Overview
This article addresses the critical need for enhancing data center cooling efficiency by leveraging established best practices and innovative technologies. It articulates the importance of key metrics such as Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) and provides a detailed comparison of air and liquid cooling methods. Furthermore, it underscores the necessity of continuous monitoring, optimization strategies, and the adoption of sustainable practices. Collectively, these elements play a significant role in reducing energy consumption and operational costs, presenting a compelling case for action in the industry.
Introduction
Data centers serve as the backbone of modern digital infrastructure, yet they are infamous for their substantial energy consumption and heat generation. As organizations pursue greater efficiency and sustainability, comprehending the complexities of data center cooling has never been more essential.
This article explores proven best practices that not only improve cooling efficiency but also significantly lower operational costs. However, with traditional methods approaching their limits, the question arises: can innovative technologies such as liquid cooling truly transform the way data centers manage heat?
Understand Data Center Cooling Fundamentals and Energy Efficiency
Data centers generate significant heat due to the high density of servers and networking equipment. Understanding the fundamentals of cooling systems is essential for improving data center cooling efficiency, maintaining optimal temperatures, and ensuring equipment reliability. Key concepts include:
-
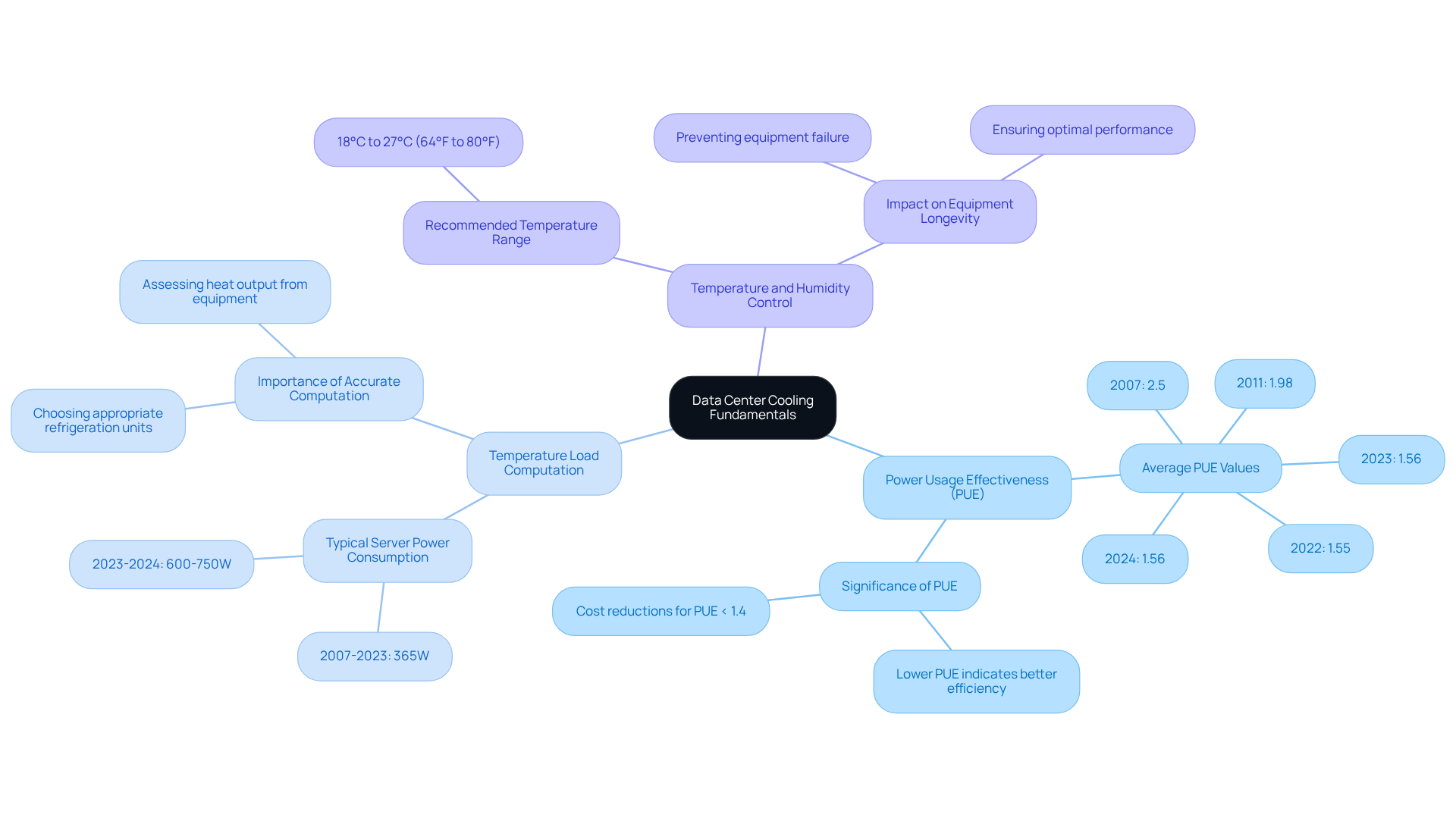
Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE): A critical metric that measures the energy efficiency of a data center. A lower PUE indicates better power efficiency, as it reflects the ratio of total building consumption to the consumption used by IT equipment. The average annual PUE across major data centers was reported at 1.56 in 2024, showing a significant improvement from 2.5 in 2007 and 1.58 in 2023, highlighting ongoing advancements in energy management.
-
Temperature Load Computation: Precisely determining the temperature load is essential for choosing the appropriate refrigeration unit. This involves assessing the heat output from servers, storage, and networking equipment. The typical dual socket server is currently consuming between 600-750W in 2023-2024, a significant rise from the former average of 365W from 2007-2023, highlighting the changing requirements on temperature regulation systems.
-
Temperature and Humidity Control: Maintaining appropriate temperature and humidity levels is crucial for preventing equipment failure and ensuring longevity. The recommended temperature range is typically between 18°C to 27°C (64°F to 80°F).
Gagner-Toomey Associates stands out as a prominent provider of innovative temperature control solutions, offering a broad product line of DC input tube axial fans and centrifugal blowers, optimized for performance and efficiency. By understanding these fundamentals, center managers can make informed choices regarding their strategies to improve data center cooling efficiency, resulting in enhanced efficiency and decreased operational expenses. For example, case studies have demonstrated that information centers attaining a PUE of 1.4 or less experience significant cost reductions over time, with enhancements in PUE from 1.6 in 2014 to 1.4 in 2023. Furthermore, shifting to renewable energy sources is becoming progressively significant in server facility operations, aligning with sustainability trends in the industry.
Explore Innovative Cooling Technologies: Liquid vs. Air Cooling
In the realm of data center cooling efficiency, two primary technologies stand at the forefront: air circulation and liquid methods, each offering distinct advantages and challenges.
-
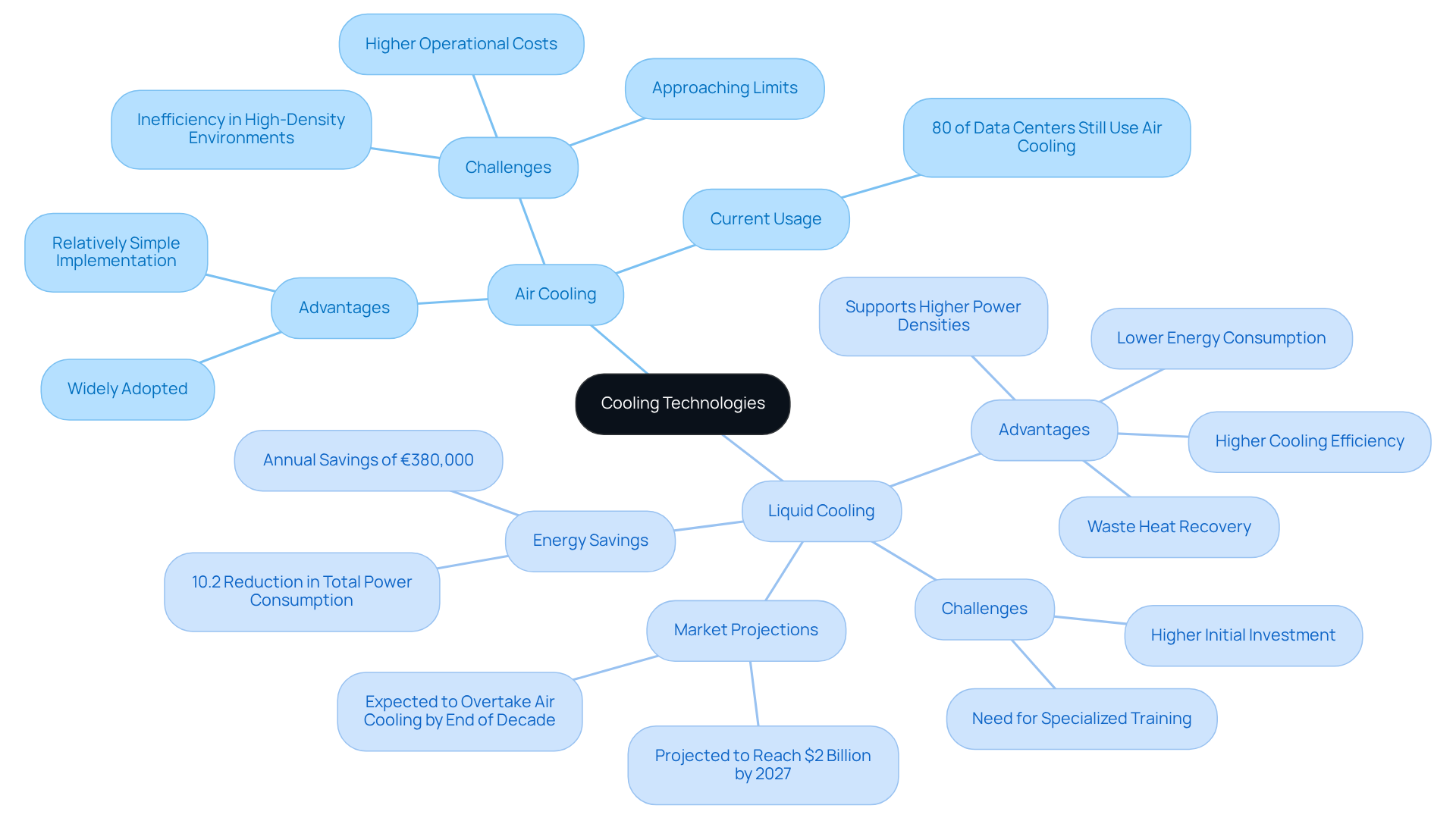
Air Cooling: This traditional method relies on fans to circulate air across servers and equipment. While it is widely adopted and relatively straightforward to implement, air circulation can be inefficient in high-density environments, impacting data center cooling efficiency. It frequently requires more effort to maintain optimal temperatures, leading to increased operational expenses. Approximately 80% of data centers still employ air temperature regulation; however, this method is approaching its limits and affecting data center cooling efficiency due to rising demands from contemporary computing workloads.
-
Liquid Cooling: This cutting-edge technology circulates a coolant, typically water, directly to heat-generating components. Liquid temperature regulation excels in data center cooling efficiency by effectively removing heat while consuming less energy. It is particularly advantageous for high-performance computing environments, where heat generation is substantial. Liquid thermal management systems can support power densities exceeding 100 kW per rack and over 40 kW per cabinet, significantly higher than the 50 kW maximum of air-based systems. Furthermore, they can minimize the physical footprint of temperature management infrastructure, enabling denser server configurations and enhanced space utilization.
Recent studies suggest that improving data center cooling efficiency through liquid temperature regulation can result in a 10.2% decrease in overall information center power usage and reduce operational costs by around €380,000 each year. Furthermore, liquid temperature control can enhance data center cooling efficiency by decreasing server energy usage by 4-15%, highlighting its efficiency advantages. The implementation of liquid temperature regulation is expected to increase, with projections indicating that almost 50% of information centers may integrate this technology in the upcoming years. Significantly, liquid temperature regulation systems also enable waste heat recovery, which can be repurposed for facility heating, further enhancing sustainability and reducing operational costs. As organizations aim for sustainability and data center cooling efficiency, liquid refrigeration is becoming the preferred method for managing heat in modern server facilities. The liquid temperature regulation market is anticipated to achieve $2 billion by 2027, underscoring its growing importance and acceptance in the sector.
Implement Monitoring and Optimization Strategies for Cooling Systems
To enhance data center cooling efficiency, information centers must adopt robust monitoring and optimization approaches. Key practices include:
-
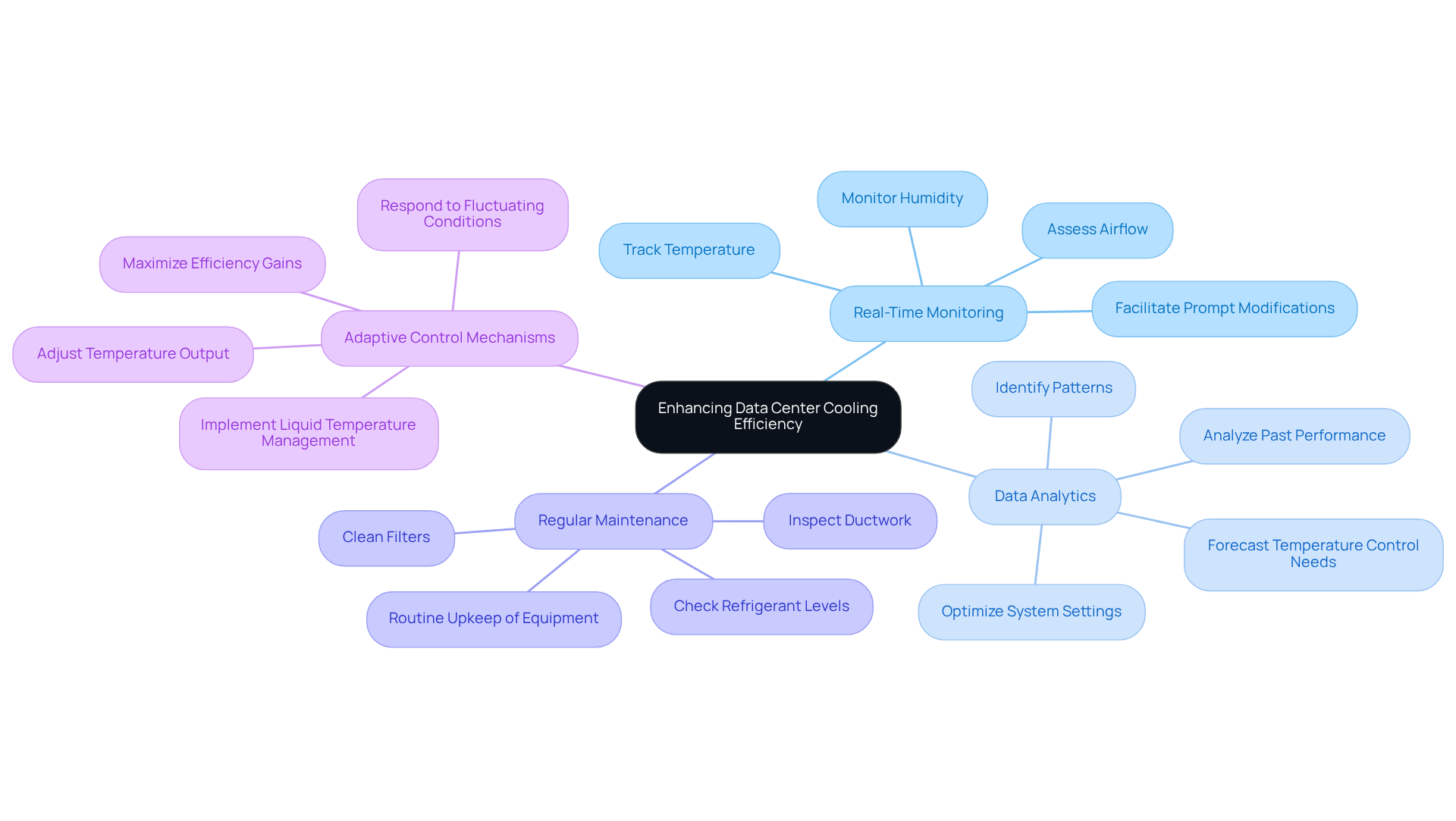
Real-Time Monitoring: Advanced monitoring systems are essential for tracking temperature, humidity, and airflow in real-time. This information facilitates prompt modifications to temperature control systems, preventing overheating and ensuring optimal performance. Efficient oversight can significantly reduce energy usage, as data center cooling efficiency typically accounts for up to 40% of a facility’s overall energy expenditure, underscoring its importance as a primary operational cost.
-
Data Analytics: Employing data analytics tools enables operators to analyze past performance and identify patterns. This information aids in forecasting temperature control requirements and optimizing system settings accordingly. For instance, studies have demonstrated that implementing machine learning algorithms can enhance predictive maintenance and energy optimization, leading to substantial efficiency gains.
-
Regular Maintenance: Routine upkeep of temperature control equipment, including cleaning filters, checking refrigerant levels, and inspecting ductwork, is vital. Regular maintenance ensures that operations run efficiently and mitigates the risk of unforeseen failures, which can lead to costly downtime and repairs.
-
Adaptive Control Mechanisms: Implementing adaptive control mechanisms that adjust temperature output based on real-time information can optimize energy use. These systems respond adaptively to fluctuating conditions within the data center, improving overall temperature management. For example, the comprehensive execution of liquid temperature management in a recent study resulted in an 18.1% reduction in facility power, illustrating the effectiveness of adaptive strategies. Fred Rebarber, President of NSW PEP, emphasizes that maximizing liquid temperature control implementation delivers the highest efficiency.
By adopting these strategies, center operators can enhance data center cooling efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and extend the lifespan of their systems, ultimately supporting sustainability objectives and lowering operational expenses. Furthermore, inadequate temperature regulation can lead to overheating, hardware failure, and potential data loss, highlighting the critical need for effective temperature management.
Adopt Sustainable Practices for Enhanced Cooling Efficiency
Sustainability in data center cooling efficiency is not merely a trend; it is essential for reducing environmental impact and operational expenses. To address this critical issue, consider implementing the following sustainable practices:
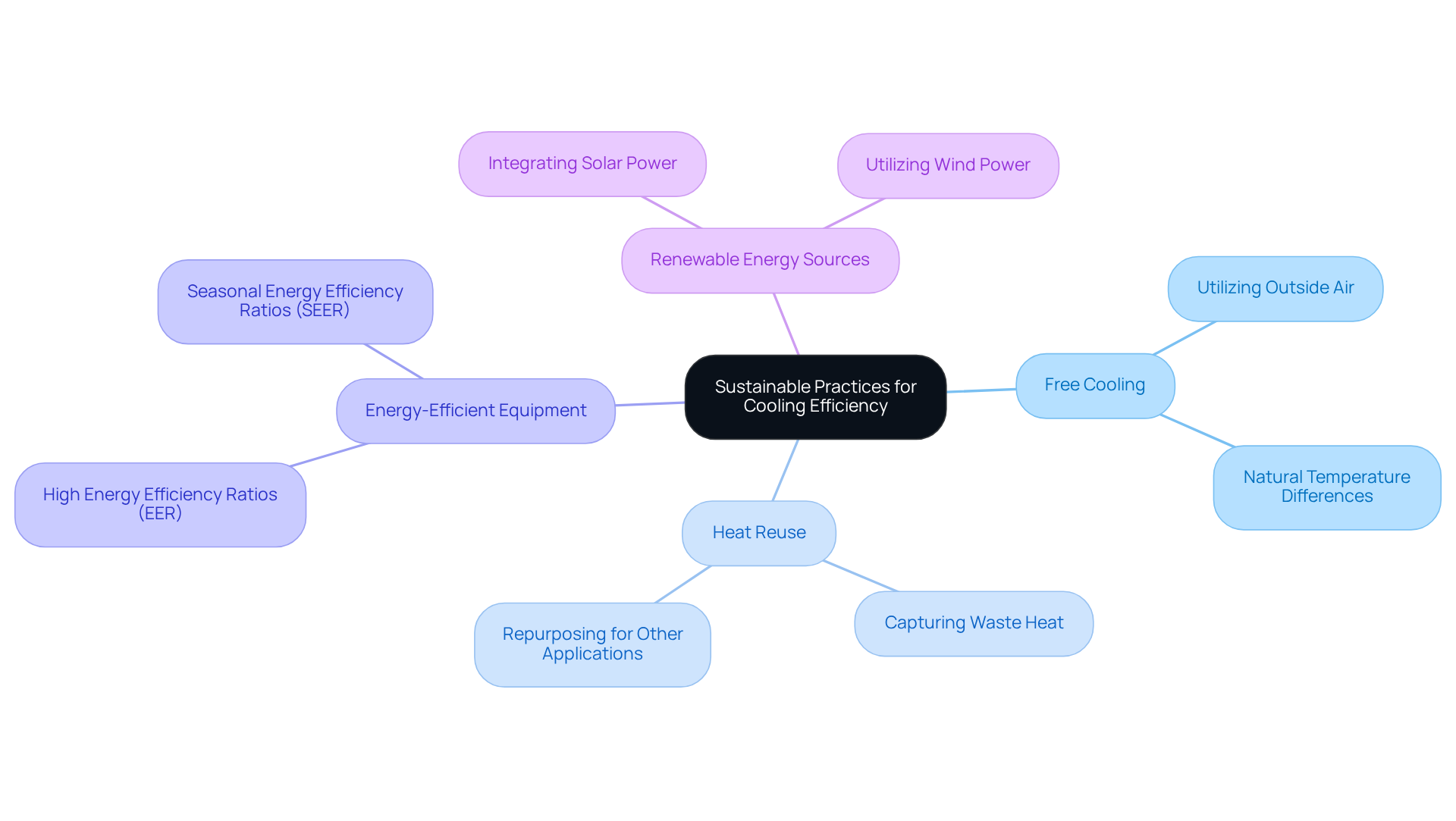
- Free Cooling: Utilize outside air for cooling when conditions permit. This strategy can significantly decrease energy usage by harnessing natural temperature differences.
- Heat Reuse: Establish mechanisms that capture waste heat from refrigeration processes and repurpose it for other applications, such as warming office spaces or water.
- Energy-Efficient Equipment: Invest in energy-efficient climate control devices and components that meet or exceed industry standards. Look for equipment with high Energy Efficiency Ratios (EER) and Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratios (SEER).
- Renewable Energy Sources: Consider integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, to offset the energy consumption of air conditioning systems.
By adopting these sustainable practices, data centers can improve their data center cooling efficiency while contributing to a greener future.
Conclusion
Enhancing data center cooling efficiency is crucial for maintaining optimal performance while minimizing energy consumption and operational costs. Understanding the foundational concepts of cooling systems—such as Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) and the significance of temperature and humidity control—enables data center managers to implement strategies that lead to substantial improvements in efficiency. The shift towards innovative cooling technologies, particularly liquid cooling, demonstrates a clear advantage in effectively managing heat generation, especially in high-density environments.
Several key strategies for boosting cooling efficiency include:
- The adoption of real-time monitoring systems
- Data analytics for predictive maintenance
- Regular upkeep of cooling equipment
These practices not only enhance operational efficiency but also contribute to sustainability efforts by reducing energy expenditure and extending the lifespan of critical systems. Furthermore, integrating sustainable practices such as free cooling and heat reuse can significantly lower environmental impact while ensuring that data centers meet the rising demands of modern computing.
The importance of effective cooling in data centers cannot be overstated, as it directly influences both performance and sustainability. By embracing best practices and innovative technologies, data center operators can achieve remarkable gains in cooling efficiency, ultimately leading to cost savings and a reduced carbon footprint. The transition towards smarter, more efficient cooling solutions is not merely a necessity; it is a strategic imperative for the future of data center operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of cooling systems in data centers?
Cooling systems are essential in data centers to manage the significant heat generated by high-density servers and networking equipment, improving cooling efficiency, maintaining optimal temperatures, and ensuring equipment reliability.
What does Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) measure?
PUE measures the energy efficiency of a data center, indicating the ratio of total building energy consumption to the energy consumed by IT equipment. A lower PUE signifies better power efficiency.
What was the average annual PUE across major data centers reported in 2024?
The average annual PUE reported in 2024 was 1.56, showing improvement from 2.5 in 2007 and 1.58 in 2023.
How has the power consumption of typical dual socket servers changed from 2007 to 2024?
The power consumption of typical dual socket servers has increased from an average of 365W from 2007-2023 to between 600-750W in 2023-2024.
What is the recommended temperature range for data centers?
The recommended temperature range for data centers is typically between 18°C to 27°C (64°F to 80°F).
Who is Gagner-Toomey Associates and what do they offer?
Gagner-Toomey Associates is a prominent provider of innovative temperature control solutions, offering a product line of DC input tube axial fans and centrifugal blowers optimized for performance and efficiency.
How can improving cooling efficiency impact operational expenses?
Improving cooling efficiency can result in decreased operational expenses, as demonstrated by case studies where data centers achieving a PUE of 1.4 or less experienced significant cost reductions over time.
What sustainability trend is becoming significant in server facility operations?
Shifting to renewable energy sources is becoming increasingly significant in server facility operations, aligning with sustainability trends in the industry.

