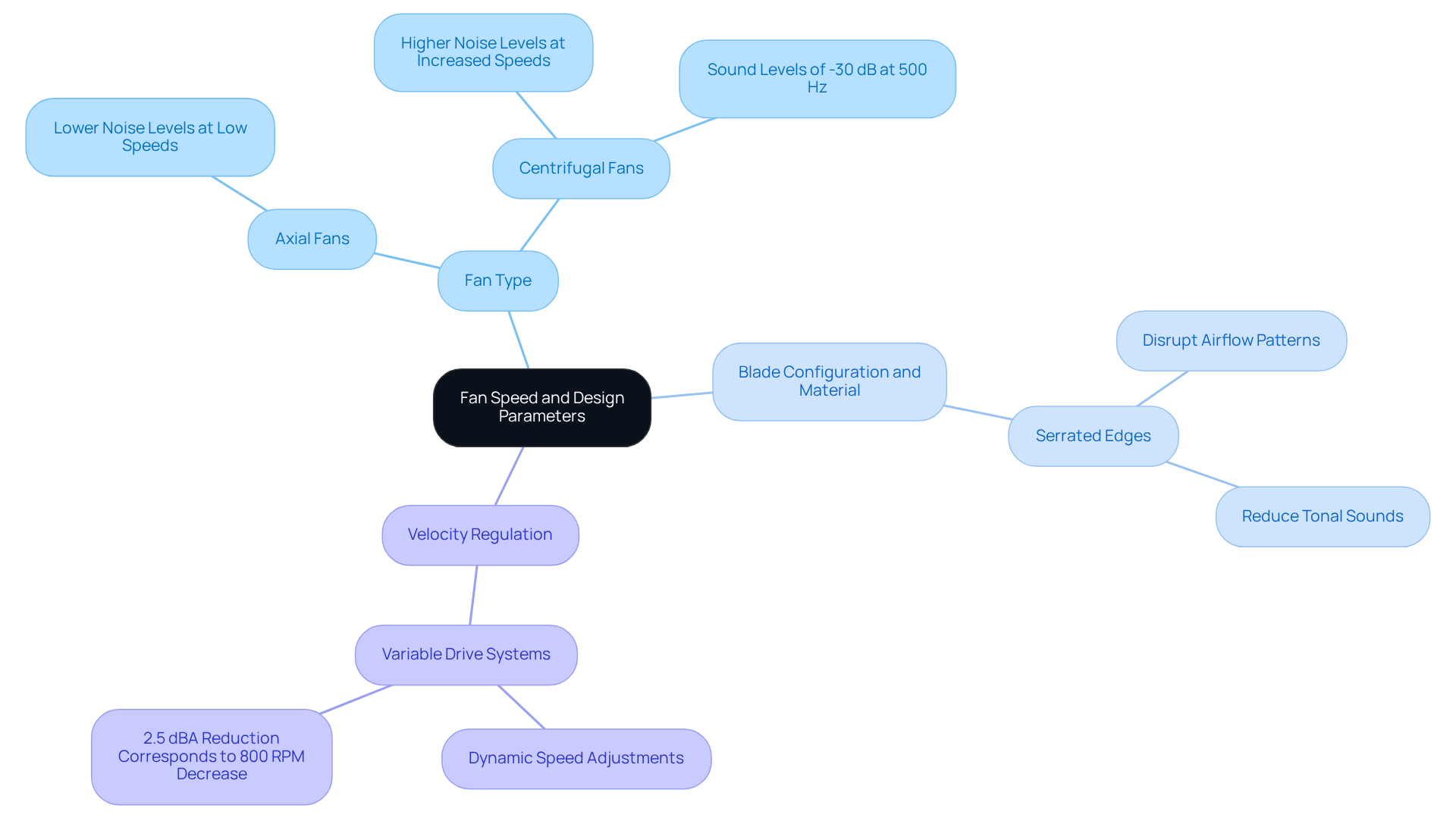
Understand Fan Speed and Design Parameters
Fan rotation plays a crucial role in determining the fan noise level within electronic systems. As fan speed increases, the fan noise level rises, often resulting in elevated sound emissions along with increased airflow. Engineers must carefully assess the following design parameters to optimize performance while minimizing noise:
-
Fan Type: The selection between axial and centrifugal fans significantly influences noise characteristics. Gagner-Toomey Associates offers an extensive range of DC input Tube Axial units and Centrifugal Blowers, available in sizes from 15 to 280mm for axial units and 15 to 225mm for blowers. Typically, axial fans operate at a lower fan noise level at lower speeds, while centrifugal fans may generate more noise as speed increases. For example, a centrifugal fan with forward-curved blades can produce sound intensities as low as -30 dB at 500 Hz, underscoring the importance of choosing the right fan type for specific applications.
-
Blade Configuration and Material: The configuration and material of fan blades are pivotal in determining the fan noise level. Gagner-Toomey’s innovative designs, featuring blades with serrated edges, can disrupt airflow patterns, effectively reducing tonal sounds. This design aspect is essential for achieving a reduced fan noise level, particularly in environments where sound sensitivity is critical.
-
Velocity Regulation: Implementing variable drive systems enables dynamic adjustments of fan speeds based on thermal requirements, significantly reducing noise during low-load conditions. For instance, a decrease of 2.5 dBA in sound corresponds to an approximate reduction of 800 RPM in fan speed, demonstrating how effective speed control can enhance user comfort without sacrificing cooling efficiency.
Moreover, most models are available with IP protection upon request, further enhancing their value across various applications. By understanding these parameters, engineers can make informed decisions that align cooling performance with reducing the fan noise level, ultimately leading to improved user satisfaction and compliance with sound standards in electronic designs. Gagner-Toomey Associates distinguishes itself as a premier provider of innovative cooling solutions, offering a comprehensive portfolio that caters to diverse applications in electronics and beyond.
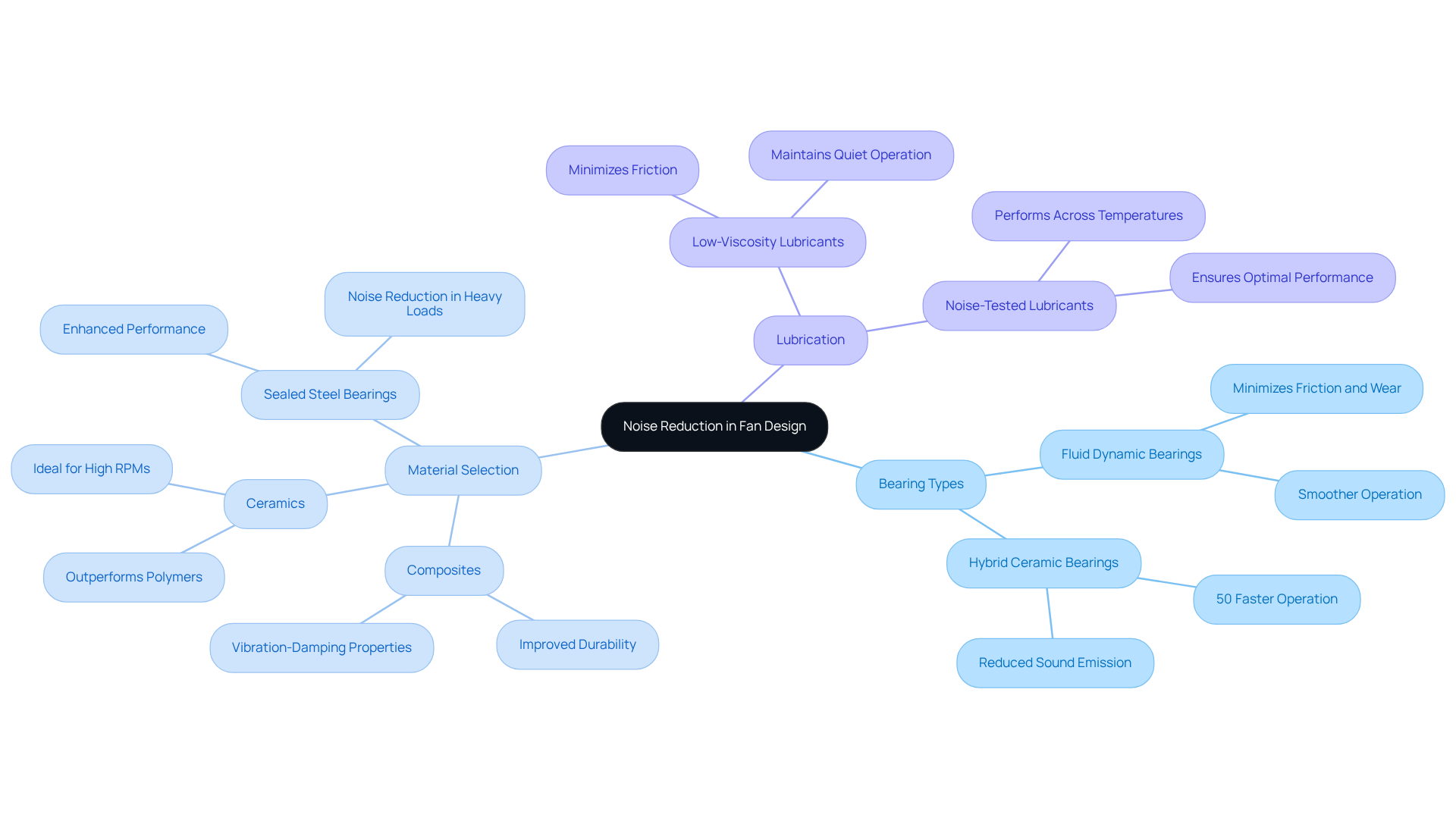
Choose Optimal Bearings and Materials for Noise Reduction
The choice of bearings and materials is crucial in controlling the fan noise level and sound intensity. Understanding this can significantly impact performance regarding the fan noise level in noise-sensitive environments.
- Bearing Types: Fluid dynamic bearings (FDB) are highly recommended for low-noise applications. Their superior ability to minimize friction and wear leads to smoother operation compared to conventional ball bearings, significantly reducing sound emission. For instance, hybrid ceramic bearings can operate up to 50% faster than traditional bearings, enhancing performance where noise control is paramount.
- Material Selection: Advanced materials like composites and ceramics can greatly improve durability while also reducing sound. These materials possess excellent vibration-damping properties, which are essential in environments where the fan noise level is sensitive. Notably, ceramic or sealed steel bearings outperform polymers under heavy loads or high RPMs, making them ideal for various applications.
- Lubrication: Effective lubrication is vital for minimizing friction and ensuring optimal performance. Engineers should select low-viscosity and noise-tested lubricants designed to perform well across varying temperatures and conditions, thus maintaining quiet operation.
By prioritizing these factors, engineers can design fans that not only operate quietly but also achieve high efficiency, aligning with the latest advancements in sound reduction technologies for 2025.
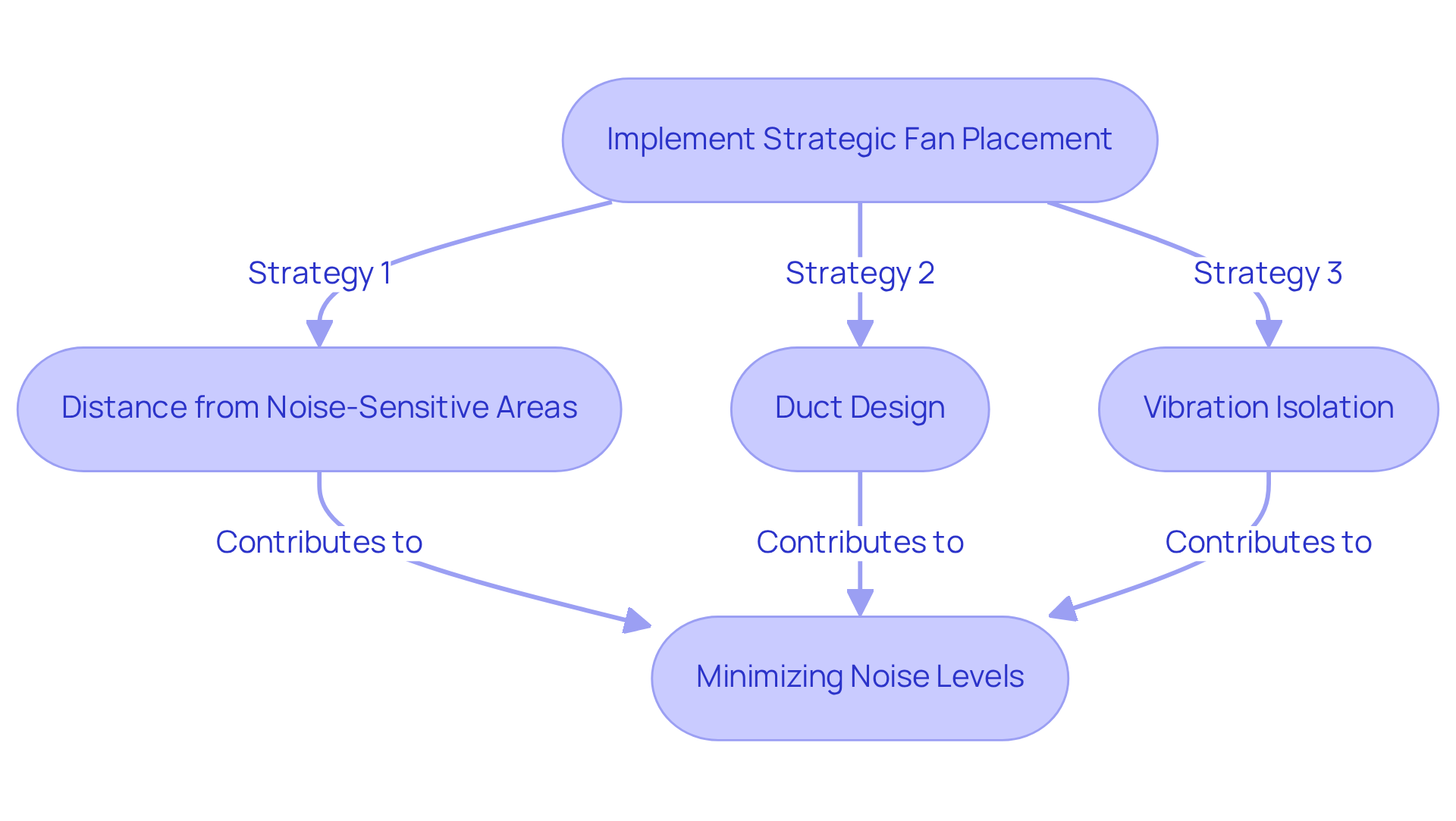
Implement Strategic Fan Placement and Installation Techniques
Proper fan positioning and installation are crucial for minimizing the fan noise level in electronic systems. To effectively address this challenge, consider the following strategies:
- Distance from Noise-Sensitive Areas: Position fans away from sensitive components or user areas to significantly reduce perceived noise, especially in consumer electronics.
- Duct Design: Implementing well-designed ducting can greatly enhance airflow while minimizing sound. Research indicates that a duct system can decrease average and peak sound intensity by as much as 12.5% at lower fan rates, thanks to optimized airflow and reduced turbulence. As noted by Sanjay Bhat, “The results show that the duct significantly decreases both average and peak sound levels, with reductions of up to 12.5% at lower fan speeds due to enhanced airflow streamlining and diminished turbulence.” This design choice not only mitigates disturbances but also improves cooling efficiency.
- Vibration Isolation: Employ vibration-damping mounts or pads to reduce the transmission of vibrations from the fan to surrounding structures, which can amplify sound. Effective vibration isolation techniques can further enhance sound reduction, especially in relation to the fan noise level, as supported by various studies in the field.
By implementing these methods, engineers can boost the efficiency of their cooling systems while effectively controlling sound, ultimately ensuring a superior user experience.
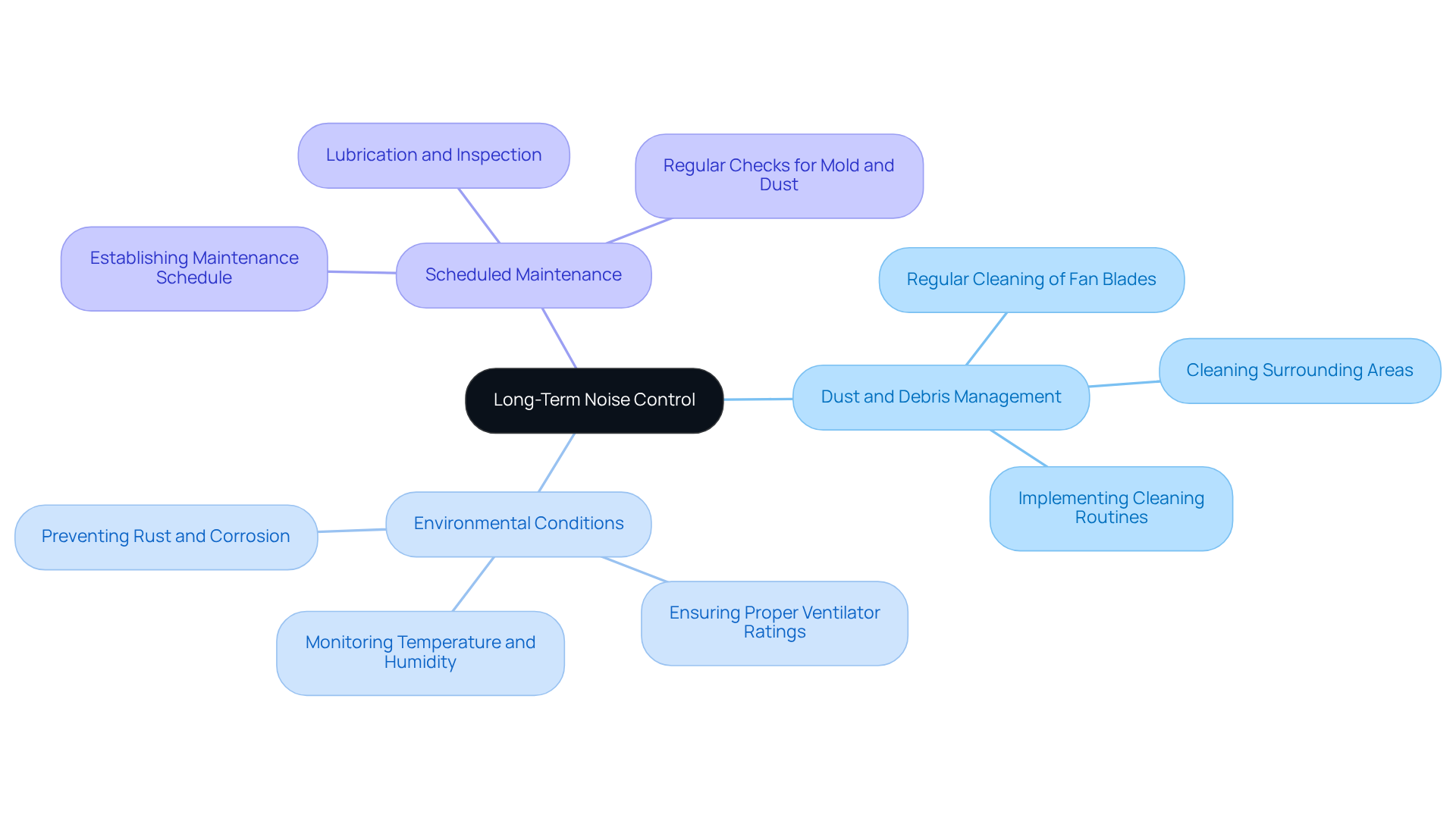
Consider Environmental Factors and Maintenance for Long-Term Noise Control
Environmental factors and regular maintenance are crucial for effectively managing the fan noise level over time. Here are key considerations:
-
Dust and Debris Management: Regular cleaning of fan blades and surrounding areas is vital to prevent dust accumulation, which can lead to increased noise levels and decreased efficiency. A dirty extractor fan can produce unsettling buzzing, humming, or rattling sounds. Implementing a simple cleaning routine can transform distracting noises into a quieter environment, ultimately enhancing indoor air quality and comfort.
-
Monitoring environmental conditions is essential, as extreme temperatures and humidity can significantly impact the fan performance and fan noise level. For example, high humidity can accelerate the collection of mold and debris, impairing fan mechanisms. Constant exposure to steam can lead to rust developing on metal components of the fan. It is crucial to ensure that ventilators are rated for specific operational conditions; devices in high-temperature environments may require special materials to prevent corrosion and maintain efficiency.
-
Scheduled Maintenance: Establishing a proactive maintenance schedule that includes lubrication, inspection of bearings, and wear checks can help identify potential sound issues before they escalate. Bathroom ventilators should be inspected every six months for mold and dust accumulation. Regular maintenance not only extends the lifespan of the fan but also reduces the risk of mechanical failures that can negatively impact the fan noise level and lead to disruptive noises. In environments like kitchens or bathrooms, where humidity is prevalent, fans should be cleaned every three months to prevent grease and mold buildup.
By addressing these factors, engineers can ensure that their cooling systems operate efficiently and quietly throughout their lifespan, ultimately contributing to a more comfortable and productive environment.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing fan noise levels is crucial for electronics engineers who aim to enhance user satisfaction and comply with sound standards. By selecting appropriate fan types, optimizing blade configurations, and employing effective installation techniques, engineers can significantly reduce noise emissions while ensuring optimal cooling performance.
Key strategies include:
- Choosing the right bearings and materials to minimize sound intensity
- Maintaining proper fan placement to mitigate noise in sensitive environments
Regular maintenance and environmental considerations are vital, as these factors play a significant role in sustaining low noise levels over time.
Ultimately, adopting these best practices leads not only to quieter electronic devices but also to a more comfortable and efficient user experience. Engineers are encouraged to implement these strategies in their designs, ensuring that noise control remains a priority in their projects as they look toward the future of electronics in 2025 and beyond.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is fan speed important in electronic systems?
Fan speed is crucial because it directly affects the fan noise level and airflow within electronic systems. As the fan speed increases, the noise level typically rises, which can impact user comfort.
What factors should engineers consider to minimize fan noise?
Engineers should assess several design parameters, including fan type, blade configuration and material, and velocity regulation, to optimize performance while minimizing noise.
How does the choice between axial and centrifugal fans affect noise levels?
The selection between axial and centrifugal fans significantly influences noise characteristics. Axial fans generally operate at lower noise levels at lower speeds, while centrifugal fans may produce more noise as their speed increases.
What are the noise characteristics of centrifugal fans with forward-curved blades?
Centrifugal fans with forward-curved blades can produce sound intensities as low as -30 dB at 500 Hz, highlighting the importance of selecting the right fan type for specific applications.
How does blade configuration and material impact fan noise?
The configuration and material of fan blades are critical in determining noise levels. Innovative designs, such as blades with serrated edges, can disrupt airflow patterns and effectively reduce tonal sounds, which is essential in sound-sensitive environments.
What is the role of velocity regulation in fan noise reduction?
Implementing variable drive systems allows for dynamic adjustments of fan speeds based on thermal requirements, which can significantly reduce noise during low-load conditions. For example, a decrease of 2.5 dBA in sound corresponds to an approximate reduction of 800 RPM in fan speed.
Are there additional features available for fans to enhance their application?
Yes, most models are available with IP protection upon request, which enhances their value across various applications, ensuring compliance with sound standards in electronic designs.
What does Gagner-Toomey Associates offer in terms of cooling solutions?
Gagner-Toomey Associates is a premier provider of innovative cooling solutions, offering a comprehensive portfolio that caters to diverse applications in electronics and beyond.

