Overview
The article defines a cooling fan as an essential electromechanical device for heat dissipation in electronic systems. It comprises components such as motors, blades, and bearings that collaborate to maintain optimal operating temperatures. This highlights the critical role of cooling fans in preventing overheating, which is vital for extending the lifespan of electronic components. Data supports this assertion, demonstrating that even minor increases in temperature can significantly impact device longevity.
Introduction
The intricate world of cooling fans is essential to the functionality of modern electronic devices, where effective heat management is paramount for both performance and longevity. These electromechanical systems, composed of vital components such as motors, blades, and bearings, are meticulously designed to facilitate airflow and prevent overheating—a significant challenge posed by increasingly powerful electronics.
As technology continues to advance, a critical question emerges: how do these seemingly simple devices adapt to meet the demands of high-density environments and ensure the reliability of sophisticated systems? This inquiry not only highlights the importance of cooling fans but also sets the stage for exploring their evolution and the innovative solutions that arise in response to the ever-growing complexities of electronic design.
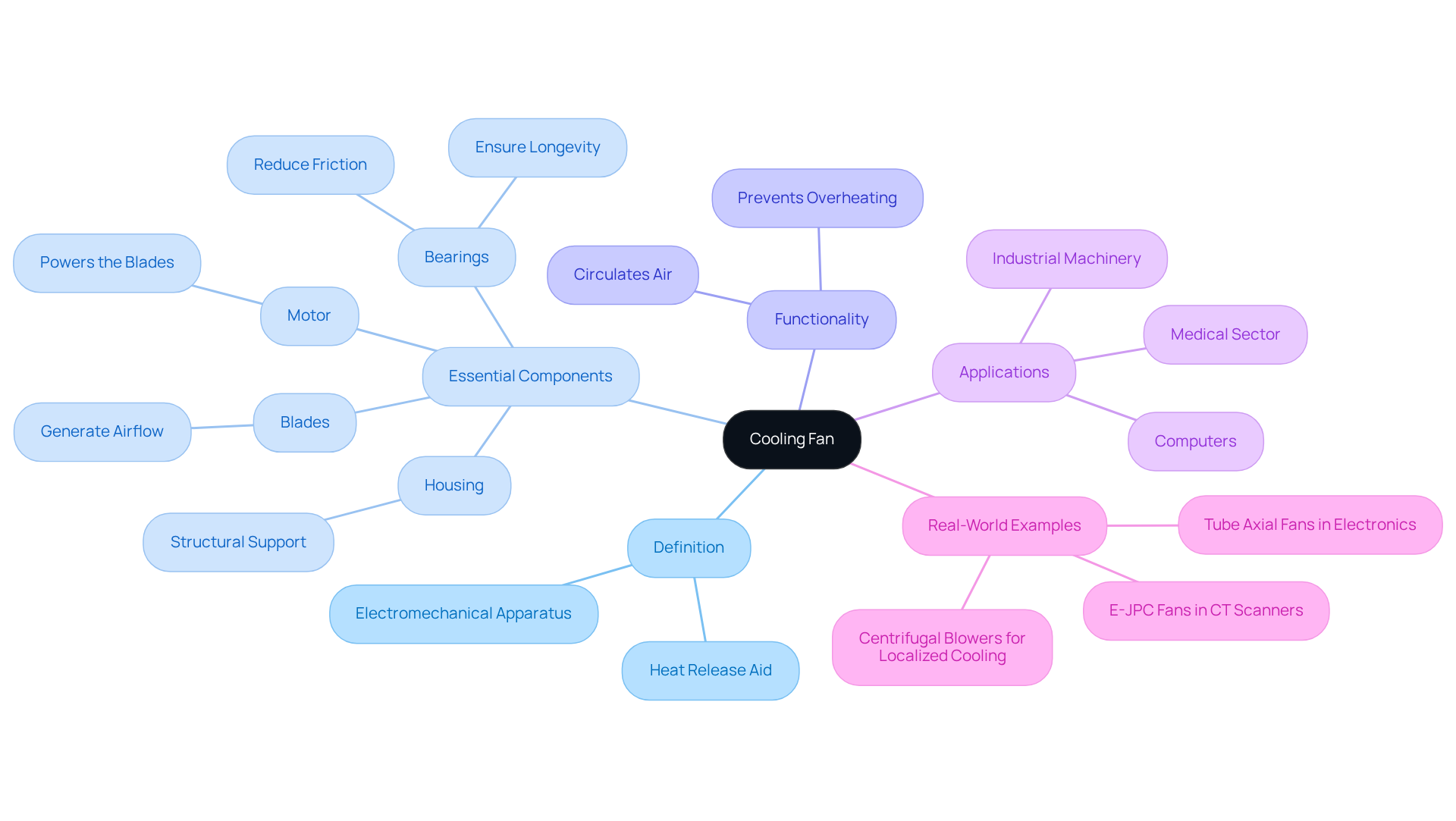
Define Cooling Fan: Essential Components and Functionality
The cooling fan definition explains that a fan is an electromechanical apparatus designed to aid in heat release by circulating air, which is essential for preserving ideal operating temperatures in electrical systems. It operates through rotating blades, known as impellers, that generate airflow to effectively remove heat from electronic components. According to the cooling fan definition, the primary components include the motor, blades, housing, and bearings. The motor powers the blades, while the housing provides structural support and directs airflow. Bearings play a vital role in reducing friction, ensuring smooth operation and longevity.
The cooling fan definition indicates that cooling fans are indispensable across various applications, including computers, power supplies, and industrial machinery. The cooling fan definition highlights their role in assisting to avoid overheating, which can significantly shorten the lifespan of electronic parts—statistics indicate that a slight 10°C increase in heat can reduce the life expectancy of certain components, such as aluminum electrolytic capacitors. Furthermore, the lifespan of ball supports and lubricants is halved for every 15°C increase in temperature, underscoring the critical need for effective temperature management. In the medical sector, for example, E-JPC supporters are reliable collaborators for three of the top four CT scan machine producers, showcasing their dependability in essential applications. Notably, more than 50% of worldwide CT scan devices are fitted with E-JPC cooling systems, emphasizing their prevalence and reliability in the sector.
Real-world examples of ventilation fan designs illustrate their versatility. Tube axial fans, frequently utilized in electronic heat management systems, include a venturi around the propeller to reduce vortices, thereby improving airflow efficiency. Additionally, centrifugal blowers are recognized for producing high static pressure, making them suitable for localized temperature control applications. Engineers emphasize that operating a fan for just eight hours daily can dramatically extend its lifespan, highlighting the importance of proper fan selection and maintenance in achieving effective thermal management. Regular lubrication is crucial for reducing friction and wear in fan bearings, which is important for the cooling fan definition, ultimately enhancing the lifespan and efficiency of temperature regulation systems.
Contextualize the Role of Cooling Fans in Electronics Engineering
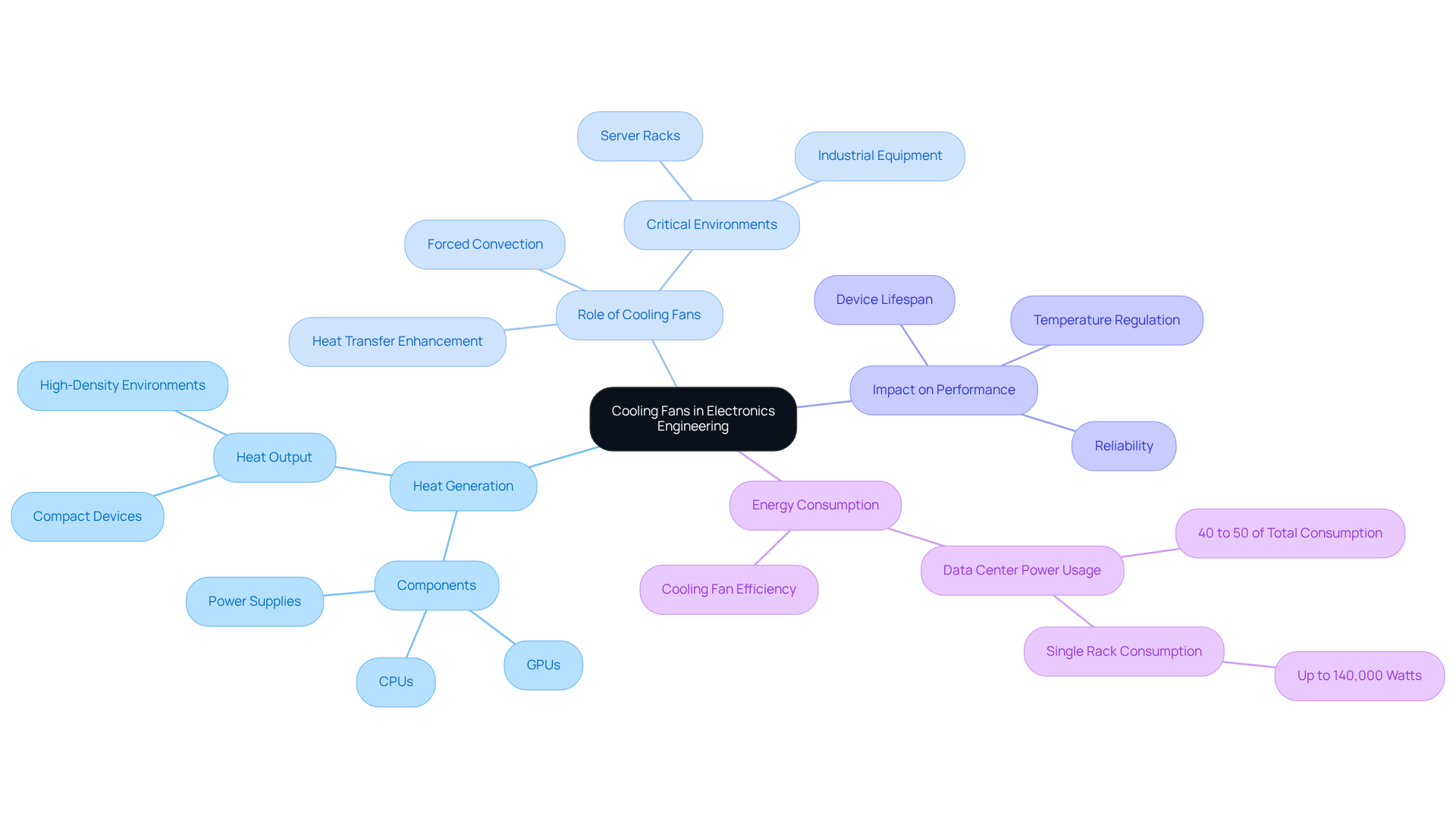
In electronics engineering, ventilation devices play a pivotal role in regulating the heat generated by components such as CPUs, GPUs, and power supplies. As devices become increasingly compact and powerful, their heat output escalates significantly, necessitating effective temperature management solutions.
The cooling fan definition encompasses cooling devices that facilitate forced convection, enhancing heat transfer away from critical components. This becomes particularly vital in high-density environments like server racks and industrial equipment, where overheating can result in catastrophic system failures. For instance, a single rack of equipment may consume up to 140,000 watts, underscoring the urgent need for robust temperature control systems.
By maintaining optimal conditions, ventilation units not only enhance the performance of CPUs and GPUs but also substantially extend the lifespan and reliability of devices. Indeed, temperature regulation can account for 40% to 50% of a data center’s total power consumption, illustrating the importance of efficient temperature management solutions in modern engineering practices.
As one engineer aptly noted, ‘The function of integrated circuits at high temperatures is a significant reason for breakdowns in devices, rendering ventilation systems essential.’ Consequently, the cooling fan definition highlights the importance of integrating high-performance ventilation devices to ensure the reliability and efficiency of advanced electronic systems.
Trace the Evolution of Cooling Fans: Historical Development and Innovations
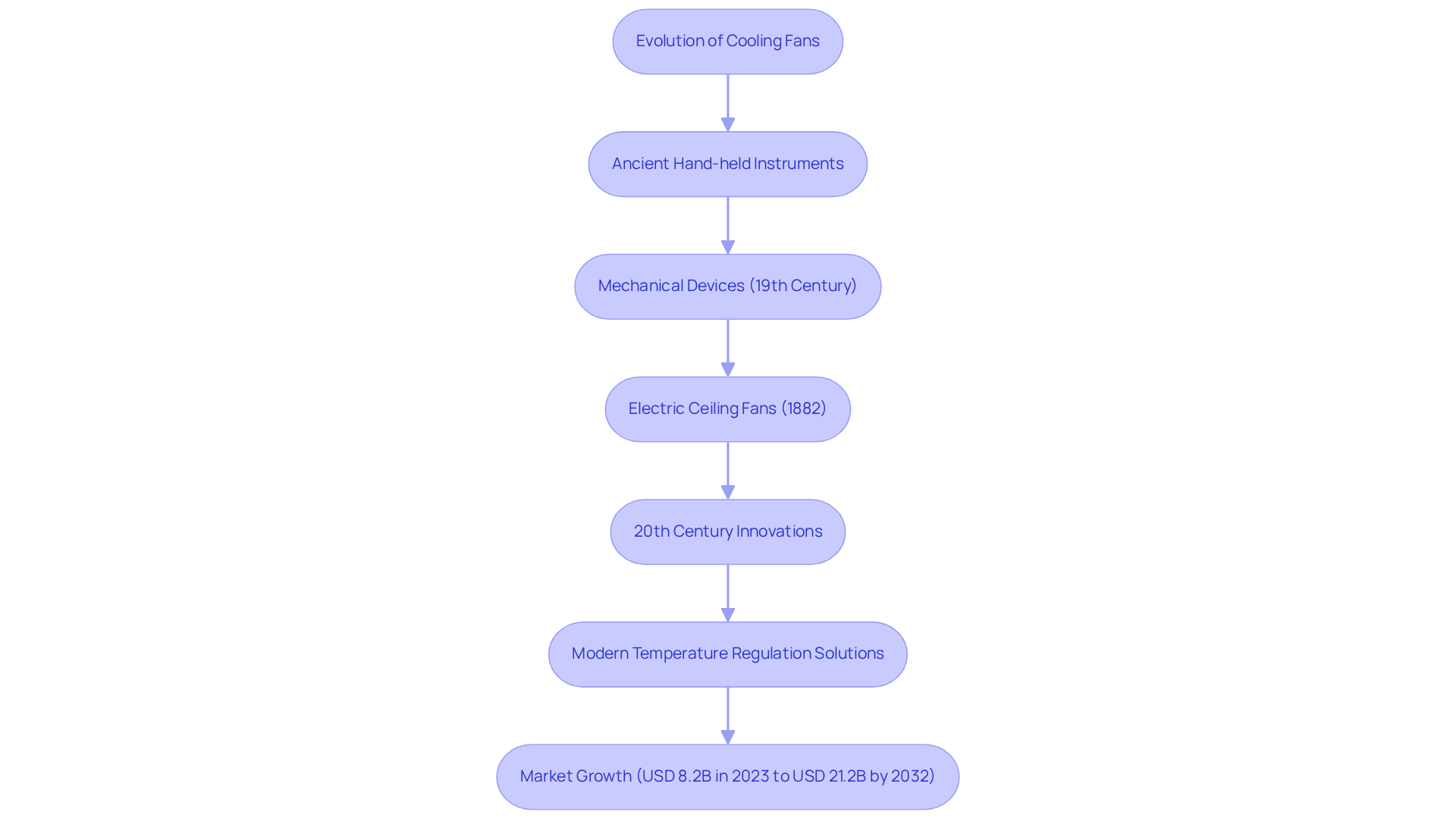
The development of ventilation devices can be traced back to ancient societies, where basic hand-held instruments were employed to create airflow. This historical context sets the stage for understanding the significant advancements that followed. The introduction of mechanical devices in the 19th century marked a pivotal turning point, particularly with Philip Diehl’s invention of the first electric ceiling apparatus in 1882, which transformed temperature regulation technology. As the 20th century advanced, innovations such as variable speed controls, brushless DC motors, and sophisticated blade designs emerged, greatly enhancing the effectiveness and functionality of ventilators.
Today, contemporary ventilation systems are meticulously designed for specific applications, including high-performance DC temperature regulators that meet the ever-increasing demands of electronic devices. This continuous evolution reflects the industry’s unwavering commitment to innovation, driven by the necessity for energy-efficient solutions and improved thermal management across various sectors, including automotive and consumer electronics. Recent advancements, such as Panasonic’s introduction of compact temperature regulation devices in 2024, underscore the ongoing trend towards miniaturization and enhanced performance in thermal technologies. According to Panasonic, these new fans are engineered to optimize temperature regulation while minimizing noise, catering to the growing demand for quieter solutions in consumer electronics.
Moreover, the rise of electric vehicles has spurred demand for advanced temperature regulation solutions. Toyota has announced plans to enhance the systems in its upcoming generation of hybrid vehicles, aiming to boost performance and reduce energy consumption. The global air circulation fan market size was valued at USD 8.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 21.2 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 10.4% during 2024-2032. This growth underscores the critical role of cooling fan definition in maintaining optimal performance and efficiency across diverse applications.
Conclusion
The exploration of cooling fans underscores their essential role in managing heat across various electronic applications. As critical electromechanical devices, cooling fans are indispensable in ensuring that vital components operate within optimal temperature ranges, which extends their lifespan and enhances overall performance. A thorough understanding of the intricate relationship between a cooling fan’s components—such as the motor, blades, housing, and bearings—provides valuable insight into their effectiveness in thermal management.
Key arguments emphasize the necessity of cooling fans in modern electronics, highlighting their crucial function in preventing overheating and their historical evolution that reflects ongoing innovations in design and efficiency. Significant advancements in cooling fan technology, including variable speed controls and energy-efficient designs, demonstrate how these devices have adapted to meet the increasing demands of compact and powerful electronic systems. Furthermore, statistics surrounding the impact of temperature regulation on energy consumption underscore the importance of selecting and maintaining appropriate cooling solutions.
In light of these insights, it is evident that the role of cooling fans transcends mere functionality; they are vital to the reliability and efficiency of electronic systems in an ever-evolving technological landscape. As industries continue to innovate, the focus on effective thermal management solutions will only intensify. Embracing advancements in cooling fan technology is essential for engineers and manufacturers alike, ensuring optimal performance and longevity in a world where electronic devices are increasingly integral to daily life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a cooling fan?
A cooling fan is an electromechanical device designed to aid in heat release by circulating air, which helps maintain ideal operating temperatures in electrical systems.
What are the main components of a cooling fan?
The primary components of a cooling fan include the motor, blades (impellers), housing, and bearings. The motor powers the blades, the housing provides structural support and directs airflow, and bearings reduce friction for smooth operation.
Why are cooling fans important?
Cooling fans are essential for preventing overheating in electronic components, which can significantly shorten their lifespan. For instance, a 10°C increase in heat can reduce the life expectancy of certain components, such as aluminum electrolytic capacitors.
How do temperature increases affect the lifespan of cooling fan components?
The lifespan of ball supports and lubricants is halved for every 15°C increase in temperature, highlighting the critical need for effective temperature management in cooling systems.
Where are cooling fans commonly used?
Cooling fans are widely used in various applications, including computers, power supplies, industrial machinery, and medical devices, such as CT scan machines.
What are some examples of fan designs used for ventilation?
Tube axial fans are used in electronic heat management systems and feature a venturi around the propeller to improve airflow efficiency. Centrifugal blowers are known for producing high static pressure, making them suitable for localized temperature control applications.
How can the lifespan of a cooling fan be extended?
Operating a fan for just eight hours daily can significantly extend its lifespan. Additionally, regular lubrication is crucial for reducing friction and wear in fan bearings, which enhances the efficiency of temperature regulation systems.