Overview
The article delineates four essential steps for mastering the design of air-to-air heat exchangers. It emphasizes the necessity of understanding the various types, applying sound design principles, and effectively troubleshooting common challenges. These steps underscore the significance of:
- Thermal transfer calculations
- Airflow requirements
- Material selection
It also addresses critical issues such as air leakage and fouling. By focusing on these elements, the article aims to enhance efficiency and performance within HVAC applications.
Introduction
Air-to-air heat exchangers are becoming indispensable in the pursuit of energy efficiency and enhanced indoor air quality. These innovative devices facilitate the transfer of thermal energy between air streams, significantly reducing energy consumption while improving comfort in both residential and commercial environments.
However, the design and implementation of these systems present unique challenges that necessitate careful consideration. Engineers must master the intricacies of air-to-air heat exchanger design to maximize their benefits and navigate common pitfalls effectively.
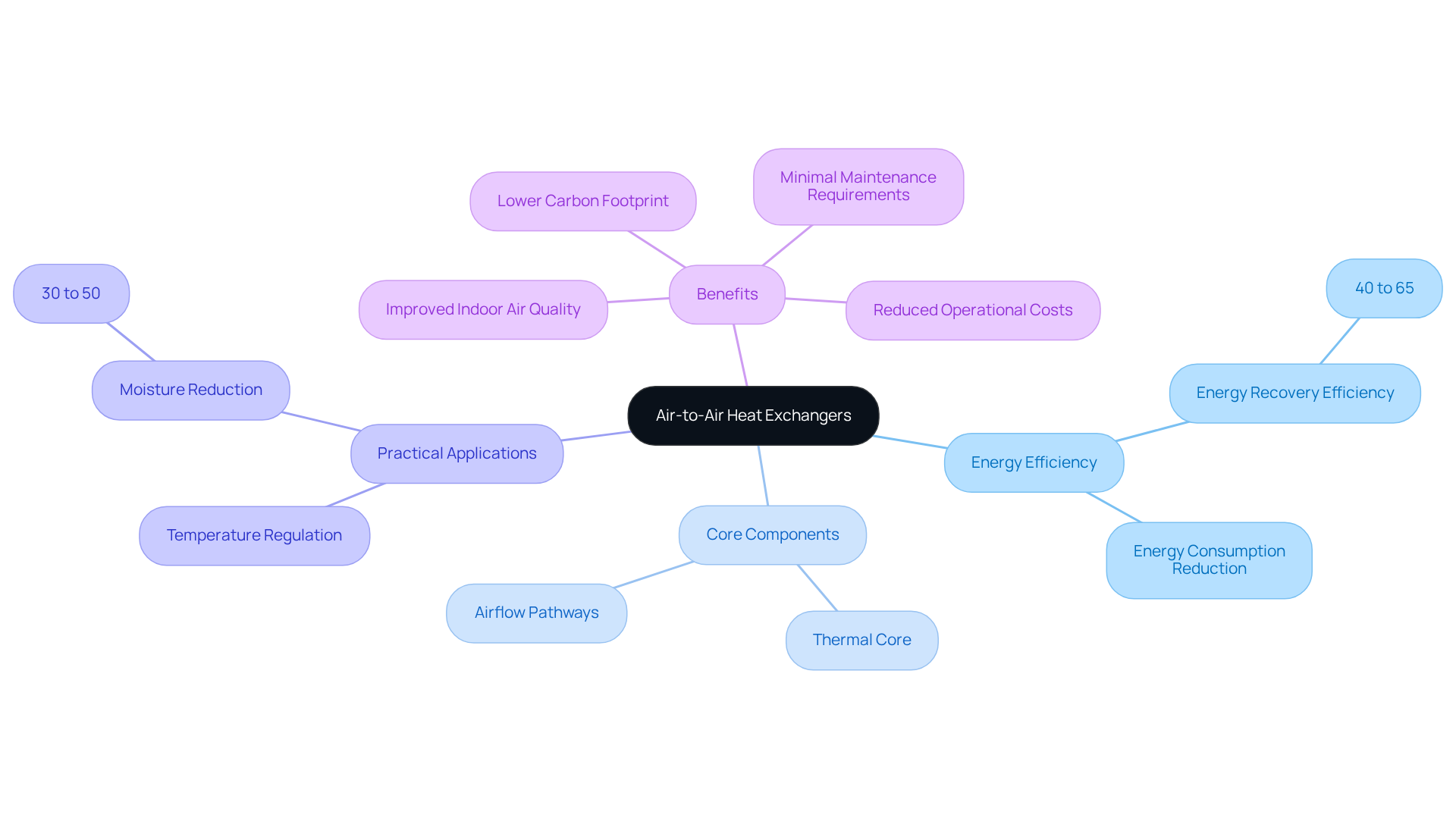
Understand Air-to-Air Heat Exchangers
Air-to-air thermal devices serve as essential instruments that facilitate the transfer of thermal energy between distinct air streams without allowing them to mix. Widely utilized in HVAC systems, these devices significantly enhance energy efficiency by reclaiming heat from exhaust air and employing it to precondition incoming fresh air. This innovative mechanism not only reduces energy consumption but also improves indoor air quality by ensuring a consistent influx of fresh air. Indeed, plate air-to-air thermal devices can achieve energy recovery efficiencies between 40% and 65%, establishing them as invaluable assets in both residential and commercial environments.
The core components of an air-to-air thermal device, including the thermal core and airflow pathways, are critical to its operational efficiency. These systems are meticulously engineered to minimize operational costs and carbon footprints, thereby contributing to a more sustainable environment. Furthermore, they can reduce moisture levels by 30% to 50%, which aids in preventing mold and mildew growth, further enhancing indoor air quality.
In practical applications, air-to-air thermal devices are vital for maintaining comfortable and regulated temperatures, significantly lowering energy expenses. Their straightforward installation process, typically completed in under a day, combined with minimal maintenance requirements, positions them as an appealing alternative to conventional HVAC systems. As manufacturers collaborate with air quality experts to refine these systems, the benefits of air to air heat exchanger design in HVAC contexts continue to expand, solidifying their role in modern energy-efficient building designs.
Explore Types of Air-to-Air Heat Exchangers
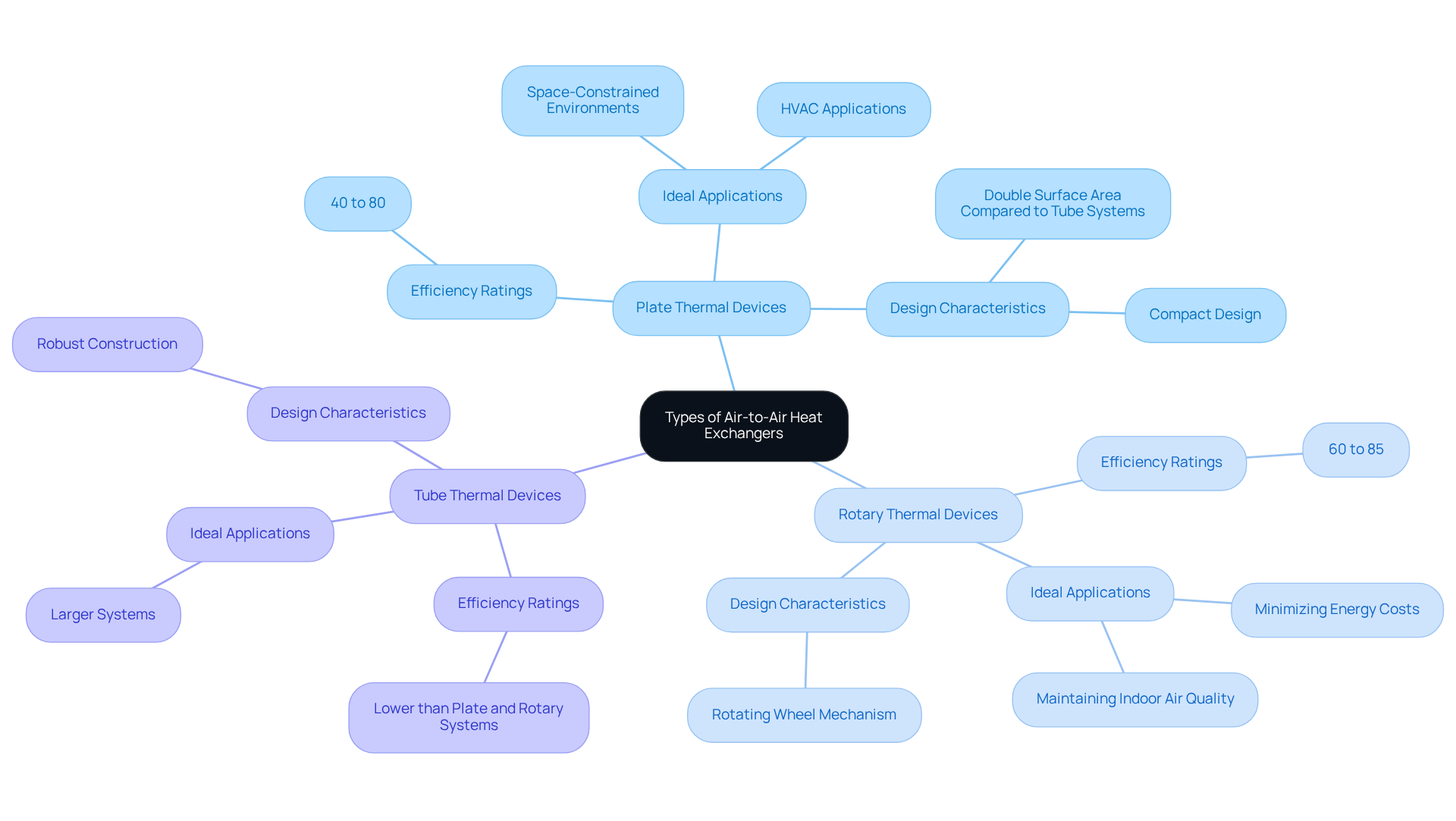
Various air to air heat exchanger designs are available, each specifically tailored to meet distinct applications and efficiency requirements.
-
Plate Thermal Devices: These systems consist of thin plates stacked together, facilitating efficient temperature transfer between air streams. Their compact design renders them ideal for space-constrained environments, and they can provide over double the surface area for thermal transfer compared to tube-type systems, significantly enhancing their efficiency in HVAC applications. Efficiency ratings for plate thermal devices typically range from 40% to 80%, making them a robust choice for a variety of applications.
-
Rotary Thermal Devices: Utilizing a rotating wheel, these systems excel in transferring energy between air flows and achieving high thermal recovery efficiency. With efficiency ratings spanning from 60% to 85%, they are especially advantageous in scenarios where maintaining indoor air quality while minimizing energy costs is paramount.
-
Tube Thermal Devices: Characterized by tubes that permit one air stream to pass through while another flows around them, tube thermal devices are known for their robustness and are frequently employed in larger systems. Although their design facilitates efficient thermal transfer, they generally exhibit lower efficiency ratings compared to plate and rotary systems.
By understanding the distinct advantages and applications of air to air heat exchanger design, engineers are empowered to make informed decisions that align with their specific project needs, ultimately enhancing both efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Apply Design Principles and Calculations
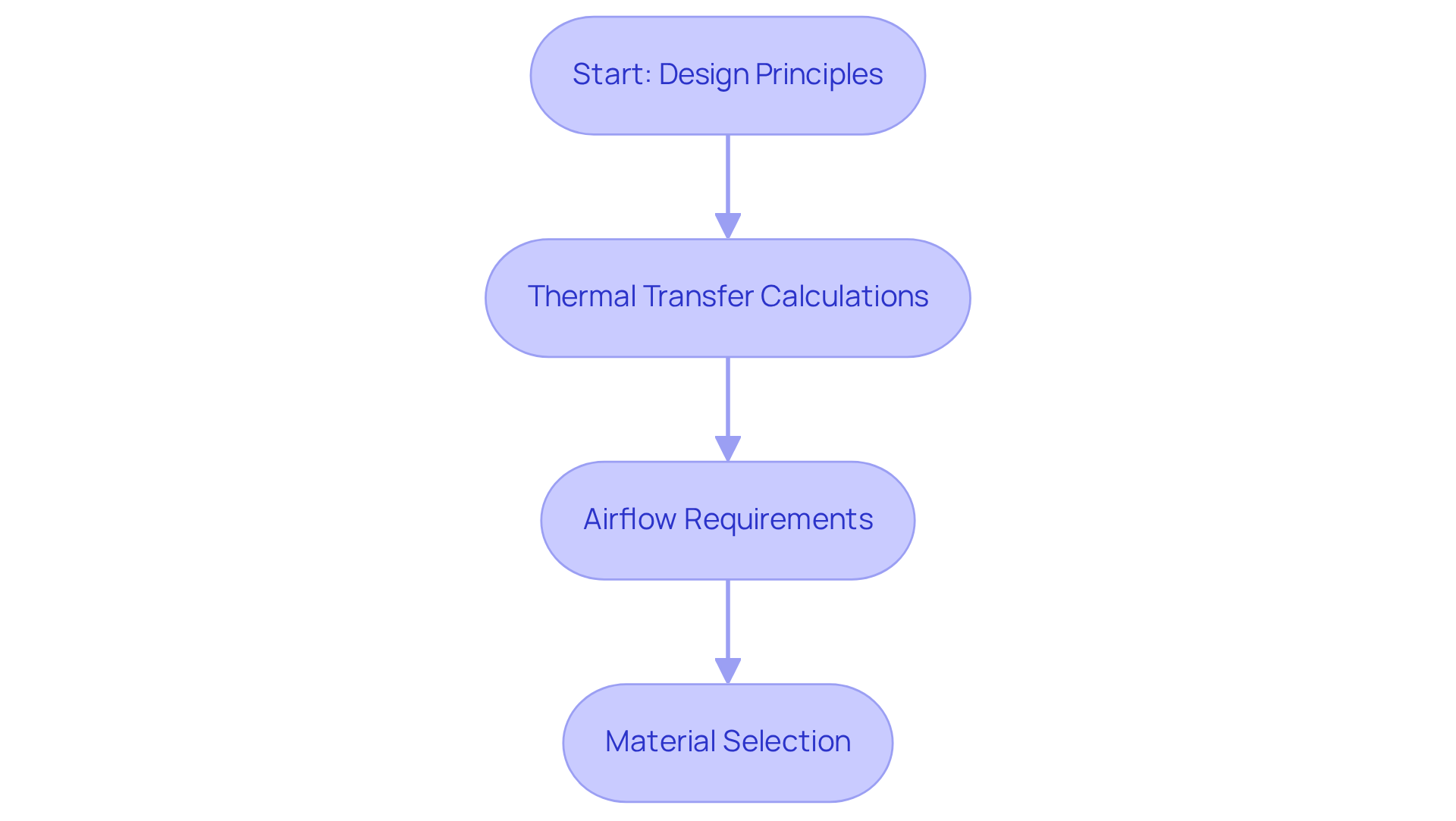
The design of an air to air heat exchanger requires a complex task that necessitates a thorough understanding of several key principles and calculations to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency.
Thermal Transfer Calculations: The first step is to determine the necessary thermal transfer rate, which is contingent upon the temperature difference between the incoming and outgoing air streams. The formula to calculate this is:
Q = U × A × ΔT
where Q represents the heat transfer rate, U denotes the overall heat transfer coefficient, A is the heat transfer area, and ΔT indicates the temperature difference. This calculation is fundamental to effective design.
Airflow Requirements: Next, it is crucial to calculate the necessary airflow rates to guarantee sufficient temperature exchange. This process involves a comprehensive understanding of the specific application and the desired indoor air quality, which ultimately influences the design choices.
Material Selection: Finally, selecting appropriate materials is vital. The chosen materials must withstand the operating conditions, including temperature and humidity levels, while ensuring minimal thermal resistance. This selection process directly impacts the efficiency and durability of the heat exchanger.
By applying these principles, engineers can design effective air to air heat exchanger designs tailored for specific applications, ensuring not only optimal performance but also significant energy savings.
Troubleshoot Common Design Challenges
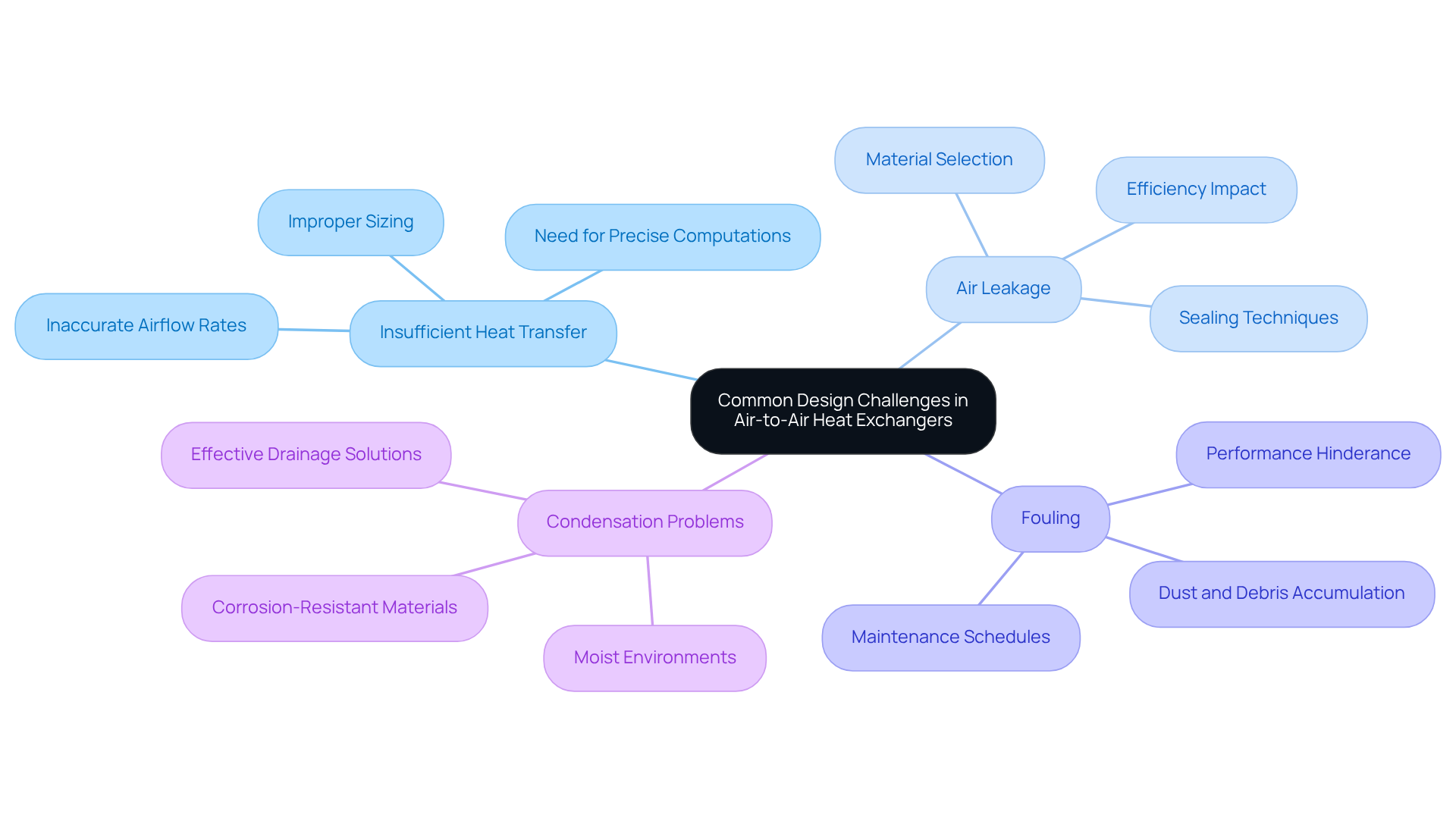
Common design challenges in air-to-air heat exchangers include:
-
Insufficient Heat Transfer: This challenge arises from improper sizing or airflow rates. It is essential to ensure that computations for thermal transfer and airflow are precise, and that the thermal device is suitably sized for the specific use case.
-
Air Leakage: Leakage between the two air streams can significantly diminish efficiency. Employing proper sealing techniques and materials is crucial to minimizing leakage.
-
Fouling: The accumulation of dust and debris can hinder performance. Establishing regular maintenance and cleaning schedules is vital to ensure optimal operation.
-
Condensation Problems: In moist environments, condensation may develop inside the thermal device, potentially causing harm. Design considerations should incorporate effective drainage solutions and materials resistant to corrosion.
By proactively addressing these challenges, engineers can enhance the reliability and efficiency of air-to-air heat exchangers, ensuring they meet the demands of their specific applications.
Conclusion
Air-to-air heat exchangers are crucial for enhancing energy efficiency and improving indoor air quality across diverse applications. By enabling the transfer of thermal energy between air streams without mixing them, these devices conserve energy and significantly contribute to the sustainability of HVAC systems. A thorough understanding of their design and operational principles is essential for maximizing their benefits in both residential and commercial settings.
This article provides key insights into various types of air-to-air heat exchangers, including:
- Plate designs
- Rotary designs
- Tube designs
Each is tailored to meet specific efficiency requirements and applications. The significance of precise thermal transfer calculations, airflow requirements, and material selection is emphasized, alongside common design challenges such as:
- Insufficient heat transfer
- Air leakage
- Fouling
Addressing these challenges proactively allows engineers to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
The integration of air-to-air heat exchangers in modern HVAC systems marks a significant advancement in energy efficiency and indoor air quality management. As the demand for sustainable building solutions increases, embracing these technologies will not only reduce operational costs but also foster a healthier environment. Engaging with the latest innovations and best practices in air-to-air heat exchanger design is crucial for professionals aiming to optimize their systems and meet evolving energy standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are air-to-air heat exchangers?
Air-to-air heat exchangers are thermal devices that facilitate the transfer of thermal energy between distinct air streams without allowing them to mix, commonly used in HVAC systems.
How do air-to-air heat exchangers improve energy efficiency?
They reclaim heat from exhaust air to precondition incoming fresh air, which reduces energy consumption and enhances energy efficiency.
What is the energy recovery efficiency range for plate air-to-air thermal devices?
Plate air-to-air thermal devices can achieve energy recovery efficiencies between 40% and 65%.
What benefits do air-to-air heat exchangers provide for indoor air quality?
They improve indoor air quality by ensuring a consistent influx of fresh air and can reduce moisture levels by 30% to 50%, which helps prevent mold and mildew growth.
What are the core components of an air-to-air thermal device?
The core components include the thermal core and airflow pathways, which are critical to the device’s operational efficiency.
How do air-to-air heat exchangers contribute to sustainability?
They are engineered to minimize operational costs and carbon footprints, contributing to a more sustainable environment.
What are the practical benefits of using air-to-air heat exchangers in HVAC systems?
They help maintain comfortable and regulated temperatures, significantly lower energy expenses, and have a straightforward installation process with minimal maintenance requirements.
How long does it typically take to install an air-to-air heat exchanger?
The installation process is typically completed in under a day.
How are manufacturers improving air-to-air heat exchangers?
Manufacturers are collaborating with air quality experts to refine these systems, expanding their benefits in HVAC contexts and solidifying their role in modern energy-efficient building designs.

