Introduction
Internal auxiliary fans play a crucial role in modern electronics, ensuring devices maintain safe operating temperatures. As technology becomes more compact and powerful, the demand for effective thermal management solutions rises, and these fans are at the forefront of that need. However, with a variety of specifications, installation techniques, and potential troubleshooting challenges, engineers and technicians face the question: how can they maximize the performance and longevity of these essential components?
This article explores the vital aspects of internal auxiliary fans, providing insights into their installation, specifications, and common issues. By understanding these elements, readers can enhance their expertise and effectively integrate these fans into electronic systems, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Define Internal Auxiliary Fans and Their Role in Electronics
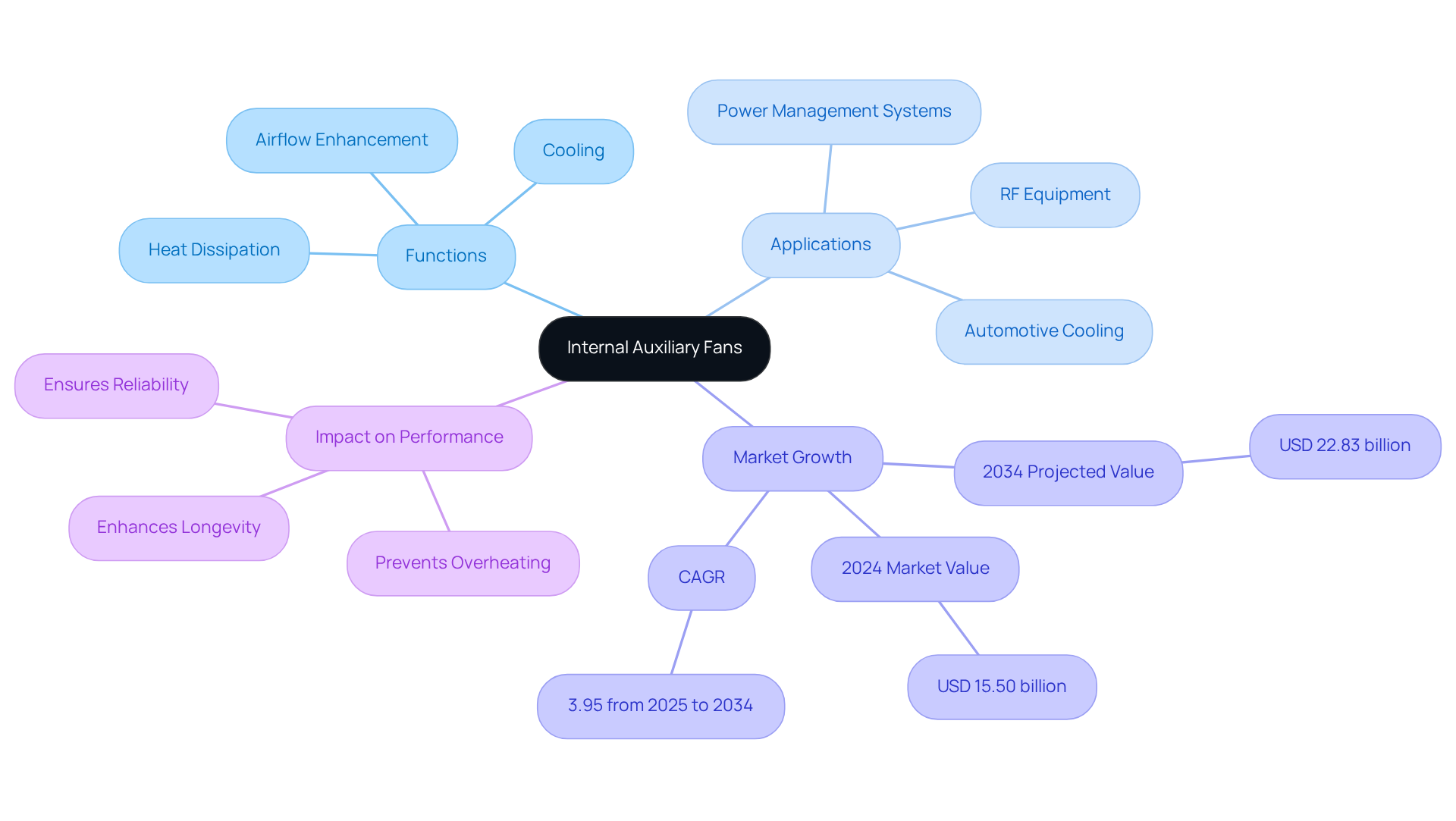
Internal auxiliary fans play a vital role in cooling electronic devices, enhancing airflow and effectively dissipating heat generated by various components. Their primary function is to maintain optimal operating temperatures, which is essential for preventing overheating and ensuring the longevity and reliability of electronic devices. These blowers are commonly found in applications such as power management systems, RF equipment, and interconnect technologies, where efficient heat dissipation is critical for performance.
The significance of internal auxiliary blowers in the electronics industry is immense. As devices grow more compact and energy-intensive, the demand for effective thermal management solutions has skyrocketed. Gagner-Toomey Associates, the world’s largest producer of standard and custom air-movers, offers a comprehensive range of DC input tube axial units and centrifugal blowers, all optimized for performance, efficiency, and low noise. These products come in various sizes, from 15 to 280mm for tube axial units and 15 to 225mm for centrifugal blowers, with IP protection available upon request. The global cooling fan market was valued at USD 15.50 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach approximately USD 22.83 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 3.95% from 2025 to 2034. This growth is fueled by technological advancements and the increasing need for efficient thermal management in high-density environments.
Industry leaders emphasize the critical role of cooling in electronic devices, noting that effective thermal management not only enhances performance but also extends the lifespan of equipment. A case study on the impact of internal auxiliary fans illustrates their contribution to improving the efficiency of power management frameworks, showcasing how these devices facilitate better thermal regulation and bolster overall reliability. As highlighted by Gagner-Toomey Associates, “In automotive situations, cooling fan modules control heat generated by high-performance engines and electronic components, ensuring reliability and safety.”
In conclusion, internal auxiliary fans are essential for ensuring optimal performance in electronic systems. Their capability to manage heat effectively makes them indispensable in modern electronics, where maintaining operational efficiency is crucial.
Explore Technical Specifications and Operational Principles
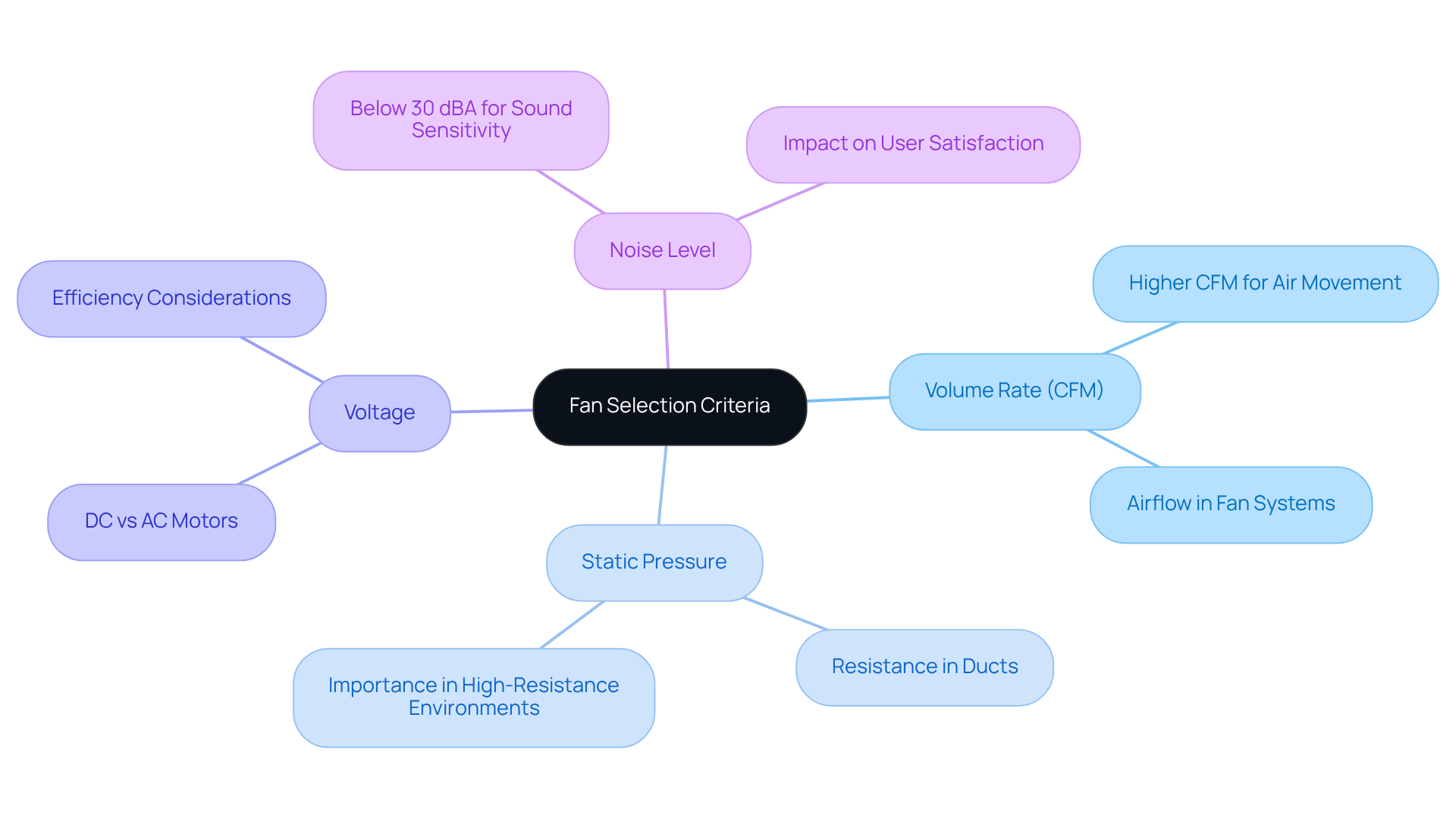
Choosing the right internal auxiliary fan is crucial for optimal performance in various applications. A thorough evaluation of technical specifications is necessary, including:
- Volume rate (measured in cubic feet per minute, CFM)
- Static pressure
- Voltage
- Noise level
For example, fans with higher CFM ratings are essential for applications that demand significant air movement. In sound-sensitive environments, engineers often seek devices that operate below 30 dBA to minimize noise disruption.
The design of the fan – whether axial or centrifugal – and the type of motor used (DC or AC) also play a significant role in determining performance characteristics. Understanding these parameters is vital for ensuring the best fan selection and seamless integration into electronic setups. Engineers should note that air movement in fan systems can achieve impressive rates, with some applications requiring air movement rates of up to 17,000 m³/h.
By prioritizing volume flow rate and static pressure during the selection process, engineers can enhance reliability and efficiency. This focus ultimately leads to improved operational outcomes, making it imperative to consider these factors carefully.
Implement Internal Auxiliary Fans: Installation and Configuration Steps
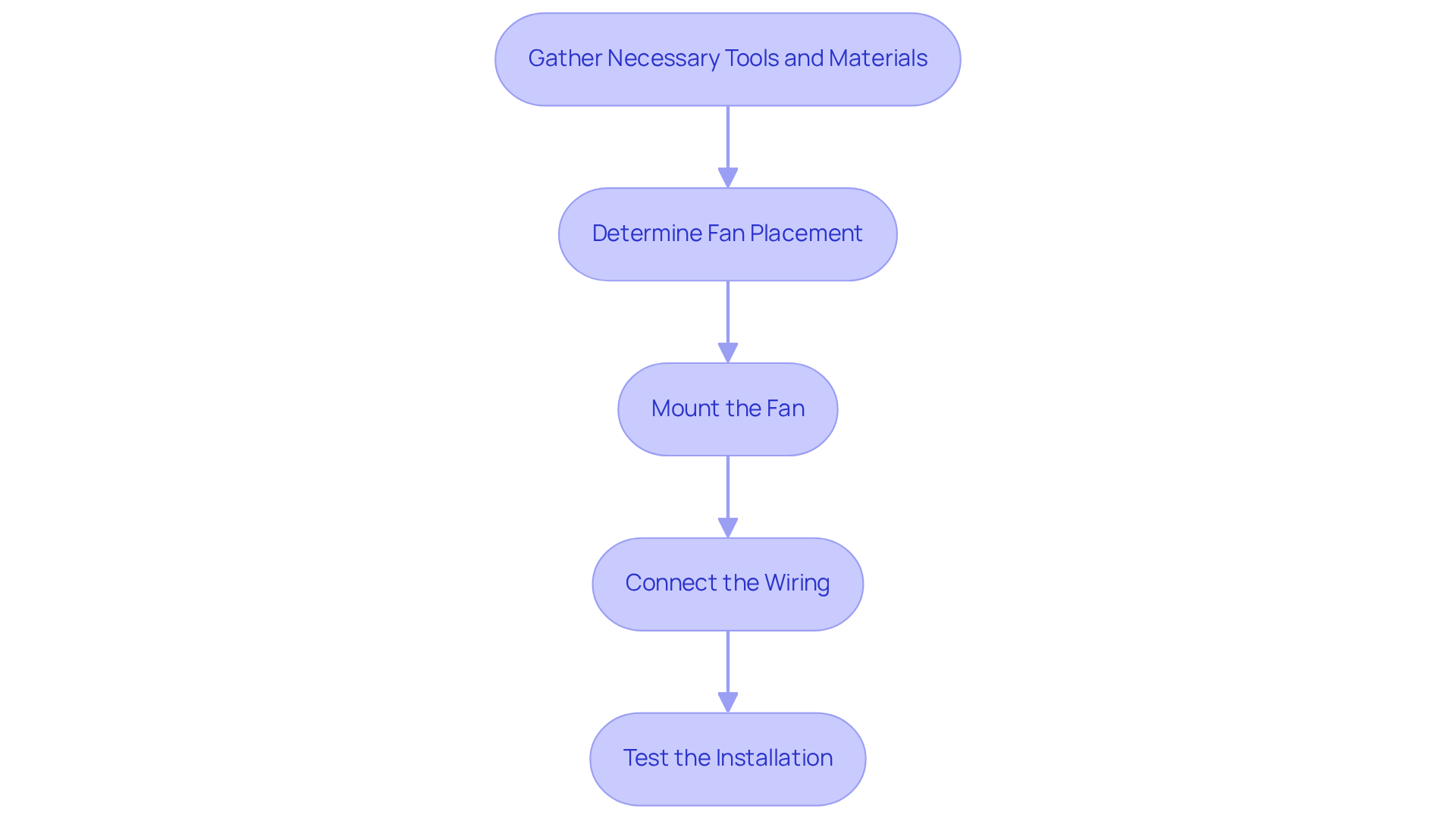
To install an internal auxiliary fan, follow these essential steps:
- Gather Necessary Tools and Materials: Ensure you have the fan, mounting hardware, wiring, and tools such as screwdrivers and wire strippers.
- Determine Fan Placement: Identify the optimal location for the fan within the electronic system. It’s crucial that the fan can effectively draw in or expel air. Consider airflow dynamics and the potential need for ductwork redesign to minimize resistance and improve airflow uniformity.
- Mount the Fan: Secure the fan using the provided mounting hardware. Ensure it is flush against the surface to minimize vibration and noise, which assists in preserving the performance and longevity of the network.
- Connect the Wiring: Follow the manufacturer’s wiring diagram to connect the fan to the power source. Ensure all connections are secure to prevent electrical issues.
- Test the Installation: Power on the device and verify that the fan operates correctly. Check for proper airflow and noise levels, adjusting the configuration as necessary to optimize performance. Additionally, consider implementing improved filtration and dust collection mechanisms if applicable, as these can significantly enhance air quality and reduce maintenance frequency.
Successful setups of internal auxiliary fans can significantly enhance system efficiency. For instance, in a pharmaceutical production facility, the installation of high-efficiency centrifugal blowers resulted in an 18% decrease in energy usage while maintaining uniform temperature distribution. Similarly, in a cement plant, upgrading to high-capacity industrial blowers improved dust control and reduced maintenance frequency by 25%. These examples underscore the importance of thoughtful installation and configuration in achieving desired operational outcomes.
Troubleshoot Common Issues with Internal Auxiliary Fans
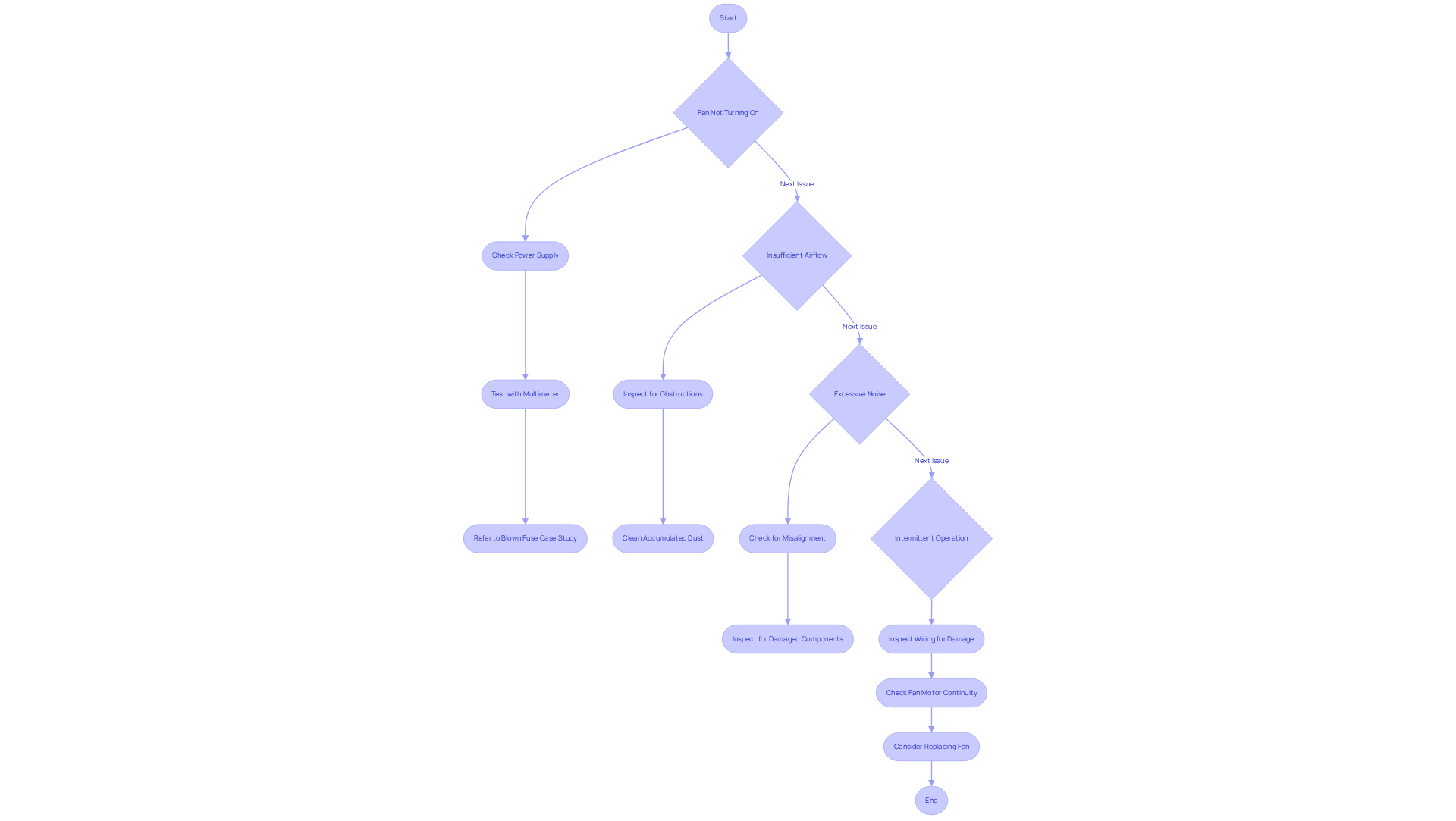
Common Issues with Internal Auxiliary Fans
-
Fan Not Turning On
Begin by checking the power supply and ensuring all connections are secure. Utilize a multimeter to test the functionality of the internal auxiliary fan, since a faulty capacitor or blown fuse may prevent it from operating. For insights on resolving this issue, refer to the “Blown Fuse” case study. -
Insufficient Airflow
Inspect for obstructions in the fan’s path, such as dust buildup or debris, which can reduce airflow efficiency by up to 20-30%. Ensure the internal auxiliary fan is mounted correctly and clean any accumulated dust to enhance its performance. -
Excessive Noise
Noisy fans often indicate misalignment or wear. Verify that the internal auxiliary fan is securely mounted and check for any damaged components, as unusual sounds from the fan may signal mechanical failures that require attention. Engineers have noted that addressing these issues promptly can prevent further complications. -
Intermittent Operation
This issue may stem from faulty wiring or a failing fan motor. Inspect the wiring for signs of damage and ensure the internal auxiliary fan has continuity. If problems persist, consider replacing the fan to restore reliable operation. The “Mechanical Components Inspection” case study illustrates the importance of thorough checks in resolving such issues.
Conclusion
Internal auxiliary fans are essential in the electronics field, playing a crucial role in maintaining optimal temperatures and ensuring device reliability. Their capacity to enhance airflow and effectively dissipate heat is vital, especially as electronic systems grow more compact and energy-intensive. To maximize performance and longevity, it’s important to understand their specifications, installation processes, and troubleshooting methods.
This article has shared key insights on selecting the right fan based on technical specifications such as:
- Volume rate
- Static pressure
- Noise levels
We outlined detailed installation steps to ensure proper setup, emphasizing careful placement and secure connections. Additionally, we identified common issues and provided troubleshooting techniques to maintain efficient operation. Collectively, these insights highlight the critical role internal auxiliary fans play in enhancing the performance and lifespan of electronic systems.
In conclusion, mastering the intricacies of internal auxiliary fans not only improves thermal management but also boosts overall system efficiency. As the demand for effective cooling solutions continues to rise, engineers and technicians must prioritize these components in their designs and maintenance practices. By doing so, they can ensure reliable operation of electronic devices, ultimately leading to enhanced performance and reduced operational costs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are internal auxiliary fans?
Internal auxiliary fans are devices used in electronics to enhance airflow and dissipate heat generated by various components, helping to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
Why are internal auxiliary fans important in electronics?
They are crucial for preventing overheating, ensuring the longevity and reliability of electronic devices, and improving overall performance, especially in compact and energy-intensive applications.
Where are internal auxiliary fans commonly used?
They are commonly found in power management systems, RF equipment, and interconnect technologies, where efficient heat dissipation is critical.
What products does Gagner-Toomey Associates offer related to internal auxiliary fans?
Gagner-Toomey Associates offers a range of DC input tube axial units and centrifugal blowers optimized for performance, efficiency, and low noise, available in various sizes.
What is the projected growth of the global cooling fan market?
The global cooling fan market was valued at USD 15.50 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach approximately USD 22.83 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 3.95% from 2025 to 2034.
What factors are driving the growth of the cooling fan market?
The growth is fueled by technological advancements and the increasing need for efficient thermal management in high-density environments.
How do internal auxiliary fans contribute to the efficiency of power management frameworks?
They facilitate better thermal regulation, which enhances performance and bolsters the overall reliability of electronic systems.
What role do cooling fan modules play in automotive situations?
Cooling fan modules control heat generated by high-performance engines and electronic components, ensuring reliability and safety.

