Overview
The article presents a comprehensive guide for configuring fan speed control using PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) through four essential steps:
- Understanding PWM basics
- Gathering necessary tools and software
- Configuring settings for optimal performance
- Troubleshooting common issues
Each step is bolstered by detailed explanations and practical advice, highlighting the significance of duty cycle adjustments and proper hardware setup to achieve efficient cooling and reduced noise in electronic systems.
Introduction
Mastering fan speed control through Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is essential for optimizing the performance of electronic systems. By adjusting the pulse widths of a signal, users can fine-tune fan speeds, enhancing cooling efficiency while minimizing noise.
However, many encounter challenges when configuring these settings, prompting inquiries about best practices and the tools required for effective implementation. This guide delves into the critical steps for:
- Configuring PWM settings
- Troubleshooting common issues
- Ensuring that fans operate at peak performance
Understand PWM Fan Speed Control Basics
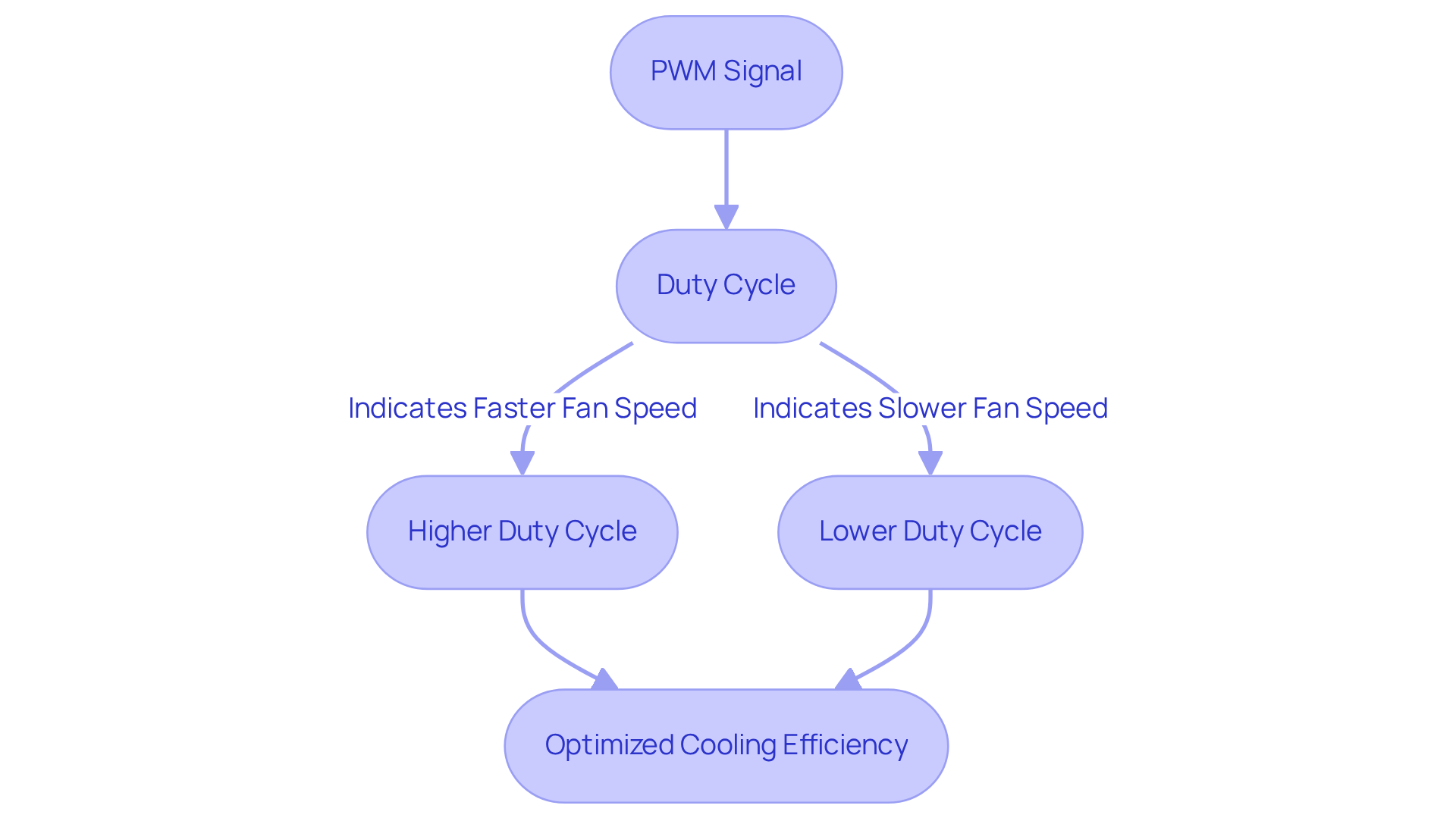
Fan speed control PWM serves as a pivotal method for regulating fan speeds by adjusting the pulse widths within a signal. In a conventional PWM fan configuration, a 4-pin connector is utilized, with the fourth pin dedicated to transmitting the PWM signal to the fan motor. The duty cycle of this signal is instrumental in determining the fan speed control PWM: an elevated duty cycle results in a faster fan operational rate, whereas a diminished duty cycle corresponds to a slower rate. Understanding this relationship is essential for in electronic systems, as it facilitates precise control over airflow and noise levels.
- Duty Cycle: This term refers to the percentage of time the signal remains ‘on’ compared to ‘off’ within a specified period. For instance, a 50% duty cycle indicates that the fan is operational half the time.
- Fan Speed Control PWM: The use of PWM technology allows for fan speed control PWM, enabling fans to operate at varying speeds, which enhances energy efficiency and reduces noise compared to traditional voltage-based regulation methods.
By mastering these foundational concepts, you will be well-equipped to effectively configure PWM settings in the subsequent steps.
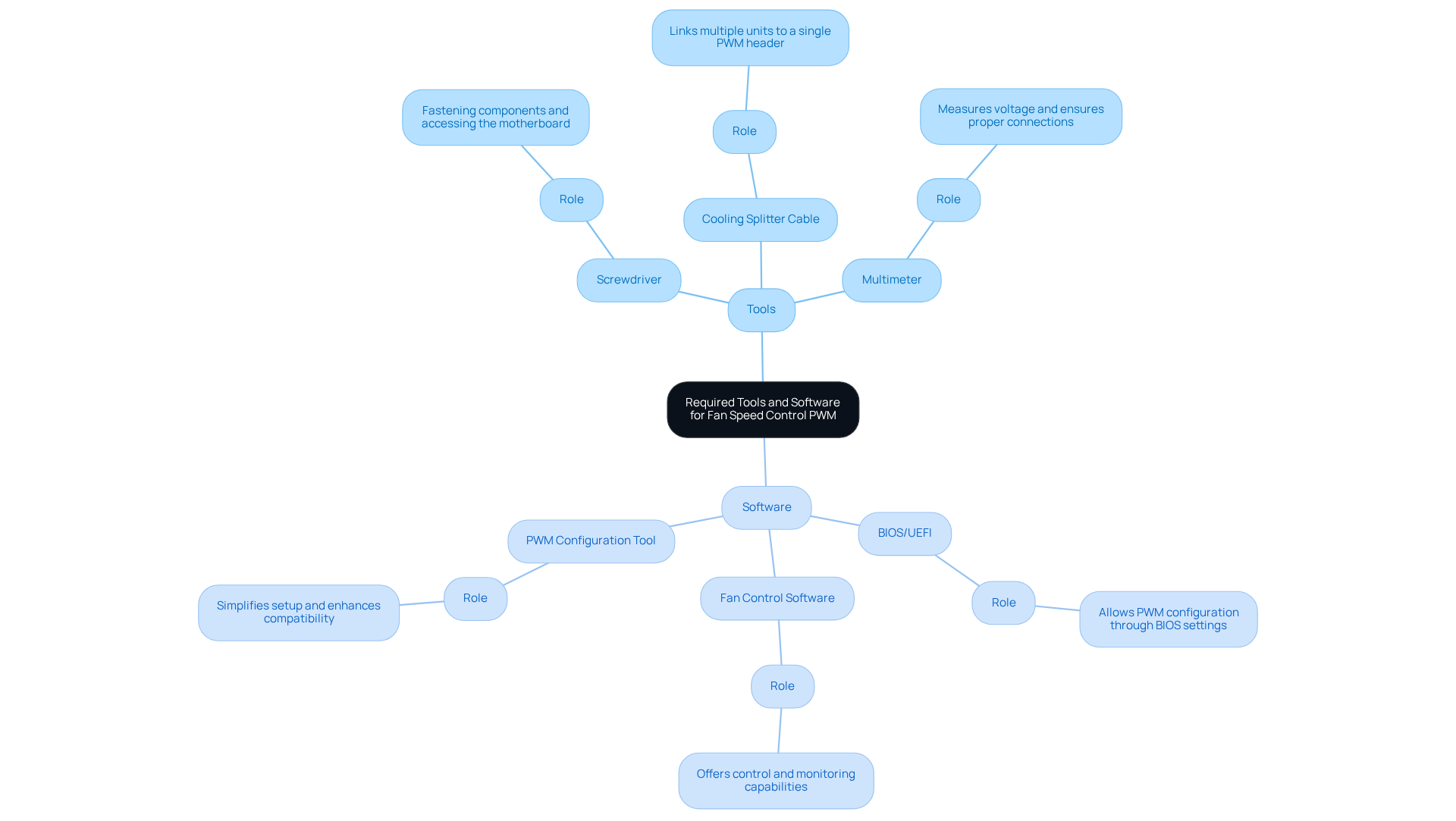
Gather Required Tools and Software
To effectively configure , it is essential to have the right tools and software at your disposal. This preparation will not only streamline the process but also ensure optimal fan performance.
Tools:
- Screwdriver: This tool is crucial for fastening components and accessing the motherboard.
- Cooling Splitter Cable: If you are utilizing several units, this cable enables you to link multiple units to a single PWM header, enhancing your setup’s efficiency.
- Multimeter: A multimeter is indispensable for measuring voltage and ensuring proper connections, which is vital for reliable operation.
Software:
- BIOS/UEFI: Most motherboards allow PWM configuration directly through the BIOS settings. Familiarize yourself with your motherboard’s manual for specific instructions to maximize your setup’s potential.
- Fan Control Software: Applications like SpeedFan or HWMonitor offer additional control and monitoring capabilities, providing you with greater flexibility in managing fan speeds.
- PWM Configuration Tool: Some manufacturers provide specific software for their fans, simplifying the setup process and enhancing compatibility.
By having these tools and software ready, you will significantly streamline your fan speed control PWM configuration process, leading to an efficient and effective fan performance.
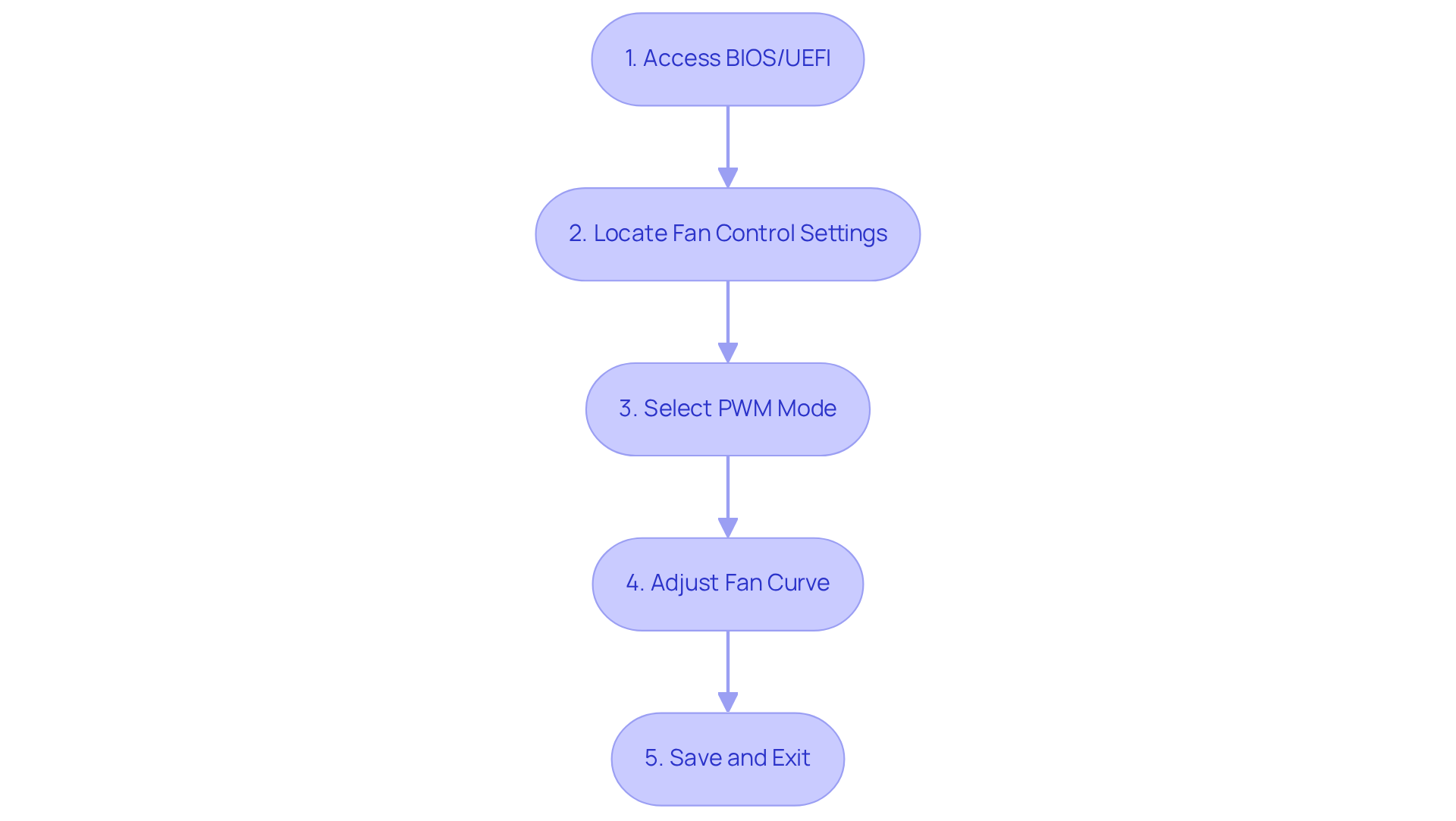
Configure PWM Settings for Optimal Performance
To configure your PWM settings effectively, follow these essential steps:
-
Access BIOS/UEFI
Restart your computer and enter the BIOS/UEFI setup by pressing the designated key (usually Del, F2, or Esc) during boot. -
Locate Fan Control Settings
Navigate to the ‘Hardware Monitor’ or ‘Fan Control’ section. Here, you will find options for adjusting fan levels, which are crucial for optimal performance. -
Select PWM Mode
Ensure that the fan header you are using is set to PWM mode. This configuration enables the motherboard to utilize fan speed control pwm to regulate the fan rotation based on the PWM signal, allowing for . -
Adjust Fan Curve
Set the fan curve according to your cooling needs. You can create a custom curve that modifies the fan rate based on CPU temperature. For example:- At 30°C, set the fan speed to 20%.
- At 50°C, increase to 50%.
- At 70°C, set to 100%.
-
Save and Exit
Save your changes and exit the BIOS. Your fans should now respond dynamically to temperature variations based on the configurations you have set.
By adhering to these steps, you will ensure that your fans operate efficiently, delivering optimal cooling while minimizing noise.
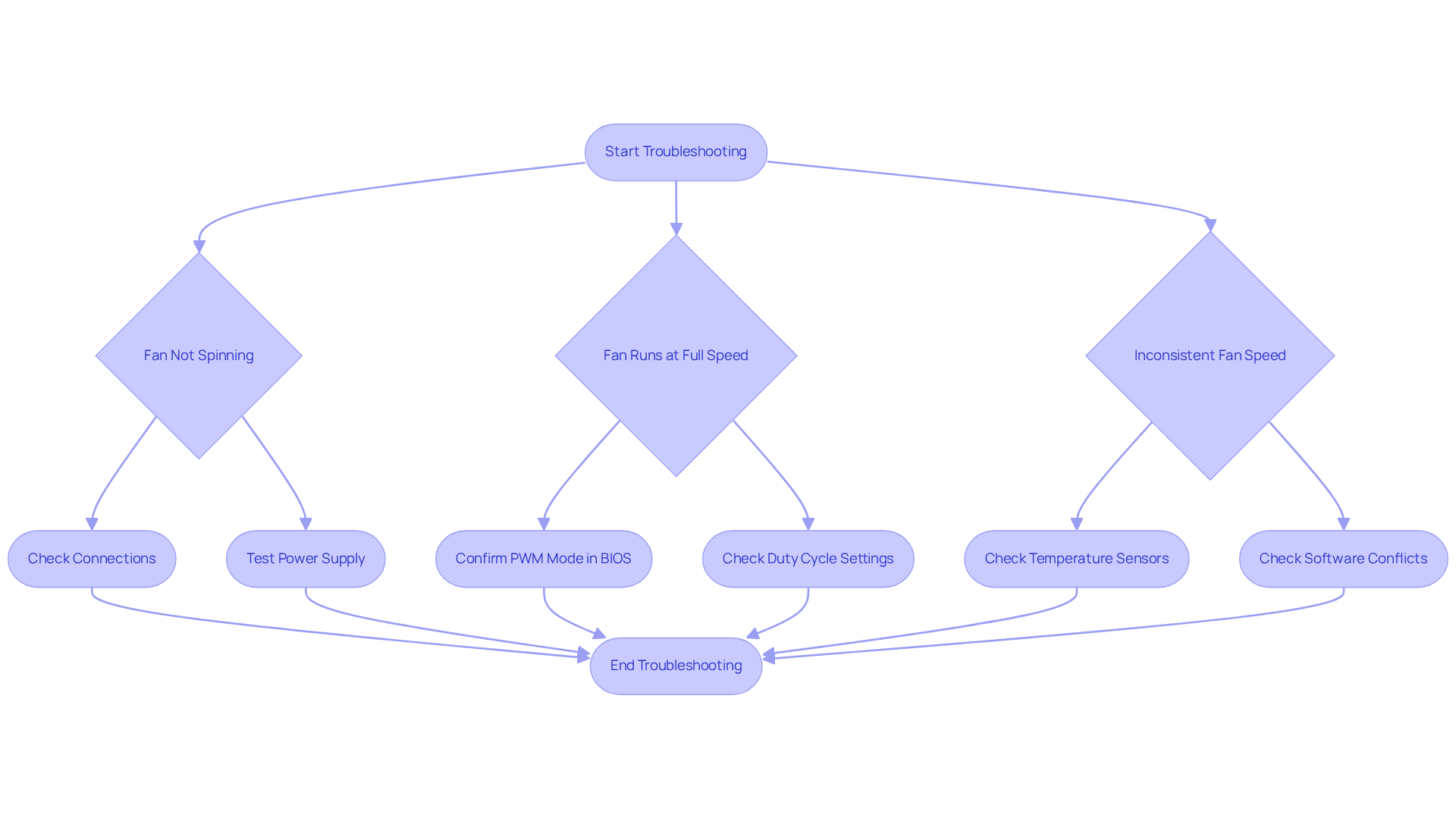
Troubleshoot Common PWM Fan Control Issues
If you encounter issues with your PWM fan control, consider the following troubleshooting steps:
Issue 1: Fan Not Spinning
- Check Connections: Ensure that the fan is properly connected to the motherboard and that the PWM pin is securely attached.
- Test Power Supply: Use a multimeter to verify that the fan is receiving power.
Issue 2: Fan Runs at Full Speed
- PWM Mode: Confirm that the fan header is set to PWM mode in the BIOS. If it’s set to DC mode, the fan will operate at maximum capacity.
- Duty Cycle Settings: Check your fan curve settings to ensure they are configured correctly.
Issue 3: Inconsistent Fan Speed
- Temperature Sensors: Ensure that temperature sensors are functioning correctly, as inaccurate readings can lead to erratic fan speeds.
- Software Conflicts: If utilizing fan management software, ensure it is compatible with your motherboard and does not conflict with BIOS settings.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can quickly resolve common issues related to fan speed control PWM and maintain optimal cooling performance.
Conclusion
Mastering PWM fan speed control is essential for achieving optimal cooling performance in electronic systems. Understanding the fundamentals of PWM technology and its role in regulating fan speeds through pulse width modulation allows effective management of airflow and noise reduction. This guide has outlined the essential tools, software, and steps necessary to configure PWM settings, ensuring fans operate efficiently in response to temperature demands.
Key insights include:
- The critical role of the duty cycle in fan speed adjustments.
- The necessity of appropriate tools such as multimeters and cooling splitter cables.
- The importance of BIOS settings for precise fan control.
Additionally, troubleshooting common issues—such as fans failing to spin or operating at full speed—offers practical solutions to maintain system performance.
Implementing these strategies not only enhances cooling efficiency but also contributes to the longevity of electronic components. By embracing effective fan speed control through PWM configuration, users can create a quieter, more energy-efficient environment, ultimately leading to improved overall system reliability and performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is PWM fan speed control?
PWM fan speed control is a method for regulating fan speeds by adjusting the pulse widths within a signal, allowing for precise control over airflow and noise levels.
How does a PWM fan configuration work?
A conventional PWM fan configuration uses a 4-pin connector, where the fourth pin is dedicated to transmitting the PWM signal to the fan motor.
What role does the duty cycle play in fan speed control?
The duty cycle determines the fan speed: a higher duty cycle results in a faster fan speed, while a lower duty cycle leads to a slower speed.
What is meant by duty cycle?
Duty cycle refers to the percentage of time the signal is ‘on’ compared to ‘off’ within a specified period. For example, a 50% duty cycle means the fan operates half the time.
What are the advantages of using PWM technology for fan speed control?
PWM technology enhances energy efficiency and reduces noise compared to traditional voltage-based regulation methods, allowing fans to operate at varying speeds.
Why is understanding PWM fan speed control important?
Understanding PWM fan speed control is essential for optimizing cooling efficiency in electronic systems, as it facilitates better management of airflow and noise levels.