Overview
The article examines the fundamentals and applications of radial blowers, underscoring their efficiency in the transportation of air and gases while highlighting their pivotal role in various engineering disciplines. It elaborates on the operational principles, key components, and selection criteria for radial blowers, illustrating their significance in optimizing system performance and enhancing energy efficiency across industries, including HVAC and automotive. This comprehensive overview not only establishes the importance of radial blowers but also provides actionable insights for professionals seeking to leverage their capabilities.
Introduction
Understanding the intricacies of radial blowers is essential for engineers aiming to enhance system performance across diverse applications. These centrifugal fans, recognized for their efficiency in transporting air and gases, play a pivotal role in optimizing cooling and ventilation systems within industries ranging from automotive to electronics. As the demand for these devices escalates, the challenges associated with their implementation and maintenance also increase. Engineers must consider strategic approaches to master the fundamentals of radial blowers and ensure their successful application in increasingly complex environments.
Explore the Fundamentals of Radial Blowers
Radial fans, commonly referred to as centrifugal fans, are engineered to transport air or gases radially outward from their center of rotation with remarkable efficiency. By harnessing the principle of centrifugal force, these devices incorporate a rapidly spinning impeller that creates a low-pressure zone, effectively drawing air in and expelling it at a right angle. This design is particularly advantageous in situations demanding high static pressure and minimal airflow resistance, making it a critical component for engineers aiming to optimize cooling and ventilation systems across various industries.
Gagner-Toomey Associates stands out as the world’s largest manufacturer of both standard and custom air-movers, boasting an extensive array of DC input centrifugal fans available in sizes ranging from 15 to 225mm. Their products are engineered for enhanced performance, efficiency, and low noise levels, with most models featuring IP protection, catering to diverse applications in electronics, automotive, and industrial sectors.
Key characteristics of radial blowers include:
- High Static Pressure: Especially effective in environments with considerable resistance, such as ductwork, where maintaining airflow is paramount.
- Compact Design: The space-efficient configuration of the radial blower facilitates installation in areas with limited space, making it adaptable for a wide range of applications.
- Versatility: The radial blower is utilized across numerous sectors, including HVAC, automotive, and medical devices, showcasing its remarkable adaptability.
Understanding these fundamentals equips engineers with the necessary knowledge to , thereby enhancing system functionality and energy efficiency. As the demand for radial blowers in HVAC and electronics continues to grow, understanding their operational principles becomes increasingly vital for successful applications and innovations in these fields. Furthermore, engineers have underscored the importance of understanding centrifugal fans, asserting that “mastering the principles of these devices is essential for optimizing system performance and ensuring reliability in critical applications.” However, it is crucial to consider challenges such as high initial investment costs and maintenance complexities when implementing these systems. Successful applications of centrifugal fans from Gagner-Toomey Associates in HVAC systems have demonstrated their effectiveness in improving cooling efficiency, further underscoring the necessity for engineers to be well-versed in their operation.
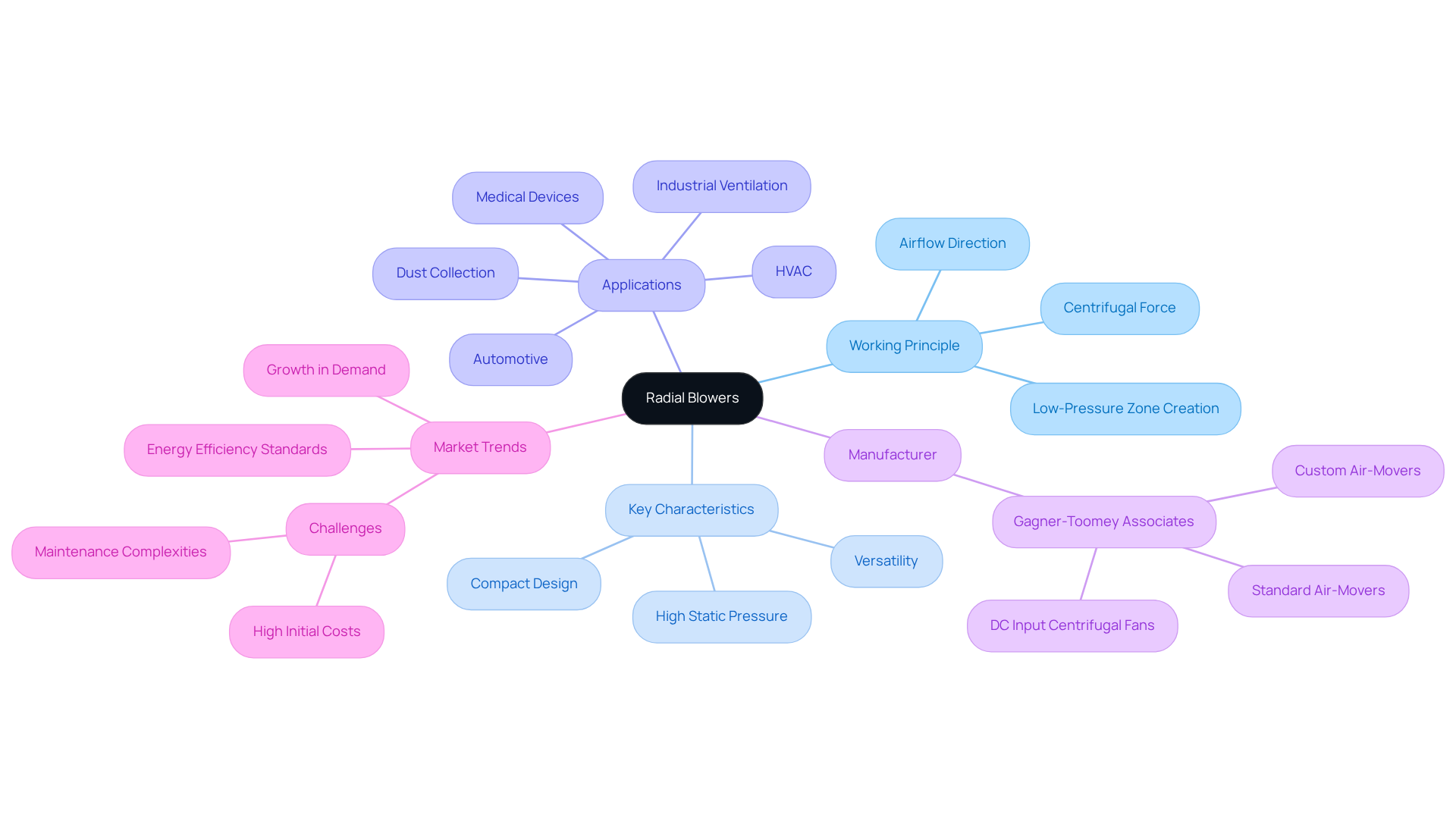
Understand the Construction and Operation of Radial Blowers
The components of a radial blower work in unison to optimize air movement. These components include:
- Impeller: Serving as the core of the blower, the impeller is responsible for generating airflow through its rotation. The design of the impeller blades significantly impacts functionality, especially in relation to Gagner-Toomey Associates’ cutting-edge cooling solutions, which are engineered for efficiency and minimal noise. Recent innovations in impeller design, characterized by aerodynamic shapes and optimized blade angles, enhance performance metrics such as static pressure and air movement efficiency.
- Housing: The outer casing that channels air and supports the impeller is meticulously designed to reduce turbulence and maximize efficiency. This is a crucial element of the comprehensive product line offered by Gagner-Toomey Associates, which includes both standard and custom designs. Efficient housing designs ensure smooth air transitions, vital for applications that require high static pressure.
- Motor: The motor powers the impeller, typically an electric motor capable of varying speeds to control airflow. Gagner-Toomey Associates provides a range of motors suitable for their DC input tube axial fans and centrifugal fans, ensuring compatibility with various impeller designs for optimal performance.
- Inlet and Outlet: The inlet draws air into the fan, while the outlet expels it, often tailored to specific ductwork or application requirements, particularly in electronics and automotive sectors. The proper design of these components is essential for maintaining consistent air movement and pressure.
The operation of a radial blower initiates when the motor rotates the impeller, creating a centrifugal force that draws air into the inlet. As the radial blower’s impeller spins, air is propelled outward and expelled through the outlet, generating high static pressure. This distinctive airflow pattern proves particularly effective in applications such as dust collection and pneumatic conveying, where maintaining air quality and efficient material transport is critical.
Understanding the is imperative for engineers aiming to integrate these systems effectively. By focusing on the interplay between impeller design and overall fan performance, engineers can ensure that their setups operate at peak efficiency, ultimately leading to enhanced productivity and reduced operational costs. Gagner-Toomey Associates offers an extensive selection of DC input tube axial fans, ranging from 15 to 280mm, and centrifugal units from 15 to 225mm, with IP protection available in most models upon request.
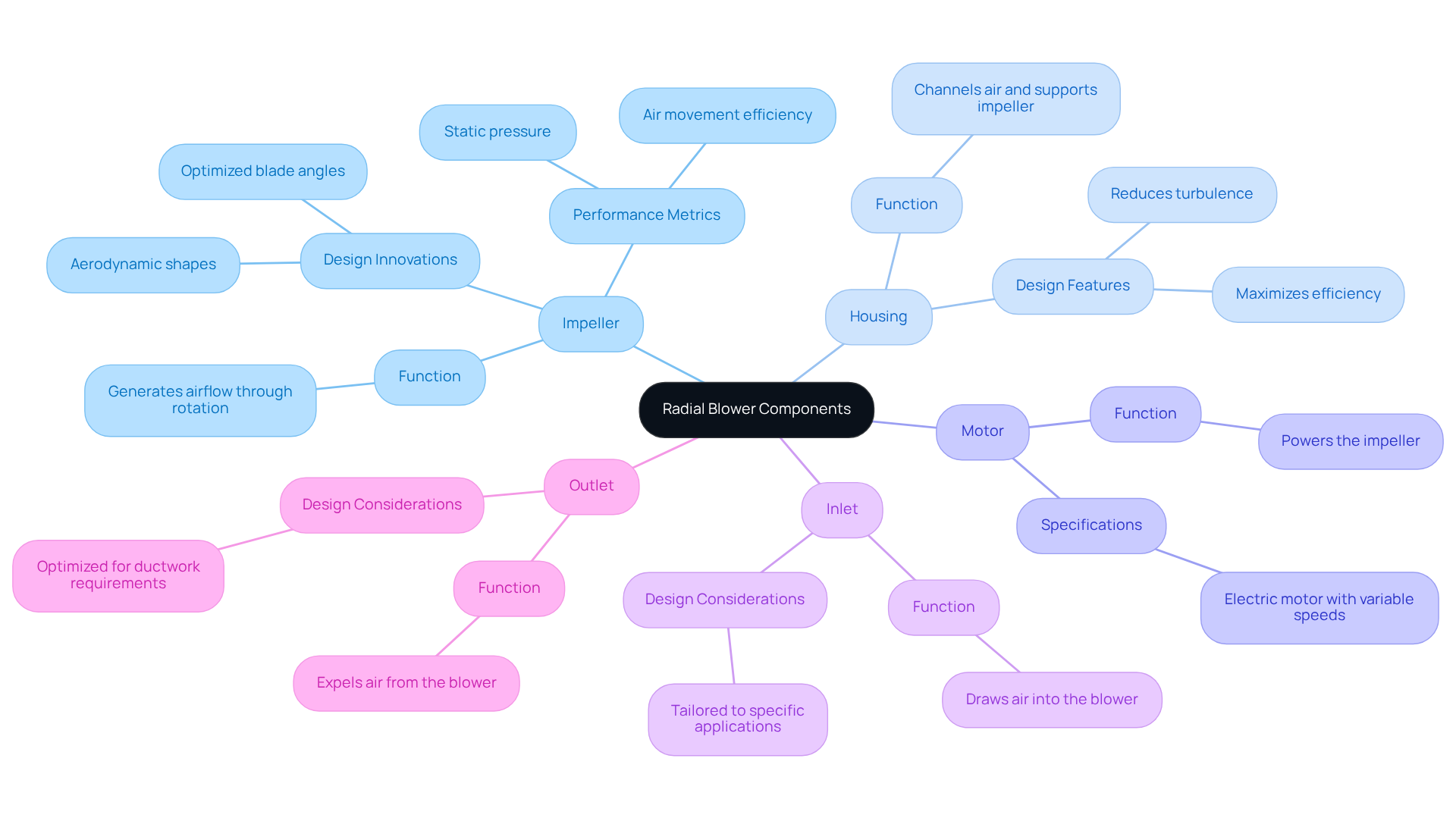
Examine Key Components: Bearings and Speed Control
Two critical components in the operation of radial blowers are bearings and speed control mechanisms:
Bearings: Bearings are essential for supporting the impeller shaft and minimizing friction during operation. The choice of bearing type—whether ball, roller, or sleeve—significantly influences the device’s efficiency and longevity. Routine maintenance of bearings is vital to prevent wear and ensure smooth functioning, ultimately enhancing the overall efficiency of the device.
Speed Control: Regulating the speed of the impeller is crucial for adjusting air movement and pressure across various applications. (VFDs) are extensively employed to modulate motor speed, allowing for precise control over blower performance. This adaptability is particularly important in scenarios where airflow requirements vary. Notably, the use of VFDs can lead to energy savings of up to 90%, while also improving comfort control in HVAC systems. Furthermore, the internal rate of return (IRR) for retrofitting aerial coolers with VFDs may reach as high as 220% for fifty 186 kW motors, underscoring their significant economic advantages.
Understanding these elements empowers engineers to make informed decisions regarding the selection and maintenance of radial blowers, thereby enhancing the reliability and efficiency of the system. As emphasized by industry specialists, effective speed regulation is not merely a technical necessity but a strategic advantage in optimizing fan applications. As James A. Michener aptly noted, “Scientists dream about doing great things. Engineers do them,” which underscores the practical impact of engineering solutions.
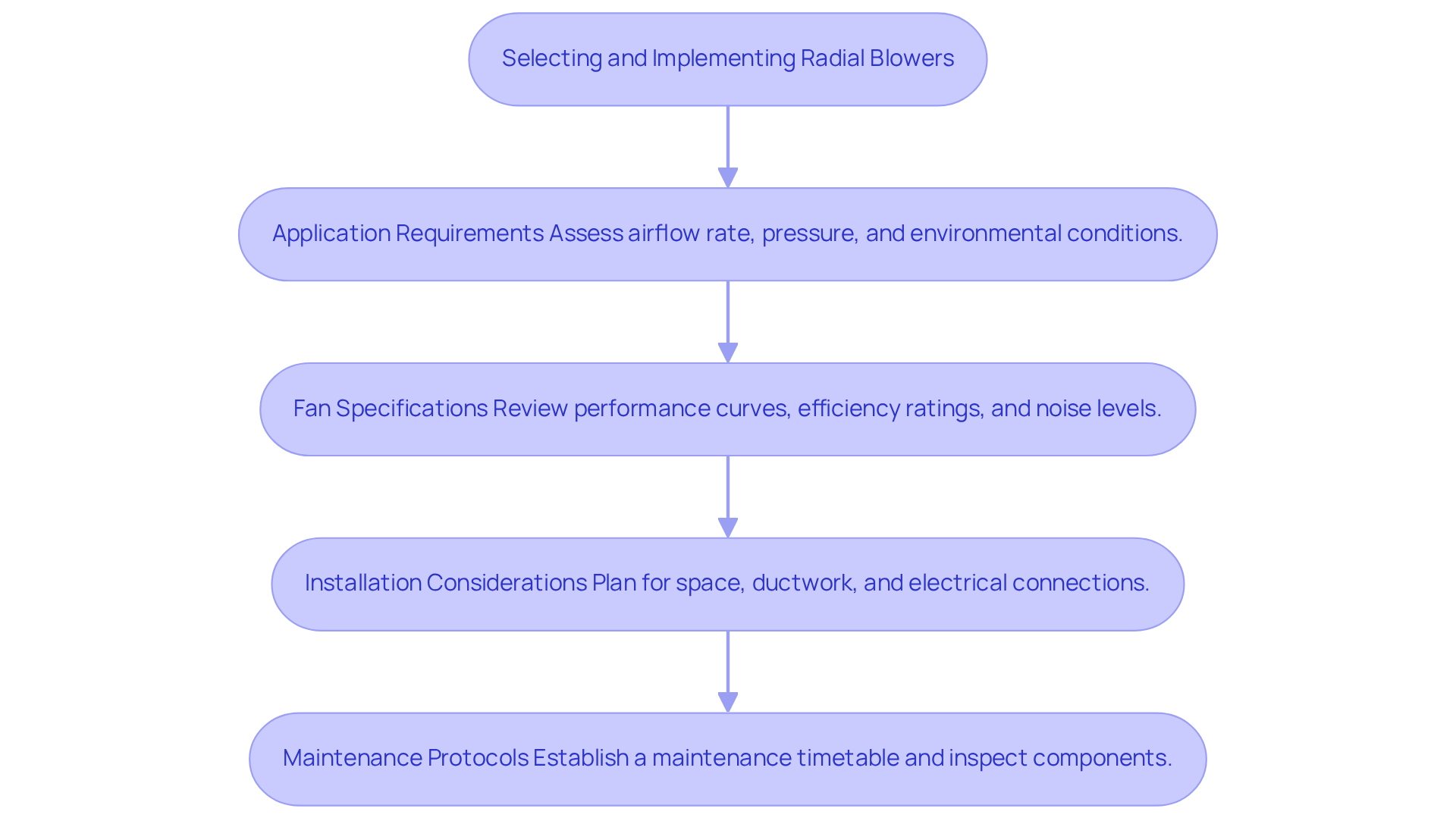
Apply Knowledge: Selecting and Implementing Radial Blowers
When selecting and implementing a radial blower, engineers must consider several key factors to ensure and project success.
- Application Requirements: Assessing the specific needs of the application is essential, including airflow rate, pressure requirements, and environmental conditions. Understanding these parameters aids in selecting a fan that can effectively meet the demands of the system.
- Fan Specifications: Engineers should thoroughly review the fan’s performance curves, efficiency ratings, and noise levels. Recent studies indicate that new fan models can exhibit a 6.29% increase in volume flow rate and a 2.67% improvement in efficiency, while also reducing noise levels by 0.04% at a power input of 120 W. The simulation study’s boundary condition was set to a flow volume of 5 m³/h, providing critical operational parameters relevant to engineers. Such specifications are essential for ensuring the fan aligns with project requirements.
- Installation Considerations: Proper planning for installation is vital. This includes ensuring adequate space, designing ductwork effectively, and making appropriate electrical connections. Frequent installation problems may occur, such as insufficient airflow or incorrect duct sizing; tackling these in advance can enhance efficiency and reduce maintenance difficulties.
- Maintenance Protocols: Establishing a consistent maintenance timetable is crucial for overseeing fan functionality. This involves inspecting bearings, cleaning parts as needed, and monitoring inlet air density, which is a critical element in fan efficiency. Senior Application Engineer Chet White emphasizes the importance of understanding fan selection to ensure project success.
By applying this knowledge, engineers can effectively select and implement radial blowers to enhance system performance, reliability, and efficiency, ultimately contributing to the success of their projects.
Conclusion
Mastering the fundamentals of radial blowers is essential for engineers aiming to optimize their applications across various industries. These centrifugal fans are meticulously designed to transport air or gases with efficiency, leveraging centrifugal force principles to achieve high static pressure and minimal airflow resistance. A thorough understanding of their construction, operation, and key components empowers engineers to enhance system performance and reliability in critical applications.
The article underscores the significance of several aspects, including:
- Impeller design
- Bearing function
- The importance of speed control mechanisms
By selecting the appropriate radial blower tailored to specific application requirements and ensuring effective maintenance, engineers can guarantee improved cooling efficiency and energy savings. The insights presented emphasize that a comprehensive grasp of these devices is crucial for successful implementation and innovation in sectors such as HVAC, automotive, and electronics.
As the demand for advanced radial blower technology continues to escalate, the necessity for engineers to be well-versed in their principles and applications becomes increasingly paramount. Embracing these fundamentals not only enhances system functionality but also positions engineers at the forefront of driving efficiency and sustainability in their projects. A commitment to understanding and applying the knowledge of radial blowers will undoubtedly yield significant benefits in both performance and operational costs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are radial blowers and how do they work?
Radial blowers, also known as centrifugal fans, transport air or gases radially outward from their center of rotation using centrifugal force. They feature a rapidly spinning impeller that creates a low-pressure zone, drawing air in and expelling it at a right angle.
What are the key characteristics of radial blowers?
Key characteristics include high static pressure, compact design, and versatility. They are effective in environments with considerable resistance, space-efficient for installation in limited areas, and adaptable across various sectors such as HVAC, automotive, and medical devices.
Who is Gagner-Toomey Associates and what do they offer?
Gagner-Toomey Associates is the world’s largest manufacturer of standard and custom air-movers, offering a wide range of DC input centrifugal fans in sizes from 15 to 225mm. Their products are designed for enhanced performance, efficiency, and low noise levels, suitable for diverse applications.
Why are radial blowers important in engineering?
Understanding radial blowers is crucial for engineers as it enhances system functionality and energy efficiency. They are particularly important in optimizing cooling and ventilation systems in HVAC and electronics, ensuring reliability in critical applications.
What challenges are associated with implementing radial blowers?
Challenges include high initial investment costs and maintenance complexities that engineers must consider when implementing these systems.
How have radial blowers been successfully applied in HVAC systems?
Successful applications of centrifugal fans from Gagner-Toomey Associates in HVAC systems have demonstrated their effectiveness in improving cooling efficiency, highlighting the importance of understanding their operation for engineers.