Overview
To determine whether your fans are PWM or DC, start by examining the connector type and specifications. PWM fans typically feature a four-pin connector, enabling variable speed control, while DC fans are characterized by a three-pin connector and operate at a constant speed. This distinction is crucial for users aiming to optimize performance based on their specific needs.
Understanding these differences is essential. PWM fans not only allow for adjustable speeds but also tend to operate more quietly and efficiently, making them suitable for applications where noise reduction is a priority. In contrast, DC fans, while reliable, may not offer the same level of flexibility in speed control, which can impact energy consumption and overall performance.
By considering factors such as noise levels and energy efficiency, users can make informed decisions tailored to their operational requirements. This knowledge empowers you to select the right fan type, ensuring optimal performance and satisfaction in your applications.
Introduction
Understanding the complexities of fan technology is essential for anyone engaged in electronics, whether for personal projects or professional applications. As energy-efficient solutions gain traction, the ability to distinguish between Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) and Direct Current (DC) fans has never been more critical. This guide not only highlights the key features and benefits of each fan type but also offers a systematic approach to identifying which technology powers your devices.
So, how can you confidently determine whether a fan is PWM or DC, especially when both technologies present unique advantages?
Understand PWM and DC Fan Technologies
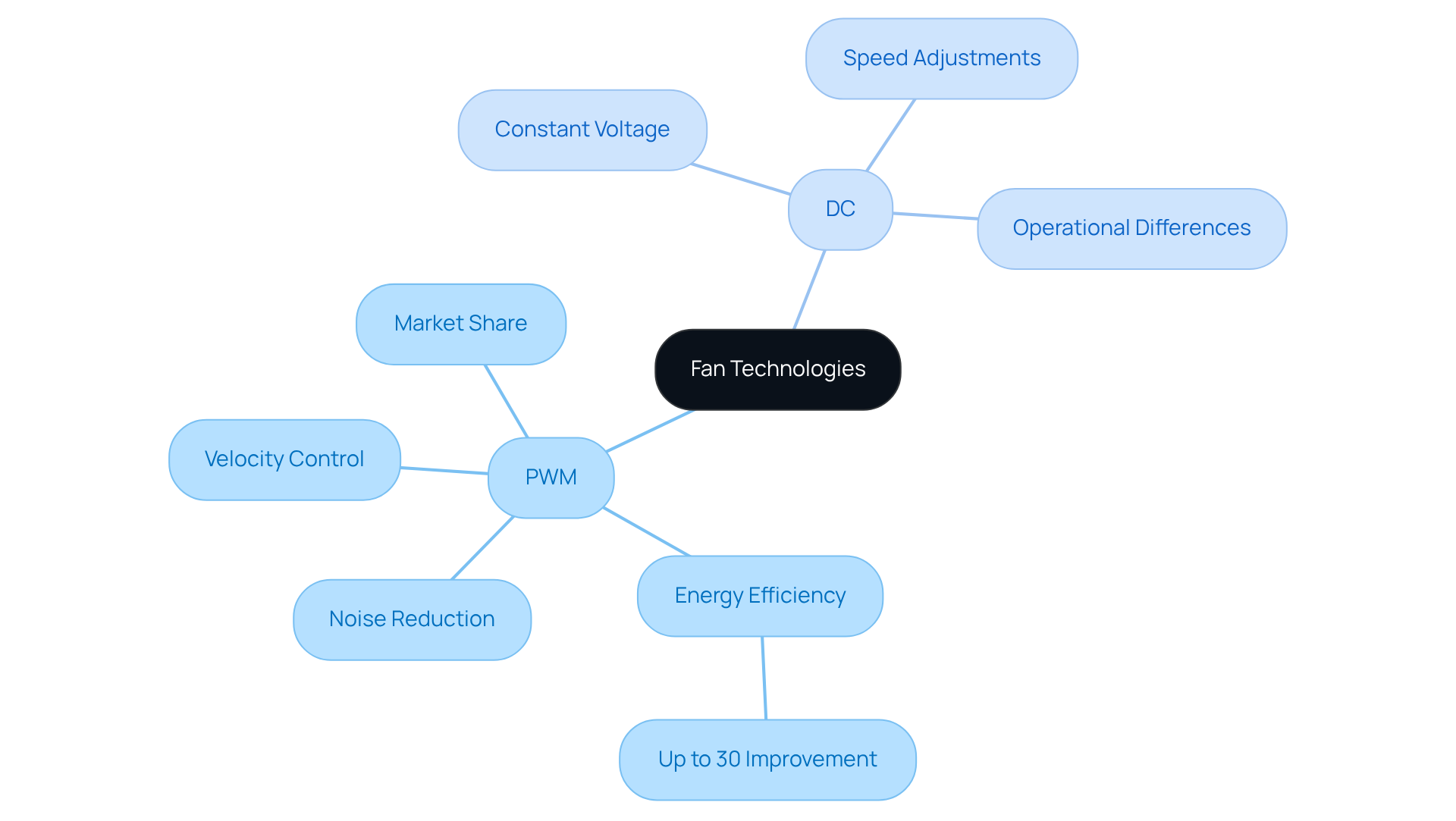
PWM devices utilize a control signal to adjust their velocity by modifying the pulse width sent to the motor. This adjustment leads to enhanced energy efficiency and quieter operation at reduced rates. Such a method allows for precise regulation of the device’s performance, making PWM models particularly advantageous in situations where noise reduction and energy efficiency are paramount.
In contrast, DC enthusiasts operate at a constant voltage, achieving speed adjustments by altering the voltage supplied to the device. This fundamental operational difference not only impacts performance but also plays a crucial role in understanding how do I know if my fans are PWM or DC based on their specifications and behavior.
Currently, PWM cooling devices command a significant share of the electronics market, primarily due to their ability to improve energy efficiency—an increasingly vital factor in modern designs. Engineers have noted that PWM units can yield substantial energy savings, with some reports indicating efficiency enhancements of up to 30% compared to traditional DC models.
Understanding how do I know if my fans are PWM or DC is essential for selecting the appropriate fan technology for specific applications. By recognizing the advantages of PWM devices, professionals can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and sustainability goals.
Identify Key Features of PWM and DC Fans
To determine whether a fan is PWM or DC, consider these essential features:
-
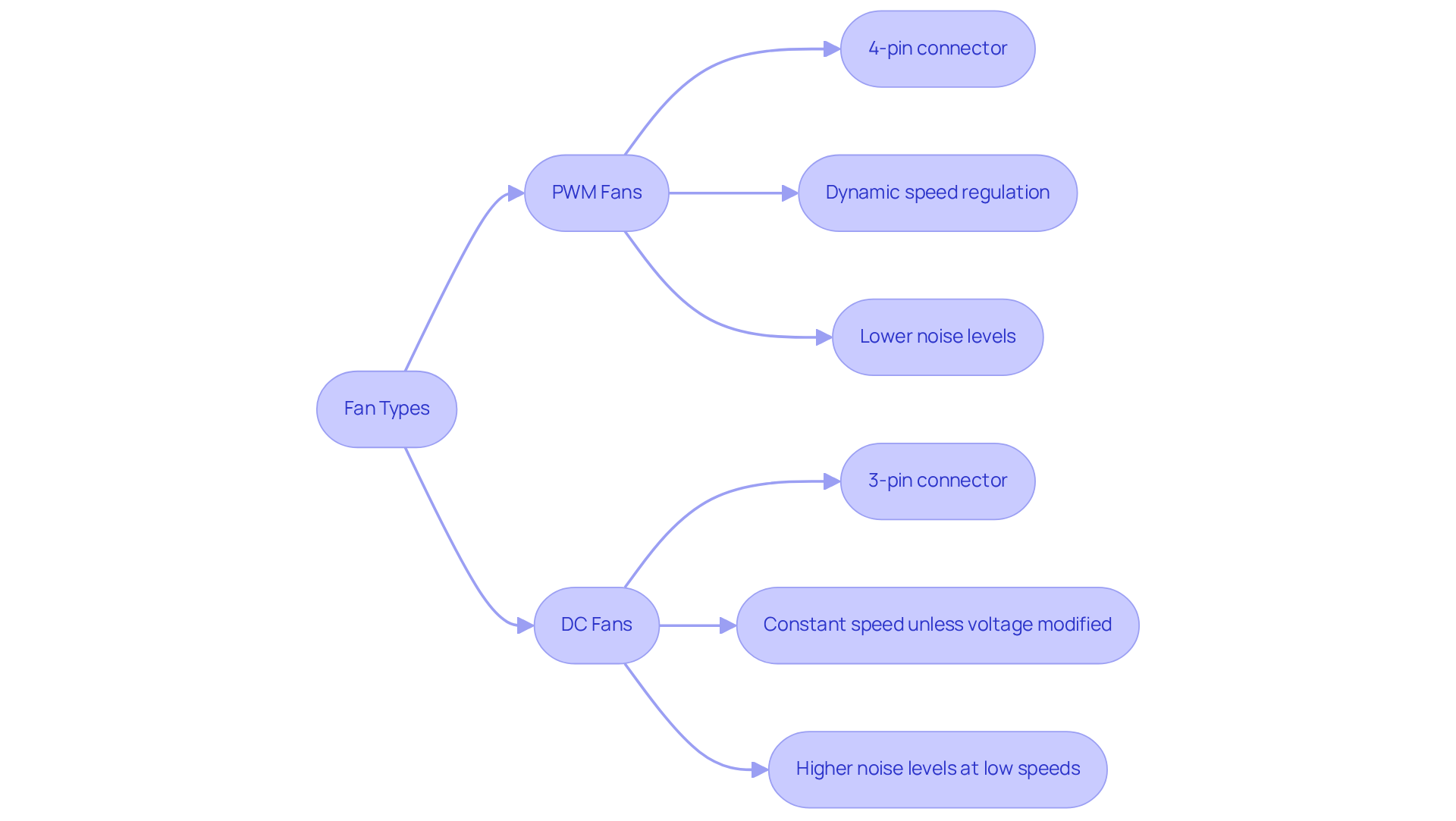
Connector Type: PWM fans are characterized by a four-pin connector, which includes one for power, one for ground, one for tachometer signal, and one for PWM control. In contrast, DC fans typically have a three-pin connector, consisting of power, ground, and tachometer.
-
Speed Regulation: PWM fans can dynamically adjust their operation based on the PWM signal, allowing for more efficient performance. On the other hand, DC fans operate at a constant speed unless the voltage is modified. Gagner-Toomey Associates offers an extensive range of DC input Tube Axial units and Centrifugal Blowers, optimized for performance and efficiency. These products are available in sizes ranging from 15mm to 280mm for Tube Axial units and 15mm to 225mm for Centrifugal Blowers, making them suitable for various applications in electronics and beyond.
-
Noise Levels: PWM fans generally operate more quietly at lower speeds due to their ability to modulate speed effectively. In contrast, DC fans may generate more noise at these speeds. Gagner-Toomey’s fans are engineered with low noise levels in mind, making them ideal for diverse applications across electronics, automotive, and industrial sectors.
Follow Steps to Determine Fan Type
To determine whether your fan is PWM or DC, follow these steps:
-
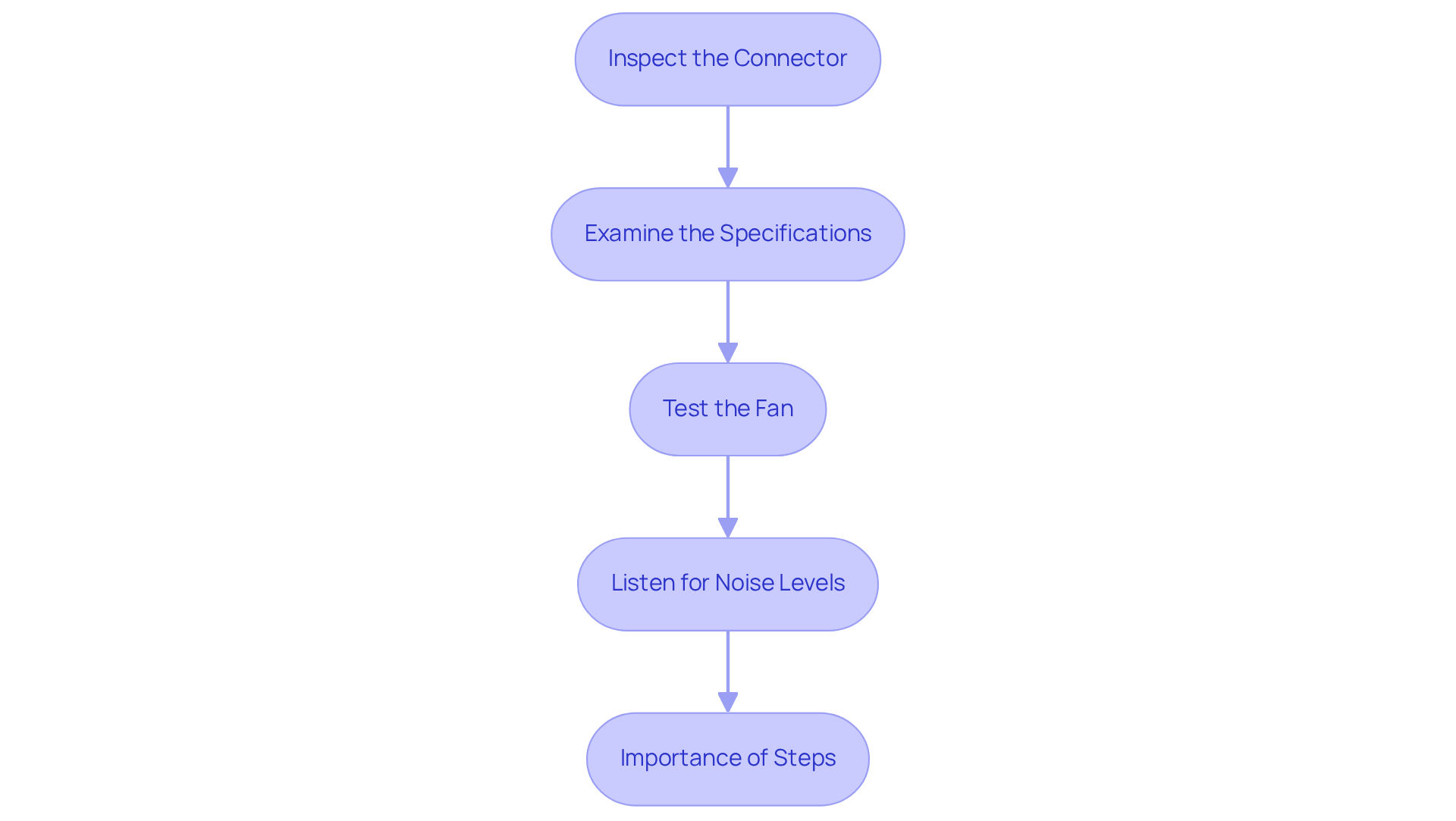
Inspect the Connector: Start by checking the number of pins on the fan plug. A four-pin connector typically indicates a PWM fan, while a three-pin connector signifies a DC fan.
-
Examine the Specifications: Review the fan’s specifications found on the manufacturer’s label or datasheet. PWM fans often showcase features that help users understand how to differentiate between PWM and DC fans, setting them apart from their DC counterparts.
-
Test the Fan: If feasible, connect the fan to a PWM controller and observe its performance. A PWM fan will modify its rate in response to varying PWM signals, whereas a DC fan will remain unaffected by these signals. Utilizing a PWM controller can help in accurately assessing the fan’s response.
-
Listen for Noise Levels: Operate the fan at various settings and pay attention to the noise levels. PWM devices are typically quieter at reduced rates compared to DC models, making them ideal for noise-sensitive uses.
Real-world testing has demonstrated that engineers frequently depend on connector inspection as a reliable technique for identifying types of cooling devices, boasting a high success rate in differentiating between PWM and DC models. Feedback from engineers emphasizes the importance of thorough specification analysis to ensure optimal fan performance in various applications. As noted, “If you’re on a budget or constructing a PC where constant speeds are necessary, DC cooling units will function just as effectively as PWM cooling units.” Furthermore, PWM fans can lead to an estimated 20% decrease in overall energy usage, underscoring their efficiency advantages.
Access Troubleshooting Tips and Resources
If you’re facing challenges in identifying your fan type, follow these essential troubleshooting tips:
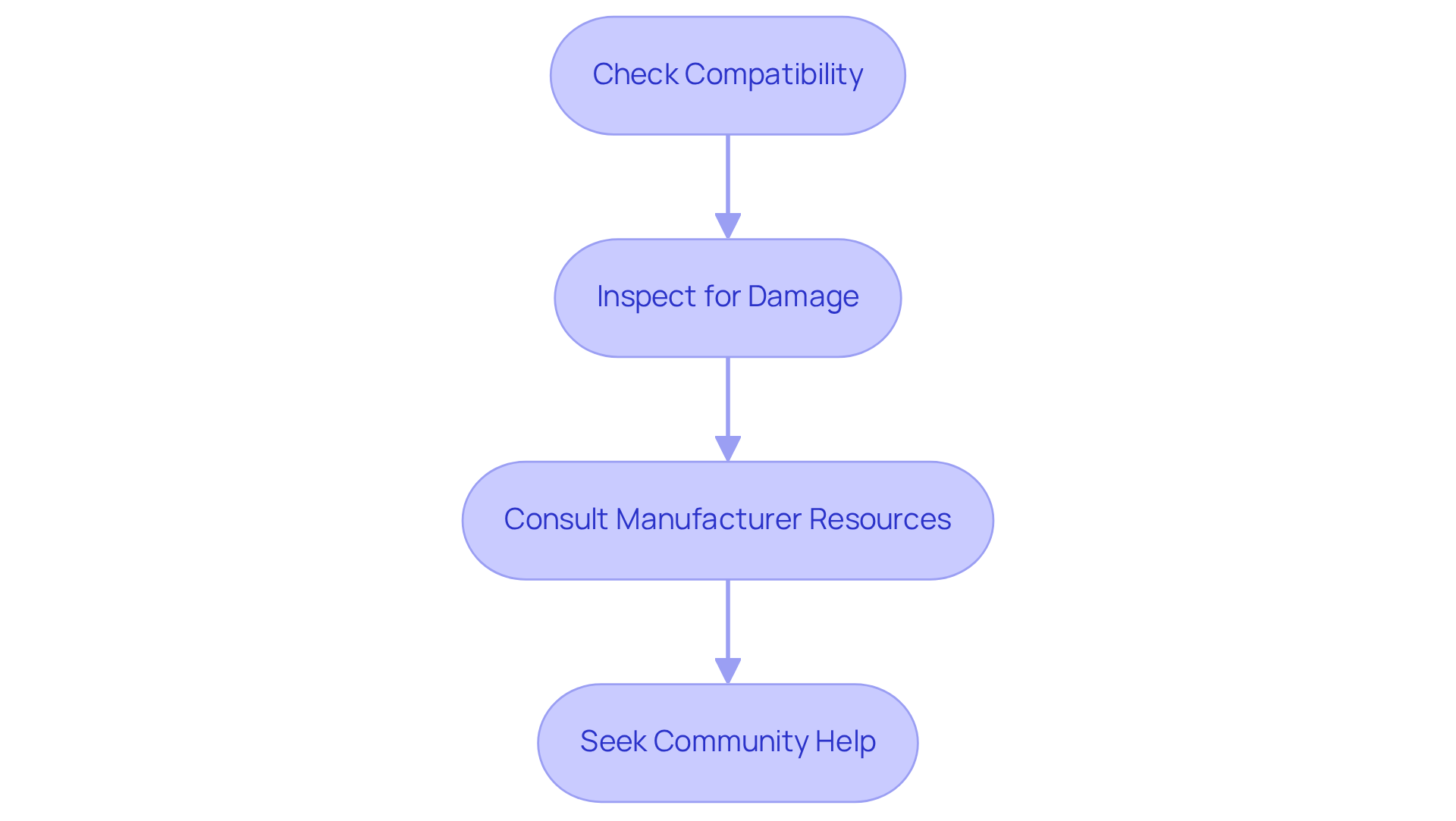
- Check Compatibility: First, confirm that your fan is compatible with the controller you’re using for testing. This step is crucial to ensure proper functionality.
- Inspect for Damage: Next, examine the fan and connectors for any physical damage. Even minor issues can significantly impact performance, so thorough inspection is key.
- Consult Manufacturer Resources: Don’t overlook the value of the manufacturer’s website. It often contains detailed specifications and support documentation that can guide you through the troubleshooting process.
- Seek Community Help: Finally, consider reaching out to online forums and communities. These platforms can provide valuable insights and shared experiences from other users who have faced similar issues.
By following these steps, you can effectively troubleshoot and identify how do I know if my fans are PWM or DC, which will ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinction between PWM and DC fans is essential for optimizing performance across various applications. This guide has provided a thorough overview of the characteristics that set these two fan technologies apart, highlighting the importance of selecting the appropriate type based on operational needs and efficiency objectives.
Key insights include:
- The unique connector types
- Speed regulation methods
- Noise levels associated with PWM and DC fans
By following the outlined steps to inspect connectors, examine specifications, test performance, and listen for noise, users can confidently identify their fan type. Furthermore, troubleshooting tips enhance the ability to address any challenges encountered during the identification process.
Ultimately, recognizing the differences between PWM and DC fans not only aids in making informed purchasing decisions but also contributes to energy efficiency and performance optimization in electronic systems. Embracing these insights can lead to smarter choices that align with sustainability goals, ensuring that the right cooling technology is employed for every unique application.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is PWM technology in fans?
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) technology uses a control signal to adjust the fan’s velocity by modifying the pulse width sent to the motor, leading to enhanced energy efficiency and quieter operation at reduced rates.
How do DC fans operate?
DC fans operate at a constant voltage and achieve speed adjustments by altering the voltage supplied to the device.
What are the advantages of PWM fans over DC fans?
PWM fans offer improved energy efficiency, with potential savings of up to 30% compared to traditional DC models, and provide precise regulation of performance, making them ideal for noise reduction and energy efficiency.
Why is it important to know whether fans are PWM or DC?
Understanding whether fans are PWM or DC is crucial for selecting the appropriate fan technology for specific applications, allowing professionals to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and sustainability goals.
What market share do PWM cooling devices hold?
PWM cooling devices currently command a significant share of the electronics market due to their ability to improve energy efficiency, which is increasingly important in modern designs.

