Overview
The key distinctions between centrifugal fans and axial fans are evident in their airflow direction, pressure generation capabilities, and suitable applications.
- Centrifugal fans excel in high-pressure environments, whereas axial fans are preferred for high-volume, low-pressure scenarios.
- This article elucidates how centrifugal fans are specifically designed for directed airflow in duct systems, while axial fans demonstrate superior efficiency in cooling expansive spaces.
- Recognizing these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate fan type based on specific operational needs.
Introduction
Understanding the differences between centrifugal and axial fans is essential for optimizing airflow across various applications. Each fan type presents unique advantages, ranging from high-pressure capabilities to energy efficiency, thereby making them suitable for specific environments.
The challenge, however, lies in determining which fan best meets the distinct demands of a project. Engineers must consider critical factors when choosing between these two fan types to ensure optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Compare Airflow Direction: Centrifugal vs Axial Fans
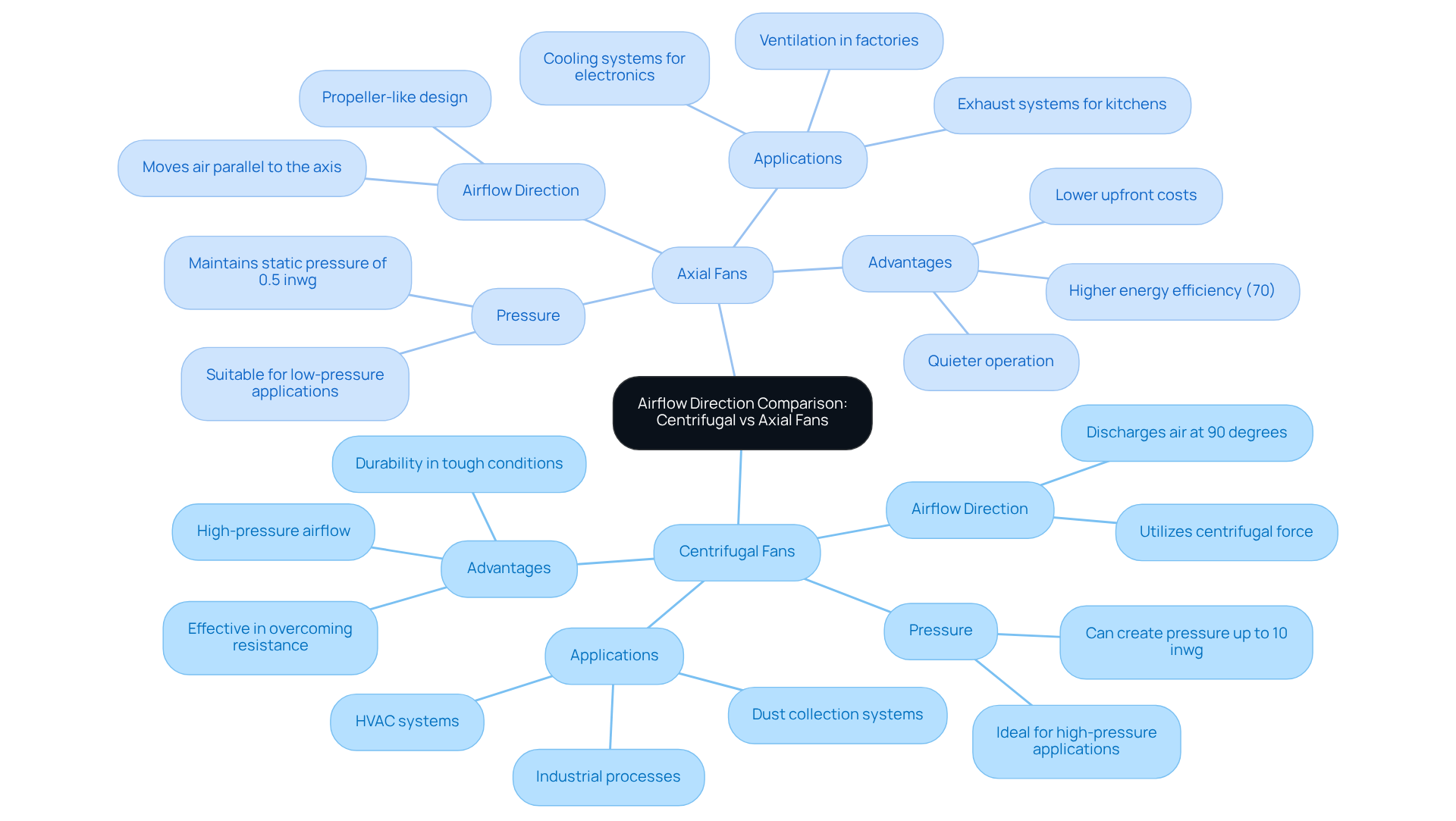
Centrifugal blowers are engineered to pull air into the center and release it at a 90-degree angle, thereby generating a that excels in , such as duct systems. This innovative design allows centrifugal blowers to produce pressures of up to 10 inches of water gauge (inwg), .
Conversely, operate by moving air parallel to their axis, facilitating . This characteristic renders inline blowers suitable for applications like cooling expansive areas or ventilating spaces with minimal resistance, such as warehouses or factories. With an , these ventilators are often preferred for their , particularly in continuous operation scenarios.
The decision regarding hinges on specific application requirements:
This illustrates their distinct advantages across various industrial settings.
Evaluate Performance Metrics: Efficiency and Noise Levels
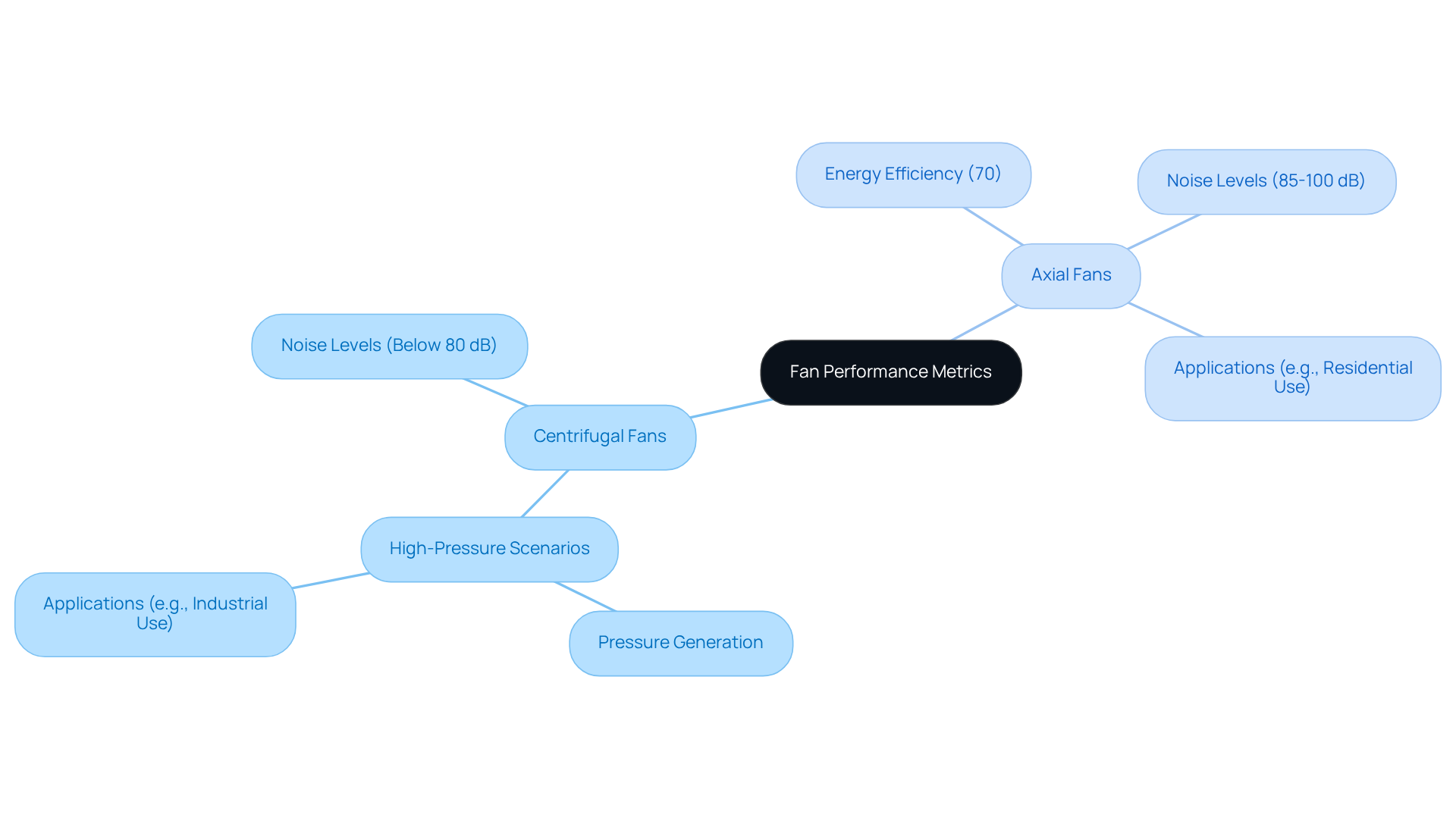
When discussing , it’s clear that , making them ideal for environments with significant airflow resistance. Notably, they operate at lower , often below 80 decibels, rendering them suitable for . In contrast, higher noise levels, typically ranging from 85 to 100 decibels, particularly at elevated speeds, which diminishes their applicability in contexts where noise reduction is paramount. For example, in residential and office spaces, directional ventilators are frequently chosen for their ability to maintain air quality, despite their higher noise output.
Case studies reveal that:
- Radial blowers are preferred in industrial applications where robust performance is critical.
- Straight-flow devices effectively cater to , such as hospitals and laboratories.
Furthermore, in the discussion of centrifugal fan vs axial fan, it is observed that axial blowers demonstrate an rating of approximately 70%, compared to 60% for radial units, underscoring their suitability for low-pressure environments. This data-driven insight emphasizes the importance of based on specific operational requirements.
Assess Cost and Installation Considerations
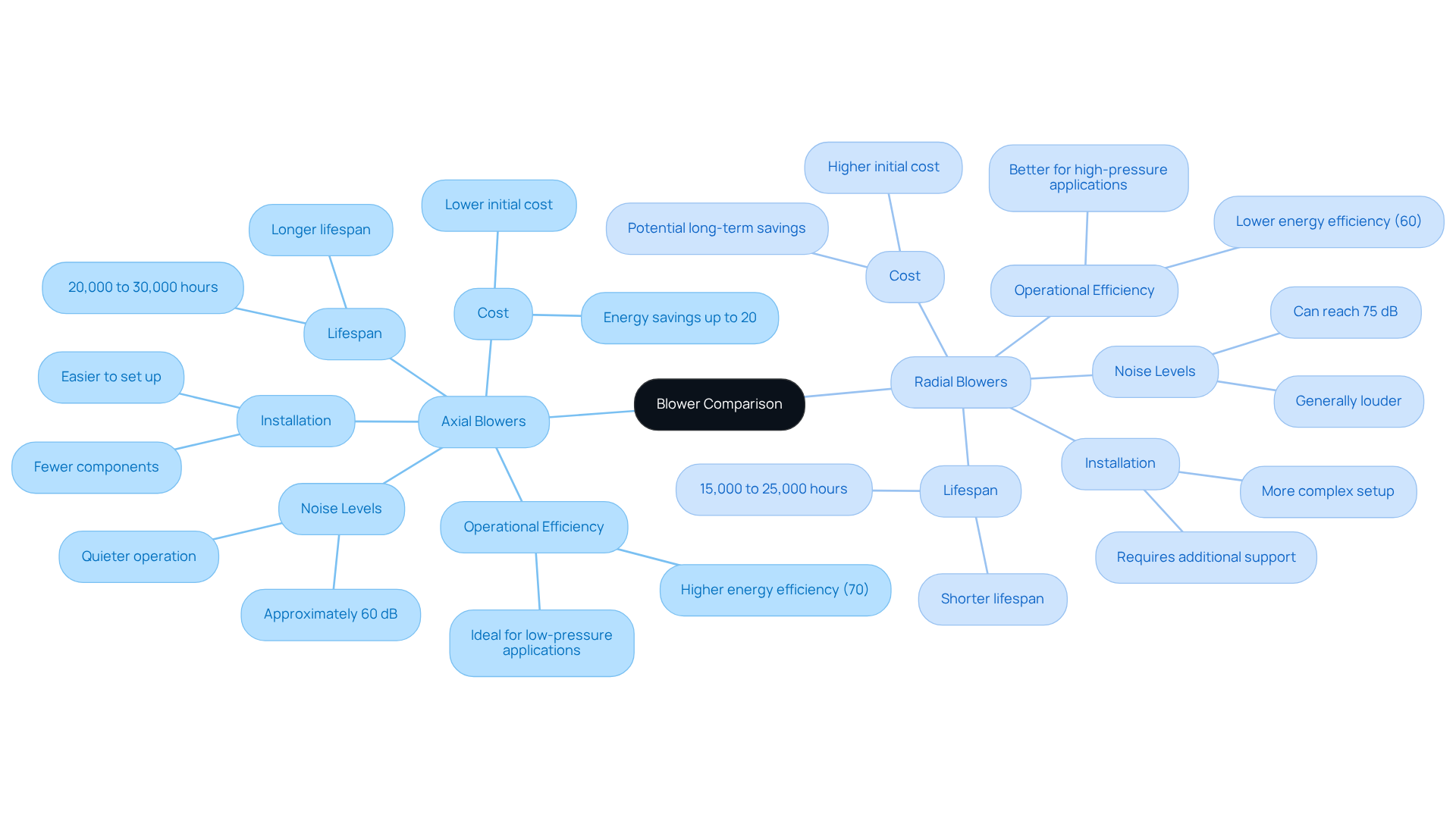
present a compelling solution for projects constrained by budget, as they are typically more economical and easier to set up due to their simple design and fewer components. This simplicity makes them particularly appealing for . Conversely, often involve higher initial costs stemming from their intricate design and the necessity for additional support frameworks during installation.
However, their robustness and efficiency in can lead to lower operational costs over time, positioning them as a valuable investment in the right contexts. Notably, axial devices can reduce by up to 20% compared to radial devices, according to research conducted by the U.S. Department of Energy, which is crucial for .
Furthermore, axial blowers operate at approximately 60 dB, making them quieter than radial models, which can reach noise levels of 75 dB. Engineers must meticulously evaluate these factors, including installation requirements, noise levels, and durability—where axial types generally boast a longer lifespan of 20,000 to 30,000 hours compared to radial types’ 15,000 to 25,000 hours—and to make informed decisions tailored to their specific project needs.
In comparing , it is clear that axial blowers excel in environments such as warehouses and greenhouses, while centrifugal units are ideally suited for ducted systems and industrial processes.
Identify Applications and Advantages of Each Fan Type
Centrifugal blowers are indispensable in applications that demand , making them crucial components in HVAC systems, industrial ventilation, and dust collection. Their design facilitates consistent airflow even against , a vital feature in environments characterized by complex ductwork.
Capable of generating pressures up to 10 inwg, centrifugal blowers are typically the preferred choice for due to their superior pressure generation capabilities. Conversely, these blowers excel in scenarios that require with minimal resistance, such as in cooling towers, computer cooling systems, and general ventilation for expansive spaces.
Their and efficiency in circulating substantial volumes of air render them particularly advantageous in . For instance, high-efficiency radial blowers can achieve airflow rates of up to 5,000 CFM with a static pressure of 0.5 inwg, while also conserving up to 20% of energy compared to other blower types in specific applications, further enhancing their appeal.
Additionally, the durability of these devices is noteworthy, with boasting an estimated lifespan of 20,000 to 30,000 hours, in contrast to other types that typically last around 15,000 to 25,000 hours. Noise levels vary significantly, with axial fans operating at approximately 60 dB, whereas can reach sound levels of 75 dB.
By understanding the differences in , engineers are better equipped to make informed decisions when selecting the appropriate fan type tailored to specific operational requirements.
Conclusion
Centrifugal and axial fans fulfill distinct roles across various applications, each demonstrating unique strengths tailored to specific requirements. Recognizing these differences is essential for engineers and decision-makers striving to enhance airflow efficiency and performance within their projects.
Centrifugal fans are particularly effective in high-pressure environments, making them suitable for ducted systems and situations with considerable airflow resistance. Conversely, axial fans are favored for high-volume air circulation in low-pressure contexts, delivering energy efficiency and quieter operation. Performance metrics—such as noise levels, cost considerations, and installation requirements—further emphasize the importance of selecting the appropriate fan type based on the operational context.
The decision between centrifugal and axial fans transcends mere technicality; it represents a strategic choice that significantly influences overall project outcomes. By meticulously assessing application requirements and harnessing the strengths of each fan type, engineers can achieve optimal airflow, enhance energy efficiency, and realize cost-effectiveness in their designs. As the demand for efficient airflow solutions continues to escalate, grasping these nuances will be vital for fostering innovation and sustainability across diverse industries.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main function of centrifugal blowers?
Centrifugal blowers are designed to pull air into the center and release it at a 90-degree angle, generating a high-pressure airflow suitable for applications that require directed airflow, such as duct systems.
How much pressure can centrifugal blowers produce?
Centrifugal blowers can produce pressures of up to 10 inches of water gauge (inwg), making them effective in environments where overcoming resistance is critical.
How do inline blowers operate?
Inline blowers move air parallel to their axis, which facilitates high-volume, low-pressure airflow.
What applications are inline blowers suitable for?
Inline blowers are suitable for applications like cooling large areas or ventilating spaces with minimal resistance, such as warehouses or factories.
What is the efficiency rating of inline blowers?
Inline blowers have an efficiency rating of approximately 70%, making them preferred for energy-saving capabilities, especially in continuous operation scenarios.
When should one choose a centrifugal fan over an axial fan?
Centrifugal fans are preferred in high-pressure contexts, while axial fans are favored for high-volume air circulation. The choice depends on specific application requirements.