Introduction
Understanding the complexities of airflow dynamics is essential for anyone aiming to enhance their PC’s cooling performance. Optimizing the exhaust side of the fan configuration can lead to significant improvements in thermal management, resulting in increased system stability and longevity. Yet, with numerous factors at play – such as fan placement, airflow direction, and the balance of intake and exhaust – how can you ensure your setup is truly optimized for maximum efficiency? This article explores best practices and advanced techniques designed to elevate your PC cooling to new heights.
Understand Airflow Dynamics in PC Cooling
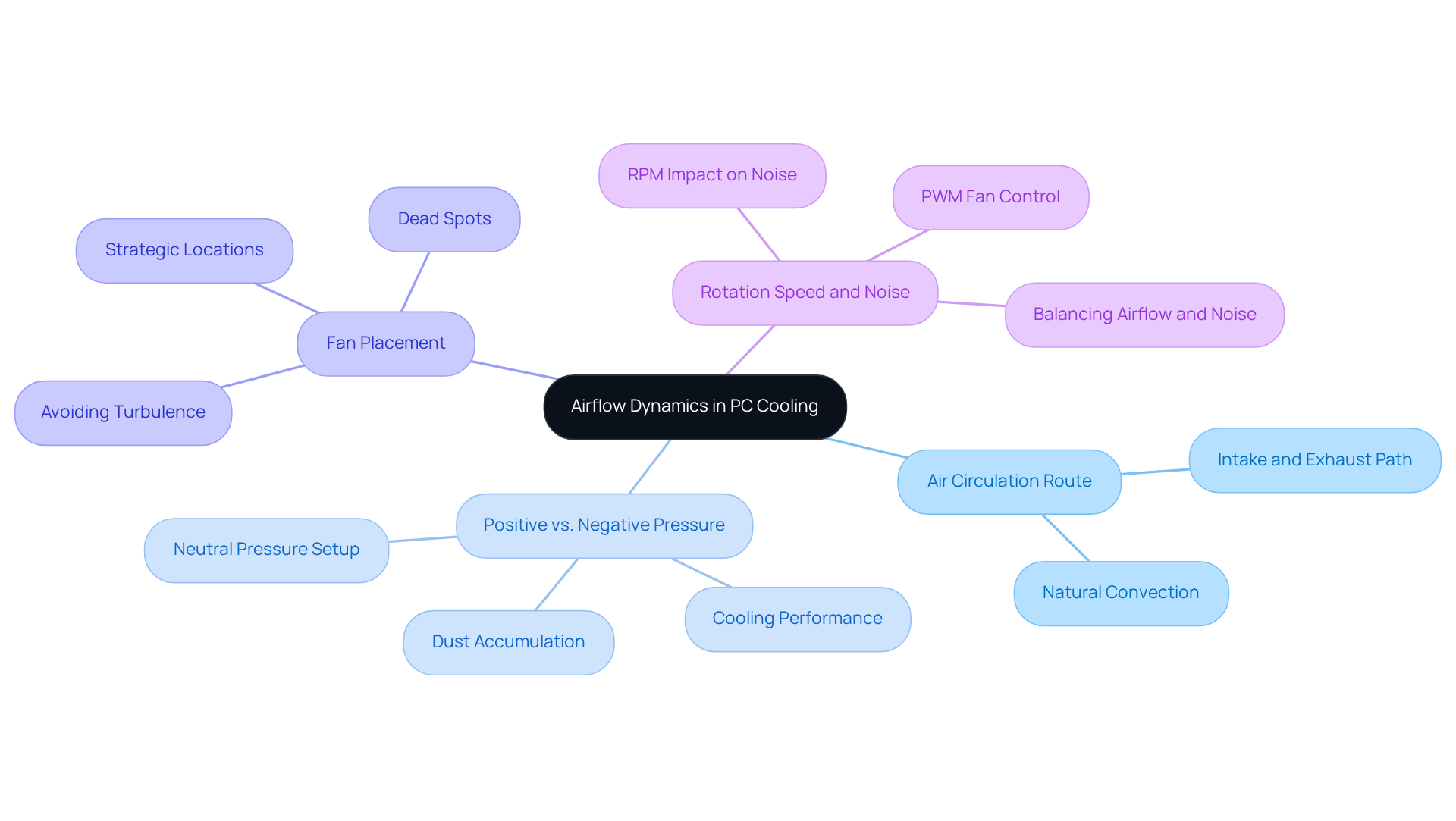
Airflow dynamics in PC cooling are fundamentally governed by principles of thermodynamics and fluid mechanics. The primary goal is to establish a consistent flow of cool air into the case while efficiently expelling hot air. Here are the key considerations:
-
Air Circulation Route: A clear air movement path from intake to exhaust is crucial. Typically, cool air enters through the front and bottom of the case, exiting through the top and rear at the pc fan exhaust side. This arrangement fosters a natural convection current, maintaining optimal temperatures throughout the system.
-
Positive vs. Negative Pressure: Achieving a balanced ventilation system is essential. Positive pressure, where intake exceeds exhaust, helps minimize dust accumulation. Conversely, negative pressure can enhance cooling performance by drawing in cooler air from outside. Striving for a neutral pressure setup often yields the best results.
-
Fan Placement: Strategic fan placement is vital to avoid turbulence and dead spots. For instance, placing intake vents at the front and bottom promotes a seamless air passage, while the pc fan exhaust side at the top and rear efficiently eliminates warm air from the case.
-
Rotation Speed and Noise: The RPM of cooling devices plays a significant role in overall system noise. Higher RPMs can increase noise levels, so balancing airflow with noise is crucial for user comfort. Implementing PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) fans allows for dynamic speed adjustments based on temperature requirements.
By understanding these dynamics, users can significantly enhance their PC’s temperature management, leading to improved system stability and longevity. Recent studies indicate that optimizing airflow paths can substantially decrease thermal resistance, underscoring the importance of careful design in temperature regulation systems. Real-world examples, such as the strategic fan configurations in high-performance gaming PCs, illustrate the effectiveness of these principles in practice.
Implement Optimal Fan Arrangements for Enhanced Performance
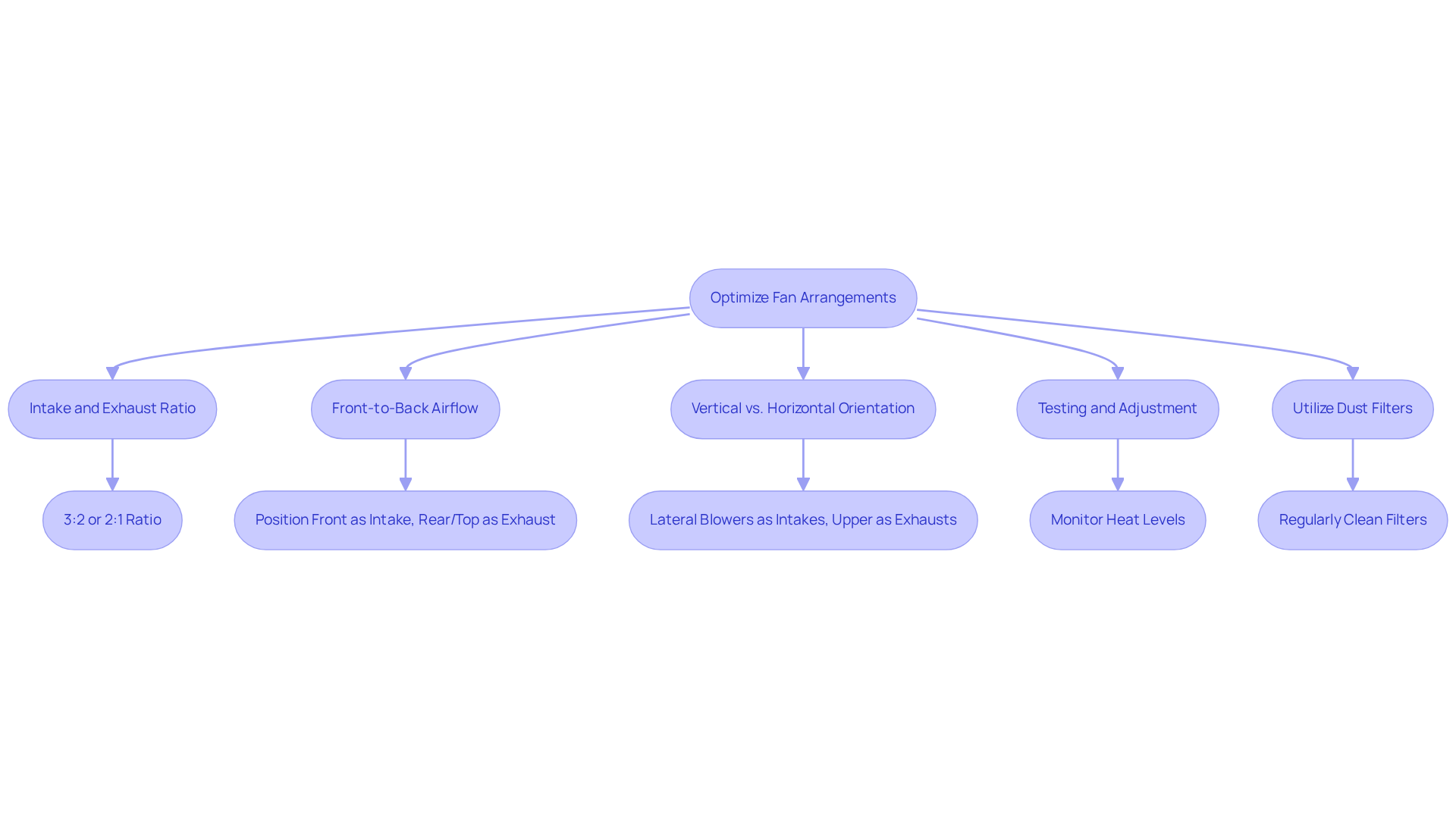
To optimize cooling performance, consider implementing the following fan arrangement strategies:
-
Intake and Exhaust Ratio: Maintaining a 3:2 ratio of intake to exhaust devices is crucial. This ensures a consistent flow of cool air entering the case, essential for keeping heat levels low. For most configurations, a 2:1 or 3:2 ratio of intake to exhaust units is optimal. Balanced circulation can reduce CPU temperatures by 5-10°C under load compared to unbalanced arrangements.
-
Front-to-Back Airflow: Position front units as intakes and rear or top units as exhausts. This configuration promotes a streamlined flow path, reducing turbulence and enhancing cooling efficiency. For example, using two 140mm units at the front and one 120mm unit at the back can establish a balanced ventilation system, achieving ideal conditions. A setup with two intake units and one exhaust unit effectively manages airflow, preventing overheating, as GPUs and CPUs can shut down automatically when temperatures reach 90-100 degrees Celsius.
-
Vertical vs. Horizontal Orientation: Depending on the case design, consider the positioning of airflow devices. In vertical scenarios, lateral blowers can function as intakes, while upper blowers should always be exhausts to enable efficient escape of hot air.
-
Testing and Adjustment: After installing the devices, monitor heat levels using software tools. Adjust fan speeds and configurations based on thermal performance. For instance, if the CPU temperature remains elevated, consider increasing the speed of the intake vents or adding extra exhaust units. Such adjustments can significantly enhance temperature regulation performance.
-
Utilize Dust Filters: Incorporate dust filters on intake fans to minimize dust buildup inside the case. Regular cleaning of these filters is essential to maintain optimal airflow and temperature regulation performance.
By optimizing the pc fan exhaust side, users can achieve a significant improvement in their PC’s temperature management capabilities, leading to enhanced performance and reliability. Additionally, for larger setups, considering the use of High-Volume, Low-Speed (HVLS) fans can provide further benefits in air circulation and temperature control.
Incorporate Advanced Cooling Solutions for Maximum Efficiency
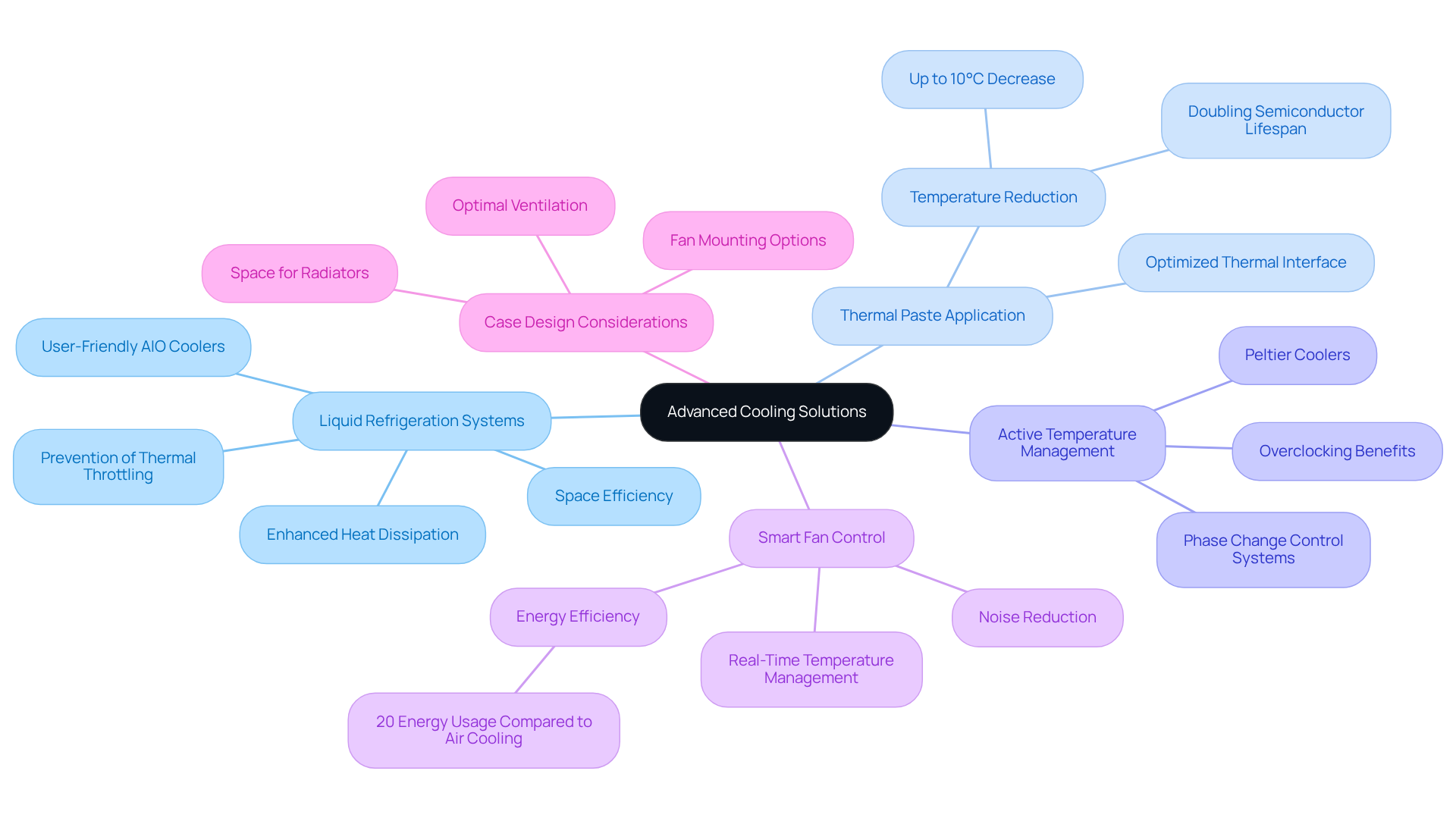
To maximize cooling efficiency, consider integrating advanced cooling solutions:
-
Liquid Refrigeration Systems: Liquid refrigeration offers enhanced heat dissipation compared to conventional air methods. All-In-One (AIO) liquid coolers are particularly user-friendly and deliver exceptional thermal performance, especially for high-end CPUs and GPUs. These systems can significantly lower heat levels under load, effectively preventing thermal throttling and enhancing overall system stability. Additionally, liquid cooling equipment occupies less space than traditional cooling alternatives, allowing for a reduced data center footprint.
-
Thermal Paste Application: The proper application of thermal paste is crucial for optimizing the thermal interface between the CPU/GPU and their coolers. A smooth, thin layer of thermal paste optimizes heat transfer efficiency, with research showing that a properly applied thermal paste can result in a decrease of up to 10°C, effectively doubling the lifespan of semiconductors. This statistic aligns with findings that a 10°C decrease in average operating temperature can more than double the lifetime of a semiconductor.
-
Active Temperature Management Solutions: For extreme performance needs, explore active thermal technologies such as Peltier coolers or phase change temperature control systems. These solutions can offer extra temperature reduction beyond standard air or liquid methods, especially advantageous in overclocked setups where heat generation is significantly higher.
-
Smart Fan Control: Implement software solutions to manage fan speeds based on real-time temperature readings. Intelligent fan regulation enhances temperature management while reducing noise, guaranteeing that fans function at increased speeds only when needed. Significantly, liquid temperature regulation utilizes only 20% of the energy relative to conventional air-cooled data centers, emphasizing its effectiveness in controlling energy usage.
-
Case Design Considerations: Choosing cases created for optimal ventilation and temperature regulation is crucial. Attributes like mesh panels, numerous fan mounting choices, and space for radiators can significantly enhance temperature regulation, permitting improved heat dissipation and airflow management.
By incorporating these advanced cooling solutions, users can achieve unparalleled thermal management, ensuring their systems operate coolly and efficiently, even under the most demanding conditions.
Conclusion
Optimizing the exhaust side of a PC fan is not just important; it’s essential for achieving superior cooling performance and maintaining system stability. By effectively managing airflow dynamics, users can ensure that cool air enters the case while hot air is expelled efficiently. This approach enhances the overall thermal management of the system and prolongs the lifespan of critical components.
Key strategies include:
- Maintaining a balanced intake-to-exhaust ratio.
- Strategically positioning fans for optimal airflow.
- Incorporating advanced cooling solutions, such as liquid refrigeration systems.
Additionally, employing smart fan control and ensuring proper thermal paste application can significantly impact temperature regulation. These practices collectively contribute to a well-cooled PC, reducing the risk of overheating and improving performance during demanding tasks.
Ultimately, prioritizing effective fan exhaust configurations and airflow management is crucial for anyone looking to enhance their PC’s cooling capabilities. By implementing the best practices outlined, users can create a more efficient and reliable computing environment, ensuring their systems perform at their best even under heavy loads. Embracing these techniques not only leads to immediate benefits in temperature management but also positions users to take advantage of the latest technologies in PC cooling systems, paving the way for a more robust and sustainable computing experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What governs airflow dynamics in PC cooling?
Airflow dynamics in PC cooling are governed by principles of thermodynamics and fluid mechanics, aiming to establish a consistent flow of cool air into the case while efficiently expelling hot air.
What is the ideal air circulation route in a PC case?
The ideal air circulation route involves cool air entering through the front and bottom of the case and exiting through the top and rear, creating a natural convection current to maintain optimal temperatures.
What is the difference between positive and negative pressure in PC cooling?
Positive pressure occurs when intake airflow exceeds exhaust, helping to minimize dust accumulation, while negative pressure enhances cooling performance by drawing in cooler air from outside. A neutral pressure setup is often considered the most effective.
Why is fan placement important in PC cooling?
Strategic fan placement is crucial to avoid turbulence and dead spots. Proper placement of intake vents at the front and bottom and exhaust fans at the top and rear helps ensure efficient air movement.
How does fan rotation speed affect PC cooling?
The RPM of cooling devices affects overall system noise; higher RPMs can increase noise levels. Balancing airflow with noise is important for user comfort, and using PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) fans allows for dynamic speed adjustments based on temperature needs.
How can understanding airflow dynamics improve PC performance?
By understanding airflow dynamics, users can enhance their PC’s temperature management, leading to improved system stability and longevity. Optimizing airflow paths can significantly decrease thermal resistance, which is essential for effective temperature regulation.

