Introduction
Choosing the right HVAC centrifugal fan is a pivotal decision that can greatly impact system performance and operational costs. Engineers encounter a complex landscape filled with various impeller types, drive arrangements, and environmental factors. How can one effectively navigate this process to achieve optimal efficiency and reliability? This article explores best practices for selecting HVAC centrifugal fans, offering essential insights and practical guidance. By equipping professionals with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions, we aim to enhance air quality and promote energy savings.
Evaluate Impeller Types for Optimal Performance
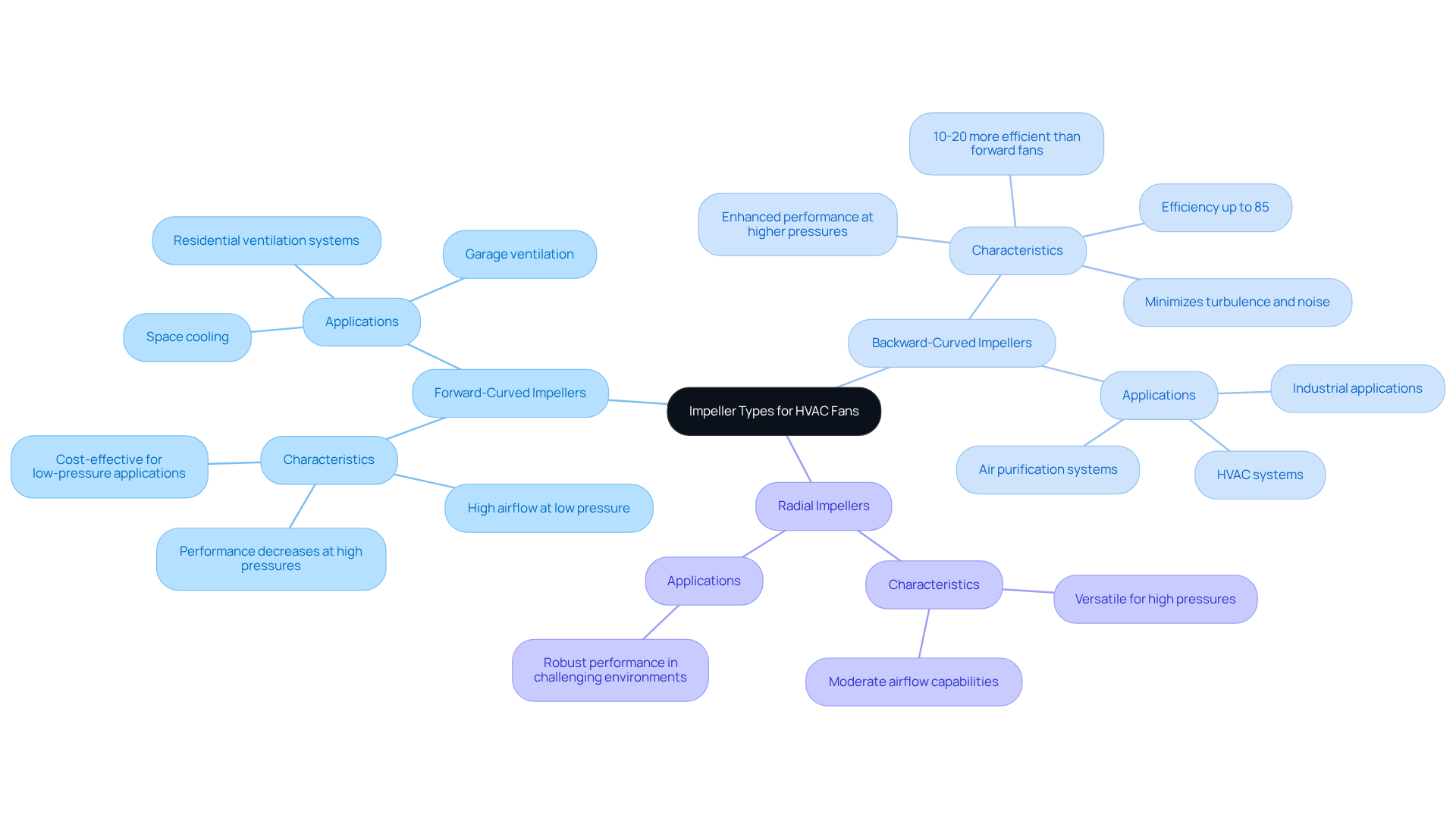
When selecting an HVAC centrifugal fan, evaluating the various types of impellers is crucial for optimizing performance. The primary types include forward-curved, backward-curved, and radial impellers, each with distinct characteristics and applications.
Forward-Curved Impellers
Designed for high airflow at low pressure, forward-curved impellers excel in applications requiring significant air movement with minimal resistance, such as residential ventilation systems. However, their performance decreases at higher pressures, making them less suitable for demanding environments.
Backward-Curved Impellers
These impellers are engineered for enhanced performance at higher pressures, making them ideal for industrial applications where noise reduction is essential. Backward-curved blowers can achieve efficiencies up to 85%, significantly reducing energy usage and operational expenses over time. In fact, they are often 10%-20% more efficient than forward fans under comparable conditions. Their design minimizes turbulence and noise, establishing them as a preferred option in environments such as HVAC setups and air purification, where reliable performance is critical. Case studies consistently show that backward-curved impellers are favored in industrial settings for their energy-efficient operations and stable performance, highlighting the role of the HVAC centrifugal fan in modern HVAC applications.
Radial Impellers
Known for their versatility, radial impellers can handle high pressures and moderate airflow, making them suitable for robust performance in challenging environments. They are frequently utilized in applications that demand durability and reliability.
Selecting the appropriate impeller type based on specific application requirements can lead to substantial improvements in efficiency and performance, ultimately resulting in reduced operational costs. The centrifugal fan impeller market is projected to reach USD 2.5 billion by 2034, underscoring the growing importance of efficient fan technologies in the industry.
Assess Velocity and Pressure Requirements
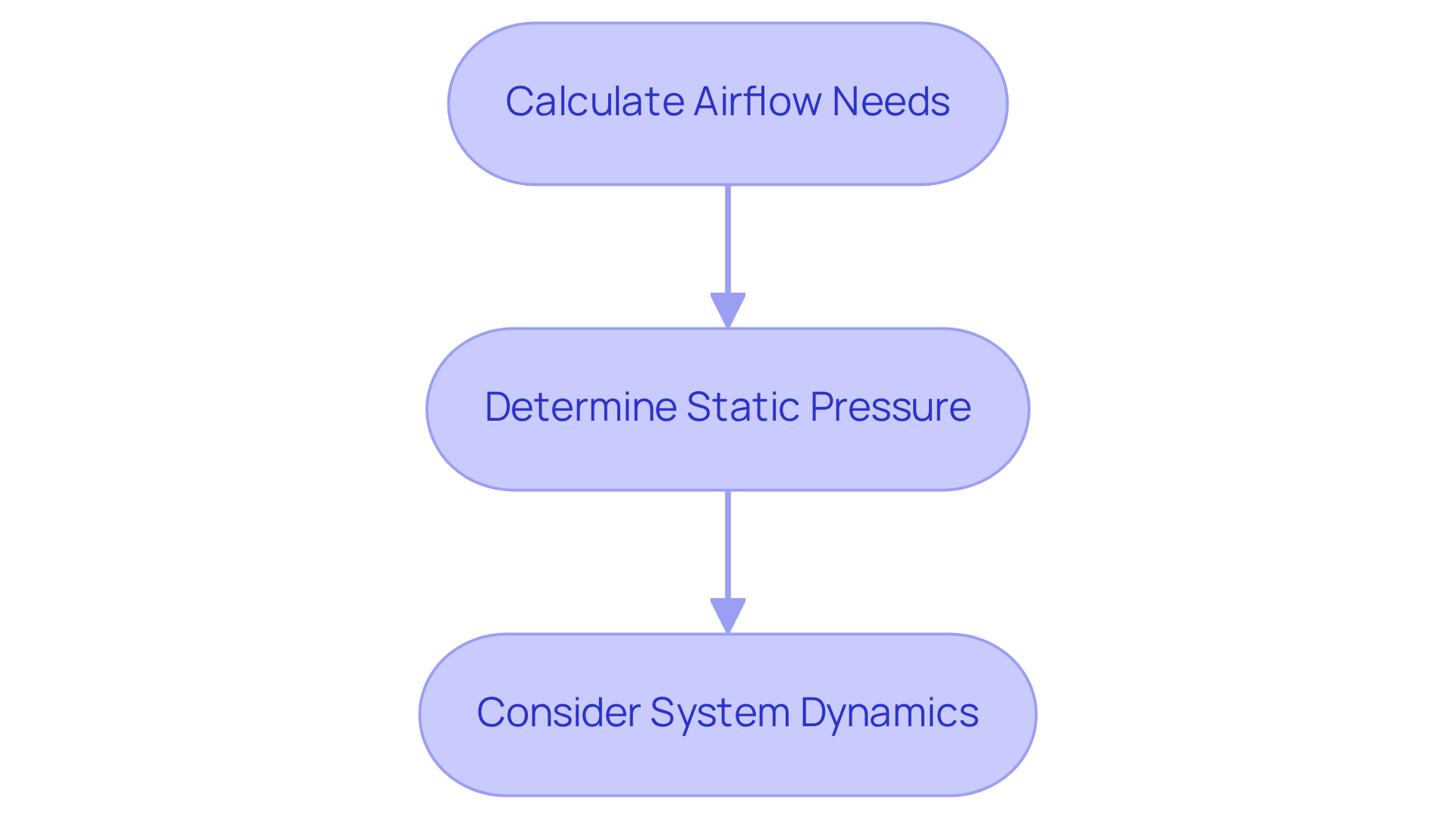
Choosing the right hvac centrifugal fan is crucial for optimal system performance. To do this effectively, you must evaluate the velocity and pressure requirements of your setup. This involves calculating the necessary airflow, measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM), and the static pressure that the fan must overcome.
- Calculate Airflow Needs: Start by determining the volume of air required for your application. Measure the space dimensions and consider the desired air changes per hour to establish your airflow needs.
- Determine Static Pressure: Next, assess the total static pressure that the fan will need to overcome. This includes losses from ductwork, filters, and other components within the system. Utilize fan curves to match the required airflow with the corresponding static pressure.
- Consider System Dynamics: Finally, understand how variations in airflow demand can impact pressure requirements. For example, increasing airflow typically raises static pressure, which must be factored into your fan selection process.
By accurately assessing these parameters, engineers can ensure that the hvac centrifugal fan selected performs efficiently and effectively in its intended application.
Consider Environmental Factors in Selection
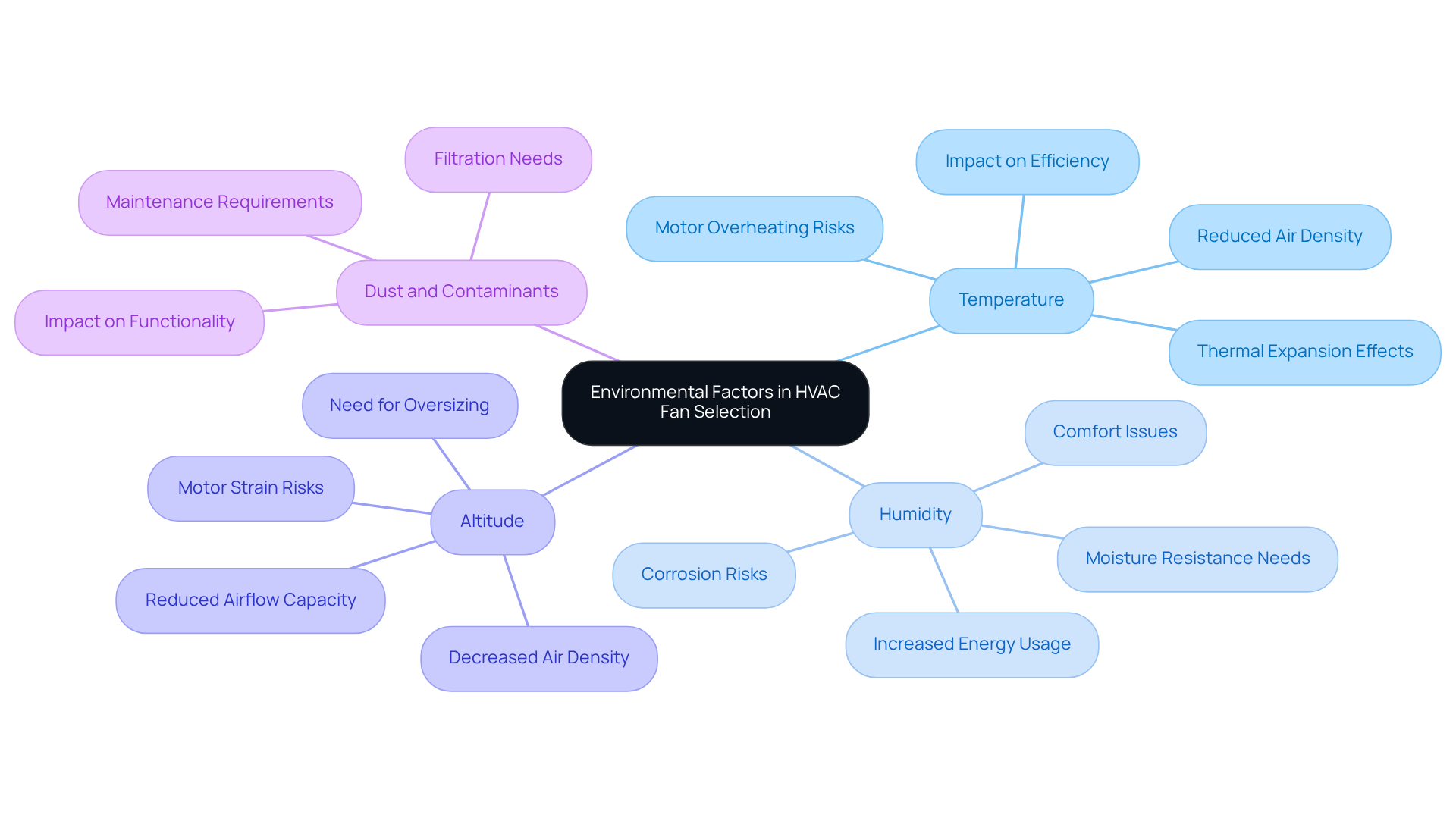
When selecting HVAC centrifugal fans, it is essential to understand the environmental factors that significantly impact their performance. These considerations can make or break the efficiency and reliability of your systems.
-
Temperature: Elevated temperatures can lead to reduced air density, adversely affecting airflow and efficiency. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures may cause thermal expansion in fan materials, impacting clearances, balance, and noise levels. Ensure that the fan is rated for the maximum expected temperature in your application to maintain optimal performance. For example, high temperatures can lead to motor overheating and decreased bearing life, making careful selection of fan components crucial.
-
Humidity: In humid environments, excess moisture can result in corrosion and diminished efficiency. Indoor humidity levels exceeding 60% can create discomfort, foggy windows, and increased electric bills. Opting for fans made from moisture-resistant materials can extend their lifespan and sustain performance. High humidity levels can compel air conditioners to run longer, raising energy usage and putting additional strain on the unit, highlighting the importance of humidity control in fan selection.
-
Altitude: At higher altitudes, the decrease in air density can significantly affect fan performance. Fans operating at higher altitudes move less mass of air per revolution compared to those at sea level, which may necessitate oversizing to compensate for reduced airflow capacity. Engineers must adjust fan selection and system design to account for these altitude effects, ensuring reliable operation.
-
Dust and Contaminants: In industrial environments, blowers often face dust and other particulates that can hinder functionality. Selecting devices with appropriate filtration and sealing mechanisms is vital to avoid damage and maintain efficiency. Regular maintenance, including inspections at least twice a year, is recommended to ensure that ventilation systems operate effectively in such challenging conditions.
By considering these environmental factors, engineers can select HVAC centrifugal fans that not only meet performance requirements but also ensure durability and reliability in demanding conditions.
Evaluate Air Quality and Fluid Compatibility
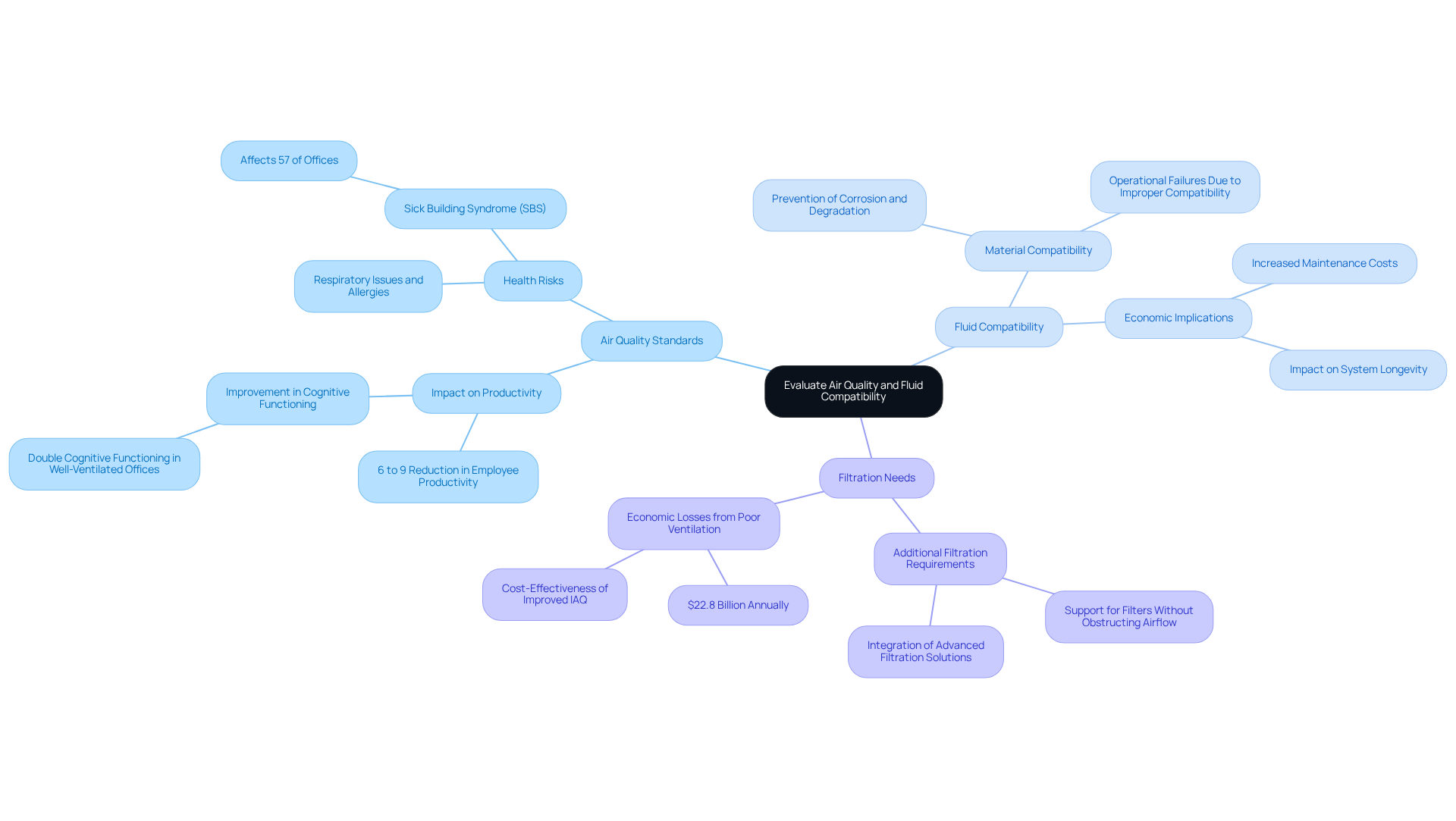
In HVAC applications, assessing air quality and fluid compatibility is crucial for selecting the right HVAC centrifugal fan. Gagner-Toomey Associates stands as the globe’s leading producer of both standard and custom air-movers, offering a diverse range of DC input centrifugal blowers, sized from 15 to 225mm, all optimized for performance and efficiency. Key considerations include:
- Air Quality Standards: It’s essential to ensure that the fan meets specific air quality requirements, such as managing particulate matter and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Poor indoor air quality can lead to a 6% to 9% reduction in employee productivity, underscoring the importance of maintaining air purity in sensitive environments like laboratories and manufacturing facilities. Gagner-Toomey’s innovative cooling solutions are designed to effectively support these standards.
- Fluid Compatibility: When tasked with moving air mixed with other fluids, verifying that the materials used in the fan’s construction are compatible with those fluids is vital. Gagner-Toomey’s HVAC centrifugal fans are built with materials that prevent issues like corrosion or material degradation, which can compromise performance and longevity. A case analysis on HVAC centrifugal fans highlighted that improper fluid compatibility can lead to significant operational failures and increased maintenance costs.
- Filtration Needs: It’s important to assess whether additional filtration is necessary to uphold air quality standards. Selecting blowers designed to support filters without significantly obstructing airflow is crucial for preserving system performance and effectiveness. Industry experts suggest that integrating advanced filtration solutions can avert economic losses estimated at $22.8 billion annually due to suboptimal ventilation-a challenge that Gagner-Toomey’s products are well-equipped to tackle.
By thoroughly evaluating these factors, engineers can ensure that the chosen fan not only maintains optimal air quality but also operates efficiently within its designated environment, leveraging Gagner-Toomey’s comprehensive range of cooling solutions.
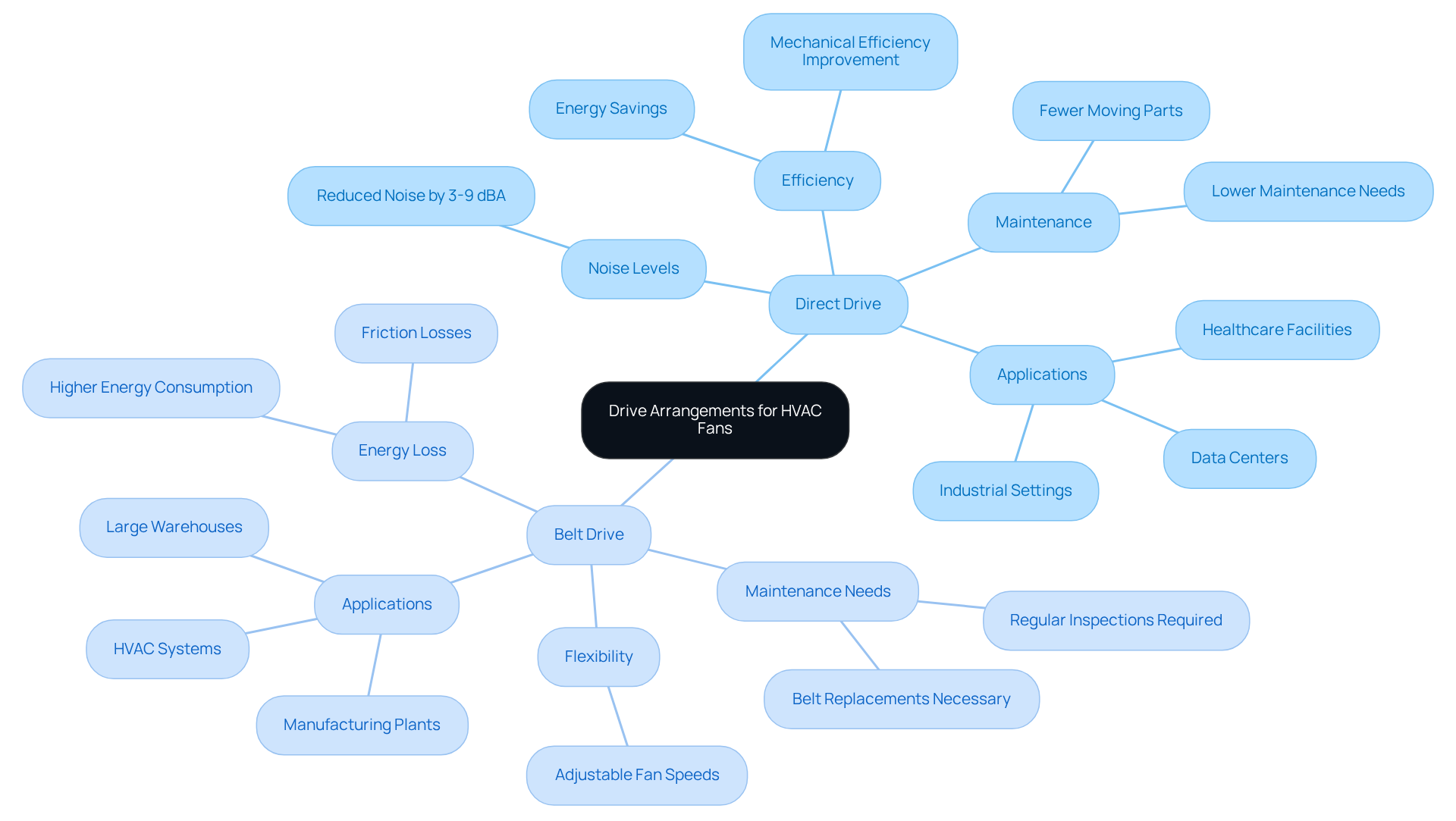
Understand Drive Arrangements for Efficiency
The drive configuration of the HVAC centrifugal fan units significantly impacts their effectiveness and overall performance. Understanding the two primary types of drive arrangements is essential:
Direct Drive: In this configuration, the motor connects directly to the fan impeller. This setup enhances efficiency and reduces maintenance needs due to fewer moving parts. In space-restricted environments where energy conservation is crucial, an HVAC centrifugal fan, particularly a direct drive blower, is particularly advantageous. They require minimal upkeep, as there are no belts to replace or lubricate, leading to lower operational costs over time. Facilities employing an HVAC centrifugal fan with direct drive mechanisms often witness mechanical efficiency enhancements of up to 5%, resulting in substantial energy savings and reduced electricity costs. Additionally, the HVAC centrifugal fan can lower noise levels by 3-9 dBA compared to belt-driven fans, making it suitable for environments where noise is a concern. As noted by an Administrator, “Direct drive mechanisms waste less energy because the motor connects straight to the fan.”
Belt Drive: This arrangement utilizes a belt to connect the motor to the fan, allowing for greater flexibility in adjusting fan speeds. While belt drive setups can be beneficial in applications requiring variable airflow, they necessitate more frequent maintenance due to wear and tear on belts and pulleys. Regular inspections and replacements are essential to maintain efficiency, which can lead to higher long-term costs. Furthermore, belt drive mechanisms may incur energy losses due to friction, making them less efficient compared to their direct drive counterparts. The necessity for regular upkeep and the associated expenses should be thoroughly evaluated when choosing a belt drive mechanism.
When selecting a drive arrangement, it is crucial to consider specific application requirements, including space constraints, desired efficiency, and maintenance capabilities. For instance, direct drive mechanisms are often favored in environments like data centers and healthcare facilities, where consistent airflow and minimal maintenance are critical. Conversely, HVAC centrifugal fans may be suitable for manufacturing plants or large warehouses where adjustable airflow is necessary, despite the increased maintenance demands. Understanding these factors ensures that the selected fan operates efficiently and reliably, aligning with operational goals.
Conclusion
Selecting the right HVAC centrifugal fan is not just a choice; it’s a pivotal decision that can dramatically influence system performance and energy efficiency. Understanding the various factors involved – from impeller types to environmental conditions – is essential for achieving optimal results in HVAC applications.
This article outlines best practices for selecting HVAC centrifugal fans, emphasizing the evaluation of impeller types – forward-curved, backward-curved, and radial – to meet specific performance requirements. It’s crucial to assess airflow and static pressure needs while considering environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and altitude. Additionally, ensuring air quality and fluid compatibility is paramount. The discussion also covers the choice between direct drive and belt drive arrangements, illustrating how each configuration impacts efficiency and maintenance.
Incorporating these best practices not only enhances system reliability but also leads to significant energy savings and reductions in operational costs. By meticulously evaluating each aspect of fan selection, engineers can ensure that the chosen HVAC centrifugal fan meets the demands of its application, contributing to sustainable and efficient operations. Embracing these strategies will ultimately foster improved air quality and operational performance across various environments, underscoring the importance of informed fan selection in HVAC systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main types of impellers used in HVAC centrifugal fans?
The primary types of impellers are forward-curved, backward-curved, and radial impellers, each with distinct characteristics and applications.
What are the characteristics of forward-curved impellers?
Forward-curved impellers are designed for high airflow at low pressure, excelling in applications requiring significant air movement with minimal resistance, such as residential ventilation systems. However, their performance decreases at higher pressures.
What advantages do backward-curved impellers offer?
Backward-curved impellers are engineered for enhanced performance at higher pressures and are ideal for industrial applications where noise reduction is essential. They can achieve efficiencies up to 85%, are often 10%-20% more efficient than forward fans, and minimize turbulence and noise.
In what applications are backward-curved impellers preferred?
Backward-curved impellers are favored in HVAC setups and air purification systems due to their energy-efficient operations and stable performance, particularly in industrial settings.
What are the features of radial impellers?
Radial impellers are versatile, capable of handling high pressures and moderate airflow, making them suitable for robust performance in challenging environments. They are frequently used in applications that demand durability and reliability.
How can selecting the appropriate impeller type impact efficiency and performance?
Choosing the right impeller type based on specific application requirements can lead to substantial improvements in efficiency and performance, ultimately resulting in reduced operational costs.
What factors should be considered when assessing velocity and pressure requirements for HVAC centrifugal fans?
It is important to calculate the necessary airflow in cubic feet per minute (CFM) and assess the total static pressure that the fan must overcome, including losses from ductwork and filters.
How do you calculate airflow needs for an HVAC application?
To calculate airflow needs, measure the space dimensions and consider the desired air changes per hour to establish the required airflow.
What is the significance of static pressure in fan selection?
Static pressure is crucial as it includes losses from components within the system. Utilizing fan curves helps match the required airflow with the corresponding static pressure.
How do variations in airflow demand affect pressure requirements?
Increasing airflow typically raises static pressure, which must be factored into the fan selection process to ensure optimal performance.

