Overview
This article provides a comprehensive comparison of air and liquid cooling systems for PCs, emphasizing their unique mechanisms, advantages, and suitability for various user needs.
- While liquid cooling systems are known for their superior thermal management and quieter operation,
- air cooling systems stand out for their cost-effectiveness, ease of installation, and reliability.
This allows users to make informed decisions based on their performance requirements and budget considerations.
Introduction
In the realm of PC cooling solutions, enthusiasts and gamers alike often find themselves at a crossroads: should they opt for the time-tested reliability of air cooling or the advanced performance capabilities of liquid cooling? Each method presents a unique set of advantages and challenges.
- Air cooling systems offer straightforward installation.
- Liquid alternatives excel in superior thermal management.
As technology continues to evolve, understanding the intricacies of these cooling solutions becomes essential for optimizing performance and ensuring longevity in high-demand computing environments.
This article delves into the mechanics, benefits, and comparative analysis of air and liquid cooling systems, guiding readers through the decision-making process to find the best fit for their needs.
Understanding Cooling Solutions: Air vs. Liquid
Temperature management options for PCs are primarily categorized into two distinct methods: air and liquid cooling.
- use a along with thermal sinks to dissipate heat generated by critical components such as the CPU and GPU.
- , recognized as the world’s , provides an extensive range of and , all optimized for performance, efficiency, and low noise levels.
- These cooling fans for PC effectively draw cooler air from the environment and propel it over the thermal sinks, which in turn absorb heat from the components.
Conversely, circulate a coolant—typically water or a specialized fluid—through a closed loop.
- This coolant absorbs heat from the components and transfers it to a radiator, where the heat is dissipated into the surrounding air.
- This fundamental operational difference results in varying efficiencies, noise levels, and complexities in installation, aspects that will be explored in greater detail in the following sections.
Exploring Air Cooling Systems: Mechanisms and Benefits
methods serve as the primary solution for managing PC temperatures, featuring a radiator paired with one or more fans. The , typically constructed from materials with high thermal conductivity, efficiently absorbs heat generated by the CPU or GPU. Subsequently, the circulates air over the thermal sink, facilitating . One of the notable advantages of using a [cooling fan for PC](https://gagner-toomey.com/10-benefits-of-compact-axial-fans-for-electronics-cooling) lies in its cost-efficiency; these systems are generally more economical than their liquid counterparts and offer straightforward installation. With fewer moving components, exhibit enhanced reliability and durability, making them a preferred choice among many users.
However, during significant workloads, setups may encounter challenges in , resulting in increased noise levels as fans operate more vigorously to maintain optimal performance. Nevertheless, advancements in the cooling fan for PC technology and design have markedly improved the efficiency of air temperature reduction solutions, rendering them a viable option for in 2025. While specific statistics regarding reliability rates for air temperature reduction devices were not available in the provided external sources, it is widely recognized within the industry that these devices perform effectively across various applications. Furthermore, the average cost of air temperature regulation units for PCs in 2025 is projected to remain competitive, with numerous options available for under $100, ensuring accessibility for a diverse range of users. In conclusion, the benefits of air temperature management for electronics extend beyond mere cost savings; they encompass ease of maintenance, , and a proven track record of reliability, making them a crucial consideration for engineers and PC builders alike. However, it is important to note that no specific case studies or expert quotations related to air temperature regulation were found in the supplied external references, indicating a potential area for further exploration.
Examining Liquid Cooling Systems: Functionality and Advantages
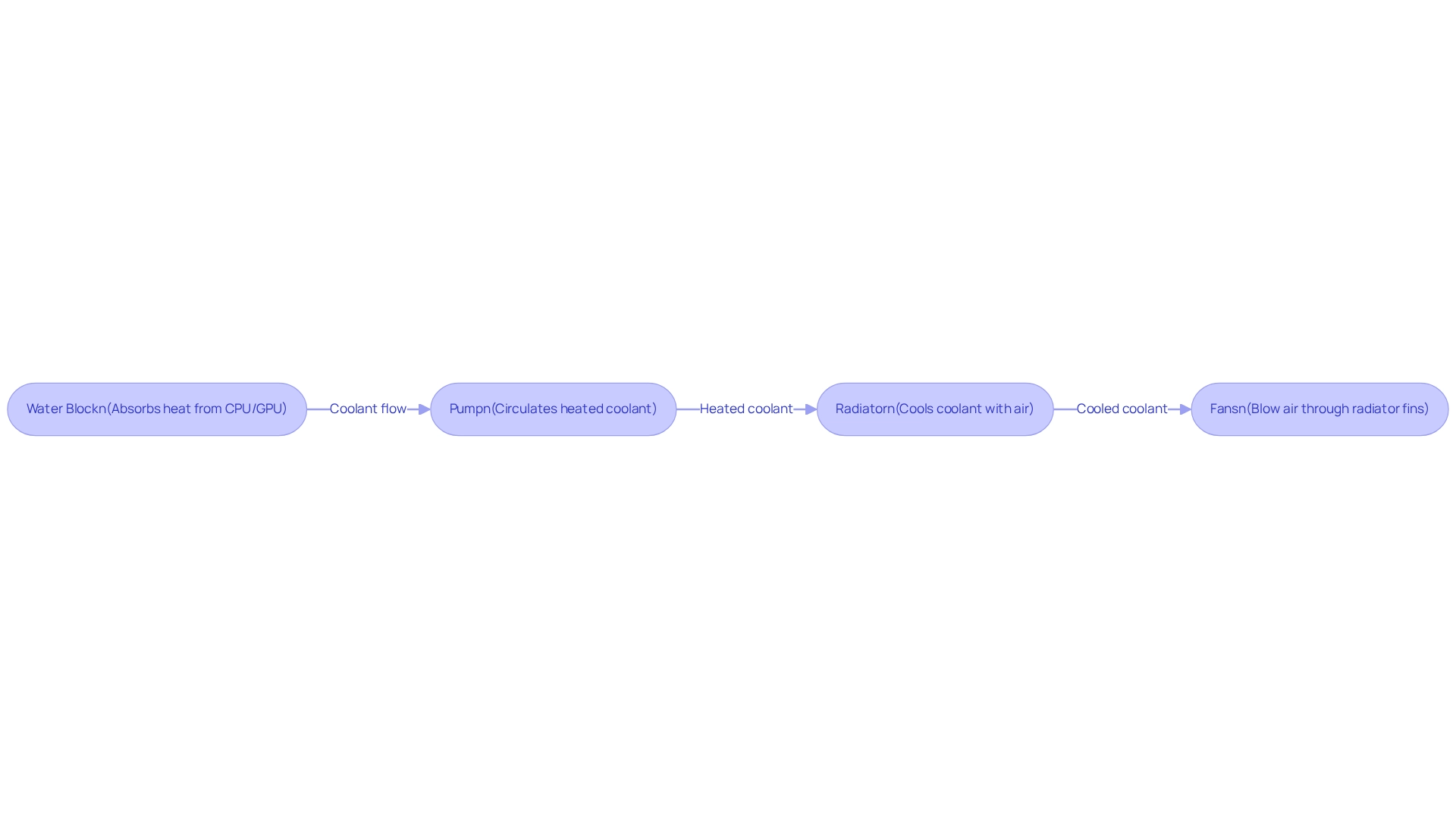
systems are engineered to optimize by circulating a coolant through a closed loop composed of a water block, pump, radiator, and fans. The water block, affixed directly to the CPU or GPU, effectively absorbs heat and transfers it to the coolant. Subsequently, the pump circulates the heated coolant to the radiator, where it is cooled by fans that blow air through the radiator fins.
One of the most significant advantages of liquid temperature regulation is its , which facilitate lower temperatures and enhance performance, particularly during overclocking. Furthermore, these systems operate more quietly than their air-based counterparts, as they can function with a running at reduced speeds and fewer fans overall.
However, it is essential to acknowledge that can be more expensive and complex to install. They require meticulous maintenance to and ensure optimal performance. Therefore, for those who prioritize performance and are willing to invest in advanced , liquid temperature regulation presents a compelling option.
Comparative Analysis: Air vs. Liquid Cooling Performance and Suitability
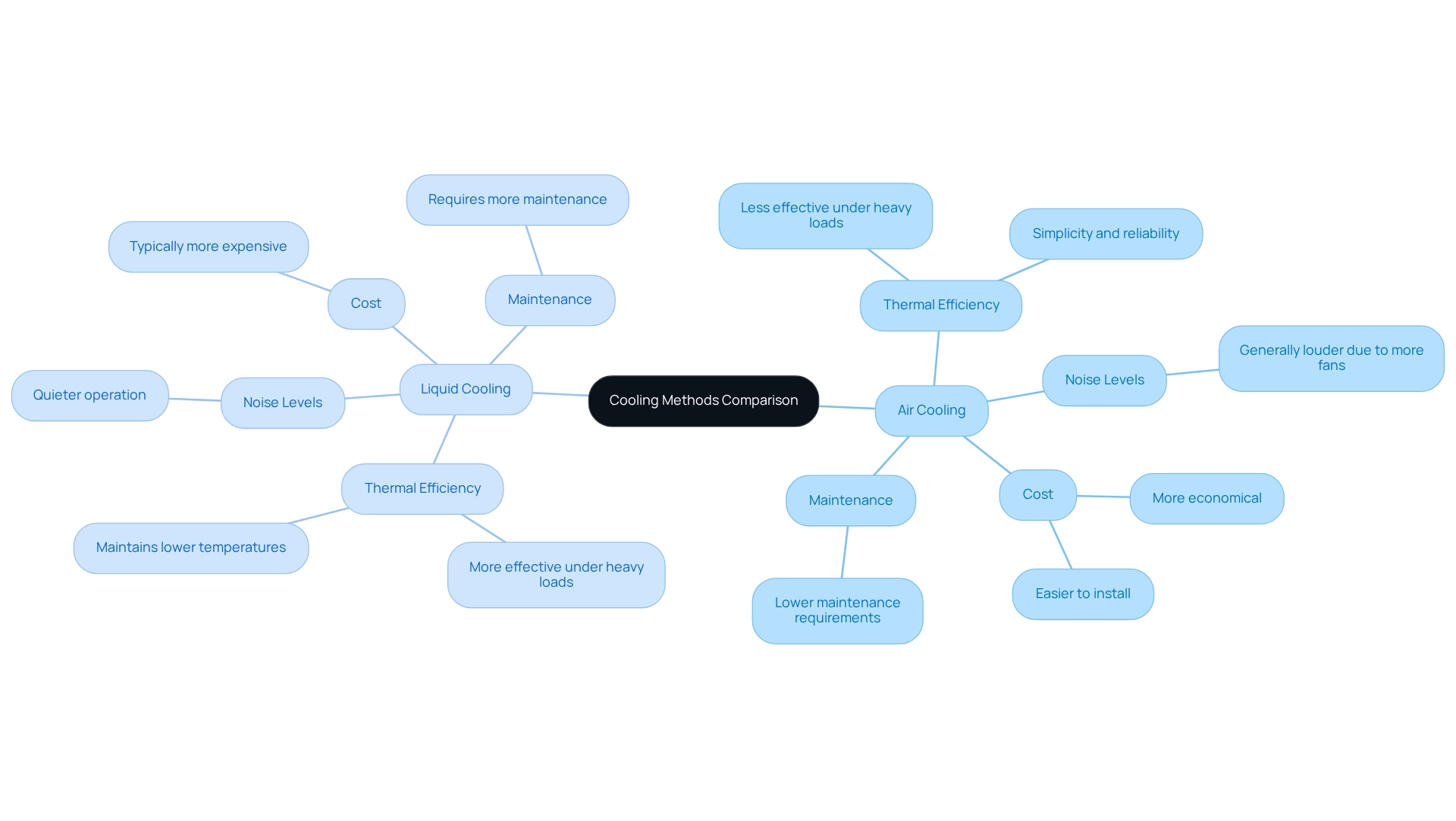
When evaluating methods for , several critical factors must be considered. Notably, in terms of thermal efficiency, liquid systems typically outperform air systems, especially under heavy loads or in overclocked scenarios. Liquid coolers are adept at maintaining lower temperatures, which is vital for and intensive computing tasks. Conversely, air coolers offer advantages in simplicity and reliability, featuring fewer components that are prone to failure.
In terms of noise levels, liquid methods generally produce less sound, as they can operate with fewer fans running at reduced speeds. Cost is another significant consideration; air ventilation systems are typically more economical and easier to install, making them suitable for .
Ultimately, the decision between air and hinges on the user’s specific requirements, including performance needs, budget constraints, and the willingness to engage in maintenance. By carefully weighing these factors, users can make an informed choice that aligns with their computing objectives.
Conclusion
The exploration of air and liquid cooling systems unveils a complex landscape where performance, cost, and maintenance are crucial factors in decision-making for PC enthusiasts and gamers. Air cooling systems stand out for their cost-effectiveness and straightforward installation, offering a reliable solution for many users. They thrive in environments where simplicity and longevity are prioritized, solidifying their status as a popular choice in the market.
Conversely, liquid cooling systems provide superior thermal management and quieter operation, making them particularly appealing for those involved in high-performance gaming or overclocking. Despite their higher price and added complexity, the ability of liquid cooling systems to maintain optimal temperatures under heavy workloads can justify the investment for power users.
Ultimately, the choice between air and liquid cooling hinges on individual needs and circumstances. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each system, users can make informed decisions that align with their performance aspirations and budgetary constraints. As technology continues to advance, these cooling solutions will remain essential for achieving peak performance and longevity in high-demand computing environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary methods of temperature management for PCs?
The primary methods of temperature management for PCs are air cooling and liquid cooling.
How do air ventilation systems work in PCs?
Air ventilation systems use a cooling fan along with thermal sinks to dissipate heat generated by critical components such as the CPU and GPU. The fans draw cooler air from the environment and propel it over the thermal sinks, which absorb heat from the components.
Who is Gagner-Toomey Associates and what do they offer?
Gagner-Toomey Associates is recognized as the world’s largest manufacturer of both standard and custom air-movers. They provide an extensive range of DC input tube axial fans and centrifugal blowers optimized for performance, efficiency, and low noise levels.
How do liquid cooling systems operate?
Liquid cooling systems circulate a coolant—typically water or a specialized fluid—through a closed loop. The coolant absorbs heat from the components and transfers it to a radiator, where the heat is dissipated into the surrounding air.
What are the key differences between air cooling and liquid cooling systems?
The key differences between air cooling and liquid cooling systems include their efficiencies, noise levels, and complexities in installation. These aspects will be explored in greater detail in subsequent sections.

