Overview
This article delves into the essential techniques for the installation and maintenance of cooling fan units, which are pivotal for regulating temperature in electronic systems. It underscores the significance of proper placement, adherence to technical specifications, and the implementation of regular maintenance practices to guarantee optimal performance and longevity of these units. Supported by case studies and comprehensive guidelines, the article provides effective strategies for integration, ensuring that readers can apply these insights to enhance their systems.
Introduction
Cooling fan units serve as the unsung heroes of modern electronics, diligently working to prevent overheating and ensure optimal performance. As technology progresses and devices become increasingly compact, the necessity of understanding the effective installation and maintenance of these units becomes paramount. However, many encounter difficulties in selecting the appropriate fan, integrating it seamlessly into their systems, and troubleshooting prevalent issues.
What essential techniques and best practices can enhance the performance of cooling fan units and prolong their lifespan?
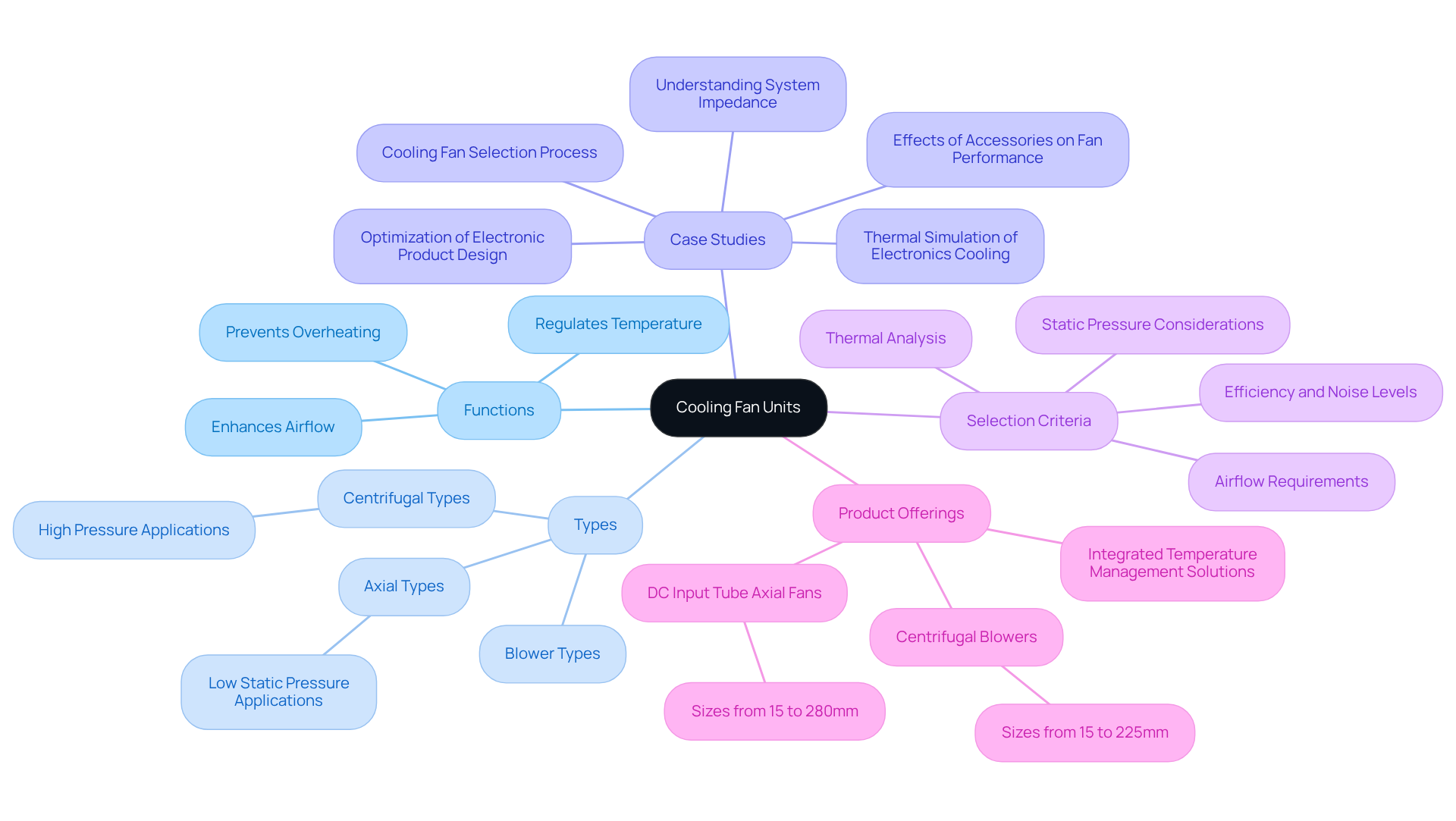
Define Cooling Fan Units and Their Role in Electronics
is a vital device that regulates temperature within electronic systems by enhancing airflow and dissipating heat. Their primary function is to prevent overheating, which can lead to performance degradation or failure of critical electronic components, through the use of a cooling fan unit. Various types of ventilation units, such as axial types, centrifugal types, and blower types, cater to different applications based on airflow needs and spatial constraints. For instance, axial ventilators are typically employed in low static pressure environments, while centrifugal blowers excel in high-pressure applications. Gagner-Toomey Associates offers an extensive range of products for temperature regulation, optimized for performance, efficiency, and low noise. This includes DC input tube axial fans ranging from 15 to 280mm and centrifugal blowers from 15 to 225mm, with IP protection available in most models upon request.
Numerous case studies illustrate the impact of cooling fan units on electronic device performance, underscoring their significance. One notable study highlighted how a more robust fan model significantly improved chip temperature management, achieving lower temperatures at higher flow rates. This exemplifies the direct relationship between effective temperature control methods and the longevity of electronic devices.
Moreover, selecting the appropriate cooling fan unit is crucial in preventing excessive heat in electronic devices. A comprehensive thermal analysis is often the initial step in this process, enabling engineers to ascertain the heat generated by components and the necessary airflow to sustain optimal operating conditions. Understanding the dynamics of airflow and static pressure is essential, as these elements influence the overall efficiency of refrigeration systems.
In conclusion, cooling fan units play a critical role in modern electronics, ensuring that devices operate within safe temperature ranges while enhancing their performance and reliability. Accessories such as filters and guards, while improving reliability, can also affect airflow and static pressure, making their consideration essential in the fan selection process. Gagner-Toomey Associates distinguishes itself as a leading provider of innovative temperature regulation solutions, offering a comprehensive portfolio that includes extruded aluminum heatsinks, copper-based heat sinks, and integrated temperature management solutions tailored to meet diverse needs.
Explore Technical Specifications and Operational Principles
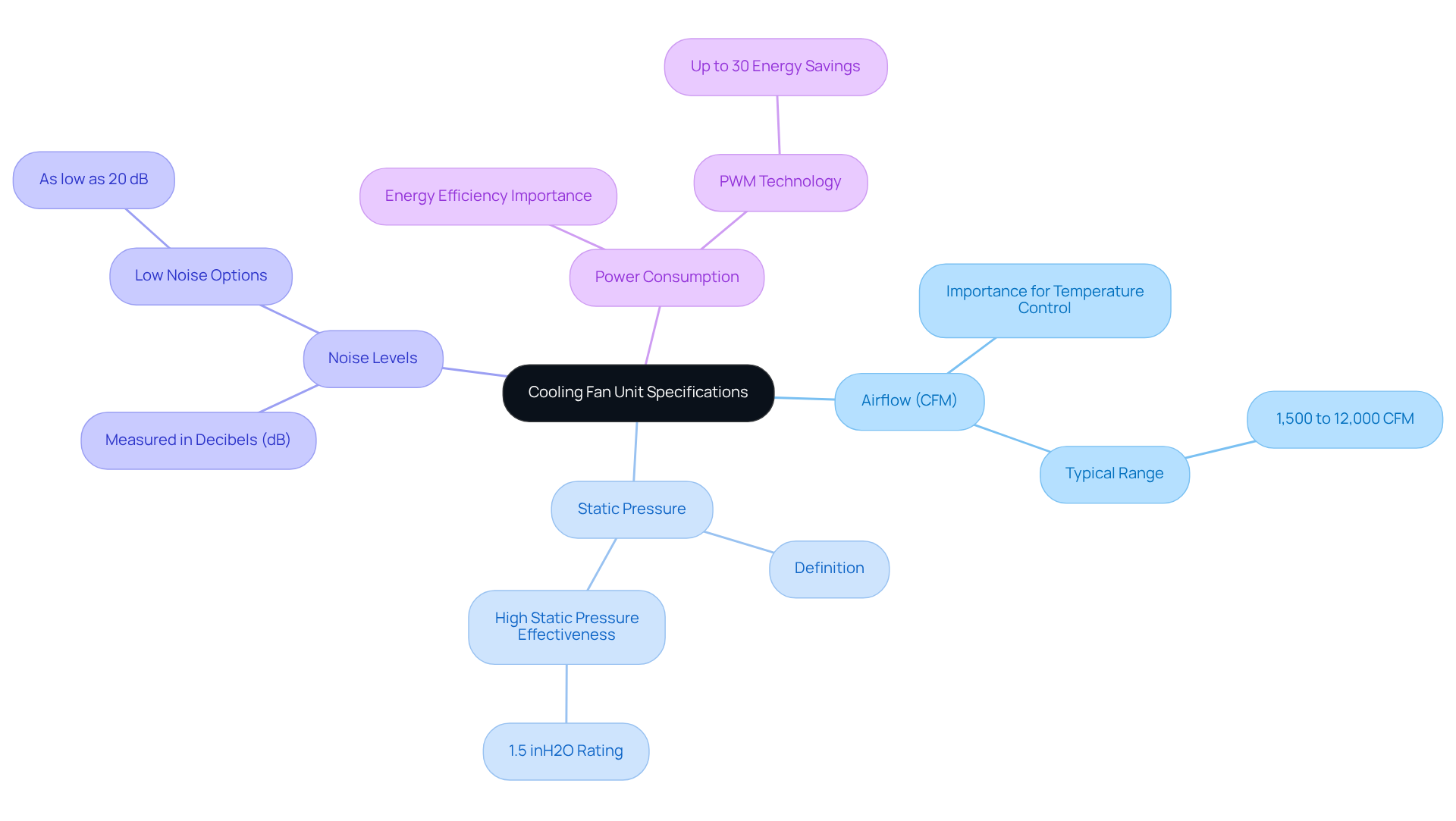
When choosing a , it is essential to take into account several key technical specifications to guarantee optimal performance.
- Airflow (CFM): This metric, measured in cubic feet per minute, indicates the volume of air a fan can move. For efficient temperature control of larger components, higher CFM ratings are essential. Ventilation devices in electronic applications generally vary from 1,500 to 12,000 CFM, based on the particular needs of the setup.
- Static Pressure: This specification measures the fan’s capability to push air through obstructions, such as filters or heat sinks. Fans designed for high static pressure are particularly effective in dense environments, where airflow is restricted. A fan with a static pressure rating of 1.5 inches of water gauge (inH2O) can significantly enhance airflow in such conditions.
- Noise Levels: Noise is a critical factor in many applications, measured in decibels (dB). Selecting a fan with a lower dB rating can greatly improve user comfort, especially in environments where sound levels are a concern. Devices created for silent functioning can reach noise levels as low as 20 dB, rendering them appropriate for delicate applications.
- Power Consumption: Understanding the energy needs of fans is essential for creating energy-efficient setups. Fans utilizing Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) technology can adjust their speed based on thermal demands, optimizing energy use and reducing operational costs. This adaptability can result in energy savings of up to 30% when compared to conventional fan setups.
These specifications directly influence the operational efficiency and effectiveness of the cooling fan unit in electronic systems. By ensuring that these factors are carefully considered, one can meet the thermal requirements of various applications while maintaining performance and reliability.
Implement Cooling Fan Units: Installation and Integration Techniques
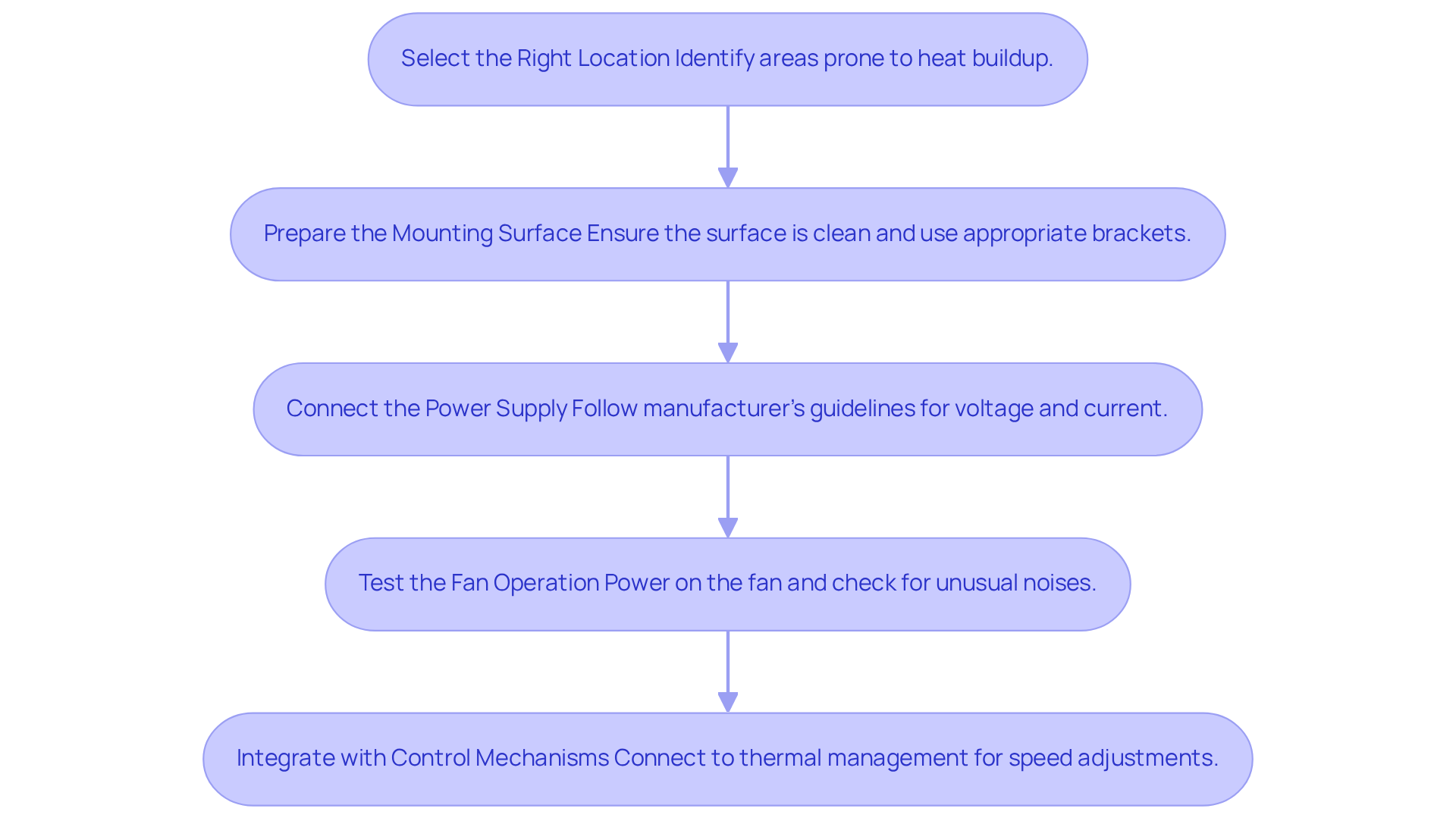
To effectively install and integrate cooling fan units, it is essential to adhere to the following best practices:
- Select the Right Location: Begin by identifying areas prone to heat buildup. This ensures that the fan can efficiently draw in cool air and expel hot air. Proper placement is crucial; studies indicate that improper fan positioning can lead to significant operational inefficiencies. As Che Kuan Yau noted, “Cool air should be in from the bottom and hot air shall be exhaust/discharge out through the top NOT reverse.”
- Prepare the Mounting Surface: Ensure that the mounting surface is clean and free from debris. Utilize appropriate mounting brackets to secure the fan, as can lead to resonance and increased noise, potentially reducing the fan’s lifespan. Statistics indicate that installation techniques can significantly influence the service life of ventilation fans, highlighting the necessity for meticulous preparation.
- Connect the Power Supply: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to connect the fan to the power supply, ensuring that voltage and current ratings align with the fan specifications. It is significant to note that using a lower voltage than specified can harm a 12V fan, underscoring the necessity of precise connections.
- Test the Fan Operation: Before finalizing the installation, power on the fan to verify proper operation. Listen for unusual noises and ensure airflow is directed as intended. This step is essential, as typical installation errors can result in fan failure or insufficient temperature management. The case study on ‘Common Faults and Solutions for the Cooling Fan Unit‘ highlights how installation errors can lead to operational issues.
- Integrate with Control Mechanisms: If applicable, connect the fan to a thermal management setup that adjusts its speed based on temperature readings. This integration not only improves efficiency but also extends the fan’s lifespan, aligning with recent advancements in temperature management technology. It is important to recognize that the service life of exhaust heat dissipation is generally shorter than that of blowing heat, which should be considered during integration.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can ensure that the fan assembly is installed properly and functions efficiently within your electronic system, ultimately enhancing thermal management.
Troubleshoot and Maintain Cooling Fan Units for Optimal Performance
To effectively maintain and troubleshoot cooling fan units, implement the following essential practices:
- Regular Cleaning: Dust and debris accumulation on fan blades can significantly reduce efficiency. It is advisable to clean the fan regularly using a soft brush or compressed air, ideally on a monthly to quarterly basis, depending on environmental conditions. Avoid using chlorine-containing chemicals, as they can damage fan blades.
- Inspect for Damage: Periodically check for signs of wear or damage, such as cracked blades or loose connections. Promptly replacing any damaged components is crucial to prevent further issues.
- Monitor Performance: Keep an eye on airflow and noise levels. A sudden increase in noise or a decrease in airflow may indicate a problem that requires immediate attention.
- Lubricate Moving Parts: If applicable, lubricate the fan motor and bearings to minimize friction and wear, ensuring smooth operation. Regular lubrication can extend the lifespan of the fan, which typically ranges from three to five years under normal conditions. Note that fans with sleeve bearings typically last around 30,000 hours, whereas those with double ball bearings can endure between 50,000 to 100,000 hours.
- Check Electrical Connections: Ensure that all electrical connections are secure and free from corrosion. Defective connections can result in sporadic operation or total failure, affecting the dependability of the refrigeration unit. It is recommended to inspect electrical connections quarterly.
By implementing these maintenance practices, you will ensure that your cooling fan unit operates at peak performance, thereby extending its lifespan and reliability. Regular inspections and maintenance not only enhance efficiency but also contribute to the overall reliability of systems such as industrial machinery and medical devices.
Conclusion
Cooling fan units are indispensable components in the realm of electronics, ensuring that devices maintain optimal operating temperatures and function reliably. Their ability to regulate airflow and dissipate heat is crucial in preventing overheating, which can compromise the performance and longevity of electronic systems. Understanding the nuances of fan types, installation techniques, and maintenance practices is essential for maximizing their effectiveness.
Throughout this article, several key insights have been discussed, including:
- The importance of selecting the right cooling fan unit based on technical specifications such as airflow, static pressure, noise levels, and power consumption.
- Proper installation techniques, such as positioning and securing the fan correctly, are paramount to its operational efficiency.
- Regular maintenance practices, including cleaning, inspecting for damage, and monitoring performance, are vital for prolonging the lifespan of cooling fan units.
Ultimately, investing time and resources into mastering cooling fan unit installation and maintenance not only enhances system performance but also safeguards against potential failures. By applying the techniques and best practices outlined, users can ensure their electronic devices operate within safe temperature ranges, thereby improving reliability and efficiency. Embracing these strategies will lead to more effective thermal management solutions, ultimately benefiting various applications across the electronics industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary function of a cooling fan unit in electronics?
The primary function of a cooling fan unit is to regulate temperature within electronic systems by enhancing airflow and dissipating heat, preventing overheating that can lead to performance degradation or failure of critical components.
What are the different types of cooling fan units mentioned in the article?
The article mentions three types of cooling fan units: axial types, centrifugal types, and blower types. Each type caters to different applications based on airflow needs and spatial constraints.
In what environments are axial ventilators typically used?
Axial ventilators are typically employed in low static pressure environments.
What applications are centrifugal blowers best suited for?
Centrifugal blowers excel in high-pressure applications.
What range of products does Gagner-Toomey Associates offer for temperature regulation?
Gagner-Toomey Associates offers DC input tube axial fans ranging from 15 to 280mm and centrifugal blowers from 15 to 225mm, with IP protection available in most models upon request.
How do cooling fan units impact electronic device performance?
Cooling fan units significantly improve chip temperature management, achieving lower temperatures at higher flow rates, which underscores the direct relationship between effective temperature control and the longevity of electronic devices.
What is the initial step in selecting the appropriate cooling fan unit?
A comprehensive thermal analysis is often the initial step, enabling engineers to ascertain the heat generated by components and the necessary airflow to sustain optimal operating conditions.
Why is understanding airflow and static pressure important in cooling fan units?
Understanding the dynamics of airflow and static pressure is essential because these elements influence the overall efficiency of refrigeration systems.
What accessories are mentioned that can improve reliability in cooling fan units?
Accessories such as filters and guards can improve reliability, but they can also affect airflow and static pressure, making their consideration essential in the fan selection process.
What additional products does Gagner-Toomey Associates provide related to temperature regulation?
Gagner-Toomey Associates provides a comprehensive portfolio that includes extruded aluminum heatsinks, copper-based heat sinks, and integrated temperature management solutions tailored to meet diverse needs.