Introduction
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) stands as a fundamental element in electronics, enabling precise voltage control across diverse applications – from motor management to LED dimming. As industries increasingly focus on energy efficiency, it becomes crucial for engineers to grasp and implement effective voltage-controlled PWM techniques to enhance system performance and reliability. Yet, mastering PWM presents challenges, including managing electromagnetic interference and ensuring thermal efficiency.
How can engineers effectively navigate these complexities to fully leverage the potential of voltage-controlled PWM?
Define Voltage Controlled PWM and Its Importance
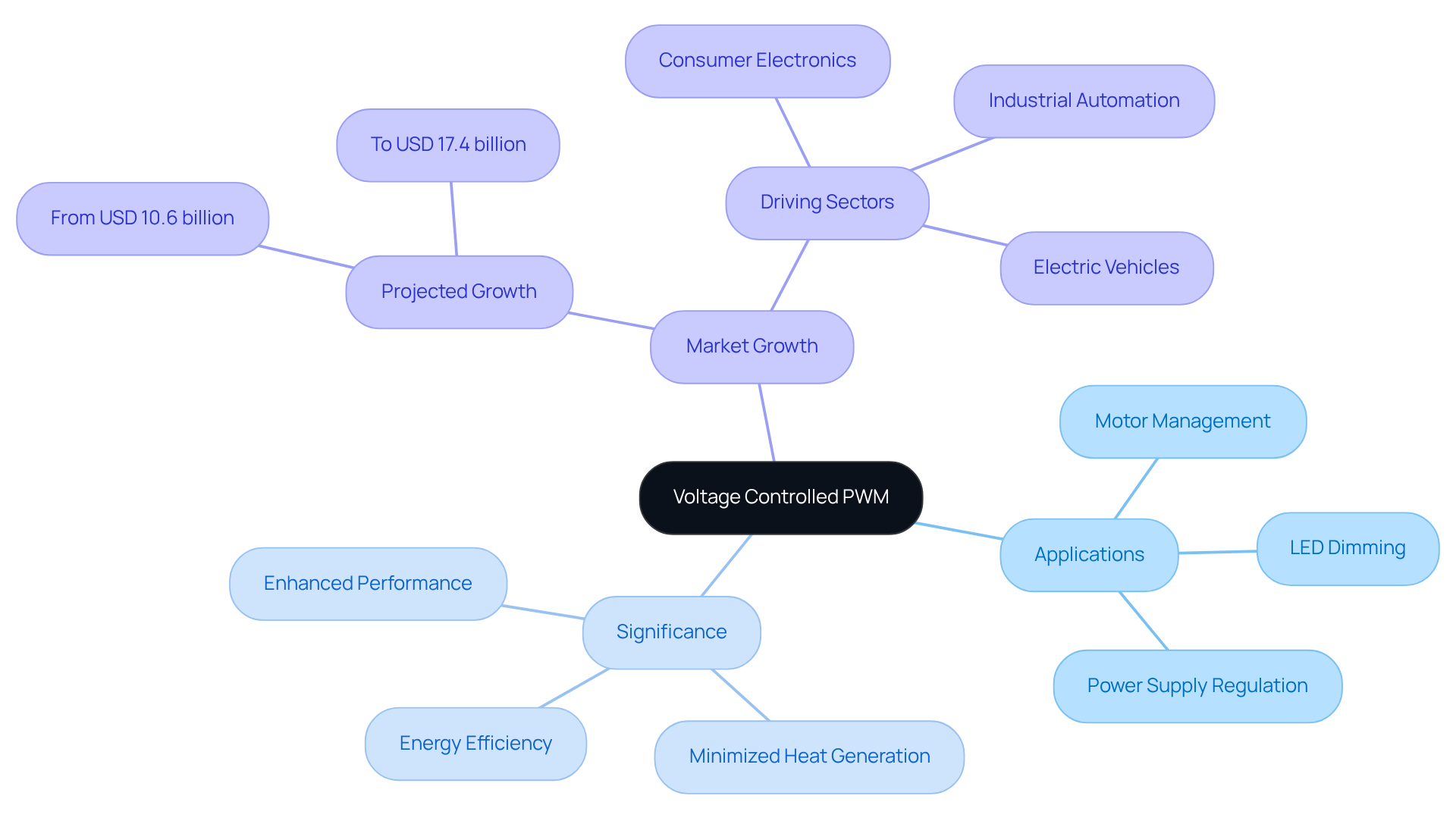
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) stands as a pivotal technique for regulating the average electric potential supplied to a load by modifying the pulse width in a PWM waveform. This method is essential in scenarios demanding precise voltage control, including:
- Voltage controlled PWM for motor management
- LED dimming
- Power supply regulation
The significance of regulated PWM is underscored by its capacity to enhance energy efficiency, minimize heat generation, and elevate the overall performance of electronic devices.
By meticulously adjusting the duty cycle of the voltage controlled PWM, engineers can optimize power delivery, leading to marked improvements in system reliability and longevity. Recent innovations in electric controlled PWM technology have achieved conversion efficiencies surpassing 95% in specific regulator modules, demonstrating its effectiveness in energy management.
Moreover, the global pulse width modulation controllers market is anticipated to expand from USD 10.6 billion in 2025 to USD 17.4 billion by 2035. This growth is propelled by the rising demand for energy-efficient solutions across diverse sectors, including consumer electronics and industrial automation. As the industry progresses, the integration of advanced modulation techniques – such as those utilized in new energy vehicles and 5G base stations – remains crucial in addressing the challenges of contemporary electronic design.
Explore Applications of Voltage Controlled PWM in Electronics
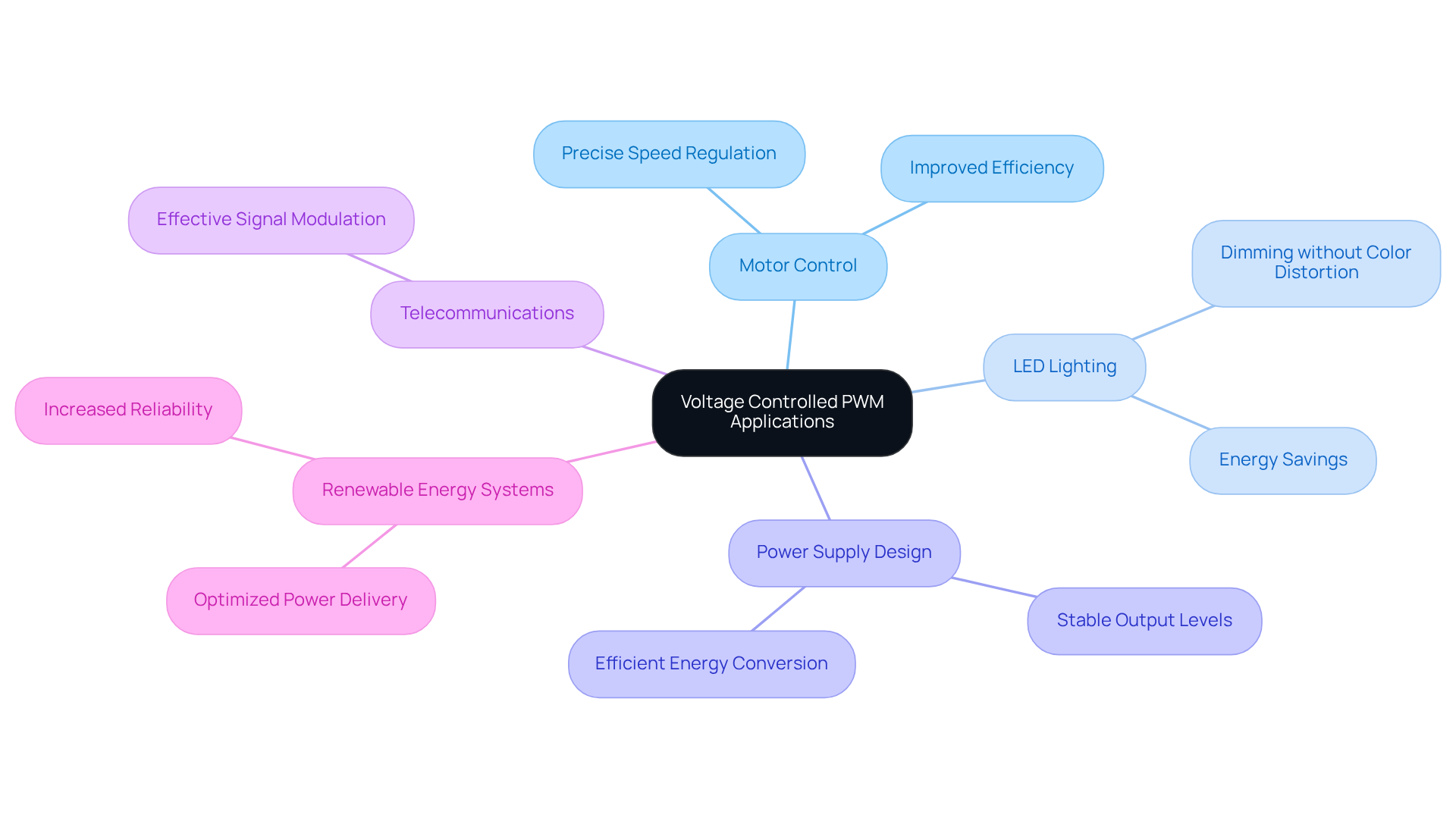
Voltage controlled PWM plays a pivotal role in numerous electronic applications, showcasing its versatility and effectiveness.
In motor control, voltage controlled PWM enables precise speed regulation by adjusting the average voltage supplied to the motor. This capability not only enhances performance but also significantly improves efficiency, making it an essential tool in modern motor systems.
In the realm of LED lighting, PWM is employed for dimming purposes, allowing for a seamless transition in brightness levels without any color distortion. This feature is crucial for applications requiring consistent lighting quality.
Moreover, in power supply design, the use of voltage controlled PWM is vital for maintaining stable output levels in switch-mode power supplies. This stability ensures efficient energy conversion, which is increasingly important in today’s energy-conscious environment.
Other notable applications include telecommunications, where PWM is utilized for effective signal modulation, and renewable energy systems, where it optimizes power delivery from solar panels and wind turbines. By leveraging PWM technology, these systems can achieve greater efficiency and reliability, underscoring the importance of this technique in advancing electronic solutions.
Implement Best Practices for Voltage Controlled PWM
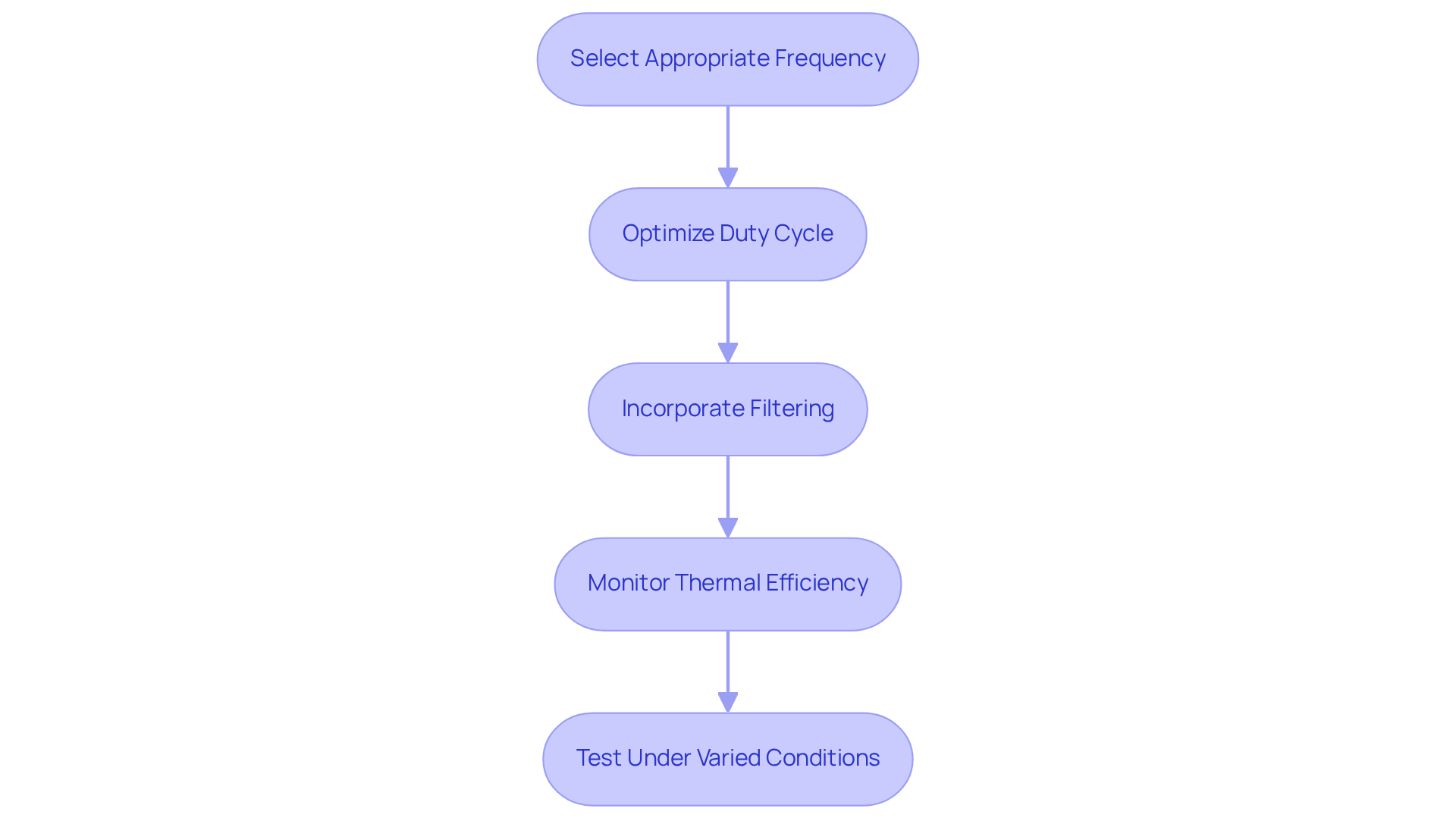
To implement Voltage Controlled PWM effectively, engineers must follow these essential practices:
-
Select the Appropriate Frequency: Choosing the right PWM frequency is crucial for balancing effectiveness and efficiency. Higher frequencies can reduce audible noise but may also increase switching losses. Case studies reveal that maintaining PWM frequencies between 9 kHz and 25 kHz optimizes motor performance without incurring excessive power loss, as shown in research on PWM frequency impacts on motor performance.
-
Optimize Duty Cycle: Meticulously adjusting the duty cycle is vital for achieving the desired output voltage while minimizing power loss. For instance, a 50% duty cycle with a 12 volts DC output effectively delivers 6 volts DC to the load, underscoring the importance of duty cycle management. Employ feedback systems, such as those provided by microcontrollers like Arduino, which can generate outputs using voltage controlled PWM with a duty cycle range from 0 to 255. This allows for dynamic modifications based on changing load conditions, ensuring effective power management.
-
Incorporate Filtering: Implementing low-pass filters is essential for smoothing out the PWM output, thereby reducing voltage ripple and electromagnetic interference (EMI). This practice is particularly critical in sensitive applications, where maintaining signal integrity is paramount.
-
Monitor Thermal Efficiency: Vigilantly observing thermal efficiency is necessary to prevent component overheating. In high-power applications, efficient cooling solutions are crucial, as excessive heat can compromise reliability and effectiveness.
-
Test Under Varied Conditions: Conducting comprehensive testing under diverse load conditions is key to validating the performance of the PWM implementation. This approach helps identify potential issues and allows for design optimization tailored to real-world applications, ensuring robustness and efficiency. Additionally, staying informed about emerging trends in PWM controllers, such as their adoption in new energy vehicles and 5G base stations, is essential for aligning with current technological advancements.
Overcome Challenges in Voltage Controlled PWM Implementation
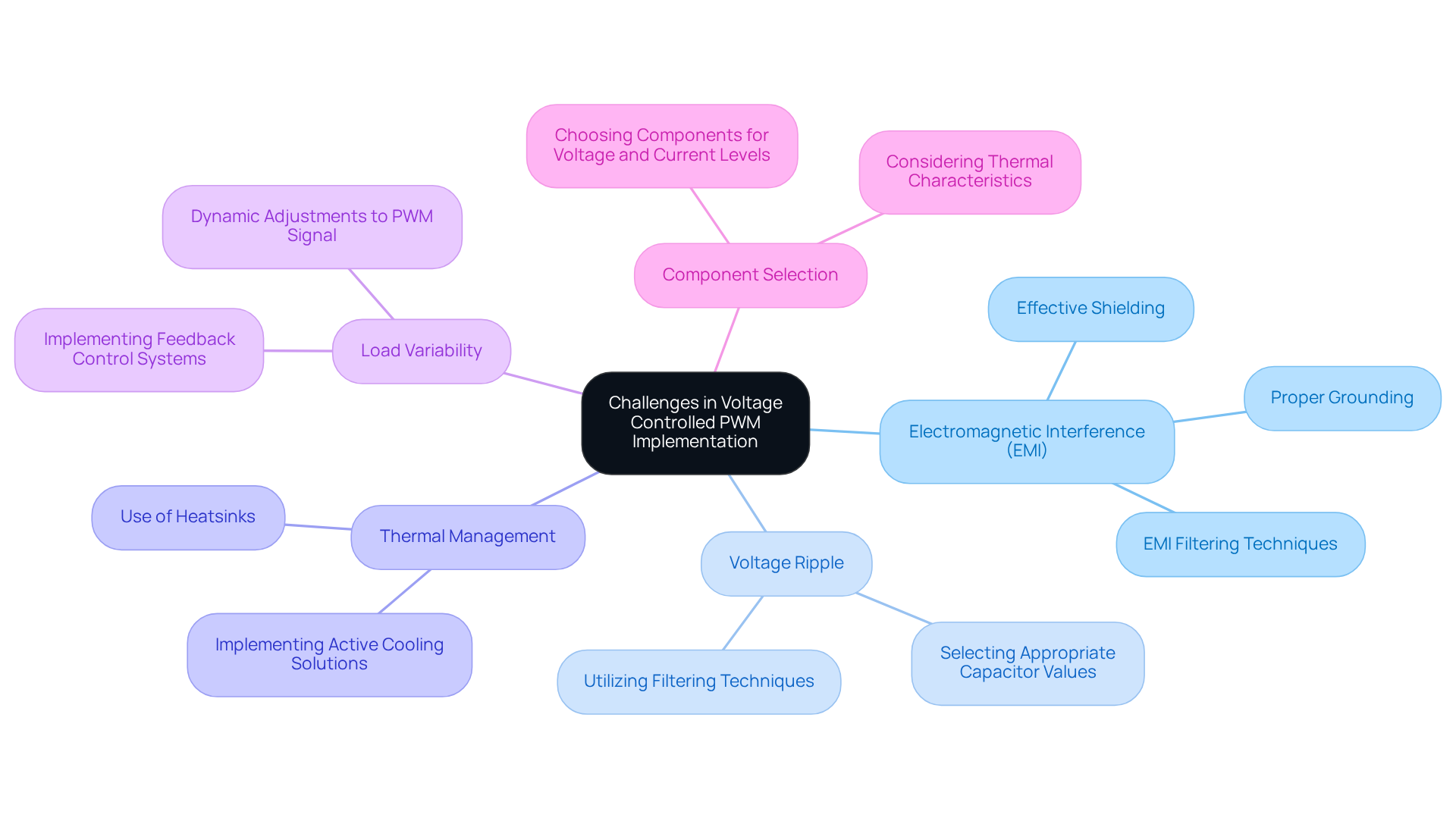
Implementing Voltage Controlled PWM can present several challenges that require careful consideration:
-
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): Rapid switching can generate EMI, potentially affecting nearby circuits. To mitigate this, it is essential to employ proper grounding techniques and effective shielding methods.
-
Voltage Ripple: PWM waves can introduce voltage ripple, which may impact sensitive components. Utilizing filtering techniques and selecting appropriate capacitor values are effective strategies to minimize issues related to voltage controlled pwm.
-
Thermal Management: High-frequency switching often leads to increased heat generation. To maintain component reliability, ensure adequate thermal management through the use of heatsinks or active cooling solutions.
-
Load Variability: Variations in load can significantly affect PWM performance. Implementing feedback control systems allows for dynamic adjustments to the voltage controlled pwm signal based on real-time load conditions, ensuring stable operation.
-
Component Selection: Choosing the right components is critical for success. It is vital to ensure that all components in the PWM circuit can handle the required voltage and current levels, while also considering their thermal characteristics to prevent failures.
Conclusion
Voltage controlled PWM stands as a cornerstone in modern electronics, underpinning efficient power management across a multitude of applications. Its capacity to modulate pulse width in a waveform facilitates precise voltage regulation, significantly boosting the performance and lifespan of electronic devices. With the escalating demand for energy-efficient solutions, grasping and applying the best practices for voltage controlled PWM is not just beneficial – it’s essential.
Key practices to consider include:
- Selecting the appropriate frequency to strike a balance between performance and efficiency.
- Optimizing the duty cycle for effective power delivery.
- Incorporating filtering techniques to reduce voltage ripple and electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Moreover, monitoring thermal efficiency and conducting comprehensive testing under varied conditions are critical steps to ensure robust and reliable PWM implementations. These strategies not only address common challenges like EMI and voltage ripple but also resonate with the ongoing technological advancements.
In conclusion, adopting voltage controlled PWM and adhering to these best practices can yield substantial enhancements in energy efficiency and device performance. As industries increasingly depend on this technology, engineers and designers are urged to remain vigilant about emerging trends and continuously refine their methodologies. By doing so, they can significantly contribute to the evolution of electronic solutions that meet the demands of a rapidly changing landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Voltage Controlled PWM?
Voltage Controlled PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) is a technique used to regulate the average electric potential supplied to a load by modifying the width of the pulses in a PWM waveform.
Why is Voltage Controlled PWM important?
It is important because it allows for precise voltage control in applications such as motor management, LED dimming, and power supply regulation. This enhances energy efficiency, minimizes heat generation, and improves the overall performance of electronic devices.
How does adjusting the duty cycle of Voltage Controlled PWM affect performance?
By meticulously adjusting the duty cycle, engineers can optimize power delivery, which leads to improvements in system reliability and longevity.
What are the efficiency levels achieved by recent innovations in Voltage Controlled PWM technology?
Recent innovations have achieved conversion efficiencies exceeding 95% in specific regulator modules, showcasing their effectiveness in energy management.
What is the projected growth of the pulse width modulation controllers market?
The global pulse width modulation controllers market is expected to grow from USD 10.6 billion in 2025 to USD 17.4 billion by 2035.
What factors are driving the growth of the Voltage Controlled PWM market?
The growth is driven by the rising demand for energy-efficient solutions across various sectors, including consumer electronics and industrial automation.
What advanced modulation techniques are important for contemporary electronic design?
Advanced modulation techniques utilized in new energy vehicles and 5G base stations are crucial for addressing the challenges of modern electronic design.

