Overview
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the step-by-step process involved in designing centrifugal fans, as well as troubleshooting common issues that may arise. It delineates essential design principles, explores various fan types, discusses material selection, and outlines effective testing methods. Furthermore, it addresses prevalent problems such as reduced airflow and excessive noise, underscoring the critical importance of regular maintenance and proper installation to achieve optimal performance.
Introduction
Centrifugal fans are integral to a multitude of industrial applications, as they convert rotational energy into effective airflow. For engineers, grasping the nuances of their design is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring reliability. Yet, the challenge arises in navigating the intricacies of various fan types, selecting appropriate materials, and troubleshooting common operational issues. To master the design process and effectively address these challenges, engineers must adopt a systematic approach that encompasses:
- Understanding
- Analysis
- Practical solutions
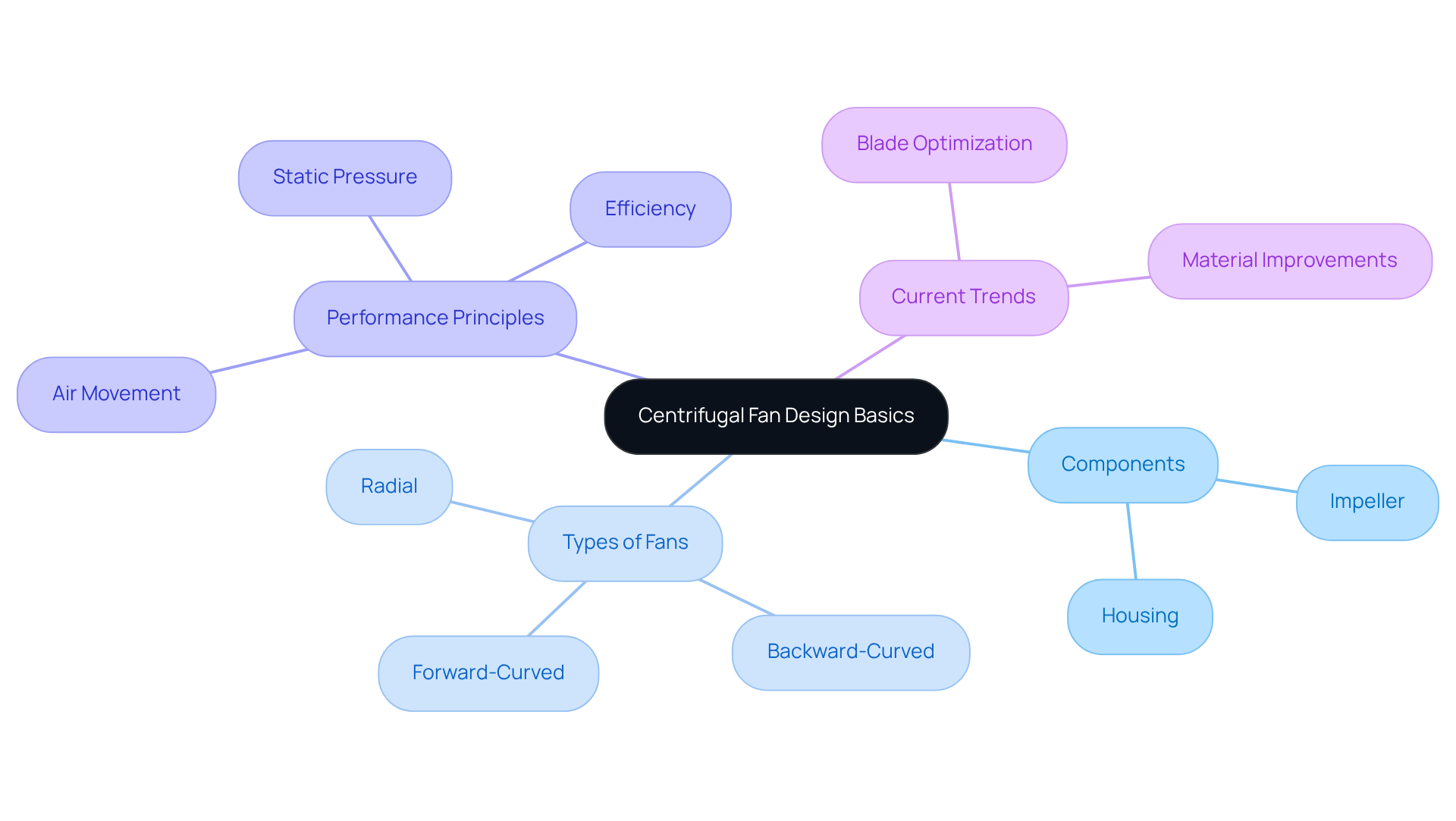
Understand the Basics of Centrifugal Fan Design
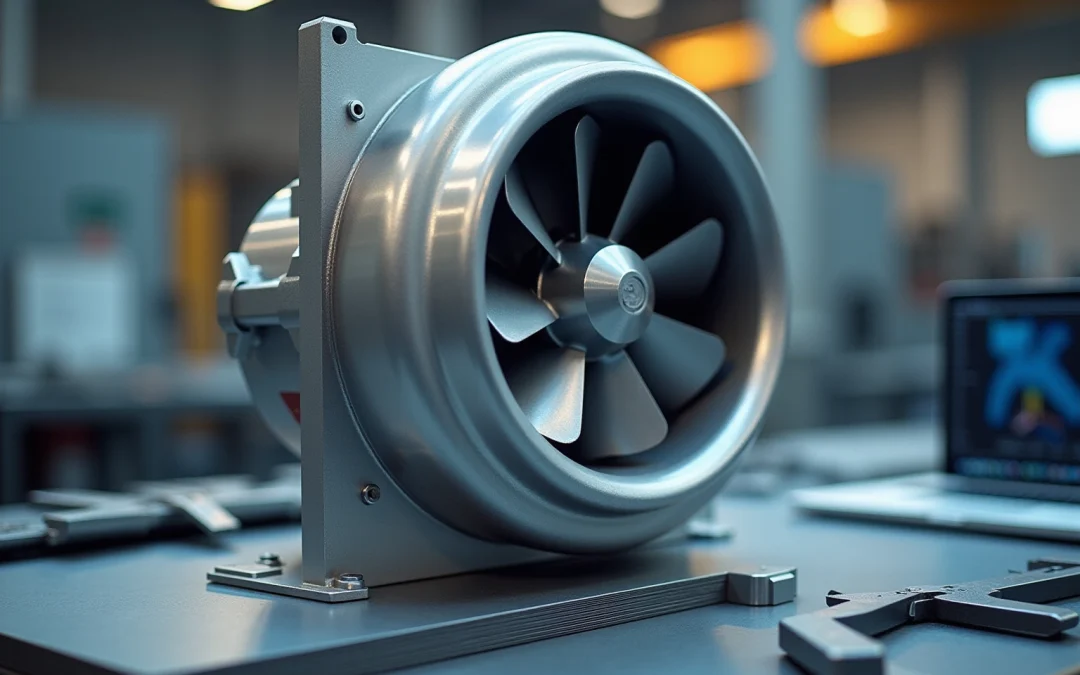
Centrifugal blowers function by converting rotational energy from a motor into kinetic energy, effectively channeling air through the system. The primary components include the impeller, which draws air in and expels it at a 90-degree angle, and the housing that directs air movement. A solid grasp of principles such as static pressure, air movement, and effectiveness is crucial for designing devices that meet specific performance standards, including air volume and pressure requirements. For instance, centrifugal blowers can achieve up to 84% static efficiency, making them indispensable in industrial applications where consistent airflow is essential.
Understanding the various types of centrifugal fans—forward-curved, backward-curved, and radial—is vital for selecting the appropriate configuration for your application. Forward-curved fans are recognized for their quiet operation and are frequently employed in HVAC systems, while backward-curved fans excel in high-pressure applications, effectively minimizing turbulence and friction losses. Current trends in centrifugal fan design are centered around optimizing blade shapes and materials to enhance performance and energy savings, with design modifications that can improve efficiency by as much as 20%. Gagner-Toomey Associates provides a comprehensive product line of DC input centrifugal blowers, ranging in size from 15 to 225mm, tailored for performance, efficiency, and low noise, with IP protection available upon request.
Case studies underscore the efficacy of centrifugal blowers across diverse environments. For example, backward inclined blowers are utilized in industrial exhaust systems to maintain air quality and comply with environmental regulations. Moreover, the integration of has resulted in significant improvements in the durability and reliability of these devices, ensuring they meet the stringent demands of various industrial settings. By mastering these principles and trends, engineers can develop a centrifugal fan design that not only fulfills but surpasses operational expectations.
Follow the Step-by-Step Design Process
- Define Requirements: Establish the airflow and pressure requirements specific to your application as the foundational step that informs all subsequent design decisions. Gagner-Toomey Associates offers a comprehensive range of DC input Tube Axial units and blowers designed with centrifugal fan design principles, optimized for performance, effectiveness, and low noise, to assist in this evaluation. Most models come with IP protection available upon request.
- Select Fan Type: Choose the appropriate fan type—forward-curved, backward-curved, or radial—based on your operational needs. Each type of centrifugal fan design presents unique performance characteristics, including efficiency and noise levels, which are essential for meeting application demands. Gagner-Toomey Associates provides a diverse selection of ventilators, including compact options for limited spaces, ensuring you find the suitable choice for your application.
- Calculate Dimensions: Utilize fan laws to determine the necessary dimensions for the impeller and housing, including the calculation of diameter and blade angle, which significantly influence airflow and pressure performance. With sizes ranging from 15 to 280mm for Tube Axial fans and 15 to 225mm for centrifugal fan design, Gagner-Toomey Associates can meet a wide array of specification requirements.
- Material Selection: Choose materials capable of withstanding operational stresses and environmental conditions. Steel is commonly favored for its strength, while stainless steel provides superior corrosion resistance. is influenced by the selected material, which directly impacts the fan’s durability and efficiency, ensuring long-lasting performance in demanding environments.
- Prototype Development: Employ CAD software to create a prototype of your concept, enabling visualization and enhancement of the fan before physical production. This ensures adherence to specifications. Gagner-Toomey Associates supports engineers during this phase by offering personalized customization options tailored to specific requirements for centrifugal fan design.
- Testing and Validation: Conduct comprehensive testing to measure airflow, pressure, and efficiency. Analyze the results and implement necessary modifications to the centrifugal fan design to enhance its performance, ensuring that the fan operates efficiently within its intended application. With Gagner-Toomey Associates’ advanced cooling solutions, you can trust that your designs will adhere to industry standards.
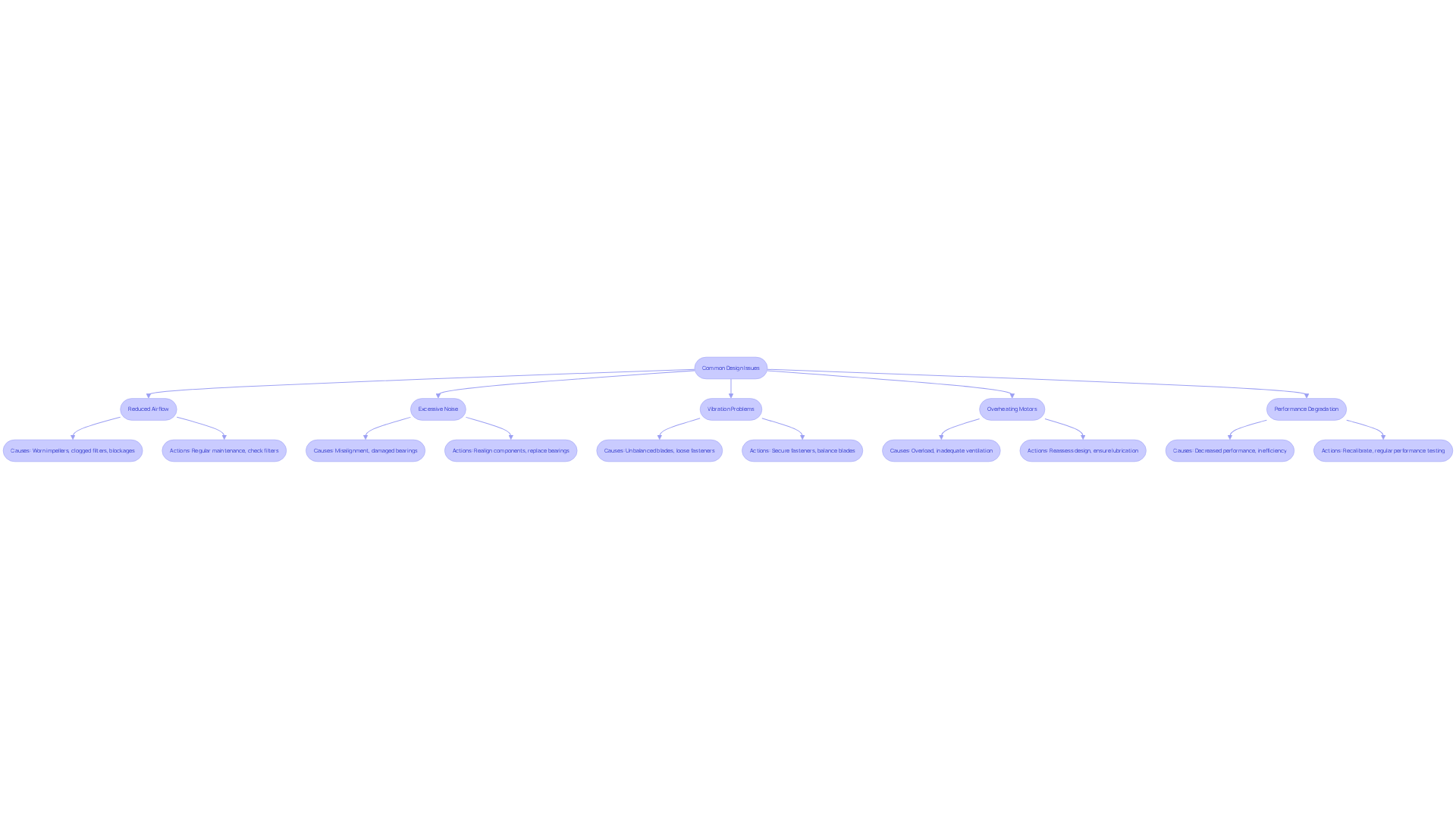
Troubleshoot Common Design Issues
- Reduced Airflow: Begin by checking for obstructions in both the inlet and outlet. Ensure that the impeller is clean and free from debris, as these factors can significantly obstruct the movement of air. Common causes of reduced air movement include worn-out impellers, clogged air filters, or blockages in the air ducts. According to industry insights, insufficient ventilation can often be traced back to these issues, emphasizing the need for regular maintenance.
- Excessive Noise: Investigate potential sources of noise, which may stem from misalignment, damaged bearings, or contact between the impeller and housing. Loose components or worn-out bearings can also contribute to excessive noise levels. Addressing these issues promptly is crucial, as noise often indicates underlying mechanical problems that require attention. As noted by Zhehong Li, proper installation and compliance with guidelines are essential for enhancing fan operation.
- Vibration Problems: Excessive vibration can arise from unbalanced blades, loose fasteners, or misalignment during maintenance. Regular inspections and maintenance are essential to prevent these issues. For instance, securing loose fasteners can effectively mitigate vibration problems, ensuring smoother operation. Additionally, material build-up on the fan wheel is a common cause of vibration, necessitating regular cleaning and maintenance to prevent issues.
- Overheating Motors: If the motor runs at elevated temperatures, it may indicate that the fan is overloaded or that ventilation is inadequate. Reassessing the design parameters of the centrifugal fan design and ensuring proper sizing can help alleviate this issue. Regular maintenance checks can also prevent overheating by ensuring adequate lubrication and airflow around the motor. It’s crucial to evaluate the effect of Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) on fan performance, as they can change speed, torque, and horsepower, influencing overall effectiveness.
- Performance Degradation: Continuously monitor the fan’s performance. If performance decreases, consider recalibrating or redesigning components to restore optimal function. Regular maintenance and performance testing are vital for ensuring reliability and efficiency, ultimately enhancing energy consumption and operational effectiveness across various applications. Case studies have shown that routine checks can significantly reduce the likelihood of faults and malfunctions, reinforcing the importance of proactive maintenance.
Conclusion
Centrifugal fan design represents a multifaceted challenge that demands a comprehensive grasp of airflow dynamics and operational prerequisites. By mastering foundational principles and adopting a systematic approach, engineers can devise efficient and reliable fans tailored to specific applications. The selection of the appropriate fan type, materials, and dimensions is critical; each decision profoundly influences overall performance and effectiveness.
Key insights underscored throughout this article stress the importance of:
- Defining requirements
- Choosing suitable configurations
- Conducting thorough testing to guarantee optimal functionality
It is imperative to address prevalent design challenges, such as:
- Diminished airflow
- Excessive noise
- Overheating motors
Through proactive maintenance and troubleshooting strategies to sustain performance. Furthermore, the integration of advanced materials and innovative design modifications significantly boosts the efficiency and durability of centrifugal fans.
Ultimately, the pursuit of mastering centrifugal fan design transcends mere technical proficiency; it encompasses the adoption of best practices and a commitment to continuous improvement. Engineers are urged to remain vigilant in their methodologies, leveraging the insights and strategies discussed to inspire innovation and attain excellence in their designs. By prioritizing comprehensive analysis and proactive maintenance, the potential for enhanced performance and energy efficiency in centrifugal fans can be fully realized.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do centrifugal blowers function?
Centrifugal blowers convert rotational energy from a motor into kinetic energy, channeling air through the system. The impeller draws air in and expels it at a 90-degree angle, while the housing directs air movement.
What are the main components of a centrifugal fan?
The primary components of a centrifugal fan include the impeller, which moves the air, and the housing that directs the airflow.
Why is understanding static pressure important in centrifugal fan design?
A solid grasp of static pressure, air movement, and effectiveness is crucial for designing devices that meet specific performance standards, including air volume and pressure requirements.
What is the static efficiency of centrifugal blowers?
Centrifugal blowers can achieve up to 84% static efficiency, making them essential in industrial applications where consistent airflow is necessary.
What are the different types of centrifugal fans?
The main types of centrifugal fans are forward-curved, backward-curved, and radial fans, each suited for different applications.
What are the characteristics of forward-curved fans?
Forward-curved fans are known for their quiet operation and are commonly used in HVAC systems.
What advantages do backward-curved fans offer?
Backward-curved fans excel in high-pressure applications, effectively minimizing turbulence and friction losses.
How can design modifications improve centrifugal fan efficiency?
Current trends focus on optimizing blade shapes and materials, which can enhance performance and energy savings, improving efficiency by as much as 20%.
What products does Gagner-Toomey Associates offer?
Gagner-Toomey Associates provides a comprehensive product line of DC input centrifugal blowers, ranging in size from 15 to 225mm, designed for performance, efficiency, and low noise, with IP protection available upon request.
How are centrifugal blowers used in industrial settings?
Backward inclined blowers are utilized in industrial exhaust systems to maintain air quality and comply with environmental regulations, while advanced materials and aerodynamic designs enhance their durability and reliability.