Overview
Data centre cooling systems are crucial for maintaining optimal temperature and humidity levels, effectively preventing overheating that can lead to hardware failures and data loss. This article underscores their significance by exploring various cooling methods, recent innovations, and market growth. It highlights how effective cooling not only safeguards equipment but also enhances energy efficiency, thereby supporting the escalating demands of modern technology.
Introduction
Data centre cooling systems are the unsung heroes of modern information facilities, diligently operating behind the scenes to ensure optimal performance and reliability. As the demand for data processing continues to surge, understanding these cooling mechanisms becomes paramount, particularly given their critical role in preventing costly hardware failures and data loss.
With a projected market growth underscoring an urgent need for energy-efficient solutions, organizations face the challenge of balancing the push for performance with the necessity of sustainability in their cooling strategies.
Define Data Center Cooling Systems
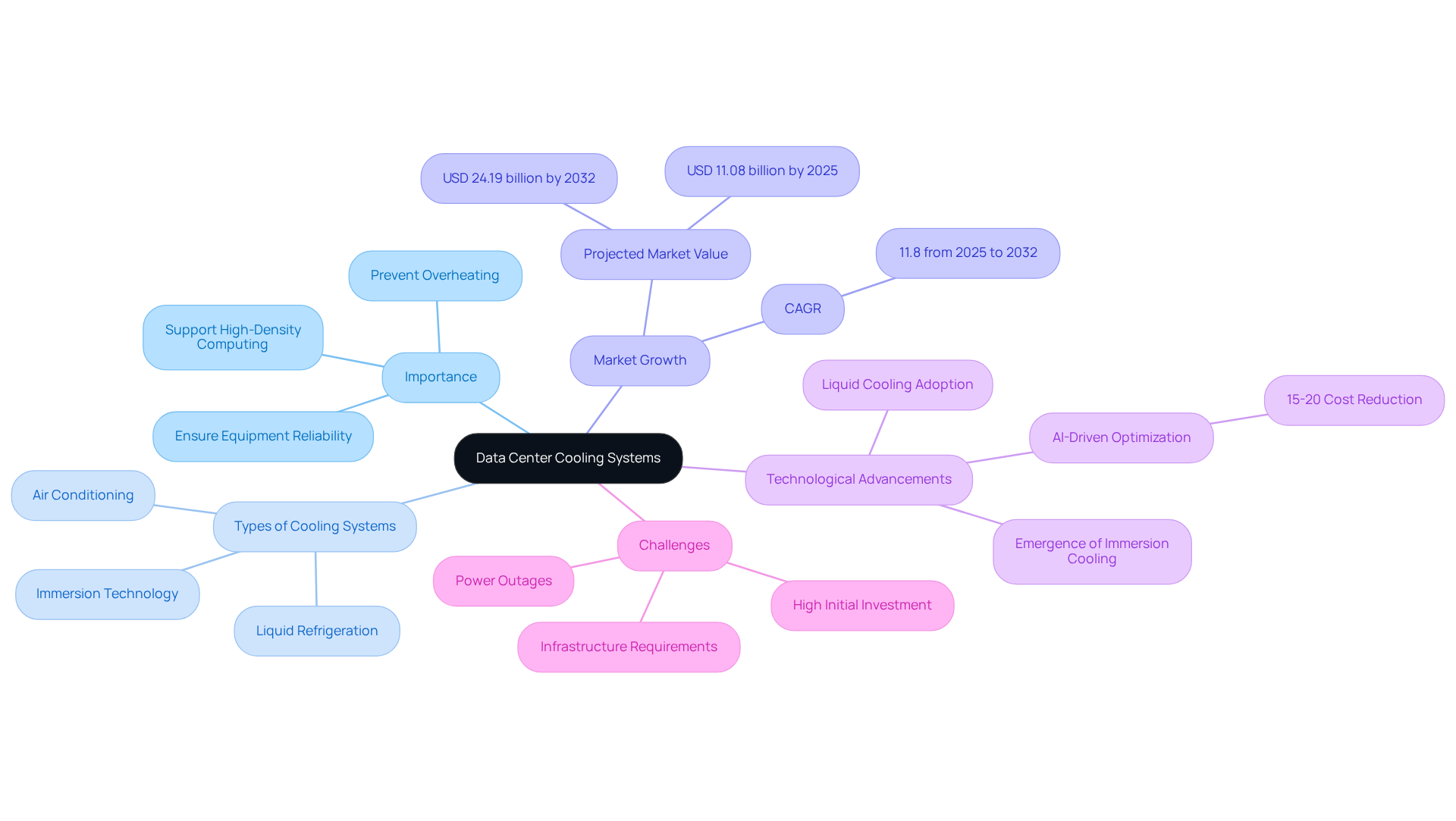
Data centre cooling systems serve as specialized mechanisms designed to manage temperature and moisture levels within information facilities, ensuring that servers and other critical equipment operate effectively and reliably. These data centre cooling systems are vital for preventing overheating, which can lead to hardware failures and data loss. Chilling techniques vary significantly, ranging from conventional air conditioning systems to advanced liquid refrigeration solutions, including data centre cooling systems, each tailored to meet the specific demands of the information facility context.
By 2025, the global server facility temperature regulation market is projected to reach approximately USD 11.08 billion, with expectations to expand to USD 24.19 billion by 2032, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.8% throughout this period. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient refrigeration options, particularly as data centre cooling systems evolve to support high-density computing and AI applications.
Industry leaders underscore the importance of these frameworks; for instance, AI-driven temperature optimization can yield a 15-20% reduction in refrigeration costs. By 2025, it is anticipated that 75% of large corporations will implement AI-enhanced infrastructure management tools to boost server performance and efficiency. Furthermore, the emergence of liquid temperature regulation technology is gaining traction in data centre cooling systems as traditional air ventilation systems prove inadequate for high-density server environments, offering enhanced thermal management and reduced energy consumption.
Effective examples of data centre cooling systems for regulating server hub temperatures include the adoption of liquid temperature management systems, such as Colovore’s solution, which accommodates rack capacities of up to 50 kW, addressing the escalating power demands of modern server facilities. Additionally, immersion temperature regulation technology has demonstrated significant improvements in information hub efficiency, showcasing a successful application of advanced temperature management solutions.
Nevertheless, information hubs face substantial challenges during power outages, which can lead to overheating and damage to sensitive equipment. This highlights the growing necessity for , which are becoming increasingly essential.
In conclusion, data centre cooling systems are crucial for maintaining optimal operating conditions, and their advancement is vital for the future of efficiency and sustainability in these facilities. The market dynamics, including government initiatives and the drive for energy-efficient solutions, further reinforce the importance of these frameworks in the contemporary information landscape.
Explain the Importance of Cooling Systems in Data Centers
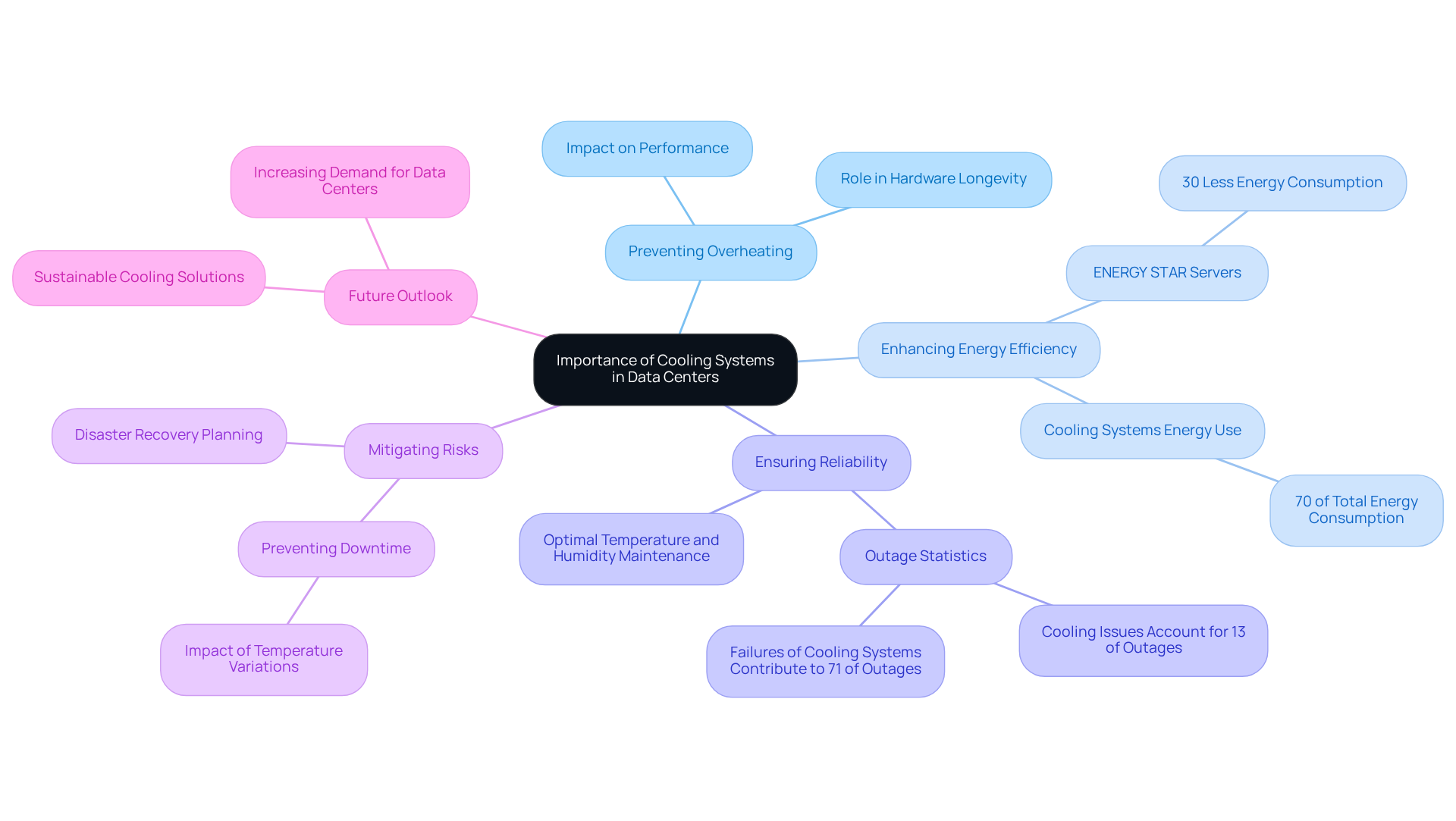
Data centre cooling systems are indispensable to the operation of information hubs, as they play a crucial role in preventing overheating, which can lead to hardware malfunctions and significantly shorten the lifespan of equipment. Effective cooling provided by data centre cooling systems not only safeguards hardware but also enhances energy efficiency; ENERGY STAR qualified servers can consume as much as 30% less energy than conventional servers.
Moreover, maintaining optimal temperature and humidity levels through data centre cooling systems is crucial for ensuring the reliability of services offered by computing facilities. Even slight temperature variations can lead to significant downtime and concerns regarding information integrity, with data centre cooling systems-related issues accounting for roughly 13% of all facility outages.
Furthermore, failures of power and refrigeration mechanisms, including data centre cooling systems, contribute to nearly 71% of all facility outages, underscoring the critical importance of these infrastructures. As we approach 2025, information hubs will continue to serve as the backbone of digital infrastructure, highlighting the undeniable significance of robust data centre cooling systems. They are essential for maintaining operations, mitigating risks, and ensuring that can support the increasing demands of contemporary technology.
Explore Different Types of Data Center Cooling Methods
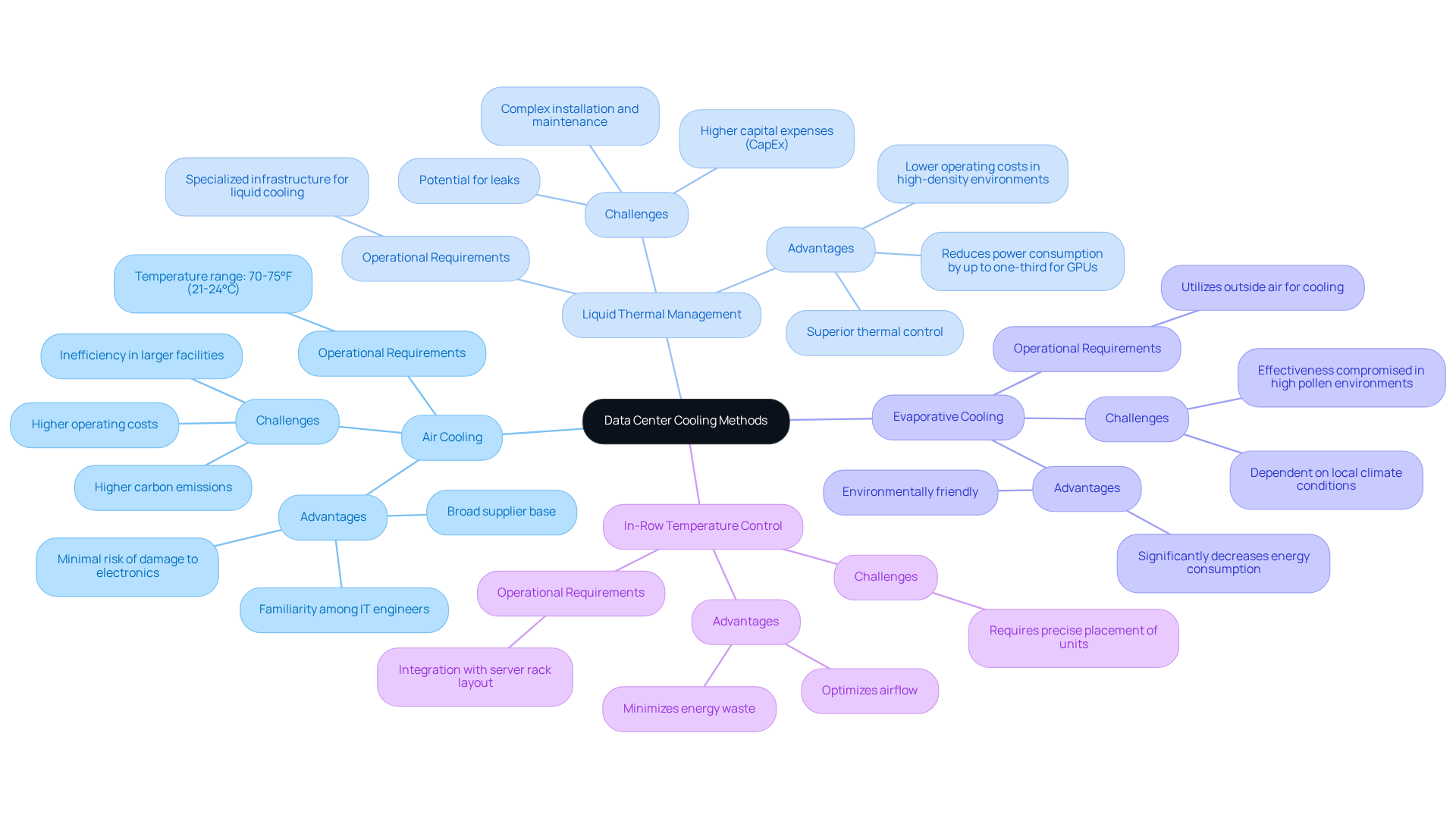
Data centre cooling systems utilize a range of temperature control techniques, each tailored to meet specific operational requirements. The most prevalent types include:
- Air Cooling: This traditional method utilizes air conditioning units to circulate cool air throughout the facility. While it is well-known and straightforward to implement, air refrigeration can prove ineffective in larger facilities, often leading to increased energy consumption. Research indicates that as much as 40% of energy in server facilities is dedicated to data centre cooling systems, leading to elevated operational costs and carbon emissions.
- Liquid Thermal Management: By circulating chilled liquid through pipes or directly to components, liquid thermal management provides superior thermal control, particularly in high-density server environments. This technique can by as much as one-third when applied directly to GPUs, making it an appealing option for modern computing facilities facing escalating heat loads. However, liquid temperature control systems typically incur higher capital expenses (CapEx) than air temperature management alternatives, which may deter some operators.
- Evaporative Cooling: Utilizing the natural process of evaporation, this method can significantly decrease energy consumption, rendering it an environmentally friendly choice. However, its effectiveness may be compromised in high pollen environments, which can introduce air pollutants into the data center. Evaporative systems can lower energy costs by utilizing outside air to refresh water, but their efficiency is contingent upon local climate conditions.
- In-Row Temperature Control: This strategy involves positioning temperature regulation units directly between server racks, enabling targeted air management that optimizes airflow and minimizes energy waste. By preventing the mixing of hot and cold air, in-row temperature management enhances overall efficiency.
Each temperature regulation technique, particularly data centre cooling systems, presents distinct advantages and challenges, with the optimal choice often hinging on the specific needs of the facility, including its size, density, and energy efficiency objectives. The recommended temperature range for data facilities is between 70 and 75°F (21 and 24°C), serving as a standard for evaluating temperature regulation techniques. As the demand for hyperscale facilities escalates, the industry is increasingly exploring hybrid solutions that integrate various temperature management technologies to achieve enhanced performance and sustainability. This hybrid approach not only boosts energy efficiency but also enhances operational flexibility.
Discuss Innovations and Trends in Data Center Cooling
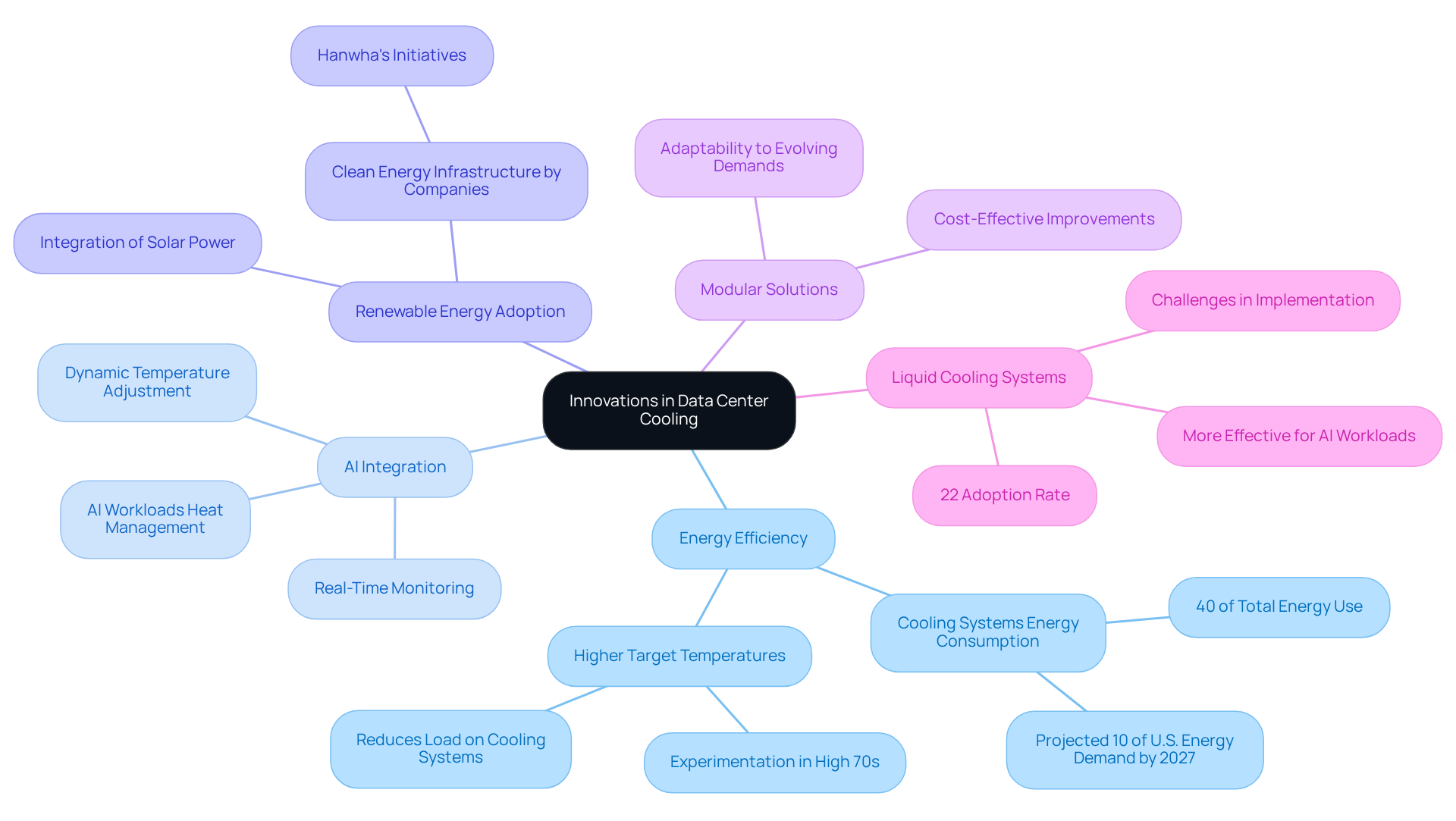
Recent advancements in data centre cooling systems for temperature regulation technologies are centered around enhancing energy efficiency and sustainability. The integration of AI and machine learning algorithms facilitates real-time monitoring and optimization of data centre cooling systems, dynamically adjusting temperatures in response to actual server loads. This approach not only improves the efficiency of temperature regulation in data centre cooling systems but also , since refrigeration systems currently account for approximately 40% of a facility’s total energy use.
Furthermore, it is projected that information facilities will consume up to 10% of the U.S. energy demand by 2027, making these innovations crucial for aligning operational efficiency with environmental responsibility. The increasing adoption of renewable energy sources, such as solar power, is becoming more common in powering these temperature control systems, which aligns with global sustainability objectives.
For instance, companies like Hanwha are exploring clean energy infrastructure to support environmentally conscious computing facilities. Another notable trend is the emergence of modular temperature control solutions, which can be readily adapted to meet the evolving demands of information hubs.
Additionally, the growing implementation of data centre cooling systems, including liquid cooling systems, is noteworthy, as these solutions are more effective in managing the heat produced by AI workloads. These innovations not only enhance performance but also play a significant role in reducing the overall carbon footprint of data centre cooling systems.
Conclusion
Data centre cooling systems are integral to the functionality and reliability of modern information facilities. These systems not only prevent overheating and hardware failures but also enhance energy efficiency, ensuring that critical equipment operates within optimal conditions. As the demand for data centers continues to escalate, understanding the significance of effective cooling solutions becomes increasingly essential for sustaining operations and supporting advanced computing applications.
The article delves into various types of cooling methods, highlighting the advantages and challenges associated with each. From traditional air cooling to innovative liquid thermal management and evaporative cooling, it is clear that the choice of cooling technique must align with the specific operational requirements of the facility. Insights into market trends, including the shift towards AI-driven optimization and the adoption of renewable energy sources, underscore the growing importance of sustainability in data centre cooling systems.
Ultimately, as data centres evolve to meet the demands of high-density computing and AI workloads, the advancement of cooling technologies will play a pivotal role in enhancing operational efficiency and reducing environmental impact. Embracing these innovations is not merely about maintaining performance; it is a crucial step towards ensuring the sustainability of digital infrastructure in the future. The imperative for robust and efficient data centre cooling systems cannot be overstated, as they are the backbone of reliable and responsible computing in an increasingly data-driven world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are data center cooling systems?
Data center cooling systems are specialized mechanisms designed to manage temperature and moisture levels within information facilities, ensuring that servers and other critical equipment operate effectively and reliably.
Why are data center cooling systems important?
They are vital for preventing overheating, which can lead to hardware failures and data loss.
What types of cooling techniques are used in data centers?
Cooling techniques vary significantly and include conventional air conditioning systems and advanced liquid refrigeration solutions, each tailored to meet specific demands of the information facility.
What is the projected market growth for data center temperature regulation?
The global server facility temperature regulation market is projected to reach approximately USD 11.08 billion by 2025 and expand to USD 24.19 billion by 2032, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.8%.
What is driving the growth of data center cooling systems?
The growth is driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient refrigeration options, especially as cooling systems evolve to support high-density computing and AI applications.
How can AI enhance data center cooling systems?
AI-driven temperature optimization can yield a 15-20% reduction in refrigeration costs, and it is anticipated that 75% of large corporations will implement AI-enhanced infrastructure management tools by 2025.
What challenges do data centers face regarding cooling during power outages?
Data centers face substantial challenges during power outages, which can lead to overheating and damage to sensitive equipment, highlighting the necessity for backup-power-compatible temperature control solutions.
What are some effective examples of data center cooling systems?
Effective examples include liquid temperature management systems, such as Colovore’s solution, which accommodates rack capacities of up to 50 kW, and immersion temperature regulation technology, which has shown significant improvements in efficiency.
What is the significance of advancements in data center cooling systems?
Advancements in these systems are crucial for maintaining optimal operating conditions and are vital for the future of efficiency and sustainability in data centers.

