Overview
This article provides essential insights into standard computer fan sizes, underscoring their significance for engineers tasked with selecting optimal cooling solutions for electronic systems. It is crucial to recognize that larger fans, such as 120mm and 200mm, deliver superior airflow and operate more quietly, making them the preferred choice for effective thermal management. In contrast, smaller fans often necessitate higher RPMs, resulting in increased noise, which can significantly influence design decisions. Understanding these dynamics is vital for engineers aiming to achieve both performance and efficiency in their systems.
Introduction
The efficiency of electronic systems often hinges on a crucial yet understated component: the computer fan. For engineers focused on optimizing thermal management and enhancing overall performance, understanding standard computer fan sizes is essential.
With an array of sizes available—from compact 40mm units to robust 200mm models—each fan size presents its own unique benefits and challenges.
How can engineers effectively navigate this intricate landscape to select the ideal fan that harmonizes airflow, noise, and spatial constraints?
Explore the Basics of Computer Fan Sizes
Computer coolers are essential components in electronic systems, primarily tasked with managing heat effectively. Gagner-Toomey Associates, the largest global producer of standard and custom air-movers, offers a diverse range of temperature regulation solutions that prioritize performance, efficiency, and minimal noise. Their extensive product line includes DC input Tube Axial devices and Centrifugal Blowers.
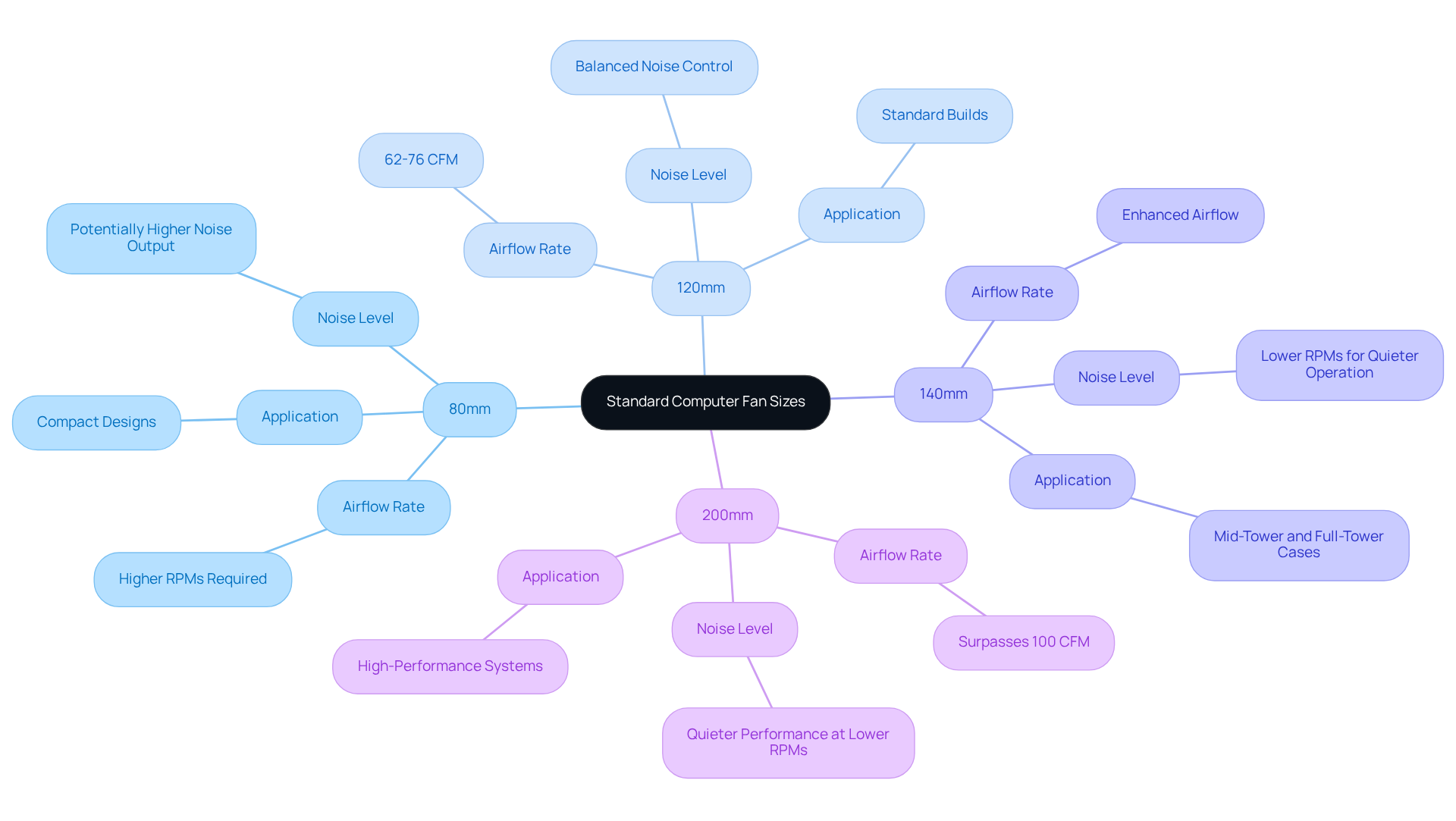
The dimensions of these coolers, typically measured in millimeters (mm), are crucial in determining both ventilation and noise levels, particularly in relation to standard computer fan sizes. Larger units, such as those in the standard computer fan sizes of 120mm and 140mm, are often favored for their ability to circulate greater volumes of air at lower RPMs, resulting in quieter operation and enhanced cooling efficiency.
For instance, standard computer fan sizes such as 120mm units are commonly selected for standard configurations due to their optimal balance of ventilation and noise management, while 200mm units are preferred in high-performance environments where maximum ventilation is critical. Conversely, smaller fans that fall under standard computer fan sizes, including 80mm and 92mm models, may require higher RPMs to achieve comparable performance levels, potentially leading to increased noise output.
An engineer noted, ‘In compact designs, every degree counts; 80mm units provide the necessary ventilation while fitting seamlessly into confined spaces.’ This underscores the importance for engineers to meticulously evaluate standard computer fan sizes in their designs to ensure effective thermal management and system reliability.
Average airflow rates differ by size, with standard computer fan sizes such as 120mm generally achieving airflow rates of approximately 62-76 CFM, while 200mm fans can surpass 100 CFM, illustrating the direct relationship between size and performance. Furthermore, the inclusion of IP protection in most models bolsters the reliability of these cooling solutions.
Ultimately, selecting the appropriate standard computer fan sizes is essential for efficient temperature control in electronic devices, influencing both operational efficiency and user experience.
Identify Standard Computer Fan Sizes and Their Applications
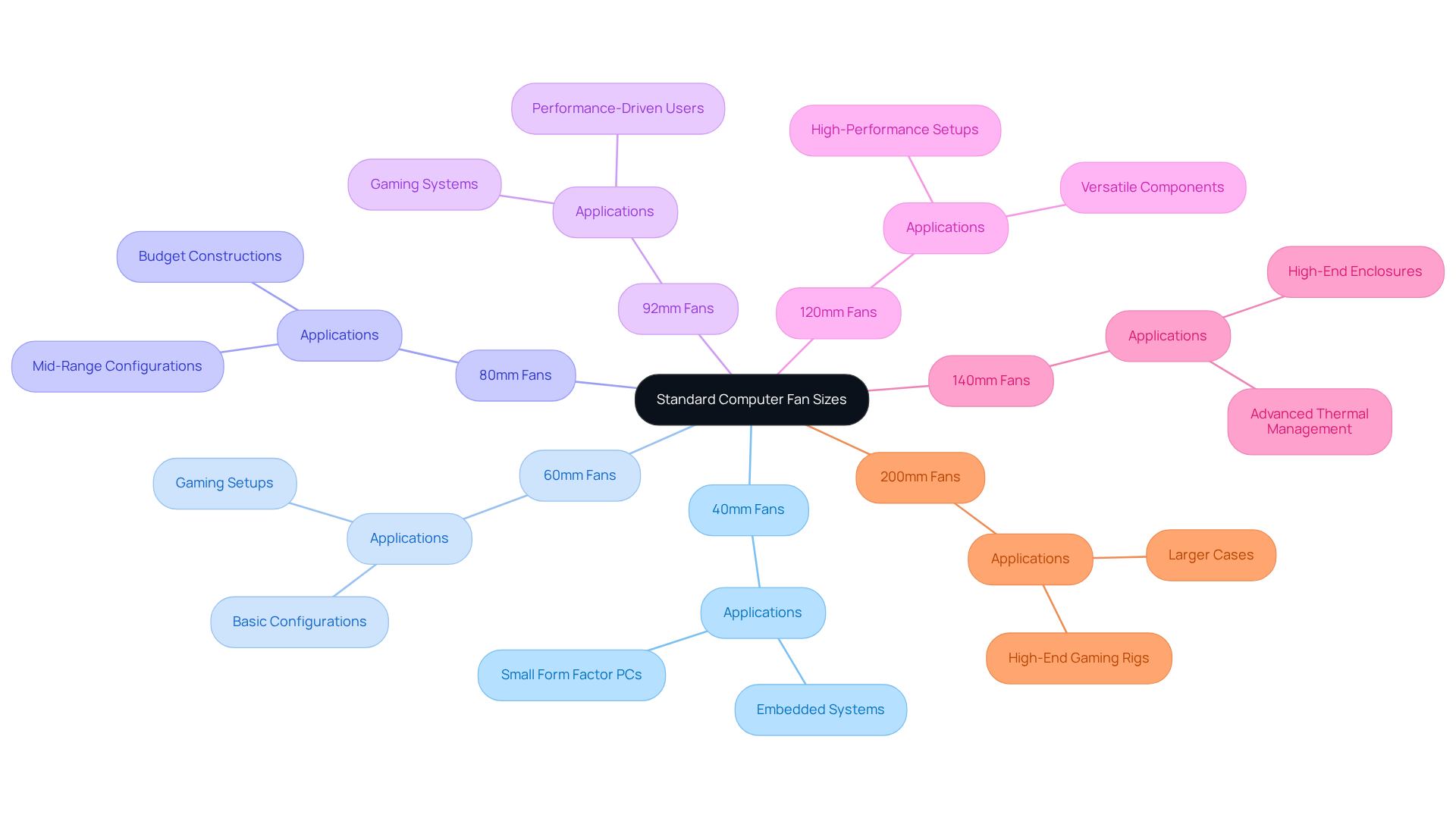
Standard computer fan sizes encompass 40mm, 60mm, 80mm, 92mm, 120mm, 140mm, and 200mm, each meticulously designed for specific applications within the electronics industry:
- 40mm Fans: These ultra-compact fans are optimal for space-constrained devices, such as small form factor PCs and embedded systems, where maximizing available space is essential.
- 60mm Units: Commonly found in basic configurations and certain gaming setups, 60mm units strike a balance between dimensions and ventilation, making them suitable for moderate temperature management.
- 80mm Units: Frequently employed in mid-range configurations, these units provide efficient airflow while maintaining moderate noise levels, rendering them a preferred choice for budget constructions. The demand for 80mm blowers has surged due to the necessity for effective temperature regulation in compact environments.
- 92mm Units: Known for their efficiency, 92mm units are often utilized in gaming systems where effective temperature management is critical without generating excessive noise, catering to performance-driven users.
- 120mm Units: The standard dimension for numerous high-performance setups, 120mm units are celebrated for their exceptional ventilation and quiet operation, allowing adaptability across various components.
- 140mm Units: Preferred in high-end enclosures and advanced thermal management systems, 140mm units deliver excellent ventilation at reduced RPMs, resulting in quieter performance—ideal for high-performance setups requiring efficient temperature control.
- 200mm Fans: Designed for larger cases, 200mm fans offer impressive airflow at lower RPMs, making them suitable for high-end gaming rigs and workstations.
Understanding the standard computer fan sizes and their associated applications is vital for engineers to select the appropriate temperature control solutions, thereby ensuring optimal performance and efficiency in their projects. Furthermore, the global refrigeration fan market size is anticipated to increase from USD 15.50 billion in 2024 to USD 22.83 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of approximately 3.95%. This growth underscores the rising demand for efficient temperature control solutions within the electronics sector. Engineers must also consider factors such as static pressure and the trend towards hybrid cooling solutions that integrate liquid cooling with traditional fan designs to refine their cooling strategies.
Measure and Select the Right Fan Size for Your System
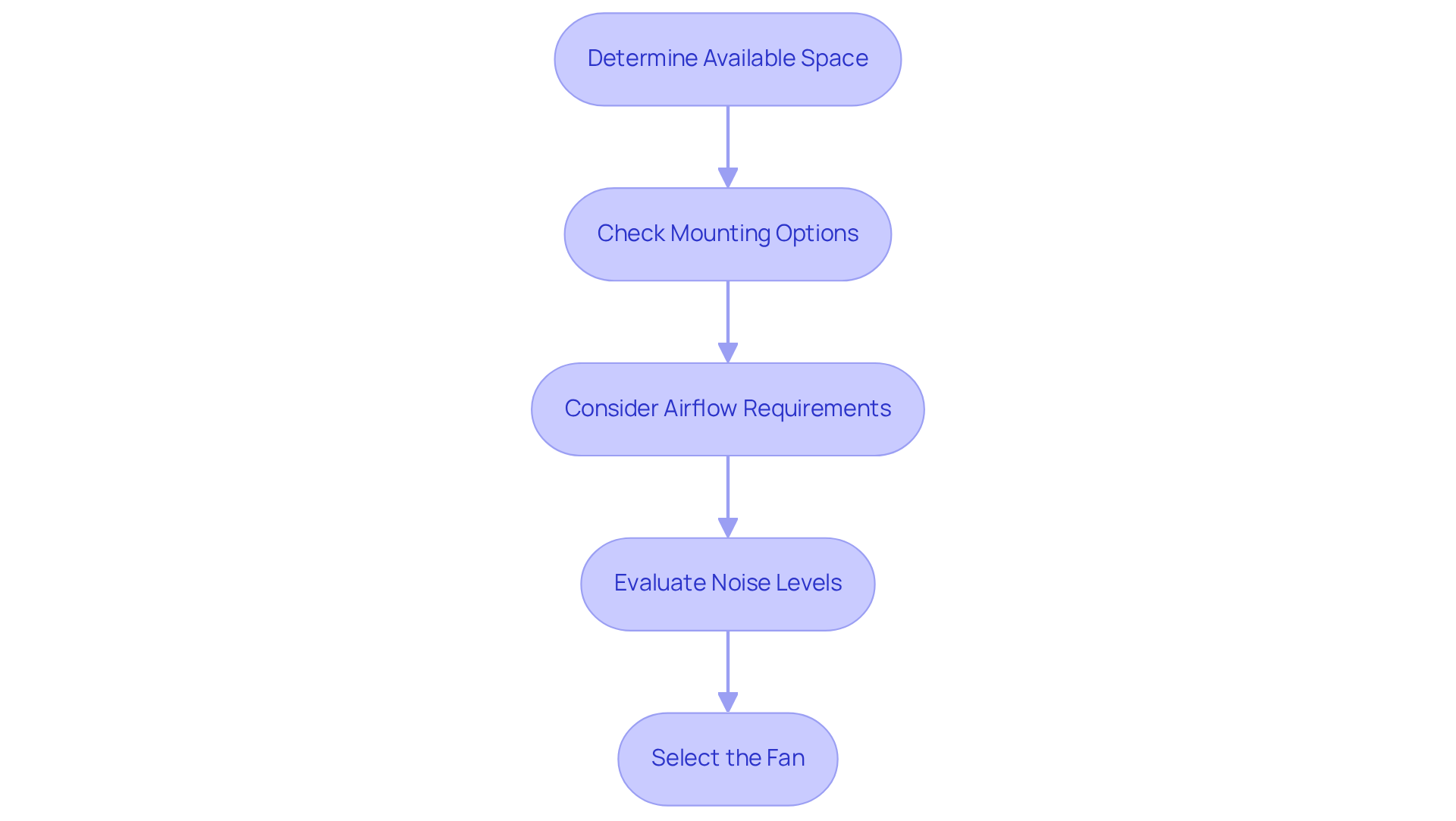
To effectively measure and select the appropriate fan size for your system, follow these essential steps:
- Determine Available Space: Begin by accurately measuring the installation area, taking into account any potential obstructions that may impact ventilation.
- Check Mounting Options: Identify the mounting holes and their spacing to ensure compatibility with standard computer fan sizes.
- Consider Airflow Requirements: Evaluate the cooling needs of your system. Typically, larger units provide enhanced ventilation while operating at reduced noise levels, making them ideal for high-performance applications. For instance, increasing the fan speed from 3,283 RPM to 3,550 RPM results in a rise in airflow from 8,000 CFM to 8,650 CFM, which is an increase of 8.13%.
- Evaluate Noise Levels: If noise is a critical factor, review fan specifications, including RPM and decibel ratings. For example, a standard 120mm fan typically operates at noise levels ranging from 20 to 30 decibels, while larger fans can achieve similar airflow with reduced noise.
- Select the fan: Based on your measurements and requirements, choose a fan size from the standard computer fan sizes that meets your setup’s cooling demands while ensuring optimal performance.
By adhering to these guidelines, engineers can successfully select the right fan size, significantly enhancing the reliability and efficiency of their electronic systems. As highlighted by industry experts, prioritizing airflow and noise considerations is crucial for effective thermal management in electronics design. Additionally, understanding static pressure is vital in scenarios with limited ventilation, such as tightly clustered electronic enclosures.
Conclusion
Selecting the correct fan size is pivotal for engineers aiming to optimize thermal management in electronic systems. Standard computer fan sizes, ranging from 40mm to 200mm, are critical in ensuring effective ventilation and noise control. By understanding the implications of these sizes, engineers can enhance system performance and reliability while addressing the specific cooling needs of their designs.
Larger fans generally provide superior airflow at lower RPMs, resulting in quieter operation and improved cooling efficiency. Conversely, smaller fans, while fitting into tighter spaces, may necessitate higher speeds that can lead to increased noise levels. Evaluating airflow rates, noise levels, and mounting options is essential for making informed decisions when selecting the appropriate fan size for various applications.
The significance of understanding standard computer fan sizes extends beyond mere specifications; it underscores the necessity for engineers to prioritize effective cooling solutions in their projects. As the demand for efficient temperature regulation continues to rise, embracing these insights will not only enhance system performance but also contribute to the overall user experience. Engineers are encouraged to leverage this knowledge to refine their cooling strategies and ensure optimal performance across diverse electronic applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary function of computer coolers?
Computer coolers are essential components in electronic systems, primarily tasked with managing heat effectively.
Who is Gagner-Toomey Associates?
Gagner-Toomey Associates is the largest global producer of standard and custom air-movers, offering a diverse range of temperature regulation solutions that prioritize performance, efficiency, and minimal noise.
How are computer fan sizes measured?
The dimensions of computer fans are typically measured in millimeters (mm).
What are the advantages of larger computer fan sizes like 120mm and 140mm?
Larger fans, such as 120mm and 140mm units, can circulate greater volumes of air at lower RPMs, resulting in quieter operation and enhanced cooling efficiency.
What standard computer fan size is commonly selected for standard configurations?
The 120mm fan size is commonly selected for standard configurations due to its optimal balance of ventilation and noise management.
When are 200mm fans preferred?
200mm fans are preferred in high-performance environments where maximum ventilation is critical.
What challenges do smaller fans like 80mm and 92mm face?
Smaller fans may require higher RPMs to achieve comparable performance levels to larger fans, which can lead to increased noise output.
What is the significance of airflow rates in computer fan sizes?
Average airflow rates differ by size; for example, 120mm fans generally achieve airflow rates of approximately 62-76 CFM, while 200mm fans can surpass 100 CFM, illustrating the direct relationship between size and performance.
How does IP protection enhance computer cooling solutions?
The inclusion of IP protection in most models bolsters the reliability of these cooling solutions.
Why is selecting the appropriate fan size important?
Selecting the appropriate standard computer fan size is essential for efficient temperature control in electronic devices, influencing both operational efficiency and user experience.

