Overview
The article delves into the various types, operational mechanisms, and selection tips for computer exhaust fans, underscoring their vital role in sustaining optimal operating temperatures within computer systems. It elucidates different fan types, including axial and centrifugal blowers, alongside their operational principles. Furthermore, it outlines essential selection criteria such as airflow requirements and noise levels, which collectively assist users in identifying the most suitable exhaust fan tailored to their specific cooling needs.
Introduction
The performance and longevity of computer systems hinge significantly on effective cooling mechanisms, with exhaust fans playing a pivotal role in this process. These specialized devices are designed to expel warm air generated by critical components, ensuring optimal operating temperatures and preventing potential hardware failures.
However, with various types of exhaust fans available, each tailored for specific applications, how can users determine the best fit for their unique cooling needs?
This article delves into the different types of computer exhaust fans, their operational principles, and essential selection tips, ultimately guiding readers toward making informed choices for enhanced system performance.
Define Computer Exhaust Fans and Their Importance
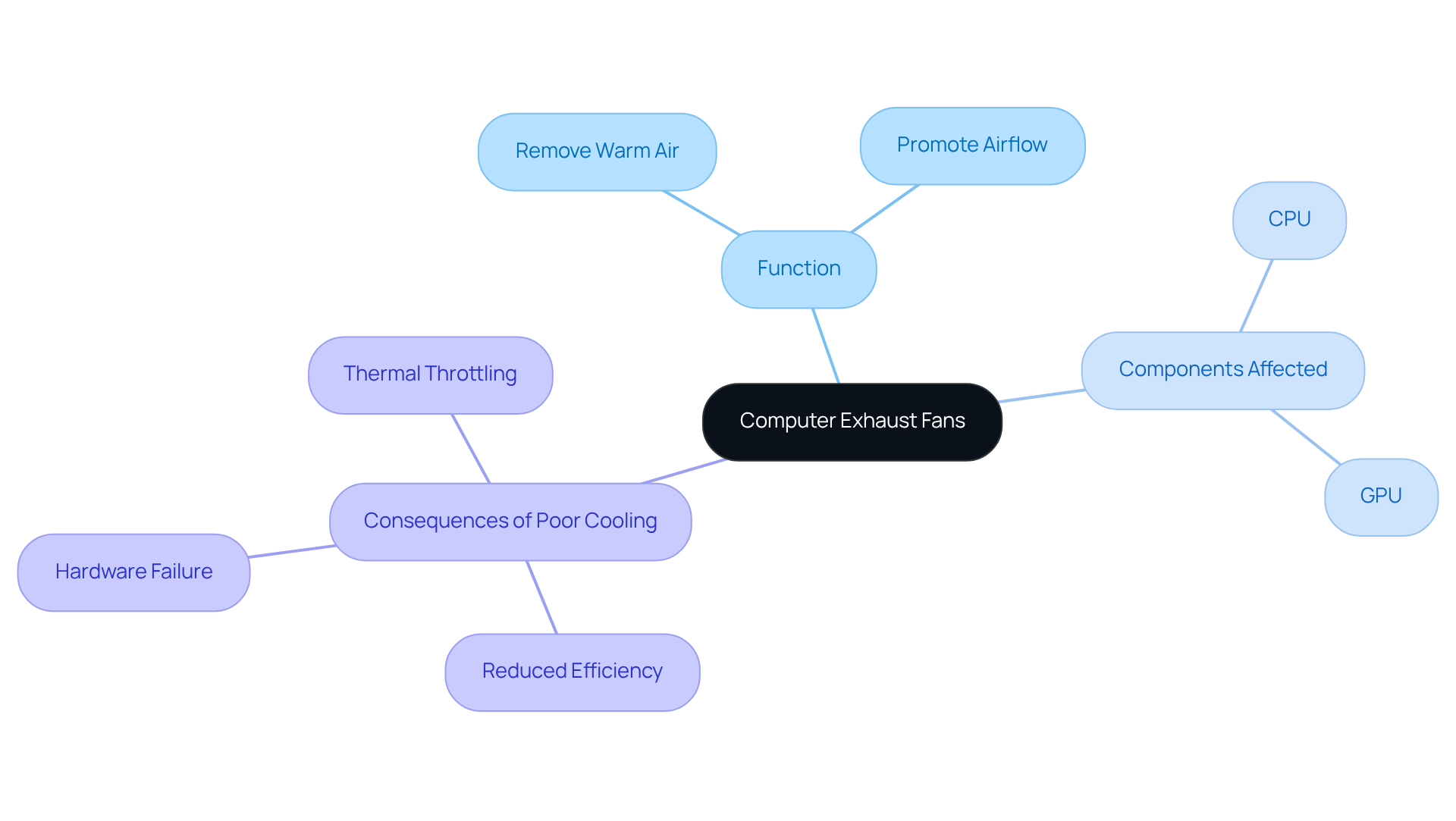
The computer exhaust fan is a specialized device designed to effectively remove warm air from within a computer casing. Their primary function is to maintain optimal operating temperatures by using a computer exhaust fan to eliminate heated air generated by critical components such as the CPU and GPU. This function is vital, as excessive heat can lead to thermal throttling, reduced efficiency, and even hardware failure.
By promoting airflow, ventilation systems play a crucial role in establishing a balanced cooling atmosphere, which is essential for the durability and effectiveness of electronic devices. When properly configured, ventilation systems, such as the computer exhaust fan, can significantly enhance the of a computer, making them an indispensable component of any construction or enhancement.
Explore Different Types of Computer Exhaust Fans
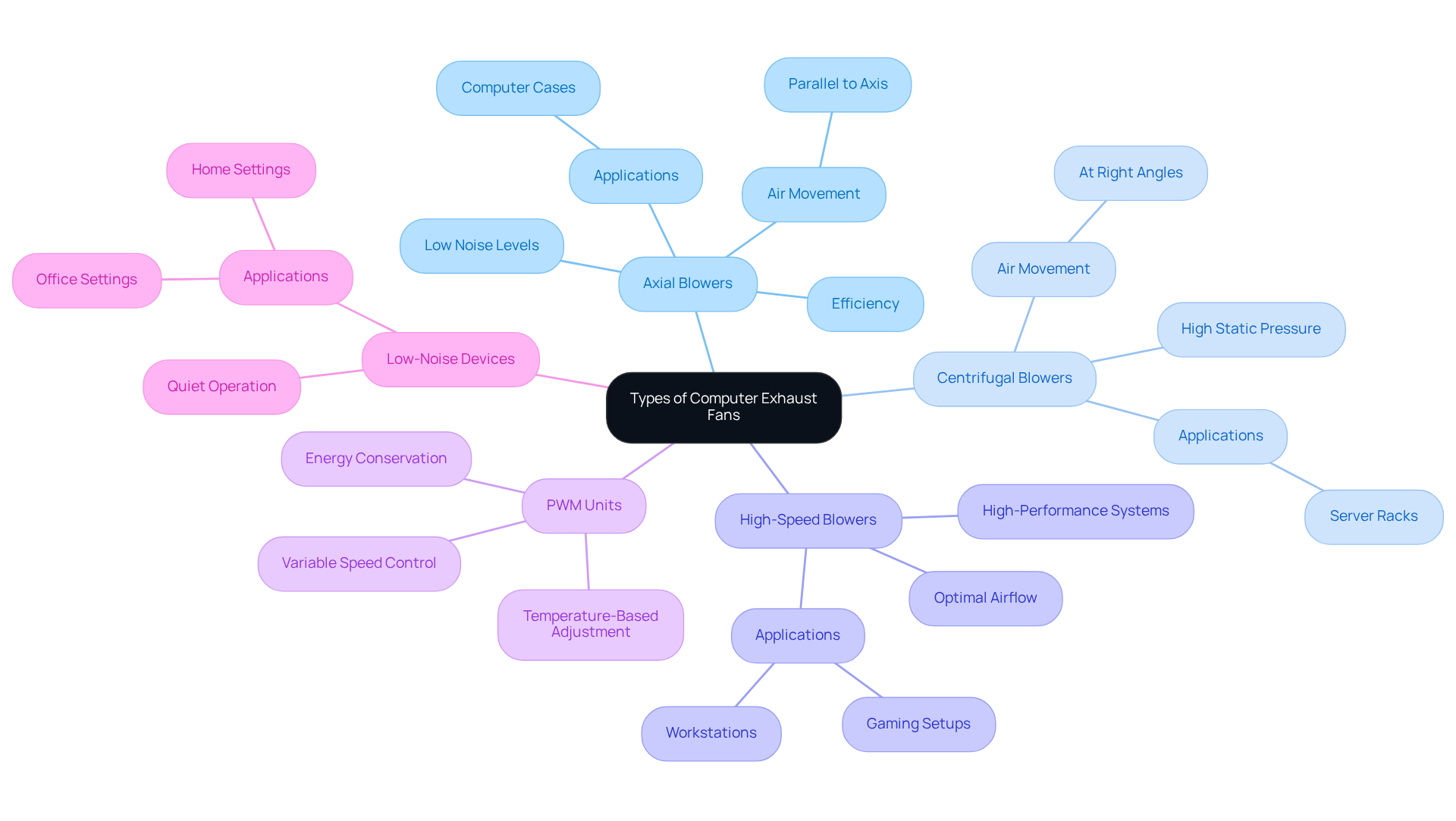
There are several types of computer exhaust fans, each specifically designed for various applications to ensure optimal cooling performance in different environments.
- Axial Blowers: The most prevalent variety of exhaust devices, axial blowers are characterized by their ability to move air parallel to the unit’s axis. Their efficiency and low noise levels make them the preferred choice for computer cases, where effective airflow is crucial.
- Centrifugal Blowers: Also known as blower units, these devices operate by moving air at right angles to the intake. They are particularly effective in scenarios that require higher static pressure, making them suitable for dense environments such as server racks, where air circulation is vital for equipment longevity.
- High-Speed Blowers: Engineered for optimal airflow, high-speed blowers are ideal for high-performance systems that generate significant heat, including gaming setups and workstations. Their capacity to handle increased thermal loads ensures system stability and performance.
- PWM Units: Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) units enable variable speed control, allowing users to adjust fan speeds based on temperature fluctuations. This capability not only results in quieter operation but also promotes energy conservation, aligning performance with environmental considerations.
- Low-Noise Devices: Specifically designed to operate quietly, these units are well-suited for home or office settings where sound levels are a concern. Their design prioritizes noise reduction without compromising cooling efficiency.
Understanding these types of computer exhaust fans is essential for users aiming to select the right fan tailored to their , ensuring optimal performance and longevity of their systems.
Understand How Computer Exhaust Fans Operate
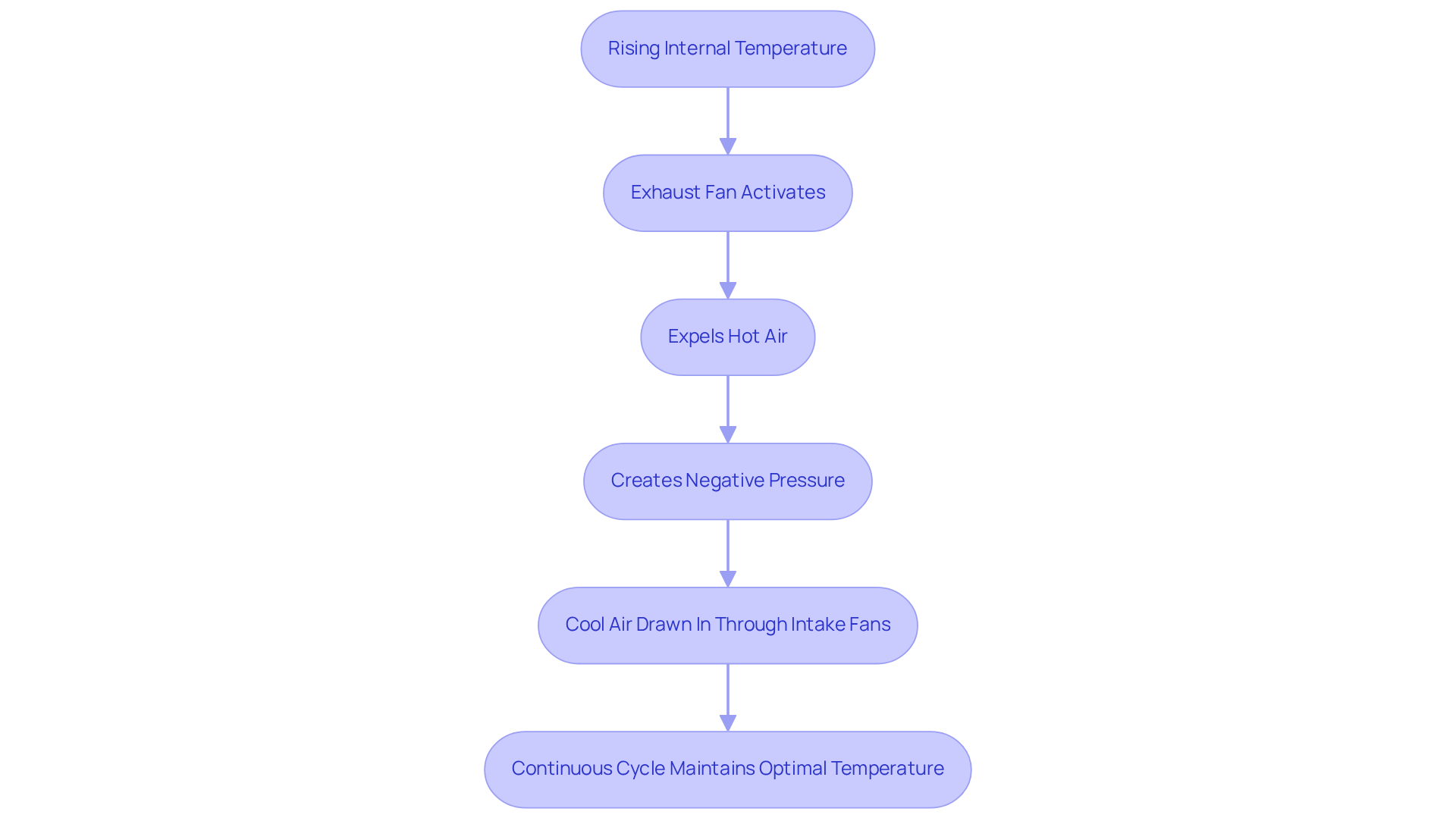
Computer cooling devices operate based on the principles of airflow and pressure differences. When the internal temperature of a computer case rises, the computer activates to expel hot air, creating a negative pressure environment that allows cooler air to be drawn in from outside the case through intake fans. This continuous cycle of air movement is essential for maintaining optimal temperatures.
Key components of exhaust fan operation include:
- Fan Blades: The design and angle of the blades are critical, as they determine the airflow rate and pressure. Various configurations can significantly enhance effectiveness for specific applications.
- Motor: The motor drives the fan blades, and its efficiency directly impacts the fan’s operation and noise levels.
- Control Systems: Many modern cooling devices are equipped with integrated sensors and controllers that adjust speed based on temperature readings, ensuring effective cooling while minimizing noise.
By understanding these elements, users can more effectively set up and maintain their ventilation systems, optimizing functionality and performance.
Evaluate Key Considerations for Selecting and Configuring Exhaust Fans
When selecting and configuring exhaust fans, it is crucial to consider several key factors that will impact the of your system.
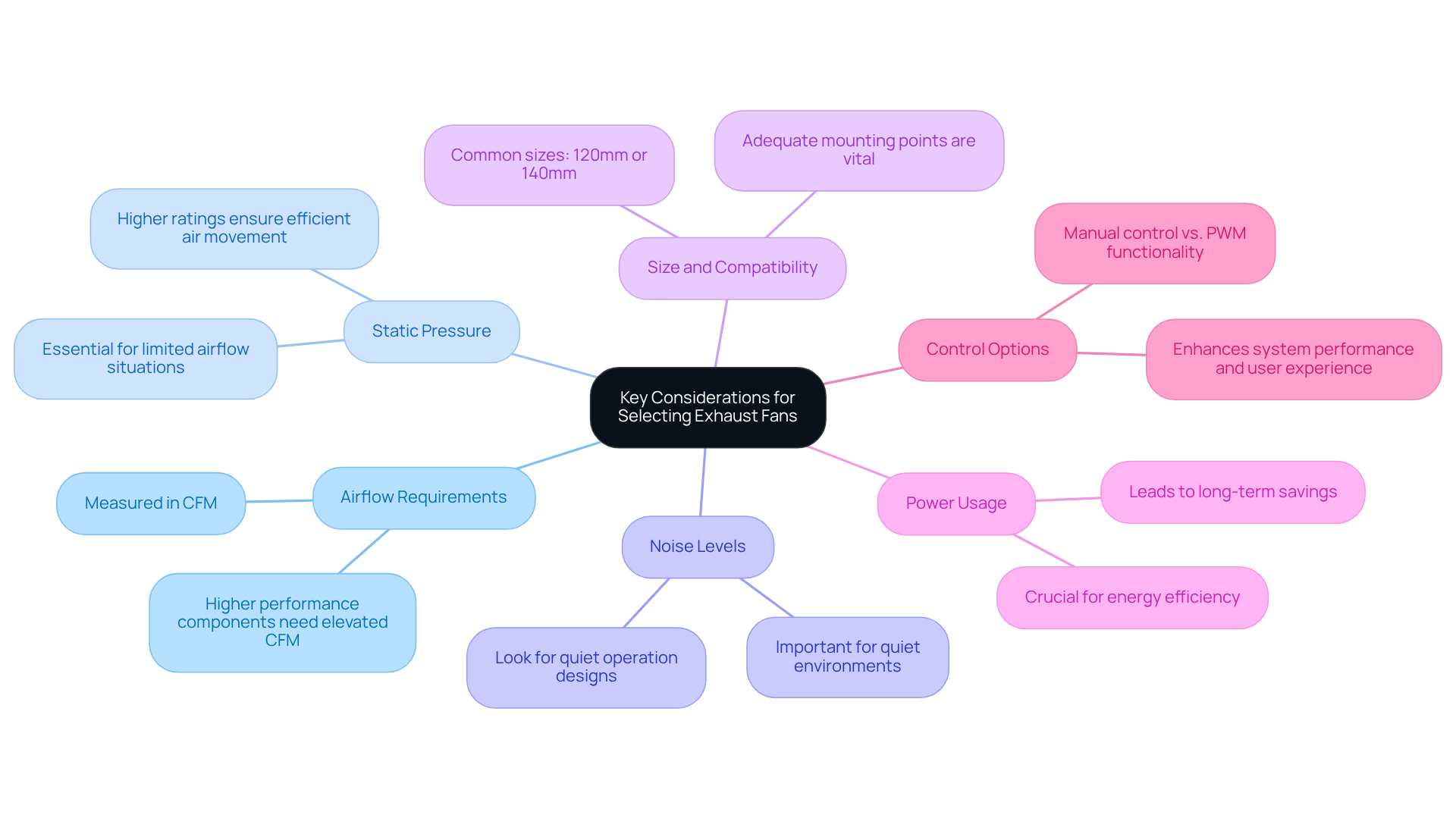
- Airflow Requirements: First and foremost, determine the required airflow, measured in CFM (cubic feet per minute), based on the components in your system and their heat output. Higher performance components may necessitate cooling devices with elevated CFM ratings to ensure optimal performance.
- Static Pressure: In situations where airflow is limited, such as those involving dust filters or confined spaces, it is essential to select devices with higher static pressure ratings. This guarantees efficient air movement, even in challenging environments.
- Noise Levels: Another important consideration is the sound output of the cooling systems. This is particularly relevant if the computer will be utilized in a quiet environment. Look for devices specifically designed for quiet operation, ensuring minimal disruption.
- Size and Compatibility: Ensure that the fan size, typically 120mm or 140mm, is compatible with your case and that there are adequate mounting points. This compatibility is vital for effective installation and performance.
- Power Usage: Assessing the power usage of these devices is also crucial, especially in systems where energy efficiency is a priority. This consideration can lead to long-term savings and a reduced environmental impact.
- Control Options: Finally, consider whether you prefer manual control or PWM functionality for automatic speed adjustments based on temperature. This flexibility can enhance system performance and user experience.
By carefully evaluating these factors, users can select and configure exhaust fans that best meet their cooling needs, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of their systems.
Conclusion
Understanding the significance of computer exhaust fans is paramount for anyone looking to optimize their system’s performance and longevity. These fans play a critical role in maintaining the ideal operating temperatures of essential components like the CPU and GPU, preventing overheating and ensuring that systems run efficiently. By effectively removing warm air, they create a balanced cooling environment that is vital for both everyday users and high-performance setups.
Throughout this tutorial, various types of computer exhaust fans were explored, including:
- Axial blowers
- Centrifugal blowers
- High-speed blowers
- PWM units
- Low-noise devices
Each type serves a specific purpose and is designed to meet distinct cooling requirements, highlighting the importance of selecting the right fan for your system. Additionally, the article delved into the operational principles of these fans, emphasizing how airflow dynamics and temperature regulation work together to maintain optimal performance.
In conclusion, selecting and configuring the appropriate exhaust fan is crucial for maximizing cooling efficiency and enhancing the overall functionality of a computer system. By considering factors such as airflow requirements, static pressure, noise levels, size compatibility, and energy usage, users can make informed decisions that align with their specific needs. Embracing these insights not only helps in achieving superior cooling but also contributes to the long-term reliability and performance of computer systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a computer exhaust fan?
A computer exhaust fan is a specialized device designed to remove warm air from within a computer casing, helping to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
Why is a computer exhaust fan important?
It is important because it eliminates heated air generated by critical components like the CPU and GPU, preventing excessive heat that can lead to thermal throttling, reduced efficiency, and potential hardware failure.
How does a computer exhaust fan contribute to the performance of a computer?
By promoting airflow and establishing a balanced cooling atmosphere, a computer exhaust fan enhances the overall functionality and durability of electronic devices.
What happens if a computer exhaust fan is not properly configured?
If not properly configured, it can lead to inadequate cooling, resulting in excessive heat buildup, which may negatively impact the performance and longevity of the computer components.

