Introduction
Frameless fan technology is transforming electronic cooling solutions, presenting engineers with a remarkable opportunity to boost device performance while reducing space and noise. By grasping the design principles and integration techniques linked to these innovative fans, engineers can achieve substantial benefits, including enhanced thermal management and energy efficiency.
However, integrating these fans isn’t without its hurdles. Engineers face challenges such as vibration issues and insufficient ventilation. So, how can they effectively navigate these complexities to fully harness the advantages of frameless fans in their designs?
Understanding these dynamics is crucial for leveraging the full potential of frameless fans, ensuring that engineers can not only meet but exceed performance expectations.
Understand Frameless Fan Technology and Design Principles
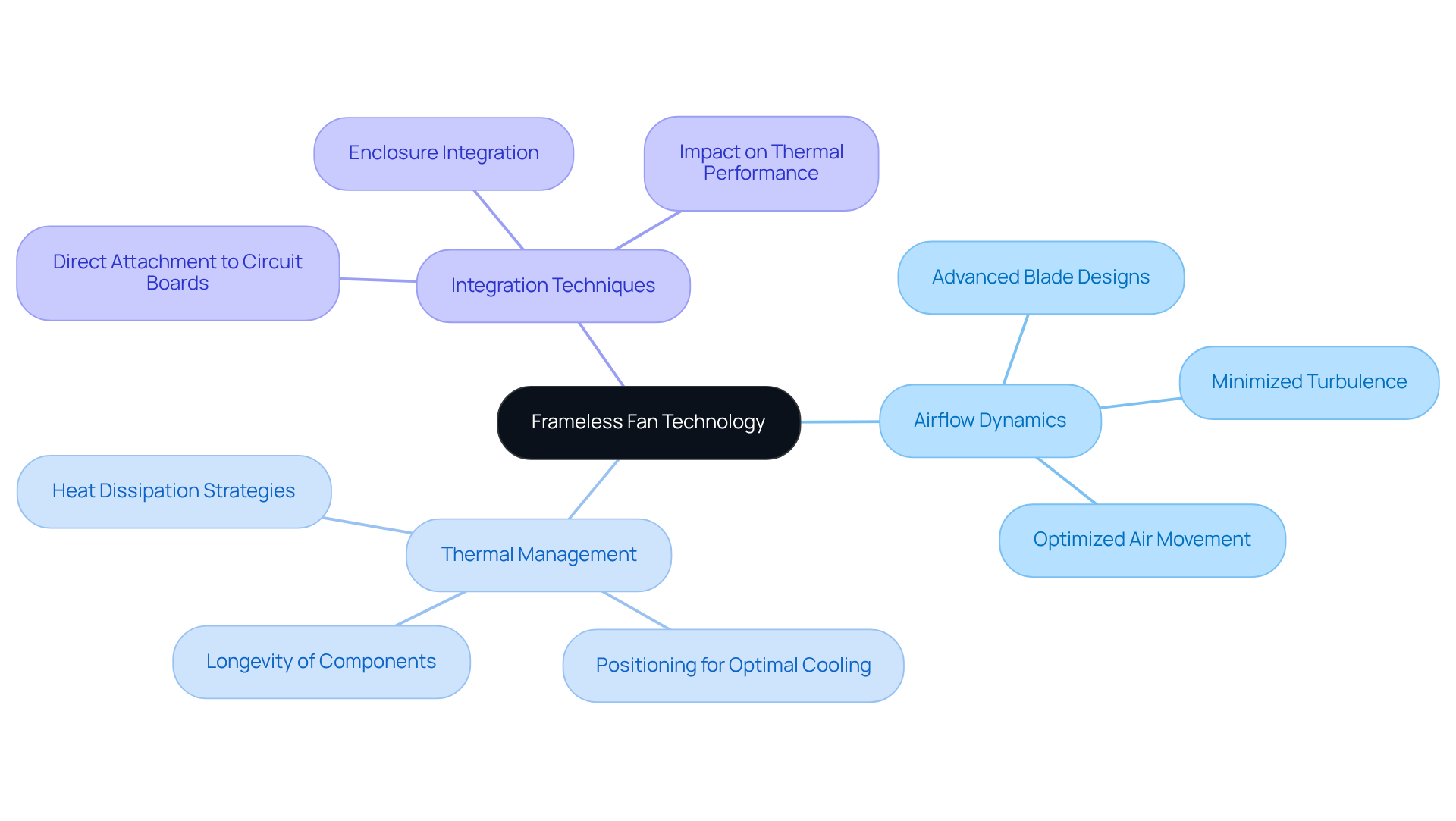
Frameless fan units are designed without conventional housing, allowing for seamless integration into electronic devices. This innovative configuration enhances ventilation efficiency and reduces overall weight, making them ideal for compact applications. Understanding the key principles behind frameless technology is essential for engineers looking to optimize their designs:
- Airflow Dynamics: Mastering how frameless fans manipulate airflow is crucial. These units often employ advanced blade designs that not only optimize air movement but also minimize turbulence, leading to improved performance.
- Thermal Management: Effective cooling is vital in electronics. Frameless blowers can be strategically positioned to dissipate heat from high-temperature components, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of devices.
- Integration Techniques: Engineers must consider how to attach these cooling devices directly onto circuit boards or within enclosures. This integration significantly impacts thermal performance and overall device reliability.
By grasping these principles, engineers can leverage frameless fan technology to improve their designs, ensuring they meet the demands of modern electronic applications.
Leverage Benefits of Frameless Fans in Electronics Applications
Frameless fans offer a range of advantages that significantly enhance electronic applications:
-
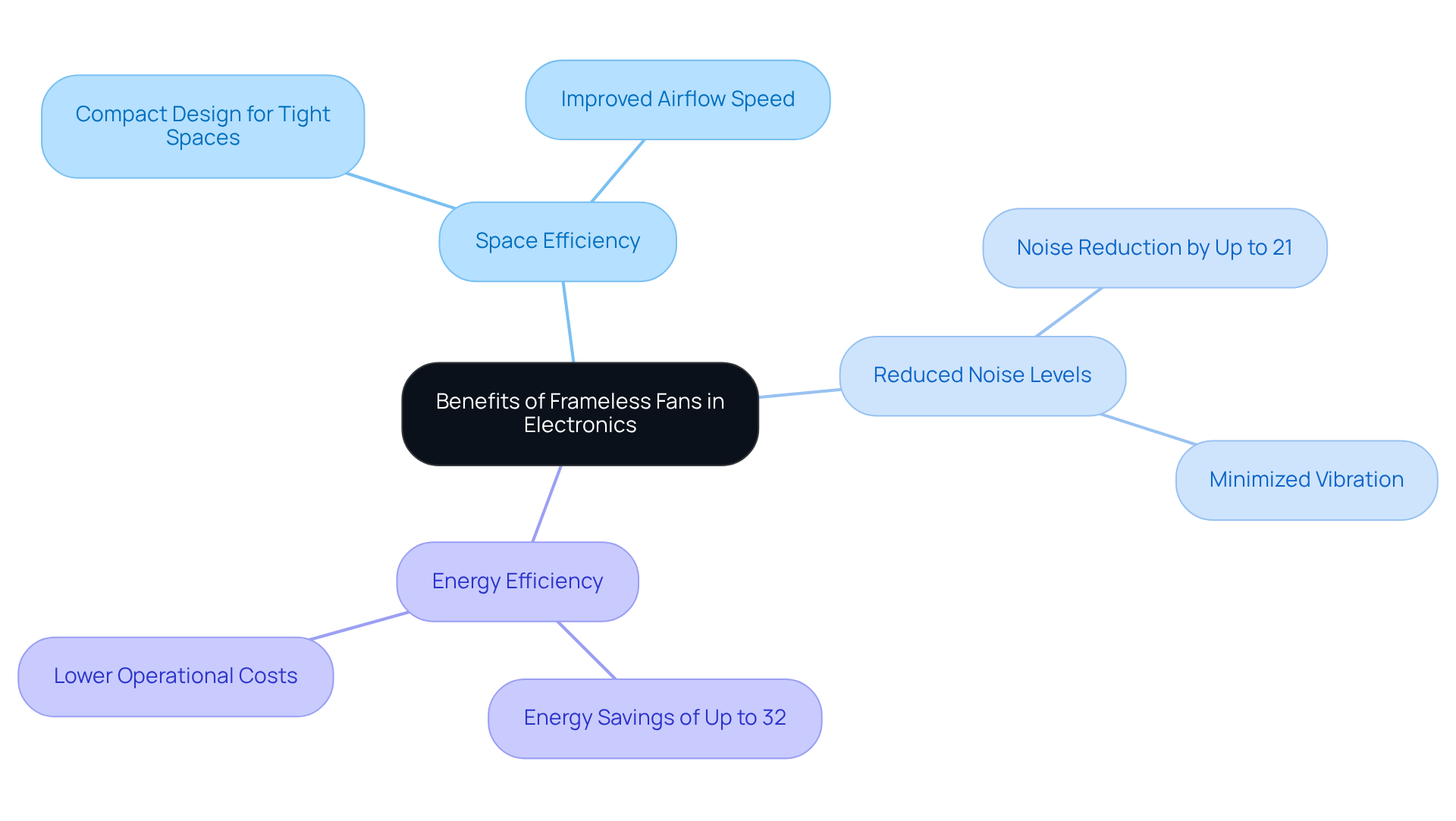
Space Efficiency: Their compact design allows for seamless integration into tight spaces, making them ideal for modern electronics where real estate is limited. This efficiency is crucial as devices shrink in size, enabling innovative designs without sacrificing functionality. Research on borderless cooling fan design highlights that this streamlined approach results in improved airflow speed and more effective cooling performance.
-
Reduced Noise Levels: By eliminating the traditional frame, these fans minimize vibration and noise, which is particularly beneficial in consumer electronics and medical devices where quiet operation is paramount. Studies indicate that borderless ventilators can reduce noise complaints by up to 21%, as noted in the research conducted by Luo et al., making them a preferred choice in sound-sensitive environments.
-
Energy Efficiency: Typically, borderless devices consume less power than their conventional counterparts, leading to lower operational costs and improved energy ratings for appliances. This efficiency is essential in addressing the increasing demand for sustainable technology solutions, with energy savings observed to reach as high as 32% when integrated with air conditioning systems, as demonstrated in the fan-integrated AC system at the BCA ZEB Plus office in Singapore.
With optimized ventilation and cooling capabilities, frameless fans contribute to enhanced performance by helping maintain ideal operating temperatures, thereby extending the lifespan of electronic components. Their design promotes enhanced airflow speed, crucial for preventing overheating and ensuring reliability in high-performance applications. According to Luo et al., prioritizing fan design is vital for maximizing cooling efficiency in electronic systems.
By leveraging these benefits, engineers can create more efficient and reliable electronic systems, paving the way for innovative solutions in the industry. Furthermore, anticipated advancements in frameless fan technology, including improvements in materials and smart control, promise to further enhance their applicability across various electronic applications.
Implement Effective Integration Techniques for Optimal Performance
To achieve optimal performance when integrating frameless fans, engineers must implement several key techniques:
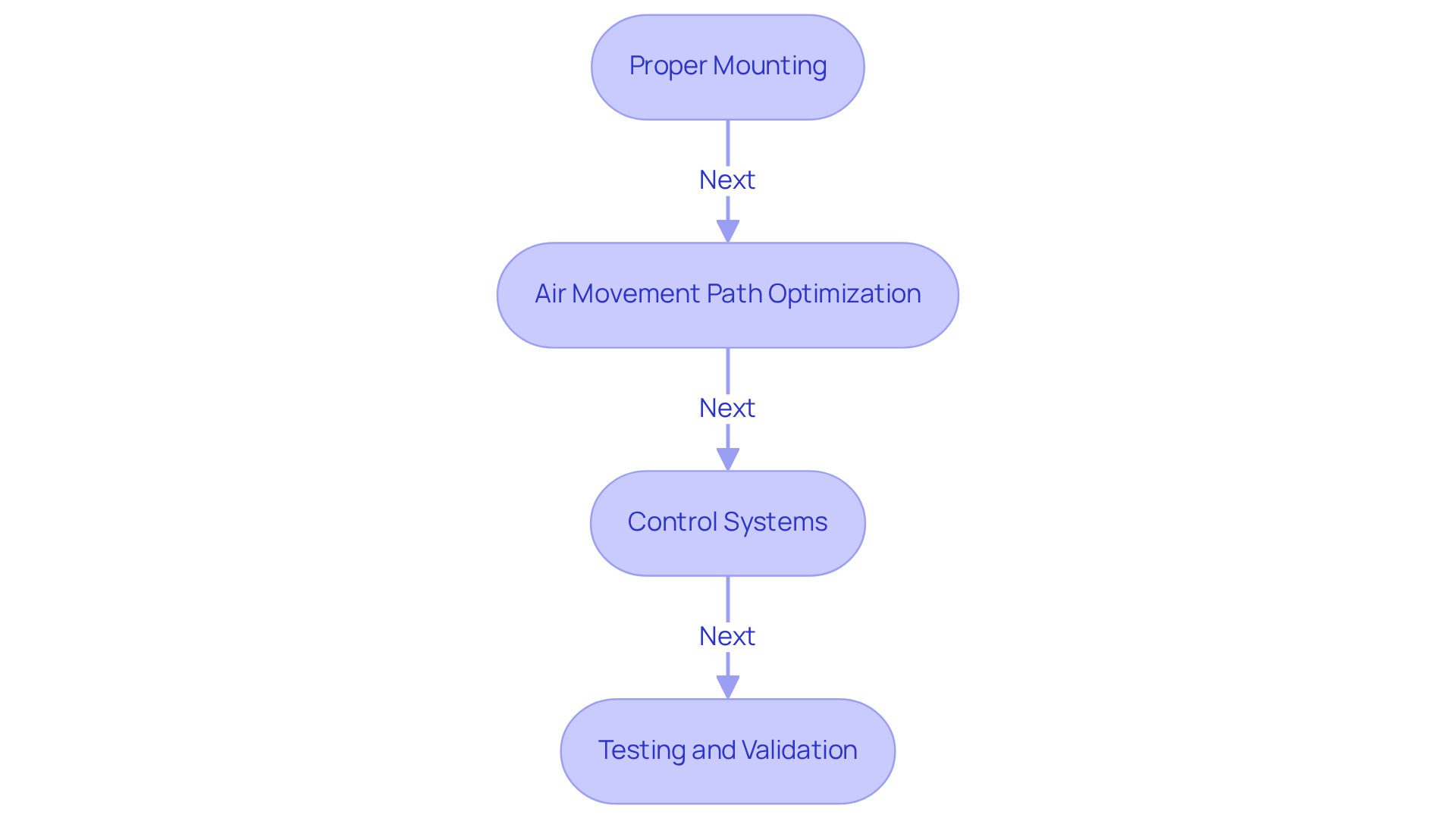
- Proper Mounting: Securely mount fans to minimize vibration and noise. Utilizing vibration-damping materials significantly enhances stability and performance. As Gagner-Toomey Associates states, “Choosing the right mounting techniques is crucial for enhancing functionality and efficiency in engineering applications.”
- Air Movement Path Optimization: Design the arrangement of components to ensure unobstructed air circulation. It’s essential to avoid positioning heat-producing parts directly in the fan’s current, as this can obstruct cooling efficiency. A case study in a pharmaceutical manufacturing facility demonstrated that optimizing ventilation led to an 18% reduction in energy consumption.
- Control Systems: Employ pulse-width modulation (PWM) control for dynamic speed adjustments based on thermal load. This approach not only enhances energy efficiency but also reduces operational noise.
- Testing and Validation: Conduct comprehensive testing to validate airflow and thermal performance. Utilizing thermal imaging can help identify hotspots, allowing for precise adjustments in fan placement.
By following these integration techniques, engineers can significantly enhance the effectiveness of frameless fans in their designs, ultimately improving thermal management and overall system performance. The industrial cooling systems market is projected to grow from $157.26 billion in 2024 to $220 billion by 2035, underscoring the increasing importance of effective fan integration techniques.
Address Challenges and Troubleshoot Frameless Fan Integration
Engineers frequently face challenges when integrating devices like the frameless fan, particularly concerning vibration and noise issues. Addressing these challenges is crucial for optimal performance. Here are key considerations and troubleshooting tips:
-
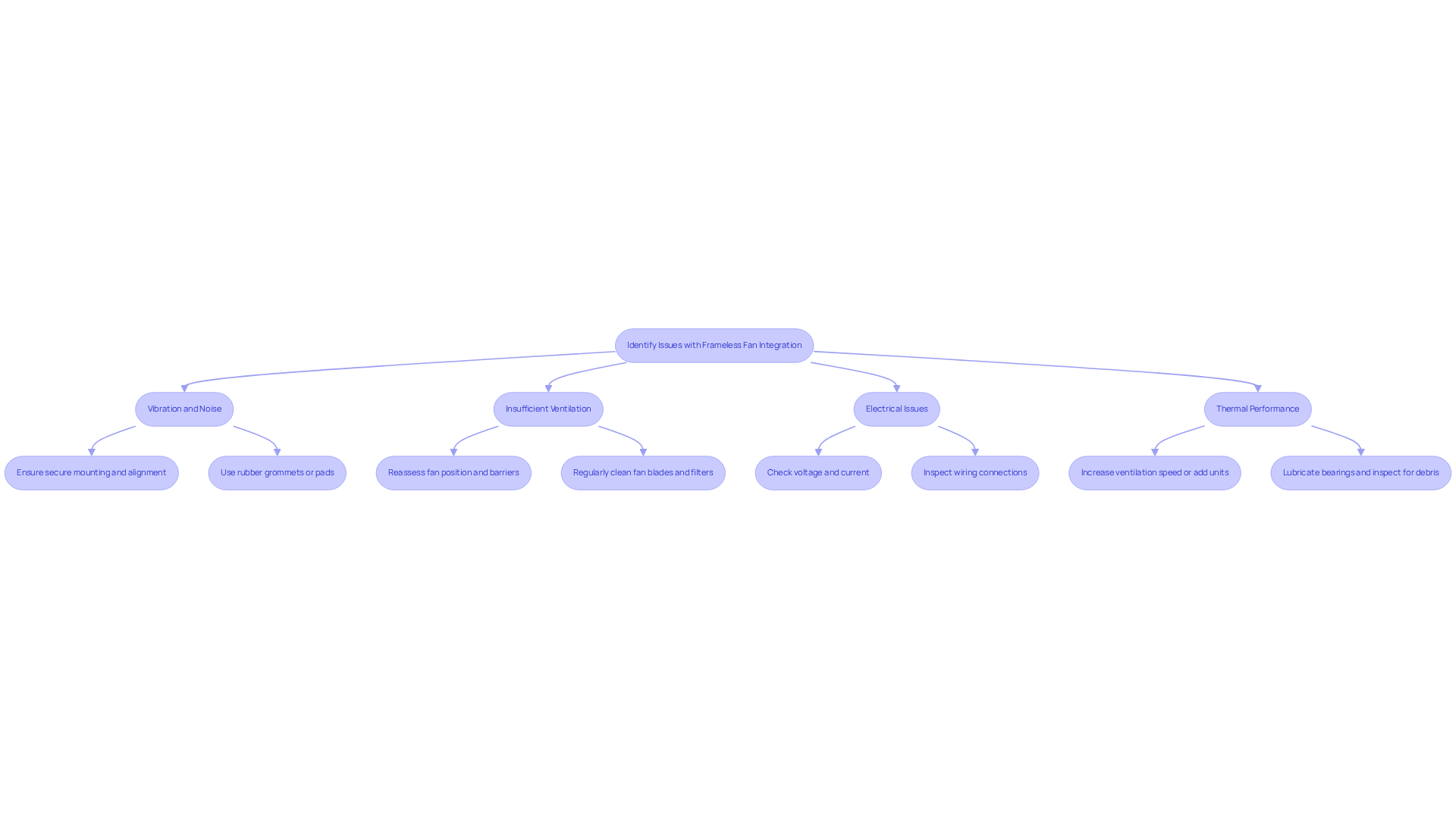
Vibration and Noise: Excessive noise or vibration often arises from improper mounting or misalignment. To mitigate these issues, ensure that fans are securely mounted and aligned correctly. Utilizing rubber grommets or pads can effectively dampen vibrations, leading to quieter operation. Case studies indicate that loose fasteners can exacerbate noise levels, allowing vibrations that result in collisions between the fan and fixed components. Be vigilant for unusual noises, such as grinding, squealing, or rattling, as these may signal underlying problems.
-
Insufficient Ventilation: Inadequate circulation can significantly hinder performance. Reassess the fan’s position and surrounding elements to eliminate any barriers in the ventilation route. Regular inspections and maintenance, including cleaning fan blades and ensuring air filters are free from dirt, are essential for maintaining optimal air circulation. Consistently checking and replacing air filters as needed can greatly enhance airflow efficiency.
-
Electrical Issues: Confirm that the fan is receiving the correct voltage and current. Employ a multimeter to check connections and troubleshoot any electrical faults. Symptoms of electrical issues may include the fan failing to start or running intermittently, which can be diagnosed through systematic checks of the power supply and wiring connections. Inspecting electrical components for cracks or dirt during maintenance can also prevent potential failures.
-
Thermal Performance: Overheating poses a significant concern. If temperatures rise excessively, consider increasing the speed of the ventilation system or adding extra units to boost cooling capacity. Regular maintenance, such as lubricating bearings and inspecting for debris, can prevent overheating and ensure efficient operation.
By proactively addressing these challenges through regular inspections and maintenance, engineers can facilitate the successful integration and optimal performance of frameless fans within their designs. This approach ultimately enhances system efficiency and reliability.
Conclusion
Frameless fan technology stands as a pivotal advancement in electronics, presenting engineers with innovative solutions that significantly enhance device performance. By removing traditional housing, these fans enable superior airflow dynamics, efficient thermal management, and seamless integration into compact electronic systems. Grasping the principles behind frameless fans is essential for engineers who aim to optimize their designs and meet the evolving demands of modern applications.
The key benefits of frameless fans are manifold: they offer space efficiency, reduced noise levels, and energy savings. These advantages are particularly valuable in consumer electronics and medical devices, where performance and quiet operation are critical. Furthermore, effective integration techniques – such as proper mounting and air movement optimization – ensure that these fans operate at peak efficiency, ultimately improving thermal management and extending the lifespan of electronic components.
As the industry continues to evolve, embracing frameless fan technology becomes crucial for engineers seeking to innovate and enhance their designs. By prioritizing these advanced cooling solutions, professionals can not only tackle current challenges but also pave the way for future advancements in electronic applications. The integration of frameless fans transcends mere technical improvement; it represents a significant step toward more efficient, reliable, and sustainable technology solutions in the fiercely competitive landscape of electronics.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are frameless fan units?
Frameless fan units are cooling devices designed without conventional housing, allowing for seamless integration into electronic devices.
What are the advantages of frameless fan technology?
The advantages include enhanced ventilation efficiency and reduced overall weight, making them ideal for compact applications.
Why is understanding airflow dynamics important for frameless fans?
Understanding airflow dynamics is crucial because frameless fans use advanced blade designs to optimize air movement and minimize turbulence, which leads to improved performance.
How do frameless fans contribute to thermal management in electronics?
Frameless fans can be strategically positioned to dissipate heat from high-temperature components, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of electronic devices.
What should engineers consider regarding integration techniques for frameless fans?
Engineers must consider how to attach frameless fans directly onto circuit boards or within enclosures, as this integration significantly impacts thermal performance and overall device reliability.
How can engineers leverage frameless fan technology in their designs?
By understanding the key principles of frameless fan technology, engineers can improve their designs to meet the demands of modern electronic applications.

