Introduction
Fluid dynamic bearing (FDB) technology is transforming the electronics design landscape, delivering unmatched benefits in longevity, efficiency, and noise reduction. With lifespans extending up to 300,000 hours, these cutting-edge fans are becoming indispensable for applications that prioritize reliability and quiet operation.
Yet, as the electronics industry evolves, a pressing question arises: how can engineers effectively incorporate FDB fans into their designs to optimize performance and efficiency?
This article explores the complexities of FDB technology, highlighting its advantages, technical specifications, and best practices for seamless integration into electronic systems.
Explore Fluid Dynamic Bearing Technology
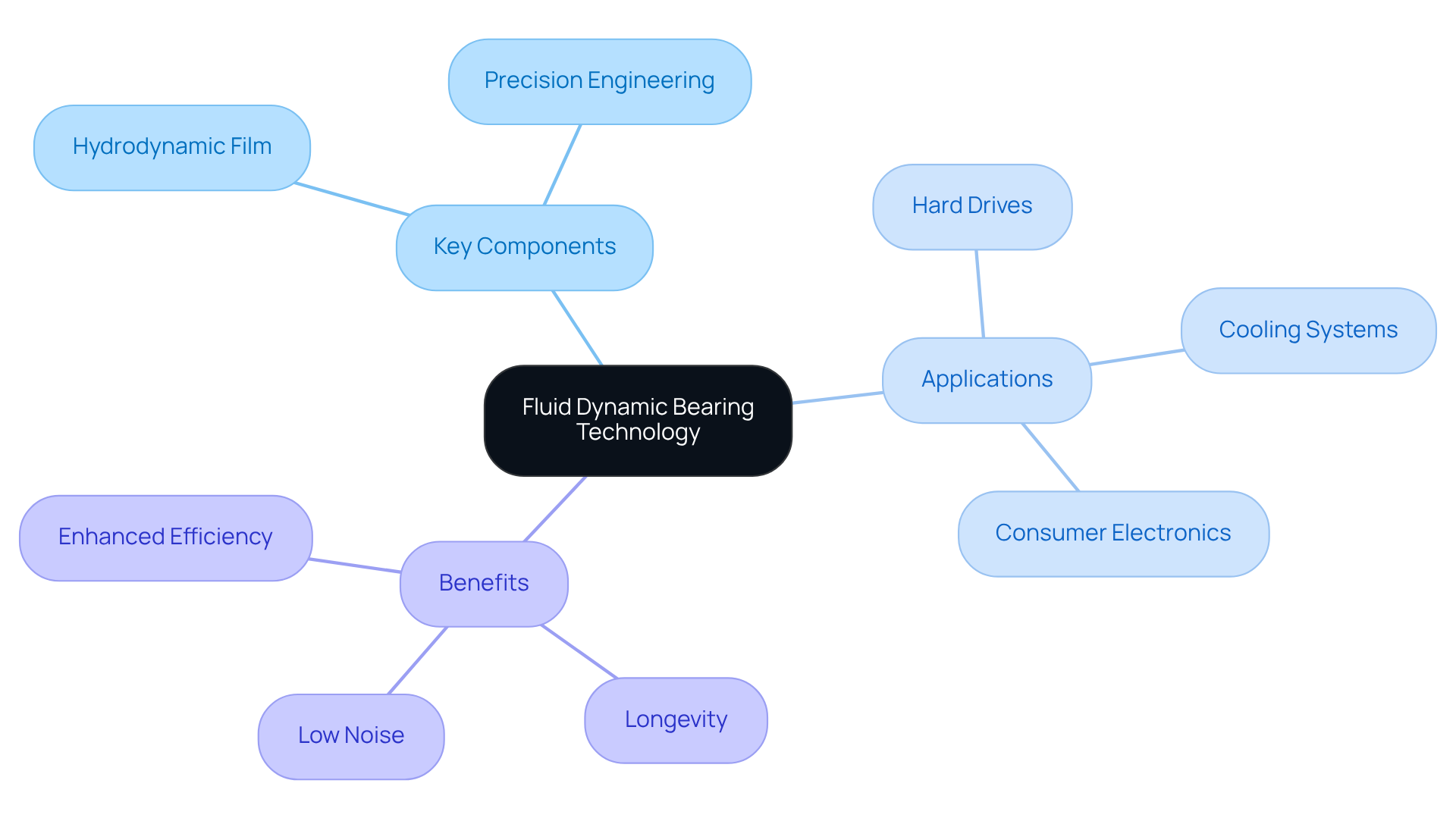
Fluid dynamic supports (FDSs) leverage a thin layer of lubricant, typically oil, to establish a hydrodynamic film that supports the rotating shaft. This cutting-edge design significantly minimizes friction and wear, leading to quieter operation and an impressive lifespan of around 300,000 hours-far surpassing traditional ball bearings, which generally last between 60,000 and 75,000 hours. Such technology is particularly beneficial in applications that require high reliability and low noise, like computers and consumer electronics, where operational efficiency is crucial.
Key Components of FDB Technology:
- Hydrodynamic Film: The lubricant forms a film that effectively separates moving parts, reducing direct contact and wear, which is vital for sustaining performance over time.
- Precision Engineering: The production of FDBs demands exceptional precision, enhancing their reliability and overall performance.
- Applications: FDBs are commonly utilized in cooling systems, hard drives, and various electronic devices where noise reduction and longevity are paramount. For example, Nidec’s UltraFlo fluid dynamic bearing fan technology is specifically engineered for thin laptop computers, demonstrating its capability to improve cooling efficiency while ensuring quiet operation.
Engineers have observed that the advantages of FDBs extend beyond mere longevity; they also enhance thermal management and system efficiency. As the electronics industry evolves, the demand for low-noise, high-performance components is propelling the adoption of FDB technology. This trend is particularly evident in the growing market for fluid dynamic supports, especially in the Asia Pacific region, where advancements in manufacturing capabilities are meeting the increasing demand for high-performance components across various sectors, including automotive and consumer electronics. Furthermore, integrating solenoid and rotary boost pumps into cooling solutions can further elevate system efficiency and performance, aligning with Gagner-Toomey Associates’ commitment to innovation in advanced pump technologies.
Identify Benefits of FDB Fans in Electronics Design
Fluid dynamic bearing fans (FDB) offer a range of advantages that are crucial for modern electronics design:
-
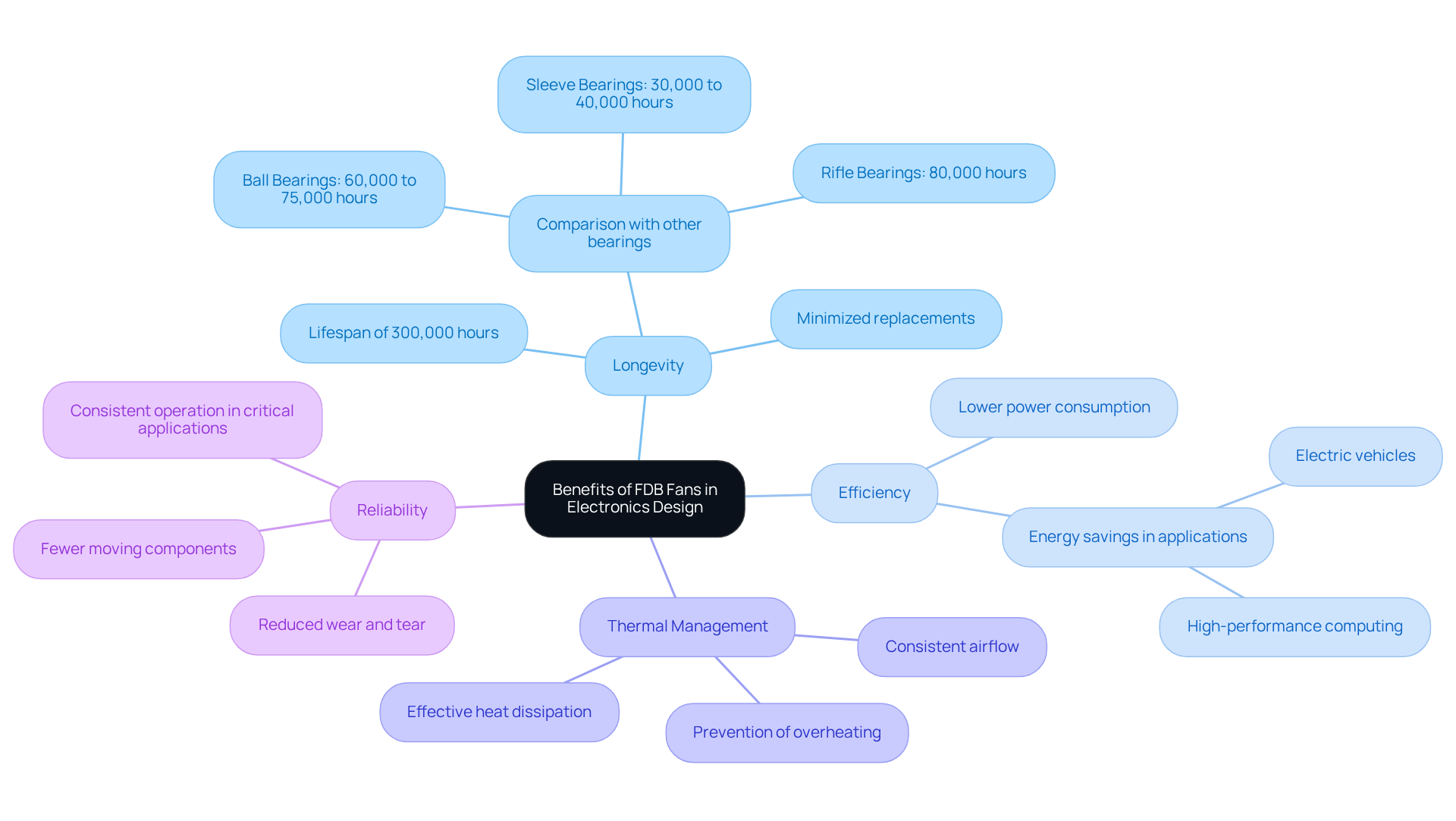
Longevity: FDB fans have an impressive lifespan of around 300,000 hours, significantly outlasting traditional bearing types. For instance, ball bearings typically last between 60,000 to 75,000 hours, while sleeve bearings range from 30,000 to 40,000 hours. This extended operational life minimizes the need for frequent replacements, thereby enhancing overall system reliability.
The fluid dynamic bearing fan creates a hydrodynamic film that effectively diminishes vibrations and noise, making it ideal for applications where sound levels are paramount. Notably, FDB fans operate at lower noise levels compared to sleeve and ball bearings, which tend to become noisier over time. -
Efficiency: With lower power consumption, the fluid dynamic bearing fan devices contribute to energy savings in electronic systems. Their design promotes higher efficiency, particularly beneficial in energy-sensitive applications such as electric vehicles and high-performance computing.
-
Thermal management: Thermal management is crucial, and a fluid dynamic bearing fan excels at maintaining consistent airflow, which is vital for effective heat dissipation. This capability is essential in preventing overheating of electronic components, thus improving the longevity and functionality of devices.
-
Reliability: Reliability is improved with a fluid dynamic bearing fan, as it features fewer moving components and reduced wear, making it less prone to failure. This reliability ensures consistent operation in critical applications, making them a preferred choice for engineers focused on durability and efficiency in their designs.
Evaluate Technical Specifications and Performance Metrics
When selecting fluid dynamic bearing fans, engineers must consider several critical technical specifications and performance metrics, especially those provided by Gagner-Toomey Associates, a leader in innovative cooling solutions:
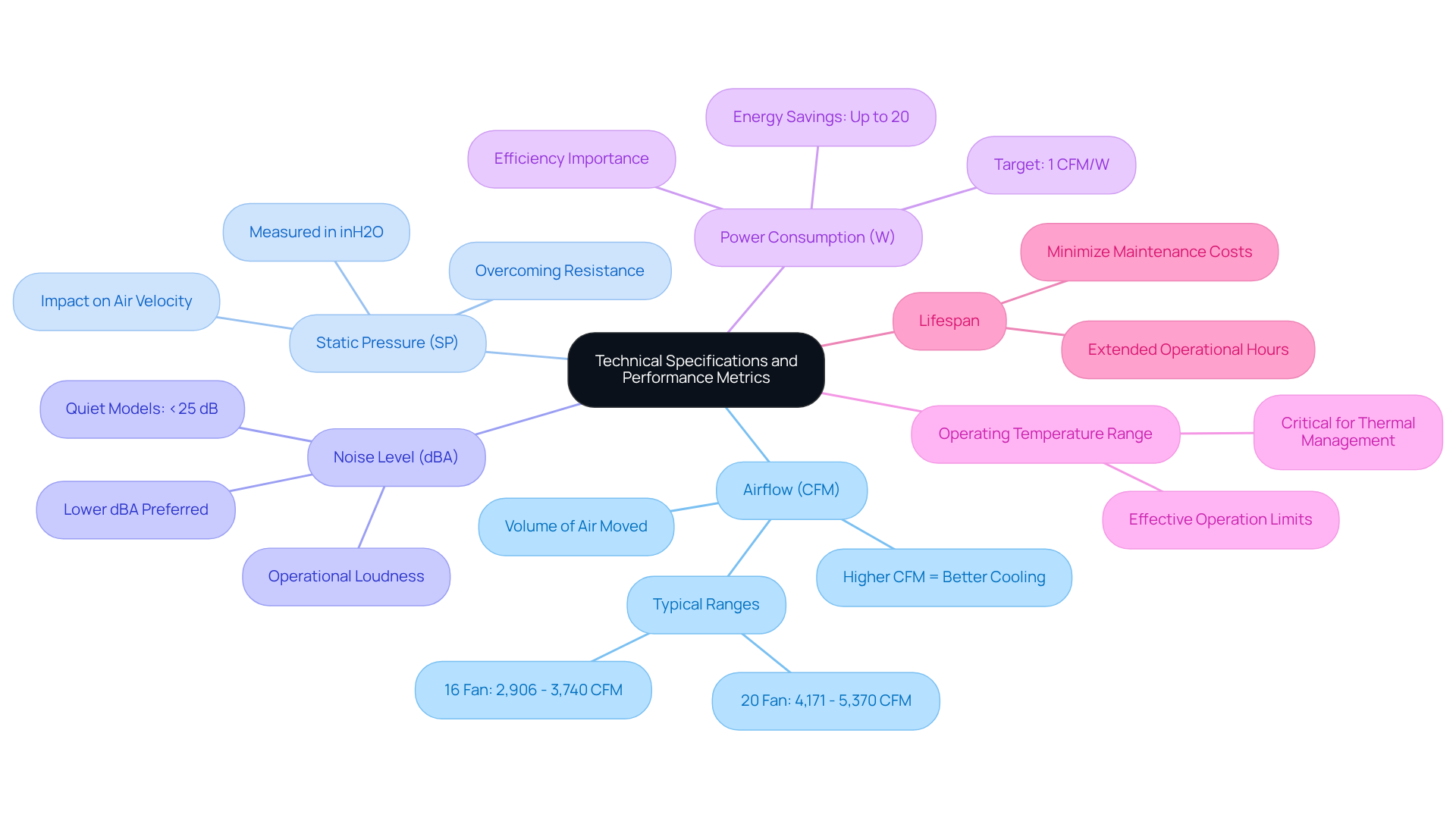
- Airflow (CFM): This measures the volume of air the fan can move. A higher CFM indicates superior cooling performance, which is essential for applications in electronics and beyond.
- Static Pressure (SP): This is crucial for applications where airflow must overcome resistance, such as in densely packed electronic enclosures. Gagner-Toomey effectively addresses this challenge with their comprehensive air-movers, which include fluid dynamic bearing fans.
- Noise Level (dBA): This indicates the operational loudness of the fan. Lower dBA values are preferable for quiet environments, a feature that Gagner-Toomey optimizes in their product line.
- Power Consumption (W): Efficiency is paramount; devices that consume less power while delivering high performance are ideal. This reflects Gagner-Toomey’s commitment to performance and efficiency.
- Operating Temperature Range: It’s vital to ensure the fan can operate effectively within the application’s temperature limits, a critical factor in Gagner-Toomey’s thermal management solutions.
- Lifespan: Seek units rated for extended operational hours to minimize maintenance and replacement costs, which is a hallmark of Gagner-Toomey’s durable designs.
Integrate FDB Fans into Electronic Systems
To effectively integrate fluid dynamic bearing (FDB) fans into electronic systems, it’s essential to follow a structured approach:
-
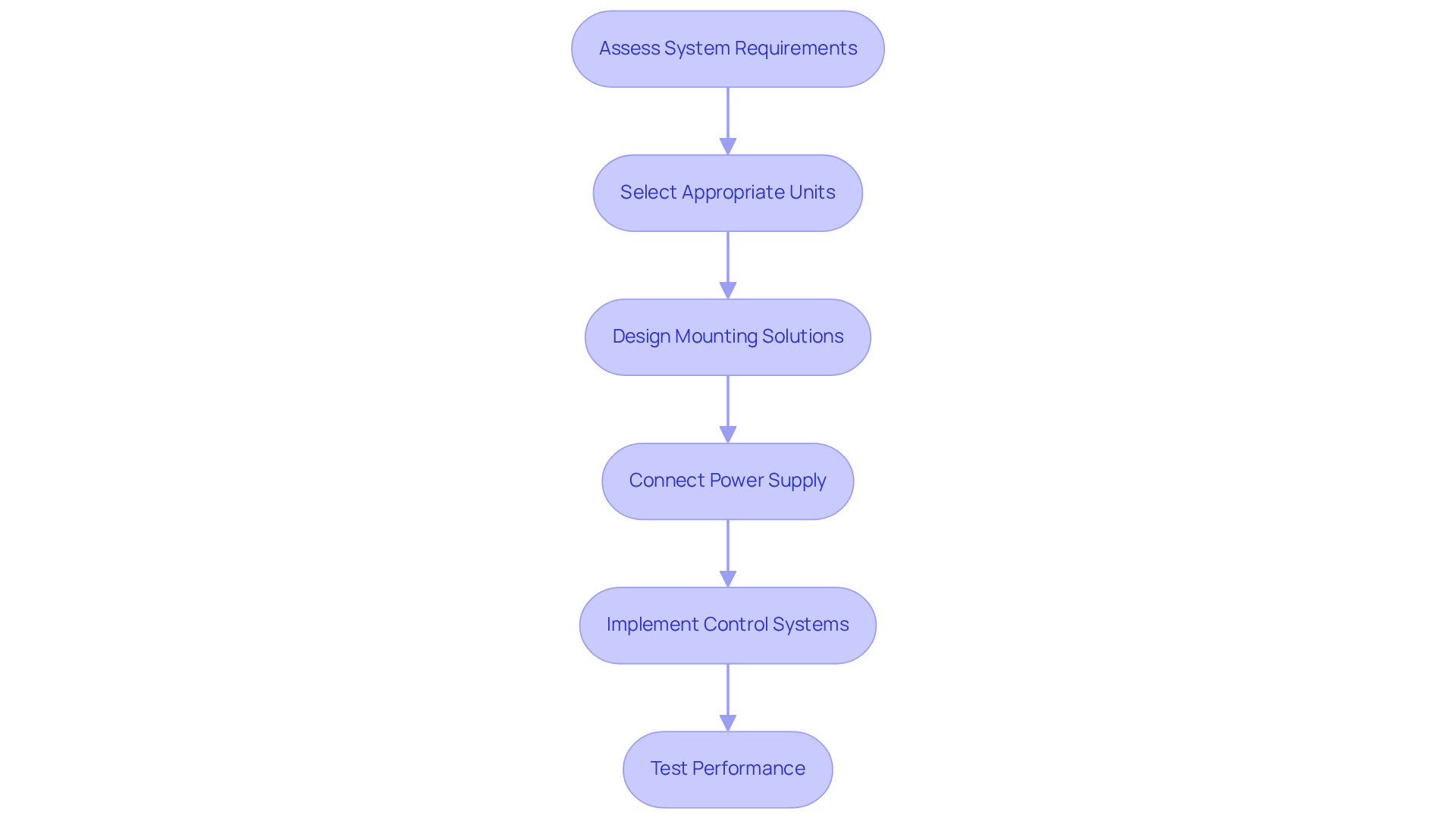
Assess System Requirements: Start by determining the cooling needs based on the heat output of components and the overall design. For example, Ventiva’s ICE9 system can efficiently cool laptops with processors drawing up to 40W. Understanding these thermal demands is crucial for selecting the right fluid dynamic bearing fan units.
-
Select Appropriate Units: Choose FDB units that align with the evaluated specifications, ensuring they meet both airflow and noise requirements. Industry specialists emphasize that selecting devices such as a fluid dynamic bearing fan, which reflect the latest advancements in cooling technology, can significantly enhance system efficiency.
-
Design Mounting Solutions: It’s vital to mount the devices securely to prevent vibrations and optimize airflow direction. Correct installation methods are key to sustaining the functionality of the units and extending the longevity of both the devices and the electronic components.
-
Connect Power Supply: Properly link the cooling devices to the power supply, paying close attention to voltage and current ratings to avoid damage. This step is critical for ensuring reliable operation, particularly when integrating advanced cooling solutions like Ventiva’s technology.
-
Implement Control Systems: Utilize fan controllers or PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) to adjust fan speed according to thermal conditions, thereby enhancing efficiency. Recent innovations in fan control systems demonstrate that intelligent software control can greatly improve energy efficiency and thermal management.
-
Test Performance: After installation, monitor the system’s thermal performance to confirm that the fans are operating as expected. Make adjustments as necessary. Engaging in thorough testing helps identify potential issues early, ensuring optimal cooling efficiency.
Conclusion
Fluid dynamic bearing (FDB) fans mark a significant leap forward in electronics design, delivering unmatched performance and longevity compared to traditional bearing types. By utilizing a hydrodynamic film, these fans effectively reduce friction and wear, ensuring quieter operation and longer lifespans. This makes them an indispensable choice for high-reliability applications within the electronics industry.
This article explores the essential components and advantages of FDB technology, emphasizing their superior efficiency, effective thermal management, and exceptional reliability. With an operational lifespan that greatly exceeds that of ball and sleeve bearings, FDB fans are perfectly suited for applications requiring low noise and high performance. Moreover, integrating these fans into electronic systems necessitates a thorough evaluation of system requirements, careful selection of suitable units, and the implementation of robust control systems to fully harness their capabilities.
As the demand for high-performance, energy-efficient, and quiet cooling solutions escalates, adopting fluid dynamic bearing technology becomes vital for engineers and designers. By capitalizing on the benefits of FDB fans, stakeholders can significantly enhance the reliability and efficiency of their electronic systems, paving the way for groundbreaking advancements in the field. The future of electronics design hinges on the embrace of such innovative technologies, ensuring devices not only operate at peak performance but also contribute to a quieter and more sustainable environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Fluid Dynamic Bearing (FDB) technology?
Fluid Dynamic Bearing technology uses a thin layer of lubricant, typically oil, to create a hydrodynamic film that supports a rotating shaft, significantly reducing friction and wear.
How does FDB technology compare to traditional ball bearings in terms of lifespan?
FDBs have an impressive lifespan of around 300,000 hours, far exceeding the 60,000 to 75,000 hours typical of traditional ball bearings.
What are the key components of FDB technology?
The key components include the hydrodynamic film, which separates moving parts to reduce wear, and precision engineering, which enhances reliability and overall performance.
In what applications are FDBs commonly used?
FDBs are commonly utilized in cooling systems, hard drives, and various electronic devices where low noise and longevity are essential.
What specific example illustrates the use of FDB technology?
Nidec’s UltraFlo fluid dynamic bearing fan technology is designed for thin laptop computers, improving cooling efficiency while ensuring quiet operation.
What additional benefits do FDBs provide beyond longevity?
FDBs enhance thermal management and system efficiency, making them advantageous in high-performance applications.
Why is there a growing demand for FDB technology?
The electronics industry’s evolution is driving the demand for low-noise, high-performance components, leading to increased adoption of FDB technology, especially in the Asia Pacific region.
How do solenoid and rotary boost pumps relate to FDB technology?
Integrating solenoid and rotary boost pumps into cooling solutions can further enhance system efficiency and performance, aligning with advancements in pump technologies.

