Overview
This article delves into the distinctions between positive displacement and centrifugal blowers, elucidating their respective advantages and disadvantages across various industrial applications. It asserts that positive displacement blowers deliver reliable airflow under consistent loads, rendering them ideal for specific tasks. Conversely, centrifugal blowers thrive in high airflow situations but exhibit sensitivity to system design. This underscores the critical importance of selecting the appropriate blower type based on application requirements and performance criteria.
Introduction
Understanding the mechanics behind blowers is essential for optimizing air and gas movement in various engineering applications. This article explores the two primary types of blowers:
- Positive displacement
- Centrifugal
These types highlight their unique characteristics, advantages, and ideal use cases. As industries increasingly seek efficient solutions for airflow management, a critical question emerges: how can one determine which blower type is best suited for specific operational needs? This consideration is particularly important when evaluating factors such as performance and maintenance.
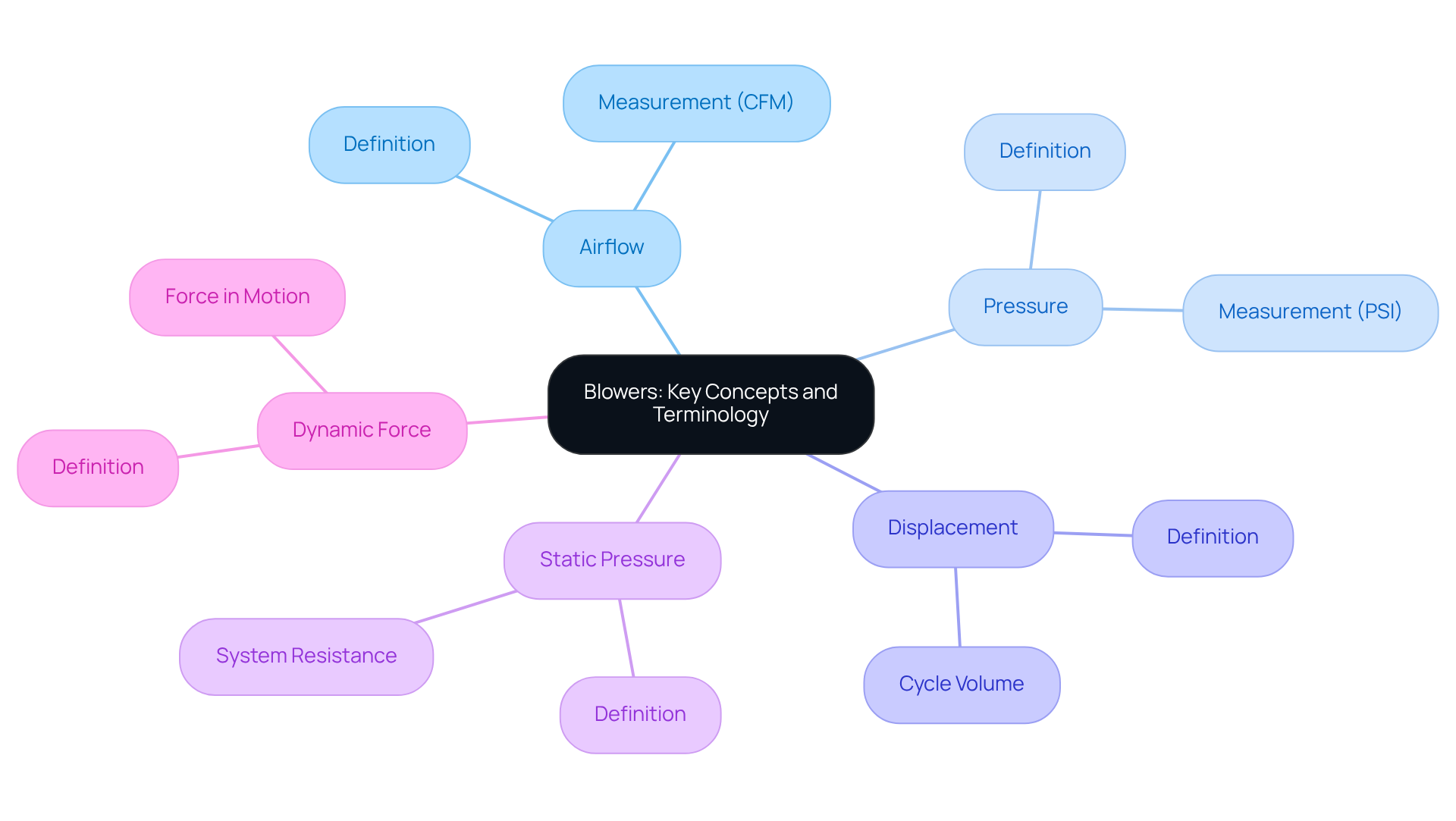
Define Blowers: Key Concepts and Terminology
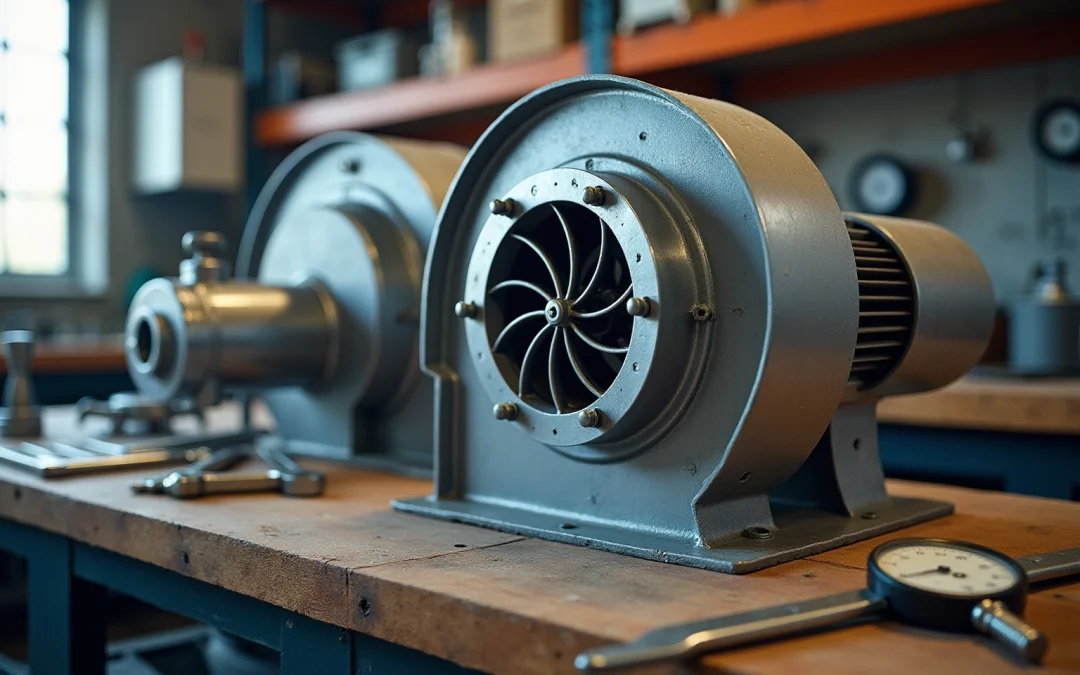
There are various types of blowers, which are mechanical devices engineered to move air or gas by enhancing its pressure and velocity. Understanding the key terminology is essential for and selecting the appropriate type for specific engineering applications. Key terms include:
- Airflow: The volume of air displaced by the blower, typically quantified in cubic feet per minute (CFM).
- Pressure: The force exerted by the air, commonly measured in pounds per square inch (PSI).
- Displacement: The volume of air transferred during each cycle of the fan.
- Static Pressure: The force within the system when the fan is inactive.
- Dynamic Force: The force of the air while in motion.
A solid understanding of these terms is crucial for making informed decisions in engineering applications.
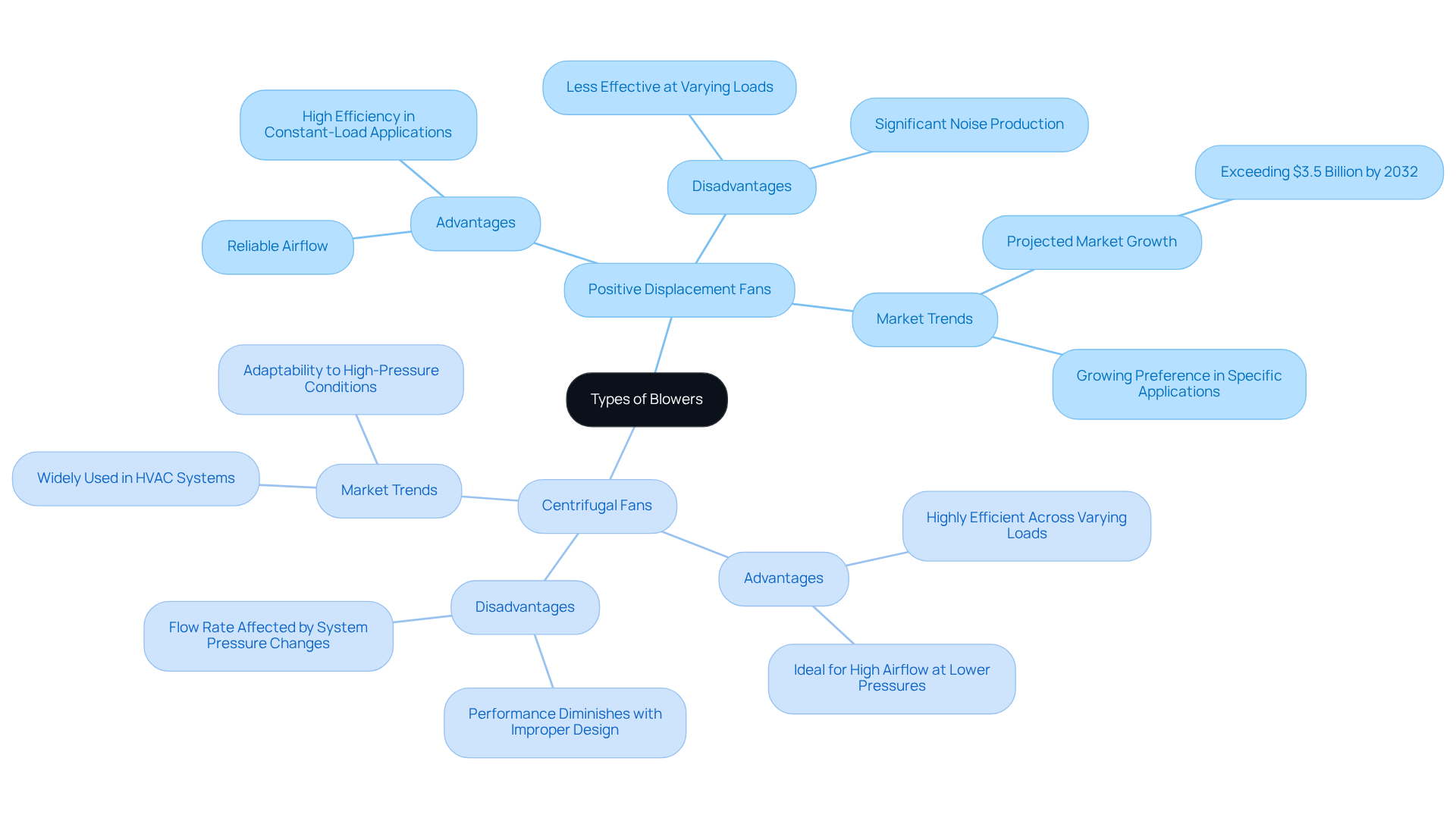
Explore Types of Blowers: Positive Displacement vs. Centrifugal
There are two primary types of blowers that are crucial for various industrial applications:
-
Positive Displacement Fans: These devices operate by capturing a specific volume of air and expelling it, ensuring a consistent flow regardless of pressure fluctuations. Common types of blowers include rotary lobe and screw compressors.
- Advantages: They deliver reliable airflow and demonstrate high efficiency in constant-load applications, making them particularly suitable for processes that require a stable air supply, such as aeration in wastewater treatment plants and pneumatic conveying in food processing.
- Disadvantages: However, they may be less effective at varying loads compared to centrifugal fans and can produce significant noise, especially in Roots systems, which necessitates the implementation of noise reduction measures to comply with workplace standards in sensitive environments.
-
Centrifugal Fans: Utilizing a rotating impeller, these devices increase air velocity, converting kinetic energy into force. They excel in applications that demand high airflow at lower pressures.
- Advantages: Centrifugal fans are highly efficient across varying loads and are ideally suited for transporting large volumes of air, making them essential for HVAC systems and industrial ventilation.
- Disadvantages: Nevertheless, their performance can drastically diminish if the system is improperly designed, particularly under conditions of high-pressure differentials.
Recent trends indicate a growing preference for positive displacement devices due to their reliability and efficiency in specific applications, despite their higher initial costs. The market for these devices is projected to exceed $3.5 billion by 2032, driven by demand in sectors such as water treatment and chemical processing. Understanding these distinctions is vital for selecting the appropriate device for your specific use case, as this decision can significantly impact and cost-effectiveness.
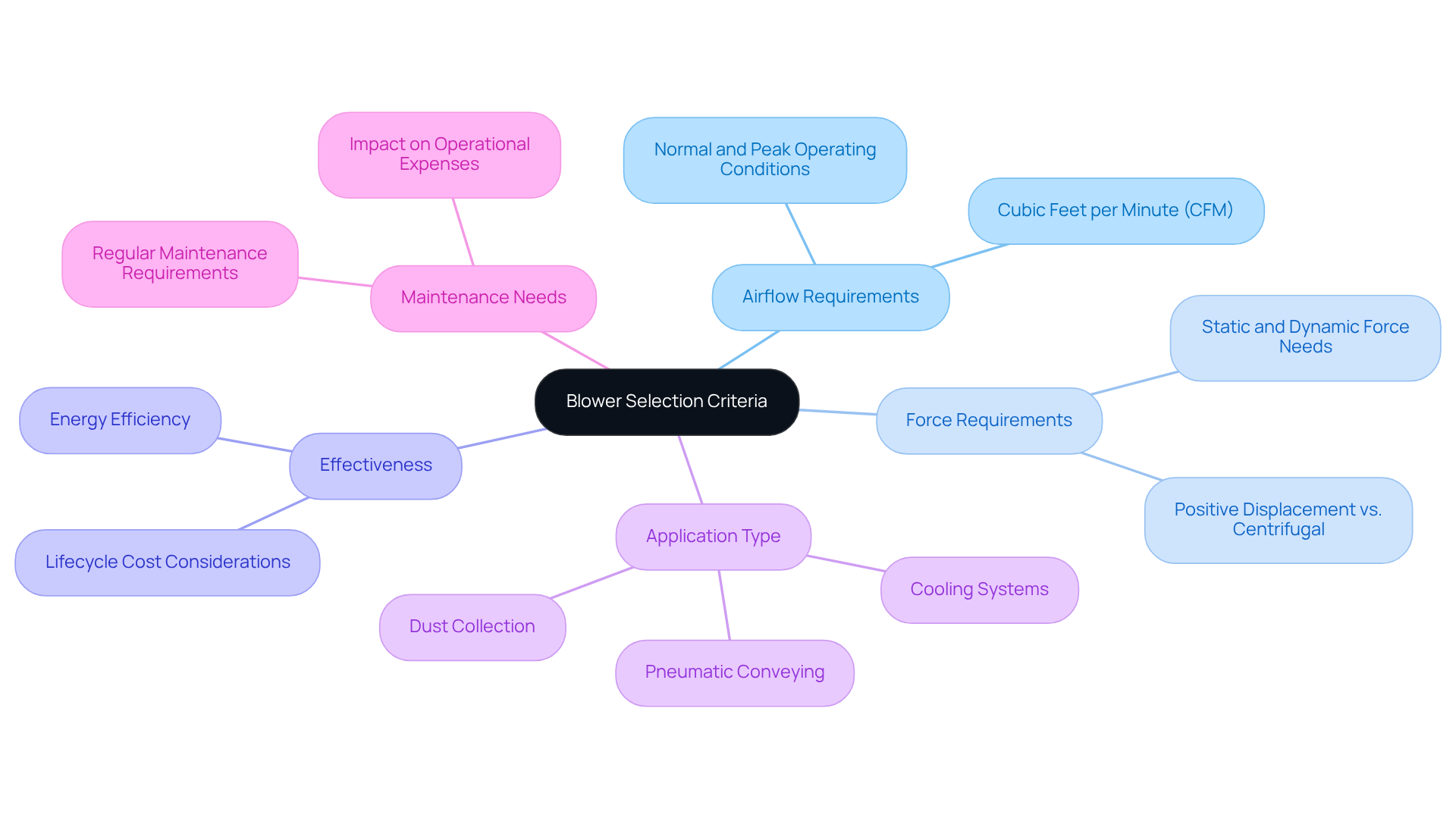
Evaluate Blower Selection Criteria: Performance and Application Needs
When selecting a blower, it is crucial to consider the following criteria:
- Airflow Requirements: Accurately determining the necessary cubic feet per minute (CFM) for your application is essential. This ensures that the fan can adequately meet system demands, particularly in cooling applications where airflow is critical.
- Force Requirements: Evaluating both static and dynamic force needs is vital. Various types of fans, such as positive displacement and centrifugal variants, excel in different pressure ranges, making this assessment crucial for optimal performance.
- Effectiveness: Focus on devices that provide high efficiency tailored for your specific use. This not only reduces energy expenses but also enhances overall system performance, as over 80% of a fan’s lifecycle cost is linked to energy usage.
- Application Type: Consider the specific application—whether cooling, pneumatic conveying, or dust collection. Each of the types of blowers is designed for specific tasks, and aligning the blower with the application is essential for efficient operation.
- Maintenance Needs: Assess the maintenance requirements associated with each of the types of blowers. Some fans may necessitate more regular maintenance, which can impact long-term operational expenses and effectiveness.
Real-world examples underscore the importance of these criteria. For instance, in a recent engineering project focused on cooling systems, engineers emphasized the significance of airflow and force requirements, noting that improper sizing could lead to overheating and increased maintenance costs. As one engineer remarked, “Understanding airflow and pressure requirements is essential; an undersized fan can operate under stress, compromising its lifespan and performance.”
Furthermore, data indicates that an insufficient fan can operate under stress, jeopardizing its lifespan and performance. A case study on the ‘Consequences of Improper Sizing’ further highlights that achieving the right balance between fan size, power, and airflow is crucial for ensuring system reliability and safety.
By meticulously considering these factors, you can select a blower that not only meets your performance needs but also operates efficiently within your system, ultimately leading to enhanced reliability and cost-effectiveness.
Conclusion
Understanding the types of blowers—positive displacement and centrifugal—is essential for making informed decisions in various engineering applications. Each type offers unique advantages and disadvantages that cater to specific operational needs. By grasping these distinctions, one can optimize performance and efficiency, ultimately leading to improved outcomes in any project involving air or gas movement.
This article delves into the critical characteristics of both blower types, highlighting the reliability and efficiency of positive displacement fans in constant-load scenarios, while also noting their limitations in varying load conditions. In contrast, centrifugal fans are showcased for their adaptability and effectiveness in high airflow applications, although they require careful system design to avoid performance issues. Furthermore, the importance of selecting the right blower based on airflow, force requirements, and application type is emphasized, reinforcing the need for a comprehensive evaluation process.
Ultimately, the choice between positive displacement and centrifugal blowers hinges on understanding specific application requirements and operational contexts. By prioritizing the right selection criteria, engineers and decision-makers can enhance system reliability, reduce energy costs, and ensure optimal performance. Embracing this knowledge not only fosters better engineering practices but also contributes to the advancement of efficient air management solutions across various industries.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are blowers?
Blowers are mechanical devices designed to move air or gas by increasing its pressure and velocity.
Why is understanding key terminology important when evaluating blowers?
Understanding key terminology is essential for assessing fan performance and selecting the appropriate type for specific engineering applications.
What is airflow in the context of blowers?
Airflow refers to the volume of air displaced by the blower, typically measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM).
How is pressure measured in blowers?
Pressure is the force exerted by the air and is commonly measured in pounds per square inch (PSI).
What does displacement mean in relation to blowers?
Displacement is the volume of air transferred during each cycle of the fan.
What is static pressure?
Static pressure is the force within the system when the fan is inactive.
What is dynamic force?
Dynamic force is the force of the air while it is in motion.

