Overview
The article emphasizes the fundamentals of commercial fans within electronics engineering, underscoring their critical role in cooling and ventilation. It distinctly categorizes axial and centrifugal fans, providing detailed insights into their operational characteristics. Furthermore, it presents market growth projections and essential specifications for selection, along with best practices for integration. Understanding these factors is paramount for effective thermal management in electronic systems, reinforcing the necessity for expertise in this area.
Introduction
Commercial fans are crucial components in the field of electronics engineering, serving essential functions for cooling and ventilation across a range of applications. There are two primary types of fans—axial and centrifugal—each meticulously engineered for specific operational requirements. Understanding their distinct characteristics is imperative for engineers dedicated to effective temperature management. As the demand for efficient cooling solutions escalates, engineers must adeptly navigate the complexities of fan selection and integration to align with the evolving standards of the industry.
Explore the Fundamentals of Commercial Fans
s are essential components in electronic systems, primarily serving . They are generally classified into two main categories: axial and centrifugal devices, each possessing distinct characteristics and applications.
- Axial Fans: These fans function by moving air parallel to the fan’s axis, making them particularly effective for applications demanding high airflow at low pressure. Their design allows for the efficient movement of substantial volumes of air, which is vital for regulating the temperature of electronic components across various devices. The is projected to sustain a significant share in electronics cooling applications due to its effectiveness in environments where space is constrained and airflow is paramount. In 2022, the axial ventilator segment accounted for a considerable share of the overall blowers and fans market, valued at USD 7.6 billion, with expectations to rise to USD 12.2 billion by 2031, indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.7%.
- : Conversely, centrifugal blowers intake air at the center and expel it at a right angle, generating higher pressure. This design is advantageous for applications requiring air movement against resistance, such as in duct systems or when ventilating components housed in enclosures. The centrifugal fan segment has significantly contributed to the market, especially in scenarios where airflow must navigate obstacles or where elevated pressure is necessary. As of 2022, centrifugal fans also held a notable market share, driven by the increasing demand for across various sectors, including electronics.
Understanding the differences between these fan types, particularly the commercial fan, is crucial for engineers, as it directly influences the selection process for . Market dynamics indicate a , fueled by the escalating need for effective solutions within the electronics sector. Furthermore, the integration of into fan systems is expected to enhance their performance and adaptability across diverse applications, aligning with the rising trend of IoT devices in the marketplace. Industry specialists emphasize that the shift towards IoT-enabled fans is poised to create new opportunities for innovation and efficiency in temperature regulation applications.
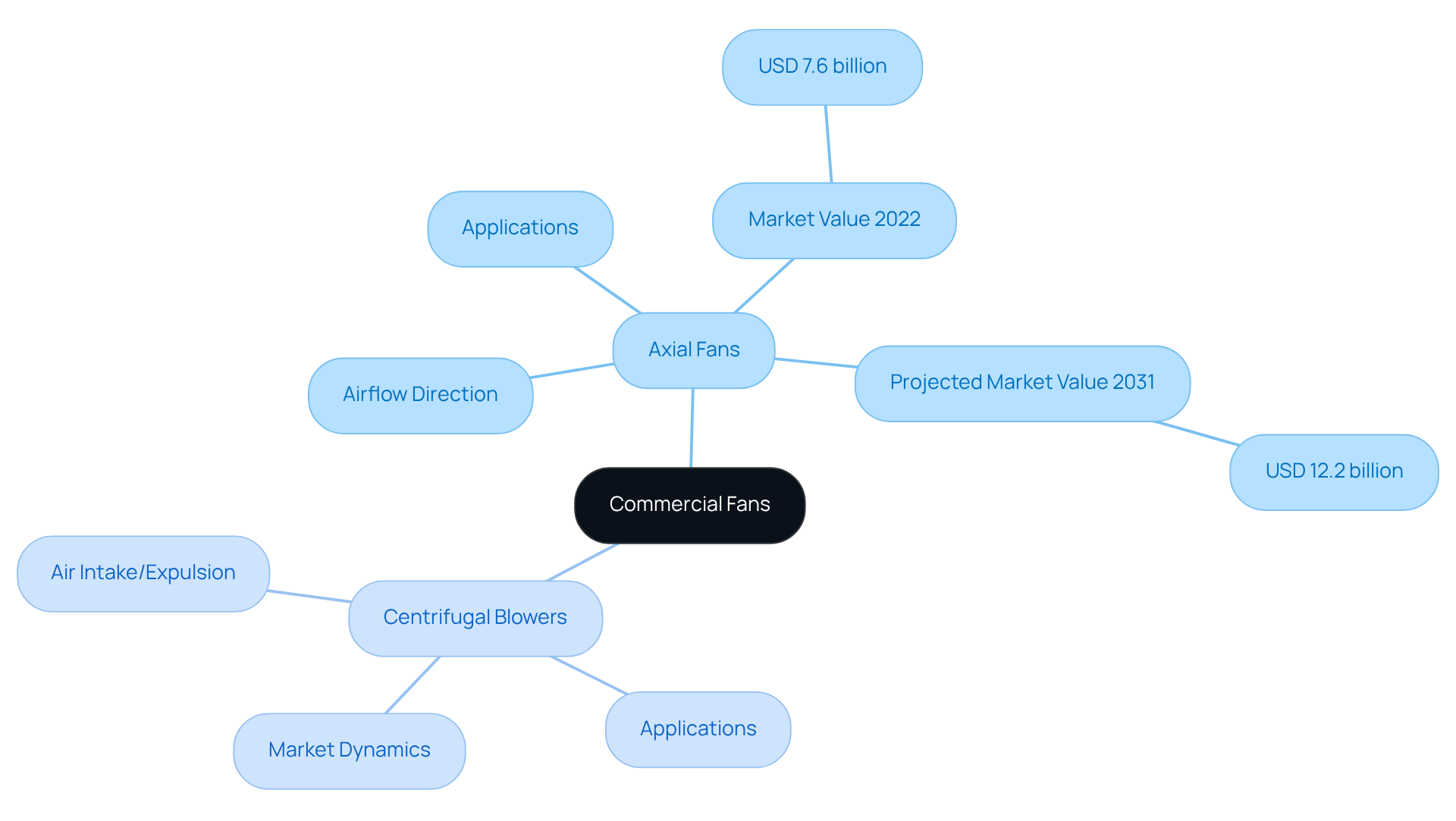
Understand Technical Specifications and Operation of Commercial Fans
When selecting a commercial fan, engineers must consider several that are critical to ensuring .
- : Airflow is quantified in Cubic Feet per Minute (CFM), representing the volume of air a fan can move. For the efficient cooling of larger devices, elevated CFM ratings are crucial, frequently surpassing 100 CFM in numerous applications. This specification is foundational for engineers aiming to match fan performance with system requirements.
- : This metric indicates the resistance the fan must overcome to move air through a system, typically measured in inches of water column (inH2O). Understanding static pressure is vital, as it ensures the fan can adequately ventilate the intended space, particularly in environments requiring 6 to 30 Air Changes Per Hour (ACH). A thorough grasp of this specification allows for effective system design.
- : Noise levels, measured in decibels (dB), can significantly affect the usability of electronic devices. Engineers should prioritize devices that operate quietly, especially in consumer electronics, as some axial models can generate noise levels exceeding 70 dB during high-speed operations. This consideration is essential for maintaining user comfort and product viability.
- : Metrics such as the Fan Energy Index (FEI) are . By choosing a commercial fan with favorable efficiency ratings, engineers can reduce , contributing to overall sustainability. This decision not only benefits the environment but also aligns with modern energy standards.
By comprehending these specifications, engineers can refine their designs for improved performance and energy efficiency, ensuring in various technological applications.
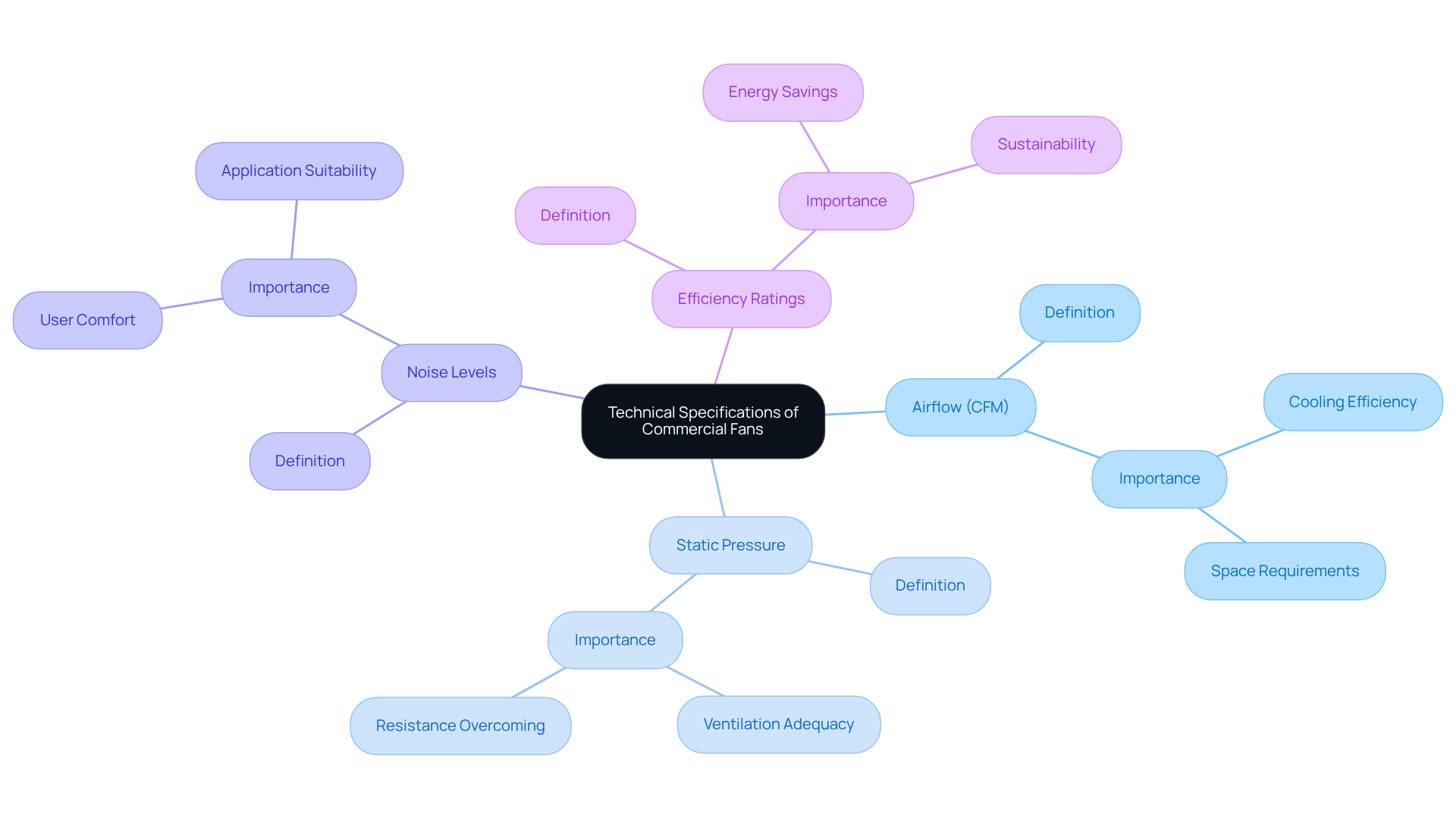
Apply Commercial Fans in Engineering Solutions
Integrating a into electronic systems necessitates careful consideration of several key factors that are essential for .
- Placement: The strategic positioning of fans is vital for effective airflow. To maximize around heat-generating components, a commercial fan must be installed, ensuring optimal cooling and preventing thermal buildup.
- : A thorough understanding of fan curves is crucial for . Engineers can utilize these curves to select blowers that not only meet specific performance standards but also minimize sound output, which is particularly important in sensitive environments. For instance, a fan can produce 20,000 CFM at 5 inches of static pressure, highlighting the necessity of selecting for the application.
- Control Systems: Employing (VSDs) allows for dynamic adjustment of fan speed based on real-time temperature data. This approach of the devices by mitigating unnecessary wear. As emphasized by Gagner-Toomey Associates, understanding the relationship between variable speed blowers and performance curves can lead to significant advancements in energy management and performance assessment.
- : The integration of fans with thermal interface materials (TIMs) significantly boosts heat dissipation from components. This combination not only enhances the cooling efficiency of the commercial fan but also contributes to the overall reliability and longevity of the system.
By implementing these best practices, engineers can develop that effectively manage heat, ensuring both performance and durability. Case studies have demonstrated that a comprehensive understanding of fan curves can lead to substantial improvements in energy management, underscoring the importance of these principles.
Conclusion
Mastering the fundamentals of commercial fans is essential for electronics engineers, as these components are pivotal in ensuring effective cooling and ventilation within electronic systems. By understanding the distinctions between axial and centrifugal fans, along with their respective applications, engineers are empowered to make informed decisions that enhance system performance and reliability.
This article explores key specifications such as:
- Airflow
- Static pressure
- Noise levels
- Efficiency ratings
These are critical factors in selecting the appropriate fan for specific applications. By considering elements like placement, fan curves, control systems, and thermal management, engineers can optimize the integration of commercial fans into their designs. This optimization ultimately leads to improved energy efficiency and system longevity.
With the rising demand for effective temperature management solutions in electronics, embracing the principles outlined in this tutorial can drive innovation and elevate performance across various applications. Engineers are urged to leverage their understanding of commercial fan fundamentals to develop advanced systems that not only adhere to current standards but also pave the way for future advancements in technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main types of commercial fans?
The main types of commercial fans are axial fans and centrifugal blowers. Each type has distinct characteristics and applications suited for different cooling and ventilation needs.
How do axial fans operate?
Axial fans operate by moving air parallel to the fan’s axis, making them effective for applications that require high airflow at low pressure. They are designed to efficiently move large volumes of air, which is essential for cooling electronic components.
What is the market outlook for axial fans?
The axial fan market is expected to grow significantly, with a projected increase from USD 7.6 billion in 2022 to USD 12.2 billion by 2031, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.7%.
How do centrifugal blowers differ from axial fans?
Centrifugal blowers intake air at the center and expel it at a right angle, generating higher pressure. This design is beneficial for applications that require air movement against resistance, such as duct systems or enclosed components.
What market trends are affecting centrifugal fans?
The centrifugal fan segment has seen notable market share growth due to the increasing demand for efficient temperature regulation solutions in various sectors, particularly in electronics.
Why is it important for engineers to understand the differences between fan types?
Understanding the differences between axial and centrifugal fans is crucial for engineers as it directly impacts the selection process for effective temperature management in electronic systems.
How is the demand for commercial fans evolving?
There is a growing demand for both axial and centrifugal fans, driven by the need for effective temperature management solutions in the electronics sector.
What role do intelligent technologies and IoT features play in commercial fans?
The integration of intelligent technologies and IoT features into fan systems is expected to enhance their performance and adaptability across various applications, aligning with the increasing trend of IoT devices in the marketplace.
What opportunities are emerging in the fan market due to IoT?
The shift towards IoT-enabled fans is anticipated to create new opportunities for innovation and efficiency in temperature regulation applications.