Introduction
Innovative cooling solutions stand as a cornerstone in electronics engineering, where the relentless pursuit of performance often leads to the challenge of overheating. Engineers face the critical task of mastering a range of cooling technologies – from traditional air cooling to advanced liquid refrigeration – each presenting unique benefits and limitations. As the demand for high-performance computing escalates, a pressing question emerges: how can engineers effectively navigate these diverse cooling methods to optimize thermal management while ensuring cost-effectiveness and sustainability? This inquiry not only highlights the complexity of the issue but also underscores the necessity for informed decision-making in the selection of cooling strategies.
Understand Cooling Technologies for Electronics Engineering
An innovative cooling solution is essential for managing the thermal performance of electronic devices. Engineers must be adept in various methods, including:
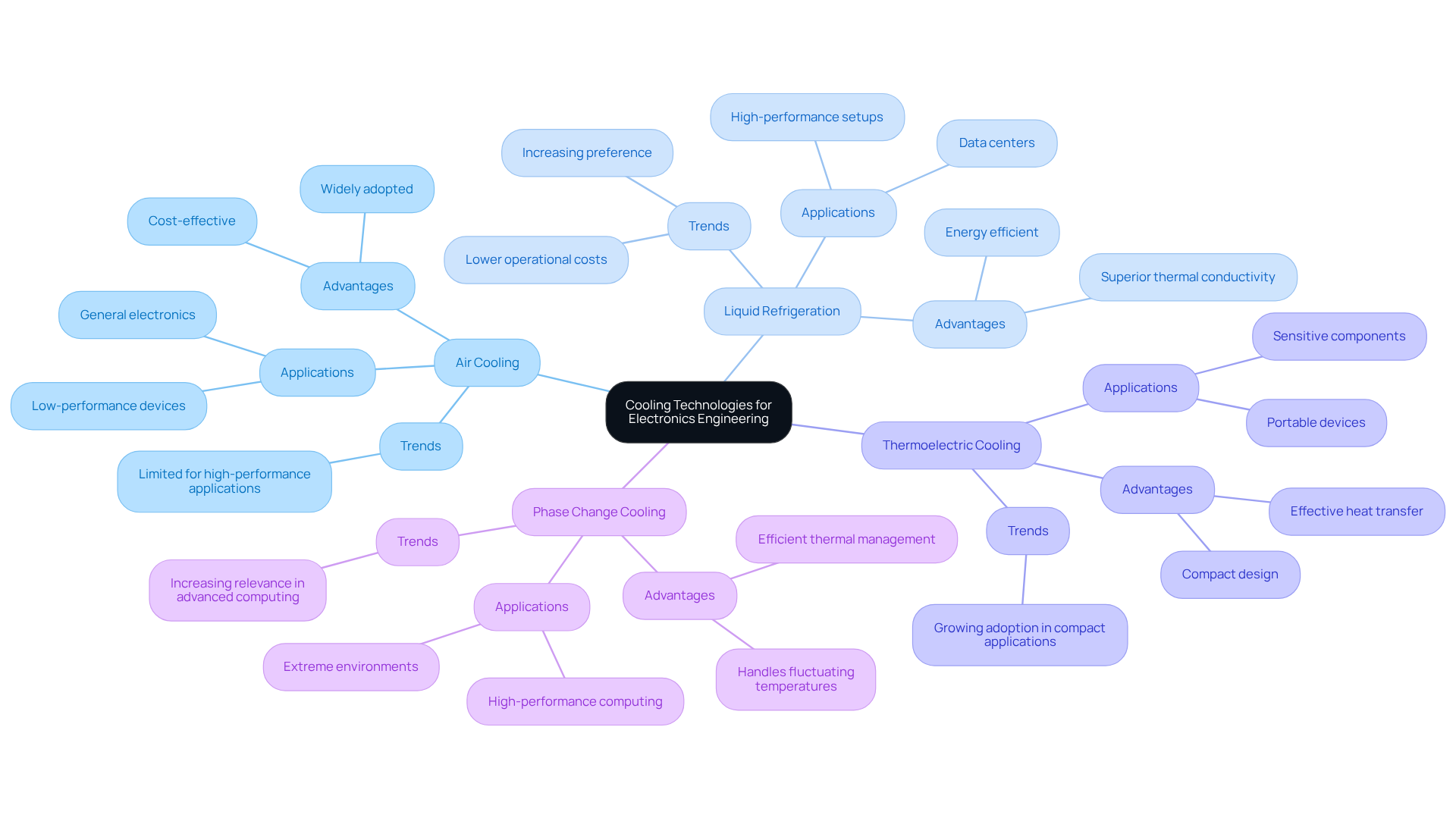
- Air Cooling: This method utilizes fans and heat sinks to dissipate heat through airflow. While it is cost-effective and widely adopted, it may not meet the demands of high-performance applications.
- Liquid Refrigeration: Known for its superior thermal conductivity, liquid refrigeration is ideal for high-performance setups. It encompasses solutions such as cold plates, thermal exchangers, and immersion systems, which significantly enhance temperature dissipation. Liquid cooling systems are increasingly preferred due to their energy efficiency, consuming less energy than traditional air cooling methods and resulting in lower operational costs.
- Thermoelectric Cooling: This technology employs Peltier devices to create a temperature differential, effectively transferring heat away from sensitive components, making it suitable for compact applications.
- Phase Change Cooling: This method uses materials that absorb heat during phase transitions, providing efficient thermal management, especially in environments with fluctuating temperatures.
Recent trends reveal a notable shift towards innovative cooling solutions for liquid temperature regulation, driven by the escalating demands of high-performance computing and AI workloads. The global data center liquid temperature regulation market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 21.6% from 2025 to 2030. This growth reflects the increasing need for innovative cooling solutions in the management of temperatures in data centers. Industry leaders emphasize that liquid temperature regulation not only enhances heat management but also aligns with sustainability goals by utilizing low-global warming potential (GWP) refrigerants. As engineers navigate these advancements, understanding the strengths and applications of each temperature regulation method is crucial for optimizing thermal performance in electronic setups.
Evaluate Cooling Solutions for Optimal Performance
When evaluating cooling solutions, engineers face several critical factors that demand attention:
-
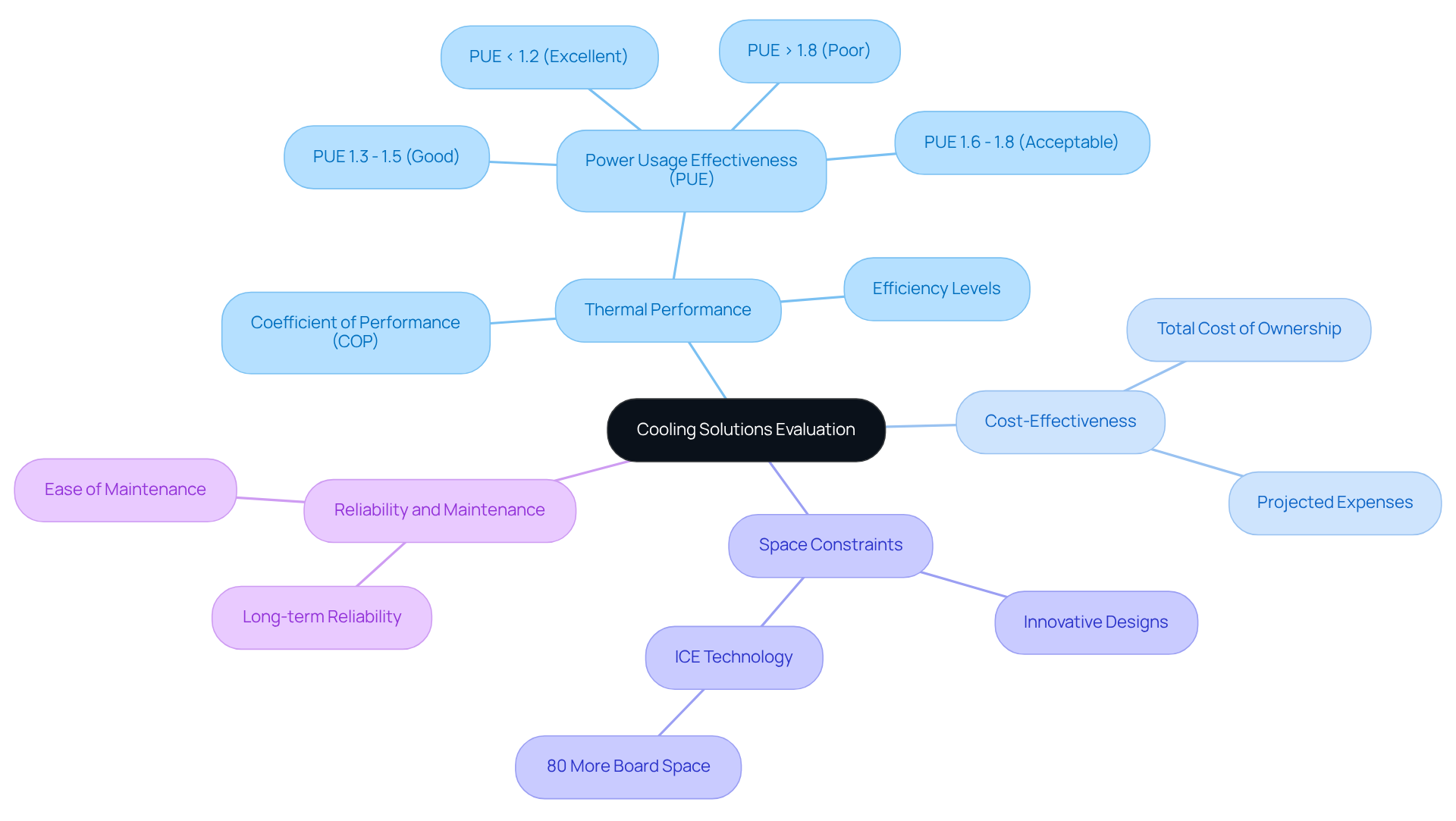
Thermal Performance: Assessing the cooling capacity and efficiency under expected operating conditions is vital. Key metrics like the Coefficient of Performance (COP) and Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) serve as crucial indicators of operational efficiency. For example, a PUE of 1.0 indicates that all energy is utilized for revenue-generating IT workloads, whereas a PUE of 2.0 suggests that only half of the total energy effectively supports IT equipment. Notably, PUE values categorize efficiency levels, with values below 1.2 being excellent and those between 1.3 and 1.5 considered good.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: A thorough analysis of the total cost of ownership is essential. This includes installation and maintenance expenses, as well as energy usage throughout the lifespan of the setup. Engineers should prioritize solutions that minimize operational expenses while maximizing performance. The projected expense of ownership for refrigeration units in electronics for 2026 should be factored into this assessment.
-
Space Constraints: The temperature regulation solution must fit within the physical dimensions of the electronic system without compromising performance. Innovative designs, such as those utilizing an innovative cooling solution like ICE technology, can free up to 80% more board space, enhancing functionality without increasing device size. This capability is supported by case studies that demonstrate the effectiveness of ICE technology in optimizing design.
-
Reliability and Maintenance: Long-term reliability and ease of maintenance are paramount. Solutions requiring minimal intervention are often preferred, as they reduce downtime and operational disruptions.
Real-world instances, such as the implementation of liquid temperature regulation in high-density data centers, illustrate the effectiveness of a thorough evaluation process. These implementations not only optimize thermal performance but also yield significant cost savings and improved energy efficiency, making them a compelling choice for modern electronics engineering. As Brian Cumpston, director of application engineering at Ventiva Electronics, notes, ‘Designers require an innovative cooling solution that meets the increasing demands of AI while still allowing for additional peripheral devices or a larger battery.
Implement Best Practices in Cooling System Design and Installation
To achieve optimal cooling performance, engineers must adhere to several key practices:
-
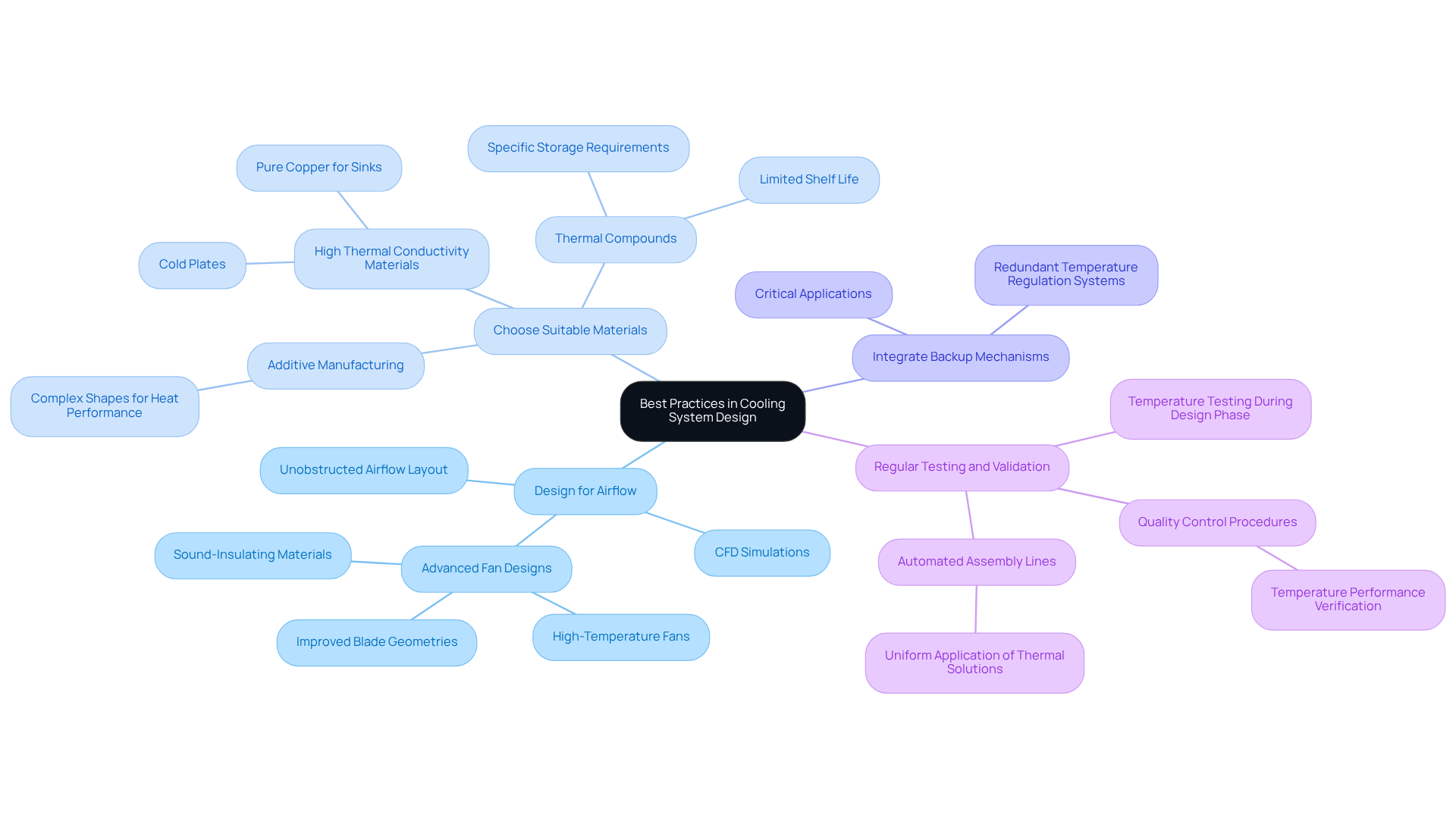
Design for Airflow: The layout of components should facilitate unobstructed airflow. Utilizing computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations can optimize airflow paths, significantly improving temperature regulation efficiency. For example, advancements in fan designs – such as high-temperature fans with improved blade geometries and sound-insulating materials – have led to notable reductions in noise while maintaining effective airflow. Traditional cooling techniques, such as sinks and fans, are increasingly inadequate for the rising power dissipation of AI processors, highlighting the urgent need for an innovative cooling solution.
-
Choose Suitable Materials: Selecting materials with high thermal conductivity, such as pure copper for sinks and cold plates, is essential. These materials enhance heat dissipation, which is critical as electronic components generate more heat due to escalating power densities. The use of advanced manufacturing methods, including additive manufacturing, allows for the creation of complex shapes that improve heat performance. Additionally, it is vital to consider the limited shelf life and specific storage requirements of thermal compounds to ensure optimal performance.
-
Integrate Backup Mechanisms: In critical applications, implementing redundant temperature regulation systems can prevent overheating in case of a failure. This strategy is particularly crucial in high-performance computing environments where system reliability is of utmost importance.
-
Regular Testing and Validation: Conducting temperature testing during the design phase is necessary to validate cooling performance under various load conditions. Quality control procedures should include temperature performance verification to ensure that manufactured devices consistently meet specifications. Automated assembly lines demand thermal solutions that can be applied uniformly with minimal variation.
By following these practices, engineers can significantly enhance the reliability and effectiveness of their cooling systems, effectively addressing the challenges posed by modern electronic designs.
Monitor and Maintain Cooling Systems for Longevity
To ensure the longevity and reliability of cooling systems, engineers must adopt a comprehensive monitoring and maintenance strategy:
-
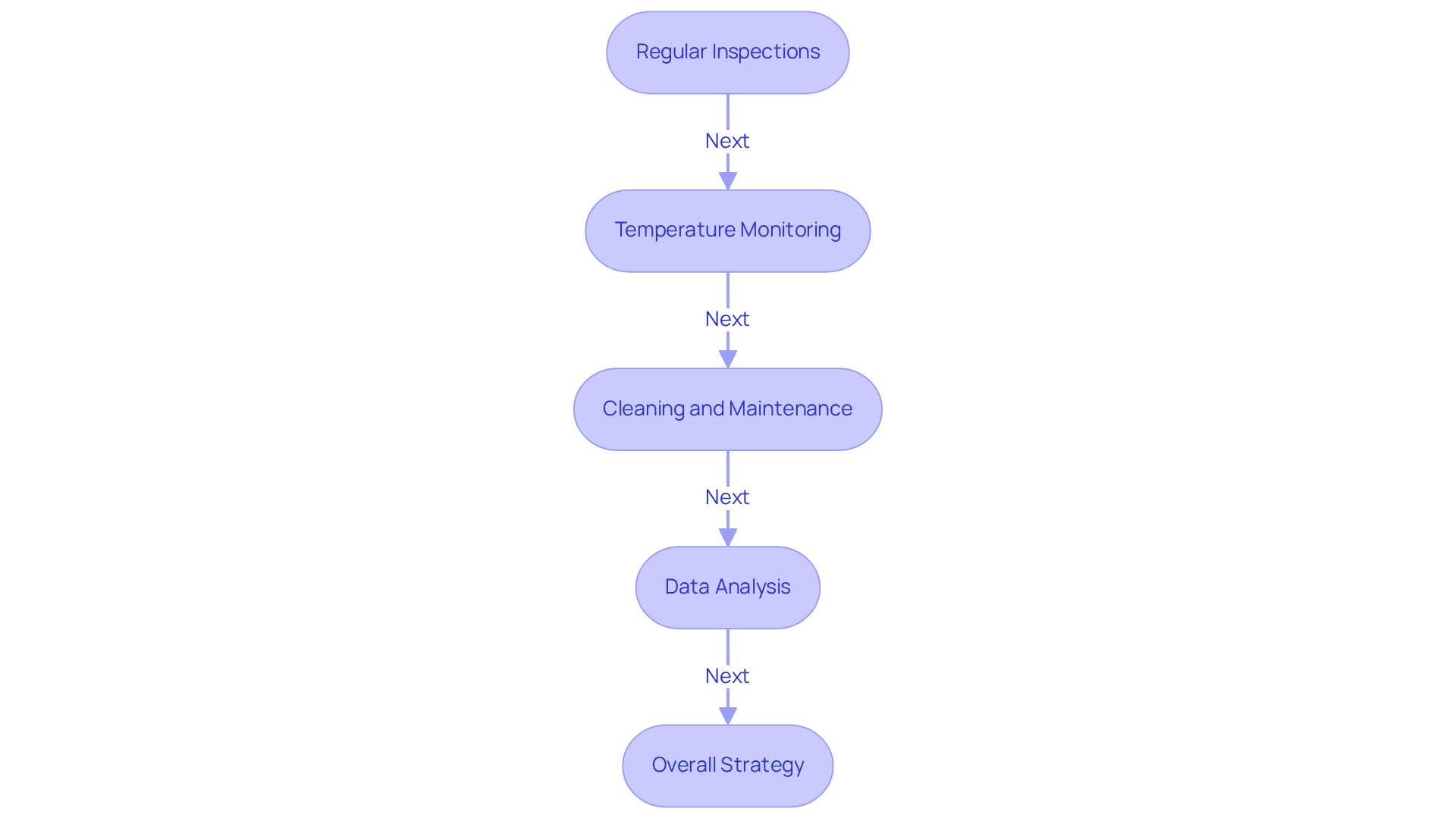
Regular Inspections: Routine inspections are crucial for identifying signs of wear, leaks, or blockages in cooling systems. These proactive measures can prevent costly failures and minimize downtime, safeguarding operational efficiency.
-
Temperature Monitoring: Advanced sensors should be implemented to continuously track temperatures, ensuring they remain within optimal ranges. Establishing alerts for unusual temperature spikes is vital, especially as modern AI-centric facilities often utilize racks consuming between 50 to 120 kilowatts, with individual GPU thermal loads exceeding 1,200 watts per chip.
-
Cleaning and Maintenance: Regular cleaning of fans, heat sinks, and filters is essential to prevent dust buildup, which can significantly hinder airflow and reduce temperature control efficiency. Given that 30 to 40 percent of electricity in conventional facilities is allocated for temperature regulation, maintaining clean components is critical for energy efficiency.
-
Data Analysis: Analyzing performance data allows engineers to identify trends and potential issues before they escalate into system failures. This proactive strategy not only enhances operational safety but also aligns with the growing demand for innovative cooling solutions, which are projected to exceed $42 billion by 2032. Furthermore, data centers in Loudoun County, Virginia, accounted for 21% of total power usage in 2023, highlighting the need for an innovative cooling solution to ensure efficient temperature control.
By prioritizing these monitoring and maintenance practices, engineers can significantly extend the lifespan of their cooling systems, ensuring enhanced reliability and operational efficiency in an increasingly demanding environment.
Conclusion
Innovative cooling solutions are crucial for the success of electronics engineering, directly influencing the thermal performance and reliability of electronic devices. Engineers must master a range of cooling technologies, including air and liquid cooling, thermoelectric methods, and phase change techniques. Each of these offers distinct advantages tailored to specific applications. As the demand for high-performance computing and AI workloads escalates, the need for advanced cooling systems becomes even more pressing. These systems not only enhance efficiency but also support sustainability goals.
Key insights emphasize the necessity of evaluating cooling solutions based on:
- Thermal performance
- Cost-effectiveness
- Space constraints
- Maintenance requirements
Implementing best practices in cooling system design-such as optimizing airflow and selecting appropriate materials-can significantly boost the reliability and efficiency of these systems. Moreover, ongoing monitoring and maintenance are vital for ensuring the longevity of cooling solutions, enabling engineers to proactively address potential issues and sustain operational efficiency.
As the landscape of electronics engineering evolves, embracing innovative cooling technologies and best practices is essential for meeting the increasing demands of modern applications. Engineers are urged to stay informed about the latest trends and advancements in cooling solutions to optimize device performance and sustainability. By prioritizing effective cooling strategies, the industry can pave the way for enhanced efficiency and reliability in electronic systems, ultimately driving technological progress.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the importance of cooling solutions in electronics engineering?
Innovative cooling solutions are essential for managing the thermal performance of electronic devices, ensuring they operate efficiently and reliably.
What are the main methods of cooling used in electronics?
The main methods include air cooling, liquid refrigeration, thermoelectric cooling, and phase change cooling.
How does air cooling work and what are its advantages?
Air cooling utilizes fans and heat sinks to dissipate heat through airflow. It is cost-effective and widely adopted, but may not meet the demands of high-performance applications.
What are the benefits of liquid refrigeration for cooling?
Liquid refrigeration offers superior thermal conductivity, making it ideal for high-performance setups. It includes solutions like cold plates and thermal exchangers, which enhance temperature dissipation and are more energy-efficient than traditional air cooling methods.
What is thermoelectric cooling and where is it used?
Thermoelectric cooling employs Peltier devices to create a temperature differential, effectively transferring heat away from sensitive components, making it suitable for compact applications.
What is phase change cooling and its advantages?
Phase change cooling uses materials that absorb heat during phase transitions, providing efficient thermal management, especially in environments with fluctuating temperatures.
What recent trends are influencing cooling technologies in electronics?
There is a notable shift towards innovative cooling solutions for liquid temperature regulation, driven by the increasing demands of high-performance computing and AI workloads.
What is the projected growth of the data center liquid temperature regulation market?
The global data center liquid temperature regulation market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 21.6% from 2025 to 2030.
How do innovative cooling solutions align with sustainability goals?
Innovative cooling solutions enhance heat management and utilize low-global warming potential (GWP) refrigerants, aligning with sustainability goals in the industry.
Why is it important for engineers to understand different cooling methods?
Understanding the strengths and applications of each temperature regulation method is crucial for optimizing thermal performance in electronic setups.

