Introduction
Understanding the complexities of computer fan dimensions is crucial for achieving optimal cooling solutions in electronic systems. With a range of standard sizes available, each fan type serves a specific purpose that can significantly influence airflow, noise levels, and overall system performance. The challenge, however, lies in selecting the right fan size that not only fits the case but also meets the thermal demands of high-performance components.
Engineers must consider several factors to ensure effective heat dissipation while maintaining quiet operation. These include:
- The fan’s airflow rating
- Static pressure capabilities
- Noise levels
Additionally, understanding the specific cooling requirements of components such as CPUs and GPUs is essential. By carefully evaluating these elements, engineers can make informed decisions that enhance system performance and longevity.
In conclusion, the right fan size is not merely a matter of fitting; it is a critical component in the overall thermal management strategy of electronic systems. By prioritizing these considerations, engineers can achieve a balance between performance and noise, ultimately leading to more efficient and reliable systems.
Explore Computer Fan Dimensions and Their Importance
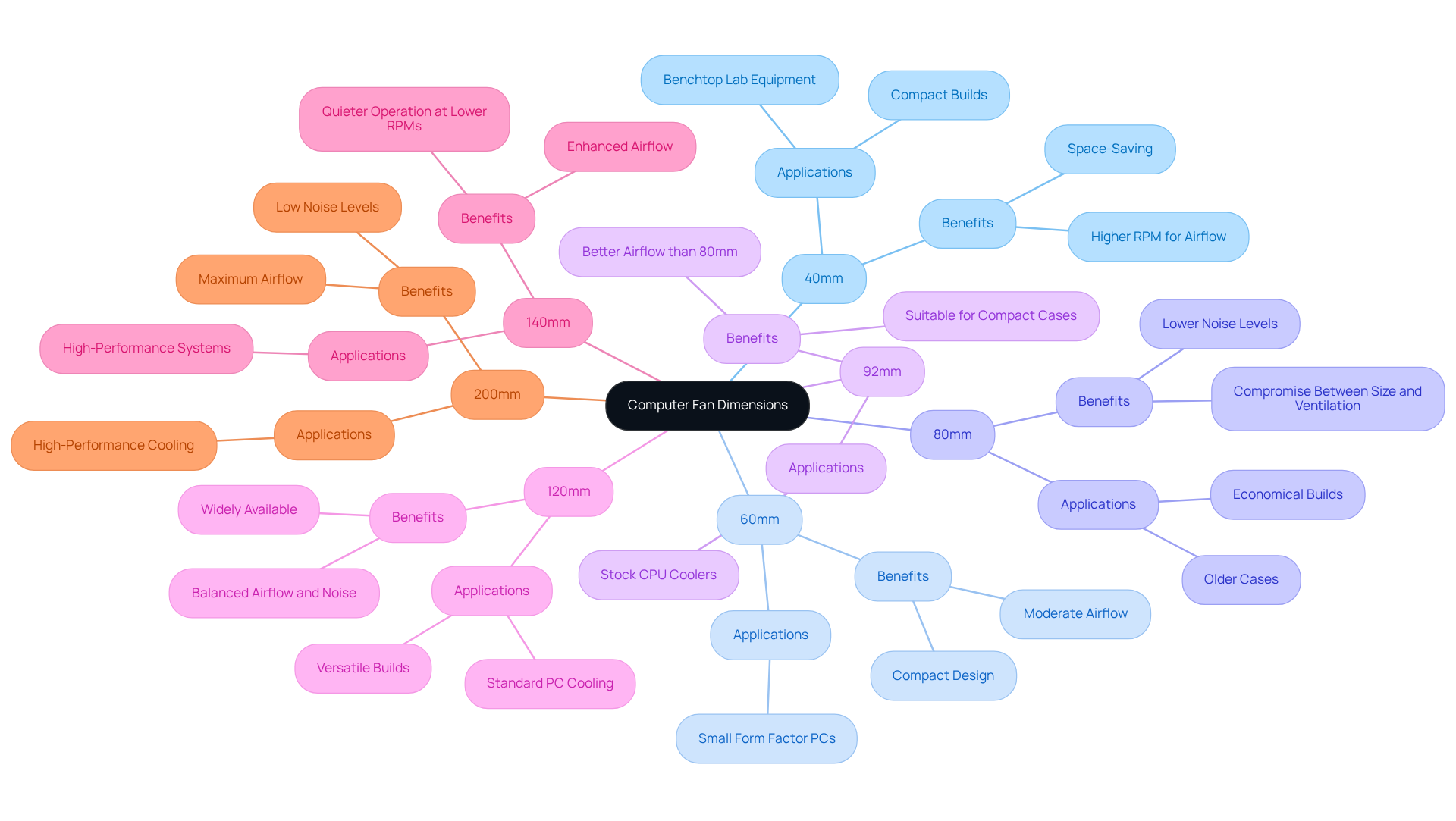
Optimizing thermal performance in electronic systems is crucially tied to understanding computer fan dimensions. Measured in millimeters (mm), standard sizes include:
- 40mm
- 60mm
- 80mm
- 92mm
- 120mm
- 140mm
- 200mm
Each size serves specific applications, with larger fans typically offering improved ventilation at lower RPMs, leading to quieter operation. For instance, 120mm fans are commonly chosen for PC ventilation, striking a balance between airflow and noise. In contrast, 140mm models excel in high-performance scenarios, moving more air while maintaining low noise levels.
Understanding the computer fan dimensions ensures compatibility within the case and effective heat dissipation from critical components like CPUs and GPUs. Properly sized fans not only enhance heat management but also bolster the reliability and longevity of electronic systems. Engineers must consider case dimensions, component heat output, and airflow needs when selecting fan sizes to improve thermal performance and minimize noise.
This strategic approach is vital for maintaining optimal operating conditions, especially in high-performance systems where effective thermal management is paramount. By prioritizing the right computer fan dimensions, engineers can significantly enhance system efficiency and reliability.
Identify Types of Computer Fans and Their Dimensions
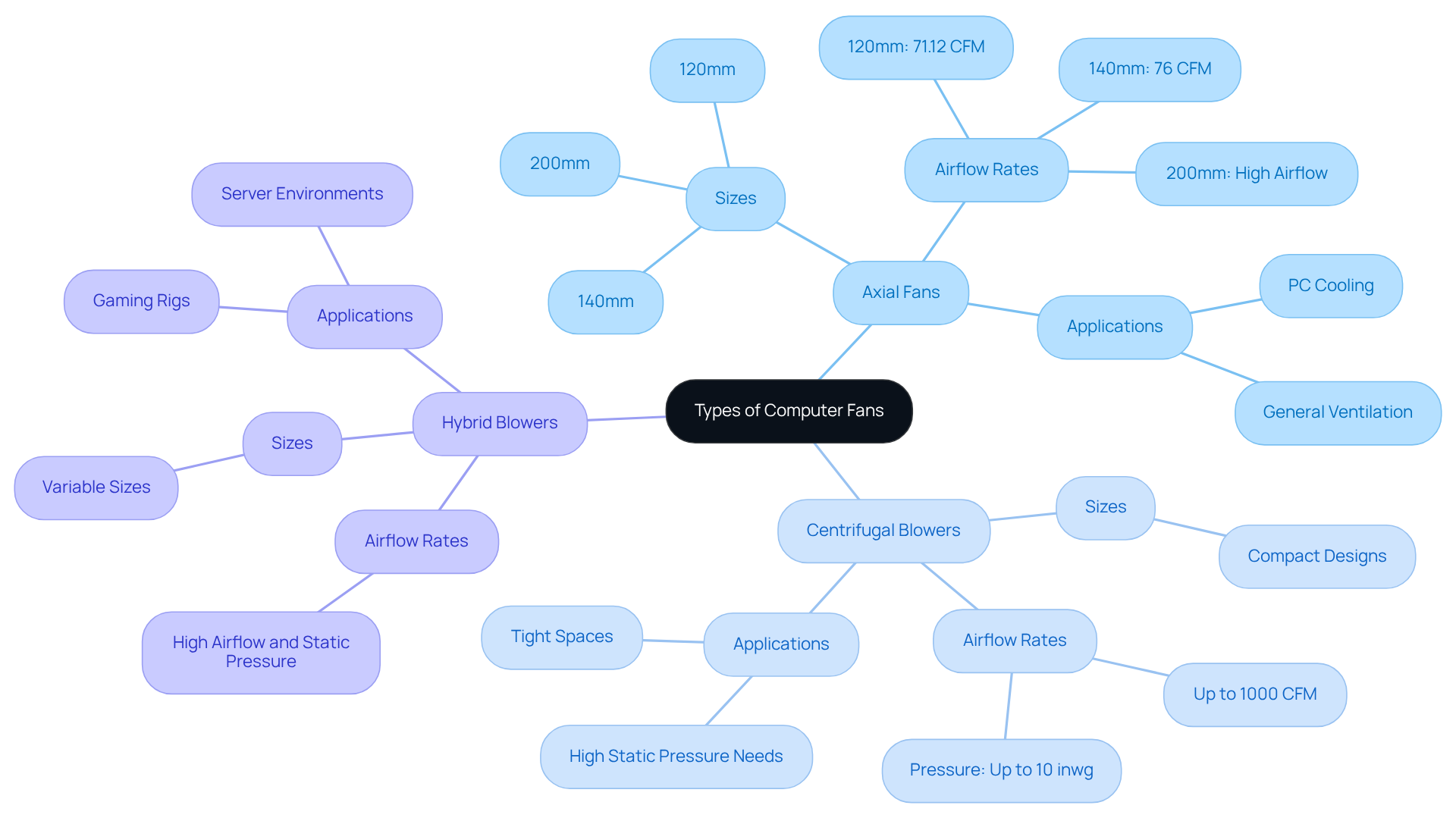
Computer blowers play a vital role in thermal regulation, with various types designed to meet specific temperature control needs. Understanding these options is essential for optimal system performance. Here’s a closer look at the most common types:
-
Axial Fans: Primarily utilized in PC cooling, these fans come in sizes like 120mm and 140mm. They operate by moving air parallel to the fan’s axis, making them perfect for general ventilation applications. Axial blowers typically deliver flow rates of approximately 71.12 CFM for 120mm models and around 76 CFM for larger 140mm units, providing effective cooling for diverse setups. Notably, 140mm and 200mm units are recognized for enhanced ventilation, making them advantageous for high-performance systems.
-
Centrifugal Blowers: Also referred to as blower units, these are designed for applications requiring high static pressure. Their compact design allows for installation in tighter spaces, ideal for environments where airflow is limited. Centrifugal blowers can generate pressures up to 10 inwg, effectively pushing air through heatsinks and other components. It’s crucial to note that noise levels between axial and centrifugal units vary significantly, influencing their suitability for different settings.
-
Hybrid Blowers: These devices combine features of both axial and centrifugal designs, offering versatility in circulation and pressure control. They are particularly beneficial in scenarios demanding both high airflow and static pressure, such as high-performance gaming rigs or server environments.
Understanding the computer fan dimensions and operational characteristics of these devices is crucial for selecting the right type for specific cooling needs, ensuring optimal thermal management and system performance. For instance, the Corsair iCUE QL120 RGB units achieve a maximum airflow of 41.8 CFM at a noise level of 26 dBA, showcasing the performance capabilities of modern units. Additionally, considering the lifespan of fans is vital; HVAC blowers generally last between 15 to 20 years, which can significantly impact maintenance decisions. Gagner-Toomey Associates, a leading provider in the electronics cooling industry, underscores the importance of choosing the appropriate fan type to meet specific operational requirements.
Select the Right Fan Size for Optimal Cooling Performance
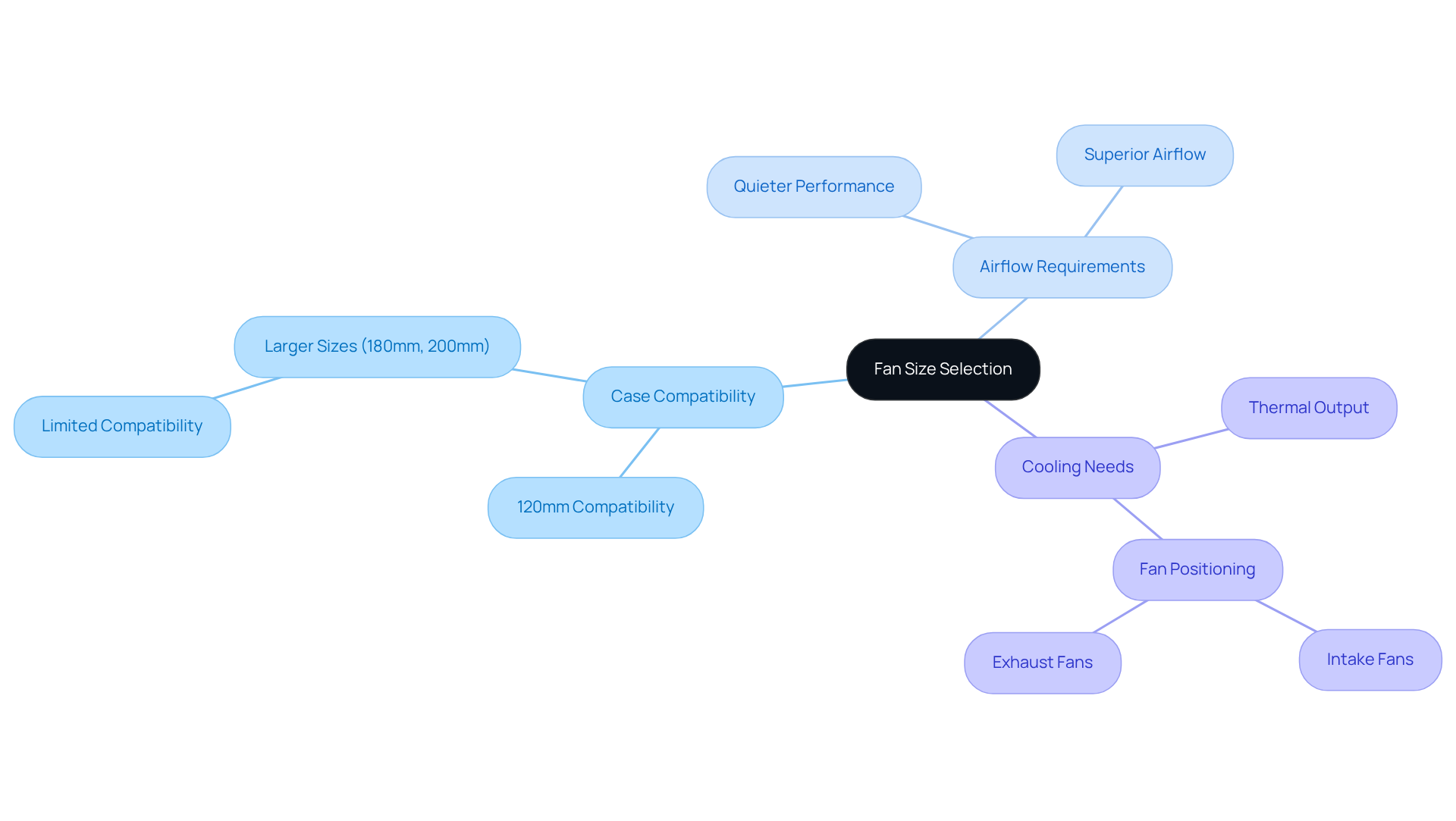
When selecting a fan size, several critical factors must be considered:
-
Case Compatibility: Ensuring that the fan dimensions align with the mounting points in your case is essential. The most prevalent dimensions, 120mm and 140mm, are compatible with the majority of modern cases, allowing for versatile installation options. Approximately 80% of users select 120mm cooling devices, while fewer than 10% of PC cases accommodate larger dimensions like 180mm or 200mm. This makes compatibility a vital factor in your selection process.
-
Airflow Requirements: Larger fans, such as 140mm types, circulate more air at reduced speeds compared to their 120mm counterparts, leading to quieter performance without compromising thermal efficiency. For instance, a 140mm fan delivers superior airflow at the same RPM as a 120mm fan, making it a preferred choice for high-performance systems. Case studies indicate that larger units offer improved temperature regulation and quieter operation, reinforcing their benefits in thermal management.
-
Cooling Needs: Evaluating the thermal output of your components is crucial. High-performance CPUs and GPUs often produce considerable heat, necessitating larger or additional cooling systems to maintain optimal temperatures. In configurations with overclocked parts or sophisticated temperature management systems, employing up to six fans can significantly enhance ventilation and heat regulation. Moreover, correct fan positioning and air movement patterns are essential for efficient temperature regulation; intake fans should draw fresh air in, while exhaust fans should expel warm air out.
By thoroughly evaluating these factors, engineers can choose a fan size that not only optimizes performance but also reduces noise, ensuring a balanced and efficient system.
Evaluate Fan Performance Metrics for Effective Cooling
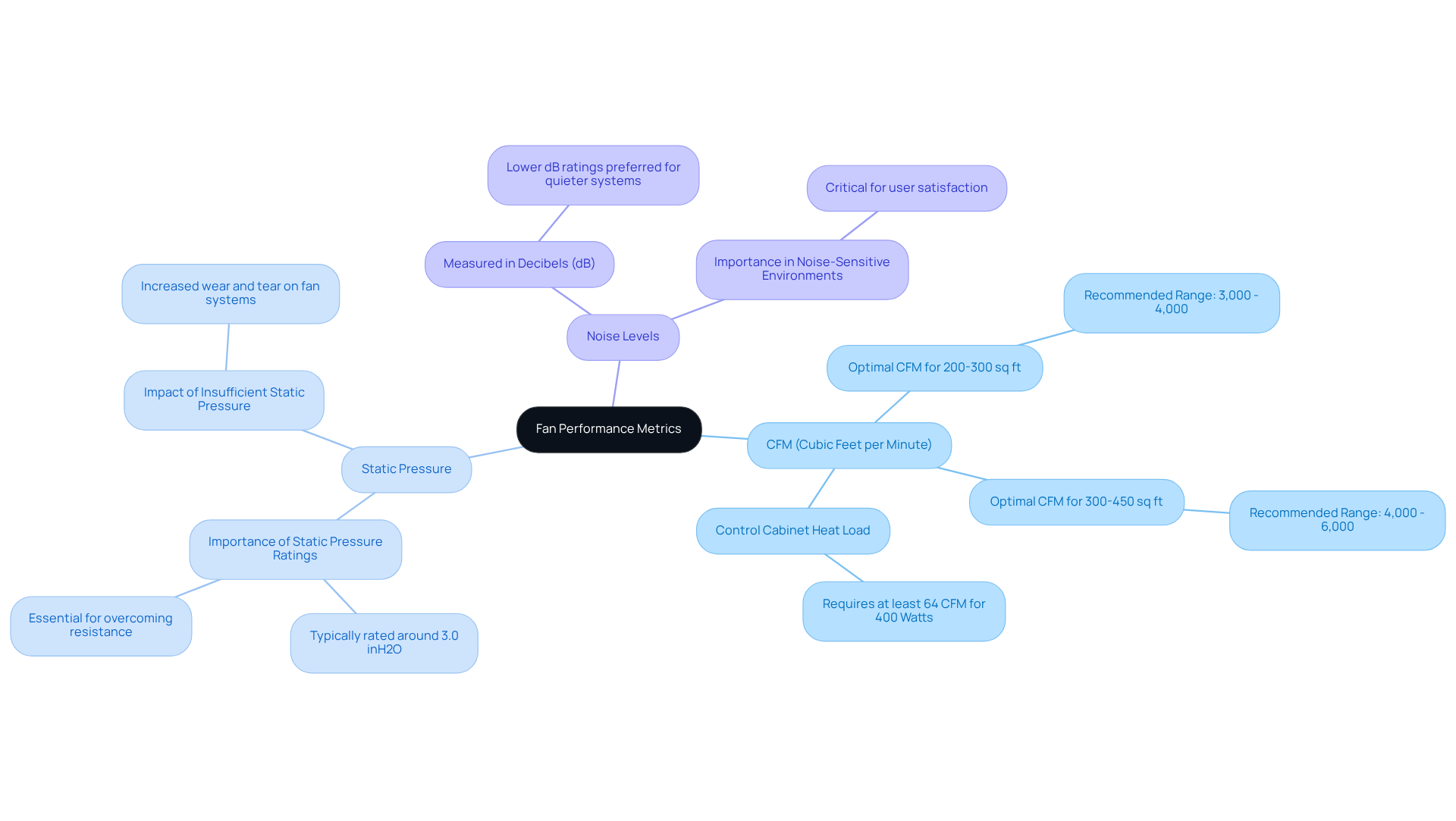
When assessing fan performance, it’s crucial to prioritize several key metrics that directly impact cooling efficiency and system reliability:
-
CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute): This metric quantifies the volume of air a fan can move. Higher CFM ratings signify superior airflow, which is essential for effective cooling. For example, a control cabinet generating 400 Watts of heat requires a blower delivering at least 64 CFM to maintain optimal temperatures. For rooms sized between 200 to 300 square feet, a recommended CFM range of 3,000 to 4,000 is optimal. In contrast, for rooms sized between 300 to 450 square feet, the recommended CFM falls between 4,000 to 6,000.
-
Static Pressure: This measurement reflects a fan’s capability to push air through obstacles like dust filters or heatsinks. Fans designed for high static pressure, typically rated around 3.0 inH2O, excel in overcoming resistance, making them ideal for applications with significant flow restrictions. Understanding static pressure is crucial; insufficient ratings can lead to increased wear and tear on fan systems. Engineers must evaluate the relationship between static pressure and airflow to ensure that the selected fan meets performance criteria.
-
Noise Levels: Measured in decibels (dB), this metric indicates the operational loudness of the fan. Lower dB ratings are preferable for quieter systems, particularly in environments where noise reduction is critical.
By comprehensively understanding these metrics, engineers can select fans that not only fit their systems but also deliver the necessary cooling performance to ensure component reliability and efficiency. Effective temperature control strategies can lead to energy savings of up to 45%, further emphasizing the importance of selecting the right fan based on CFM and static pressure.
Conclusion
Understanding the dimensions of computer fans is crucial for achieving optimal cooling solutions in electronic systems. The right fan size not only ensures compatibility within the case but also enhances thermal management, leading to improved reliability and longevity of critical components. By prioritizing the appropriate dimensions, engineers can effectively manage airflow and noise levels, creating a balanced and efficient cooling environment.
Key points discussed in this article include various standard fan sizes, such as 120mm and 140mm, along with their specific applications in different scenarios. The distinctions between axial, centrifugal, and hybrid blowers underscore the importance of selecting the right type based on airflow needs and spatial constraints. Furthermore, evaluating performance metrics such as CFM, static pressure, and noise levels is essential in determining the most suitable fan for a given system.
Ultimately, careful consideration of fan dimensions and performance metrics can lead to significant improvements in system efficiency and thermal regulation. Engineers and enthusiasts alike are encouraged to leverage this knowledge to make informed decisions that enhance cooling performance, ensuring that their systems operate optimally under various conditions. By mastering the art of fan selection, one can achieve a quieter, more efficient, and reliable electronic environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the standard dimensions of computer fans?
Standard computer fan sizes include 40mm, 60mm, 80mm, 92mm, 120mm, 140mm, and 200mm.
How do fan sizes affect performance?
Larger fans typically offer improved ventilation at lower RPMs, leading to quieter operation. For example, 120mm fans balance airflow and noise, while 140mm fans excel in high-performance scenarios by moving more air quietly.
Why is understanding fan dimensions important?
Understanding fan dimensions ensures compatibility within the computer case and effective heat dissipation from critical components like CPUs and GPUs. Properly sized fans enhance heat management and increase the reliability and longevity of electronic systems.
What factors should engineers consider when selecting fan sizes?
Engineers should consider case dimensions, component heat output, and airflow needs when selecting fan sizes to improve thermal performance and minimize noise.
Why is thermal management crucial in electronic systems?
Effective thermal management is vital for maintaining optimal operating conditions, especially in high-performance systems, as it significantly enhances system efficiency and reliability.

