Introduction
Air cooler heat exchangers (ACHEs) are pivotal in optimizing thermal management across diverse applications, facilitating efficient energy transfer from process fluids to ambient air. Understanding how to select and integrate ACHEs is essential for maximizing performance and reliability. However, navigating the complexities of this critical technology can be daunting.
With numerous factors to consider – from thermal load calculations to material selection – how can one effectively avoid common pitfalls? This guide provides the insights needed to tackle these challenges head-on, ensuring that you can make informed decisions in your ACHE applications.
Understand Air Cooler Heat Exchanger Basics
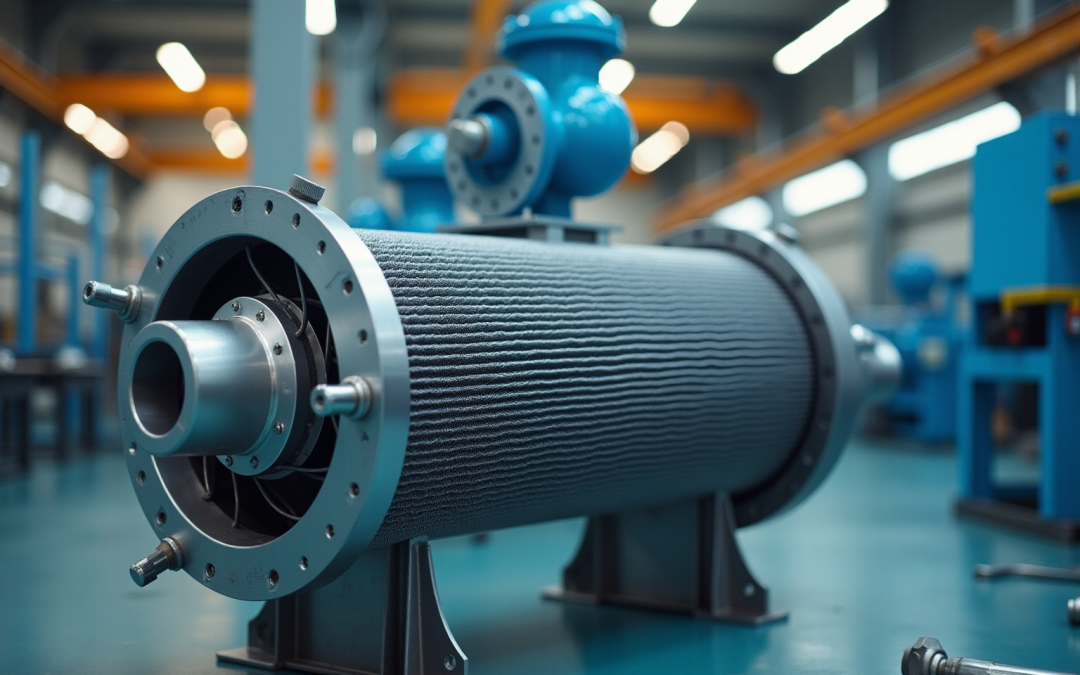
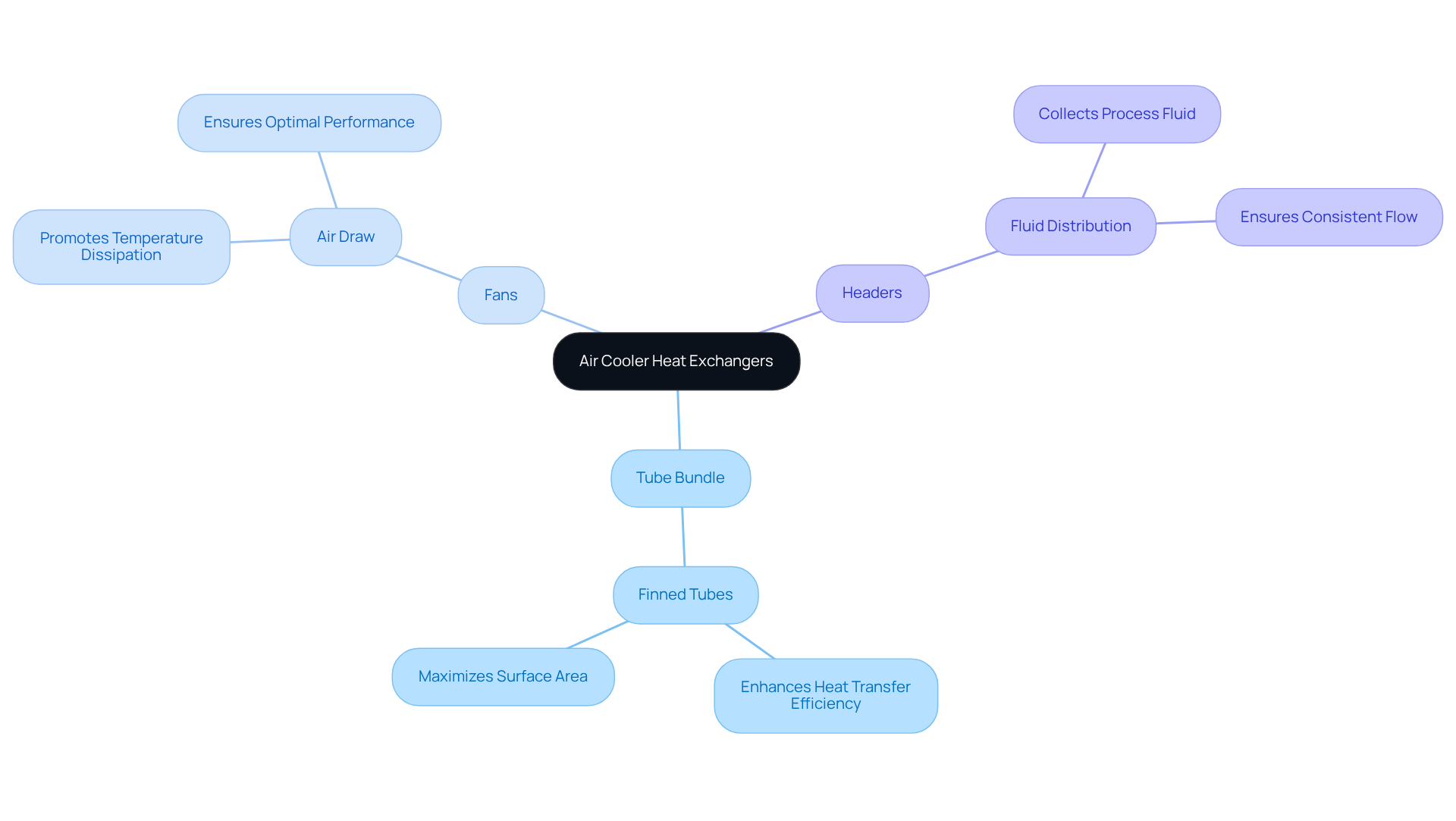
Air cooler heat exchangers (ACHEs) are vital devices that enable the transfer of energy from a process fluid to the surrounding air via convection. This process involves ambient air absorbing heat from the fluid circulating within a series of specialized tubes. Understanding the key components of ACHEs is crucial for effective application:
- Tube Bundle: Comprising finned tubes, this component enhances heat transfer efficiency by maximizing the surface area available for heat exchange.
- Fans: These draw air over the tube bundle, promoting effective temperature dissipation and ensuring optimal performance.
- Headers: Headers are vital for collecting and distributing the process fluid to the tubes, ensuring a consistent flow throughout the system.
A solid grasp of these components and their functions is essential for the effective selection and integration of air cooler heat exchangers across various applications. As you delve deeper into air conditioning systems and their latest technological innovations, understanding concepts such as thermal efficiency, airflow, and pressure drop will be indispensable.
Evaluate Key Selection Criteria
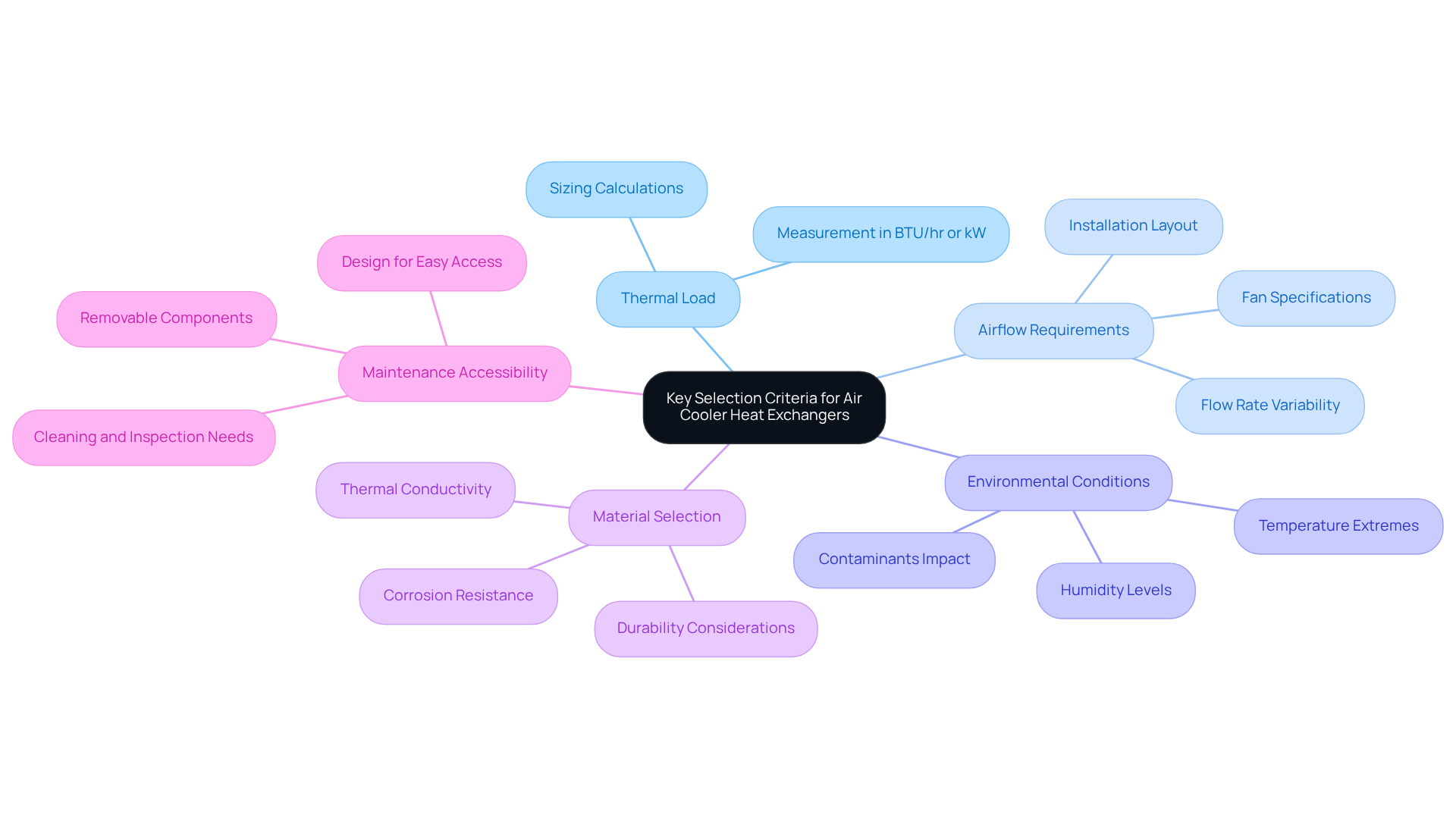
When selecting an air cooler heat exchanger, it’s crucial to evaluate several key criteria to ensure optimal performance and reliability:
-
Thermal Load: Accurately determining the thermal load that needs to be dissipated is essential. This measurement directs the dimensions of the thermal device, ensuring it can manage the necessary temperature transfer efficiently. Understanding the thermal duty requirement, typically measured in BTU/hr or kW, is vital for sizing calculations.
-
Airflow Requirements: Assessing the necessary airflow is vital for achieving the desired cooling effect. This involves evaluating fan specifications and the layout of the installation site. Airflow needs for industrial air cooler heat exchanger thermal devices can vary significantly depending on the application, with specific designs needing to handle different flow rates to enhance thermal transfer.
-
Environmental Conditions: The operational surroundings significantly impact the performance of thermal transfer devices. Factors such as temperature extremes, humidity levels, and potential contaminants must be considered, as they can affect the efficiency and longevity of the unit. For example, air cooler heat exchangers are particularly advantageous in areas where water is scarce, but they may encounter performance constraints in extreme ambient temperatures.
-
Material Selection: Choosing the right materials is critical for durability and efficiency. Materials must withstand operating conditions, including corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity. Investing in corrosion-resistant materials minimizes the risk of leaks and unscheduled shutdowns, which can be costly.
-
Maintenance Accessibility: Ensuring that the design allows for easy maintenance and access to components is essential for long-term reliability. Removable tube bundles, for instance, facilitate thorough cleaning and inspection, especially in fouling applications where regular maintenance is necessary.
By thoroughly assessing these criteria, you can select an air conditioning unit that not only meets your specific requirements but also guarantees dependable and effective performance throughout its operational lifespan.
Implement and Integrate the Air Cooler Heat Exchanger
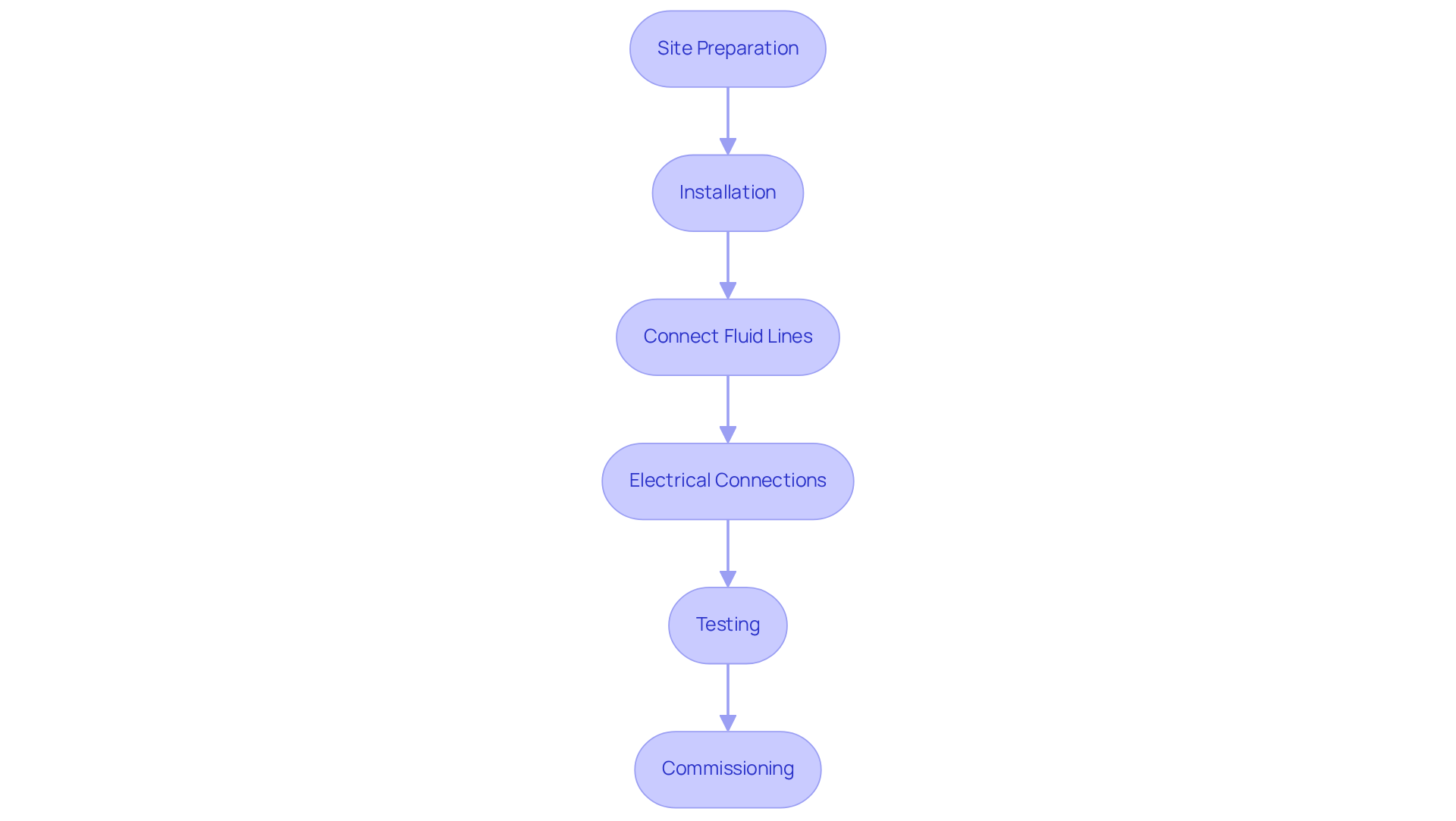
To successfully implement and integrate your air cooler heat exchanger, follow these essential steps:
-
Site Preparation: Start by ensuring the installation site is clean and free of obstructions. Confirm that the space can adequately support the dimensions and mass of the thermal device.
-
Installation: Securely attach the thermal transfer unit according to the manufacturer’s specifications. It’s crucial that the unit is level and stable to prevent any vibrations that could affect performance.
-
Connect Fluid Lines: Next, connect the inlet and outlet fluid lines to the thermal device. Use appropriate fittings and ensure that all connections are leak-free to maintain system integrity.
-
Electrical Connections: If your unit includes fans or controls, connect the electrical components according to the wiring diagram provided by the manufacturer. This step is vital for ensuring proper operation.
-
Testing: Before full operation, conduct a thorough test run. Check for leaks, ensure proper airflow, and assess overall functionality. Monitor the system for any unusual noises or vibrations that could indicate issues.
-
Commissioning: Once testing is complete, fully commission the system by adjusting settings for optimal performance based on the thermal load and environmental conditions.
By following these steps, you will ensure a successful integration of your air conditioning unit with the air cooler heat exchanger in your cooling system, maximizing both efficiency and reliability.
Troubleshoot Common Issues and Challenges
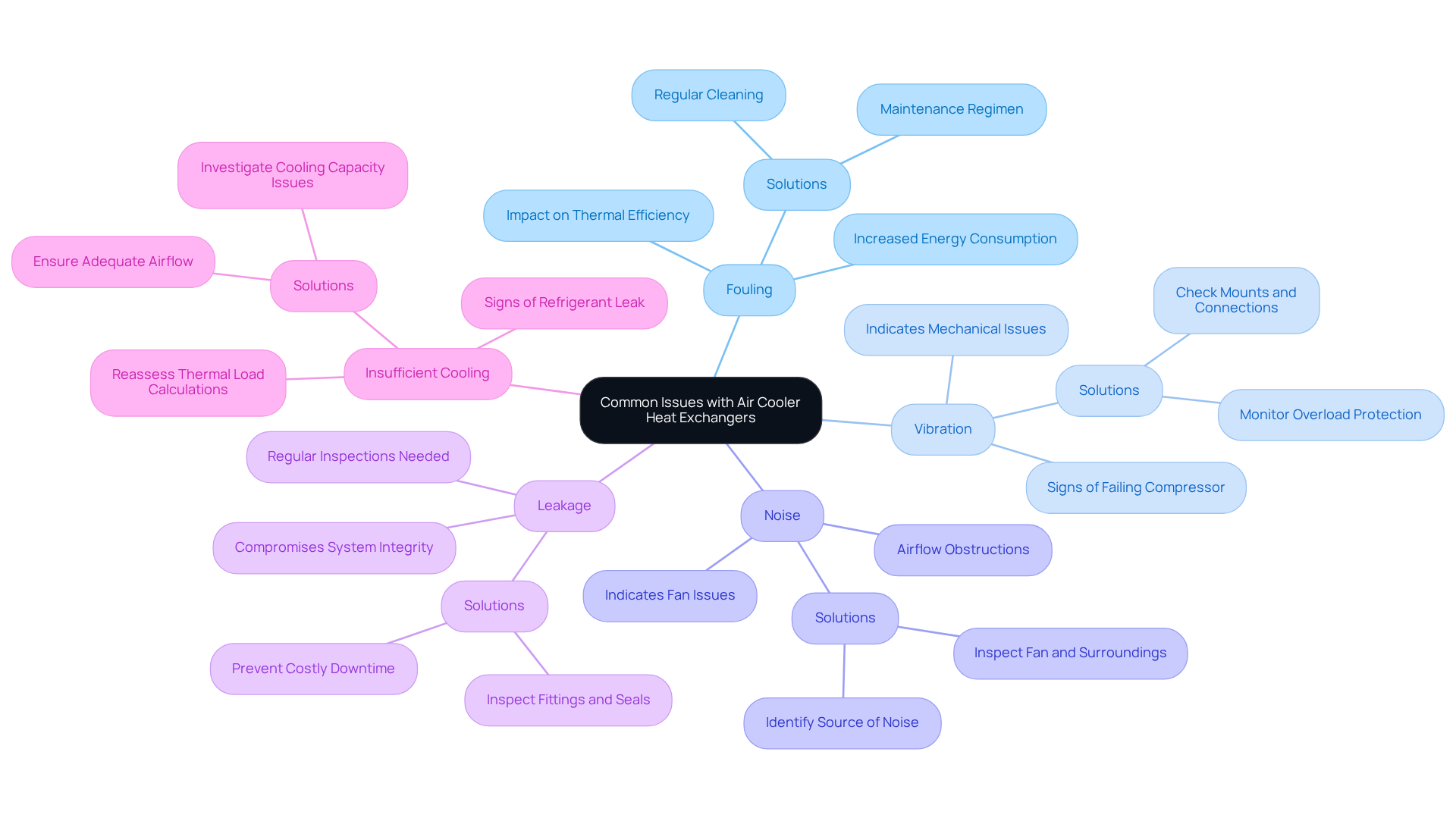
Common issues with air cooler heat exchangers include:
-
Fouling: The buildup of dirt and debris on the fins significantly reduces thermal transfer efficiency, often leading to increased energy consumption. In fact, fouling can decrease the overall thermal transfer coefficient by as much as 51.60%. Regular cleaning and a strict maintenance regimen are essential to prevent fouling, as fouled coils can force the system to work harder, raising operational costs.
-
Vibration: Excessive vibration can indicate loose components or misalignment, which may lead to mechanical failures. Increased vibration can also be a sign of a failing compressor. It is crucial to check all mounts and connections for security. Frequent tripping of the compressor’s overload protection may also signal underlying vibration issues that need addressing.
-
Noise: Unusual noises, such as grinding or knocking, may signal fan issues or airflow obstructions. These noises can indicate internal wear or operational issues. Inspecting the fan and surrounding areas for blockages can help identify the source of the noise, ensuring smooth operation.
-
Leakage: Fluid leaks often occur at connection points, which can compromise system integrity. Regular inspections of all fittings and seals are necessary to maintain operational reliability and prevent costly downtime.
-
Insufficient Cooling: If the system fails to cool effectively, it is vital to reassess thermal load calculations and ensure that airflow is adequate. Signs of a refrigerant leak, such as decreased cooling capacity and unusually low suction pressure, should also be investigated to avoid further complications. High energy consumption is often caused by fouled condenser or evaporator coils, incorrect refrigerant charge, or poor water treatment, leading to scale buildup.
By being aware of these common challenges and implementing proactive solutions, engineers can enhance the efficiency and reliability of the air cooler heat exchanger.
Conclusion
Mastering the selection and integration of air cooler heat exchangers is crucial for optimizing energy transfer across various applications. Understanding their fundamental components – such as tube bundles, fans, and headers – provides a solid foundation for effective implementation. By carefully evaluating key selection criteria, including thermal load, airflow requirements, environmental conditions, material selection, and maintenance accessibility, engineers can ensure that the chosen unit meets specific operational demands.
This article has shared critical insights into the necessary steps for successful integration, from site preparation and installation to testing and commissioning. Moreover, being aware of common challenges – like fouling, vibration, noise, leakage, and insufficient cooling – equips engineers with the knowledge needed to troubleshoot and maintain these systems effectively.
The significance of air cooler heat exchangers in enhancing system efficiency cannot be overstated. By applying the best practices highlighted in this guide, engineers and technicians can improve performance and reliability while contributing to energy savings and sustainability in their operations. Embracing these principles will lead to a more efficient and effective cooling solution, ensuring optimal performance in any setting.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary function of air cooler heat exchangers (ACHEs)?
ACHEs enable the transfer of energy from a process fluid to the surrounding air via convection, allowing ambient air to absorb heat from the circulating fluid.
What are the key components of an air cooler heat exchanger?
The key components of an ACHE include the tube bundle, fans, and headers.
How does the tube bundle contribute to the efficiency of ACHEs?
The tube bundle, which comprises finned tubes, enhances heat transfer efficiency by maximizing the surface area available for heat exchange.
What role do fans play in the operation of air cooler heat exchangers?
Fans draw air over the tube bundle, promoting effective temperature dissipation and ensuring optimal performance of the heat exchanger.
What is the purpose of headers in an air cooler heat exchanger?
Headers are vital for collecting and distributing the process fluid to the tubes, ensuring a consistent flow throughout the system.
Why is it important to understand the components and functions of ACHEs?
A solid grasp of these components and their functions is essential for the effective selection and integration of air cooler heat exchangers across various applications.
What concepts should one be familiar with when exploring air conditioning systems and ACHEs?
Understanding concepts such as thermal efficiency, airflow, and pressure drop is indispensable when delving into air conditioning systems and their latest technological innovations.

