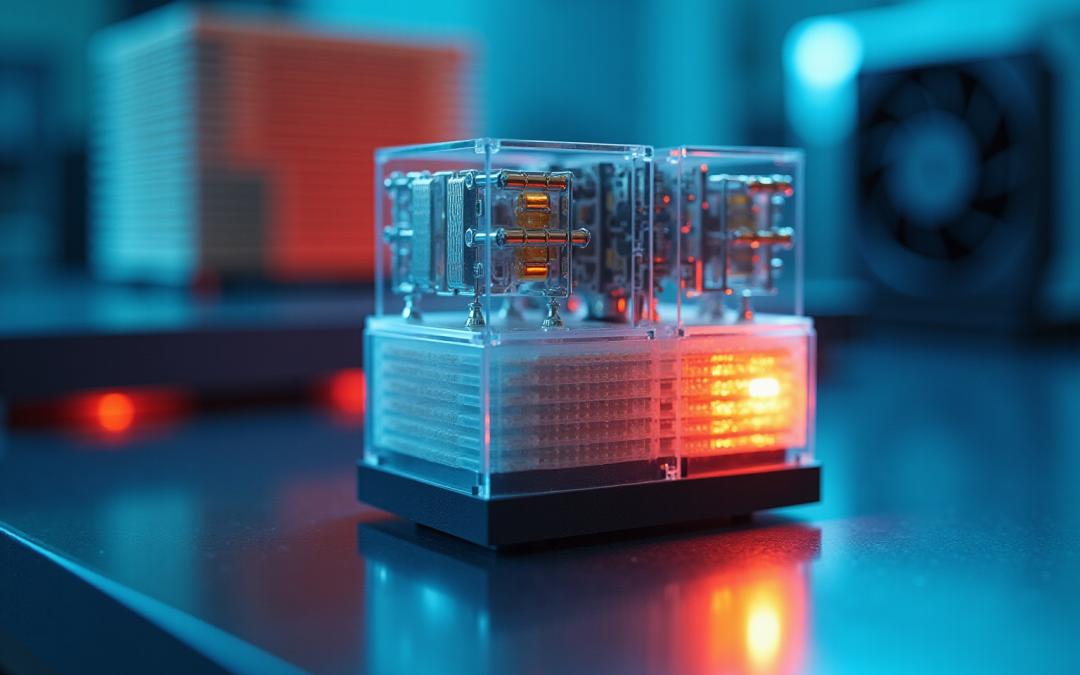
Introduction
Thermoelectric cooling technology is revolutionizing modern thermal management by harnessing the Peltier effect to create efficient temperature differentials. This cutting-edge approach not only offers enhanced cooling solutions across a spectrum of industries – from automotive to healthcare – but also introduces unique challenges and considerations for implementation. As the demand for energy-efficient cooling solutions escalates, it’s crucial to examine the key advantages and limitations of thermoelectric systems.
How can engineers optimize their performance for diverse applications? Understanding these factors is essential for leveraging the full potential of this technology.
Understand Thermoelectric Cooling Principles and Mechanisms
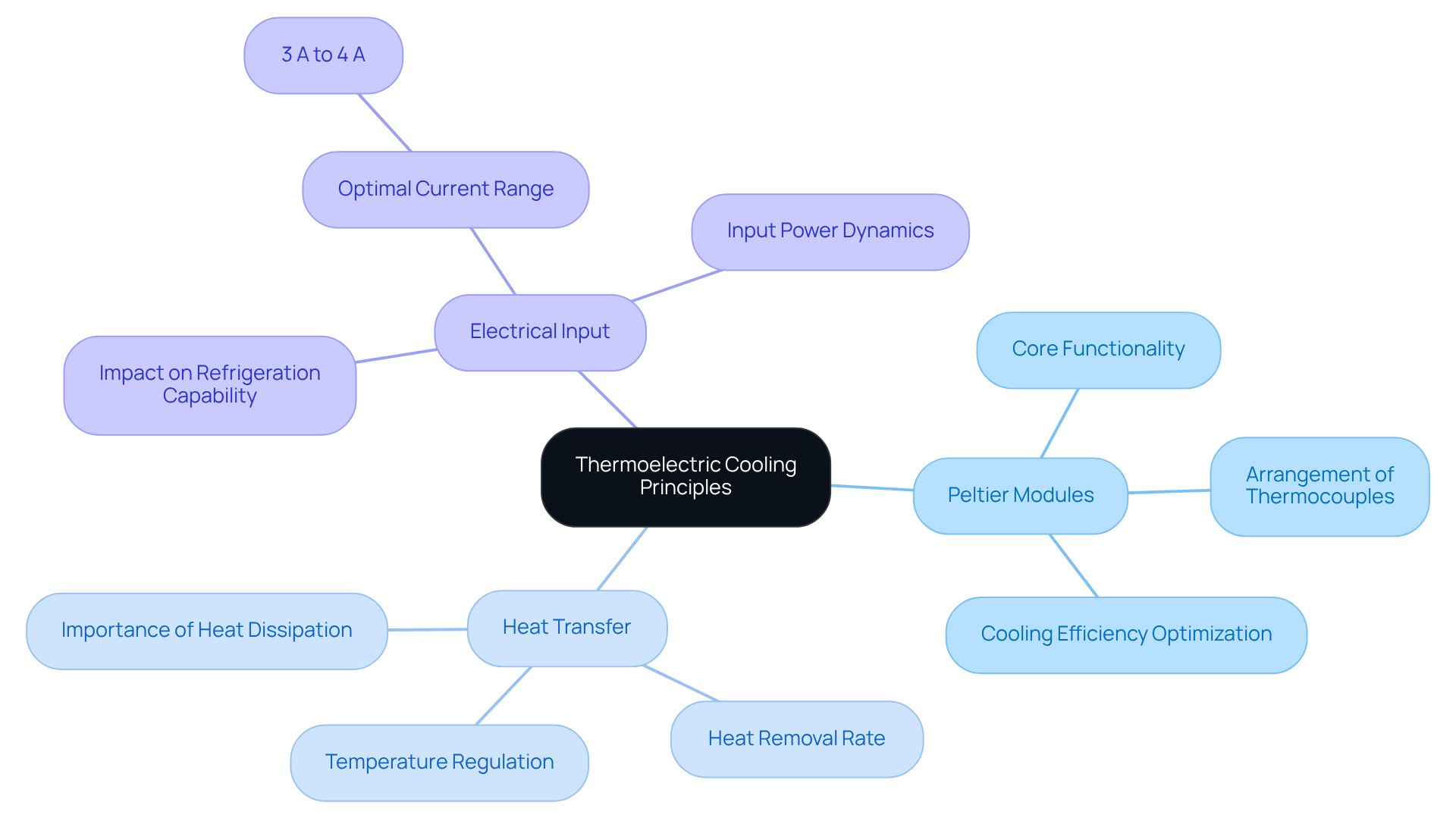
Thermoelectric refrigeration harnesses the Peltier effect, a phenomenon that occurs when an electric current flows through two dissimilar conductors, creating a temperature differential. This effect enables heat absorption on one side of the module while releasing it on the opposite side, making thermoelectric cooling technology a pivotal solution in thermal management.
Key Components of Thermoelectric Refrigeration:
- Peltier Modules: These modules are the core of thermoelectric coolers, consisting of numerous thermocouples arranged in series to optimize cooling efficiency.
- Heat Transfer: Effective heat dissipation from the hot side is crucial for maintaining optimal performance. The ability to regulate temperature is directly tied to how efficiently heat is removed.
- Electrical Input: The current supplied to the temperature-regulating module significantly impacts its refrigeration capability and overall efficiency. Research indicates that the optimal input current for maximizing performance typically ranges between 3 A and 4 A, where the temperature coefficient peaks at 32.
Understanding these principles is vital for improving the design and application of thermoelectric cooling technology in heat transfer systems across various industries, including consumer electronics and automotive sectors. Recent advancements in energy conversion module design, particularly those integrating heat pipes and fans, have demonstrated enhanced coefficients of performance (COP), achieving values as high as 0.53. This underscores the potential for superior thermal management solutions in modern technology.
Explore Applications of Thermoelectric Cooling Across Industries
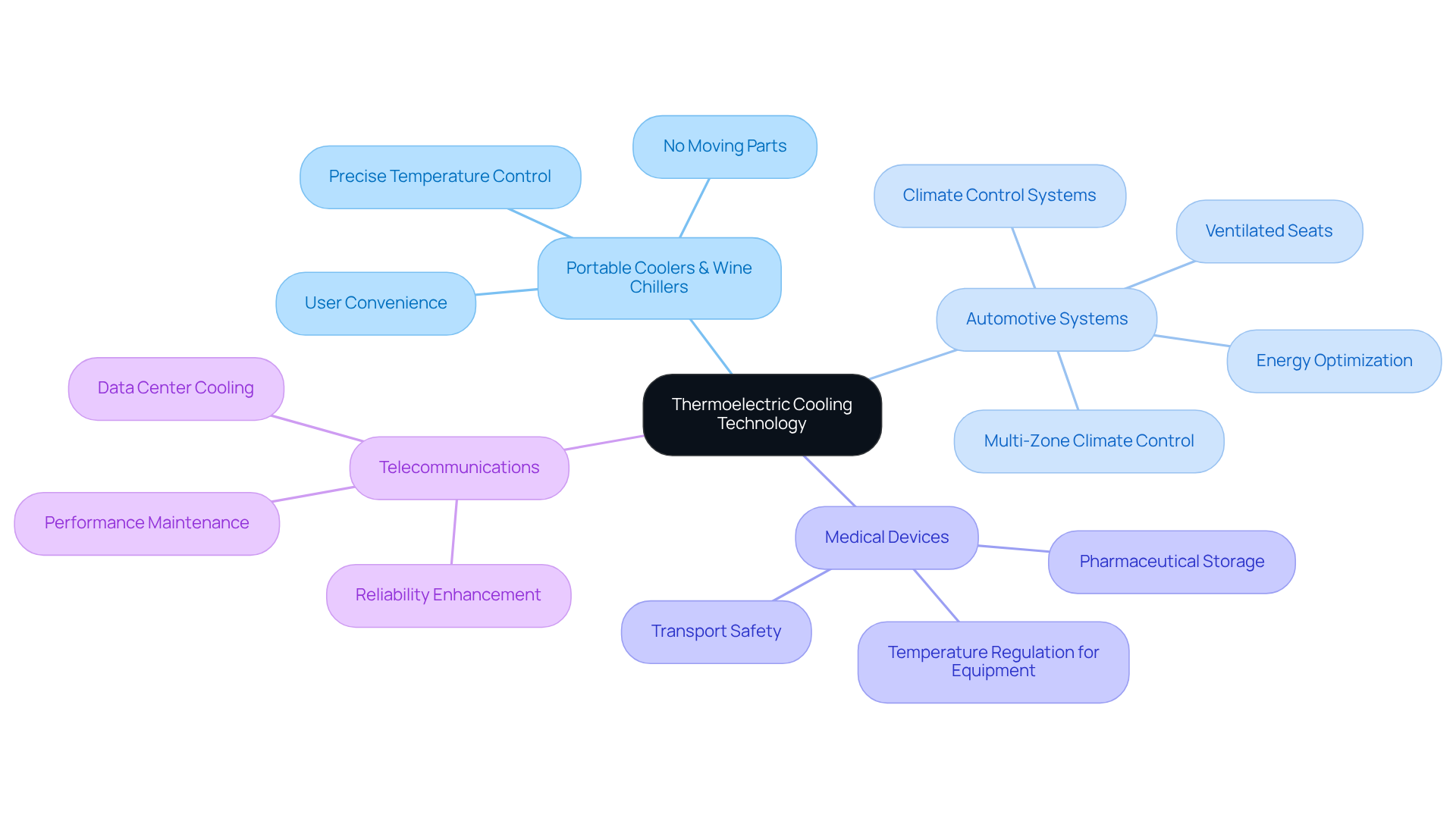
Thermoelectric Cooling Technology: A Versatile Solution Across Industries
Thermoelectric cooling technology is gaining recognition for its versatility across multiple applications, making it a significant player in various sectors.
In devices like portable coolers and wine chillers, thermoelectric cooling technology offers precise temperature control without moving parts. This innovation enhances user convenience and reliability, making it an attractive option for consumers seeking efficiency.
- Automotive Systems: Within the automotive sector, TECs are crucial for climate control systems. They significantly enhance passenger comfort while optimizing energy consumption. Industry leaders emphasize that integrating thermally driven systems can improve features such as ventilated seats and multi-zone climate control, ultimately making vehicles more efficient and comfortable.
- Medical Devices: In healthcare, maintaining the right temperature is vital for preserving delicate equipment and pharmaceuticals. Thermoelectric cooling technology ensures its effectiveness and safety during storage and transport, underscoring its importance in medical applications.
- Telecommunications: Telecommunications equipment requires thermoelectric cooling technology (TECs) to regulate temperature, which is critical for maintaining performance and reliability in data centers. As demand for data processing continues to rise, the role of TECs becomes increasingly vital.
These applications highlight the versatility of thermoelectric cooling technology, establishing it as a key solution across various sectors. Particularly in the automotive field, where energy efficiency and passenger comfort are paramount, the adoption of TECs is not just beneficial but essential.
Evaluate Advantages and Limitations of Thermoelectric Cooling
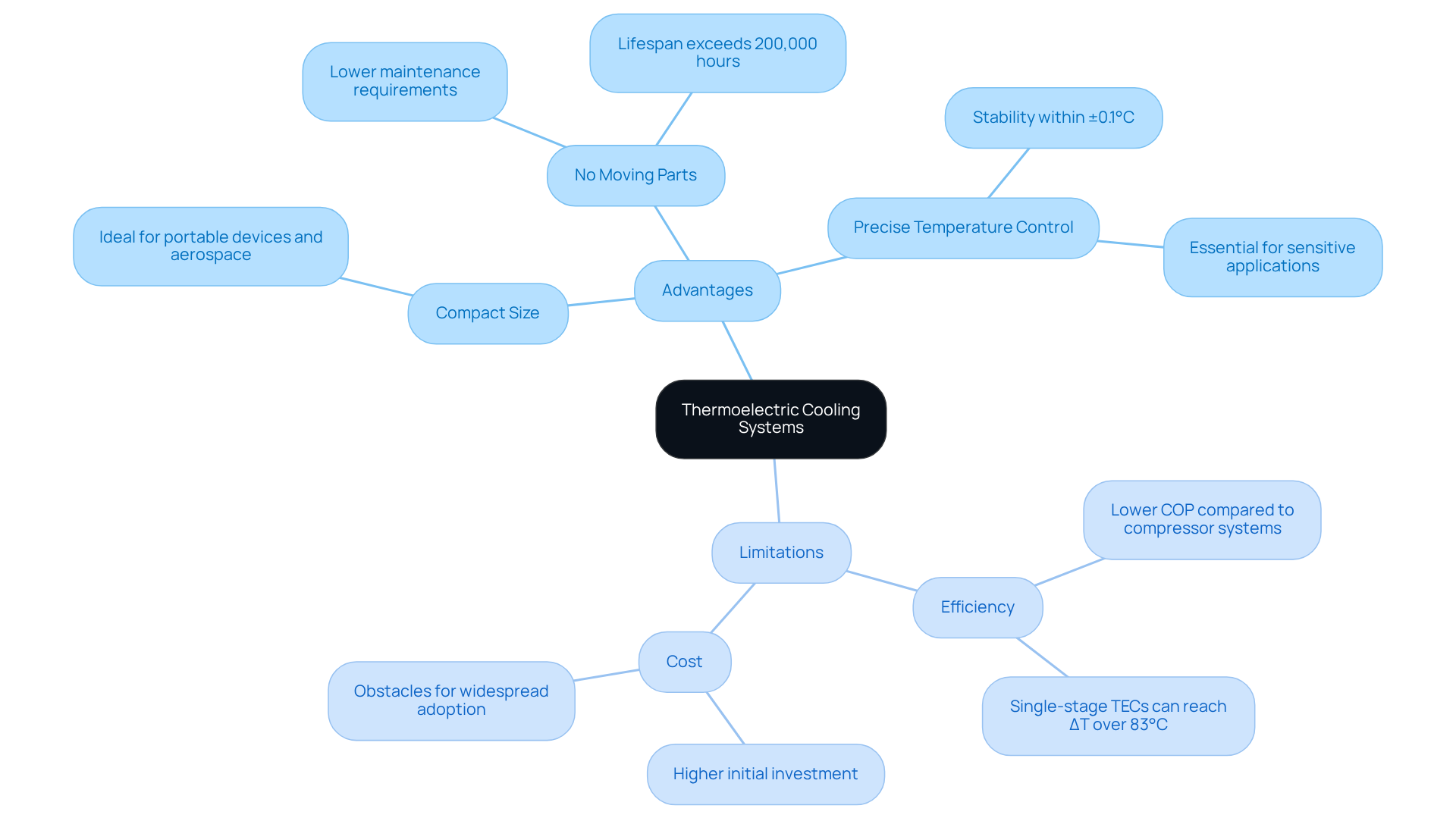
Advantages of Thermoelectric Cooling Systems
Thermoelectric cooling systems offer several notable advantages that make them a compelling choice for various applications:
- Compact Size: Thermoelectric coolers (TECs) are small and lightweight, making them ideal for applications with stringent space constraints, such as portable devices and aerospace technologies.
- No Moving Parts: The solid-state design of TECs eliminates moving components, resulting in lower maintenance requirements and increased reliability. Lifespans often exceed 200,000 hours under optimal conditions.
- Precise Temperature Control: TECs can achieve temperature stability within ±0.1°C, which is essential for sensitive applications like medical diagnostics and telecommunications.
Limitations to Consider
Despite these benefits, significant limitations warrant careful consideration:
- Efficiency: Thermoelectric coolers generally exhibit lower efficiency compared to traditional refrigeration methods. For instance, while single-stage TEC modules can reach a temperature differential (ΔT) of over 83°C, recent studies indicate a 210% improvement in power density for temperature reduction compared to leading commercial devices. However, their coefficient of performance (COP) often falls short of compressor-based systems, particularly in high-demand scenarios.
- Cost: The initial investment for thermoelectric cooling technology systems can be higher compared to traditional refrigeration solutions. This cost factor can pose an obstacle for widespread adoption, especially in budget-sensitive scenarios.
Real-World Implications
Real-world examples illustrate these limitations. In data centers, while TECs can reduce temperature management consumption by up to 30%, their lower thermal power density compared to traditional methods can lead to increased electrical consumption, particularly in large TEC arrays. Engineers frequently raise concerns about the trade-offs between the compactness and effectiveness of TECs versus conventional refrigeration methods, especially in high-performance scenarios where heat loads are significant. As U.S. Secretary of Energy Jennifer M. Granholm noted, integrating cooling devices is becoming a strategic imperative for data centers aiming to enhance operational efficiency while addressing rising energy demands.
Conclusion
Understanding these benefits and drawbacks is essential for engineers and designers when assessing temperature-regulating solutions tailored to their specific applications.
Implement Best Practices for Thermoelectric Cooling Solutions
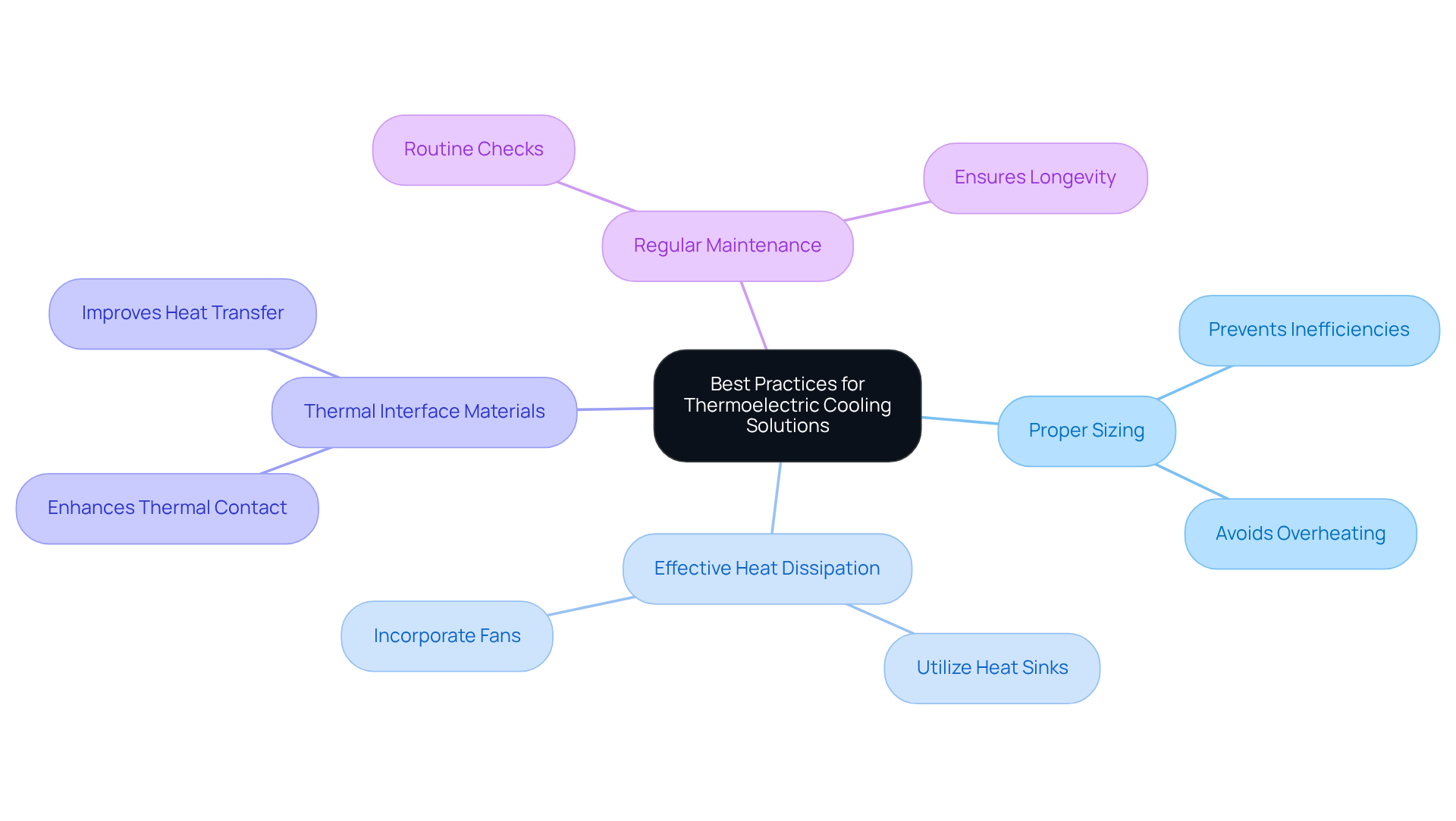
To ensure optimal performance of thermoelectric cooling technology, it’s crucial to implement effective strategies. Here are some best practices that can significantly enhance efficiency and reliability:
- Proper Sizing: Ensure that the thermoelectric cooler (TEC) is appropriately sized for your specific application. This prevents inefficiencies and overheating, which can compromise performance.
- Effective Heat Dissipation: Utilize heat sinks or fans to facilitate better heat transfer from the hot side of the TEC. This step is vital for maintaining optimal performance levels.
- Thermal Interface Materials: Apply high-quality thermal interface materials to enhance thermal contact between the TEC and the surfaces it cools. This ensures efficient heat transfer and improves overall system effectiveness.
- Regular Maintenance: Schedule routine checks to clean and maintain the temperature regulation system. Consistent maintenance is key to ensuring longevity and reliable performance.
By adhering to these best practices, engineers can significantly boost the reliability and efficiency of thermoelectric cooling technology solutions, ultimately leading to enhanced system performance.
Conclusion
Thermoelectric cooling technology stands as a pivotal solution in thermal management, harnessing the Peltier effect to establish efficient temperature differentials. This innovative approach not only amplifies cooling capabilities across a spectrum of applications but also presents distinct advantages, including compact size, reliability, and precise temperature control. As industries increasingly emphasize energy efficiency and performance, grasping the principles and mechanisms of thermoelectric cooling is crucial for optimizing design and implementation.
This article delves into the essential components of thermoelectric refrigeration, underscoring the importance of Peltier modules, effective heat transfer, and optimal electrical input. It explores the diverse applications of this technology, ranging from automotive climate control systems to medical device temperature regulation, showcasing its versatility and growing significance across various sectors. Furthermore, a thorough analysis of both advantages and limitations offers a comprehensive perspective, highlighting the necessity for careful consideration in adopting thermoelectric cooling solutions.
In conclusion, as industries evolve and demand more efficient thermal management solutions, the role of thermoelectric cooling technology is set to expand. By embracing best practices in implementation and maintenance, organizations can significantly enhance the effectiveness of these systems, paving the way for innovative applications in the future. The insights gained from this exploration emphasize the potential of thermoelectric cooling as a cornerstone of modern thermal management strategies, urging engineers and designers to integrate this technology into their solutions for improved performance and sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is thermoelectric refrigeration?
Thermoelectric refrigeration is a technology that utilizes the Peltier effect, where an electric current flowing through two dissimilar conductors creates a temperature differential, allowing for heat absorption on one side of a module and heat release on the opposite side.
What are the key components of thermoelectric refrigeration?
The key components include Peltier modules, which consist of numerous thermocouples arranged in series for optimized cooling efficiency, effective heat transfer mechanisms for dissipating heat from the hot side, and electrical input, where the current supplied affects the refrigeration capability and efficiency.
What is the optimal current range for thermoelectric modules to maximize performance?
Research indicates that the optimal input current for maximizing performance typically ranges between 3 A and 4 A, where the temperature coefficient peaks at 32.
Why is effective heat dissipation important in thermoelectric cooling?
Effective heat dissipation from the hot side is crucial for maintaining optimal performance, as the ability to regulate temperature is directly tied to how efficiently heat is removed.
How have recent advancements improved thermoelectric cooling technology?
Recent advancements, particularly in energy conversion module design that integrates heat pipes and fans, have demonstrated enhanced coefficients of performance (COP), achieving values as high as 0.53, which indicates improved thermal management solutions in modern technology.
In which industries is thermoelectric cooling technology applied?
Thermoelectric cooling technology is applied across various industries, including consumer electronics and automotive sectors, for effective thermal management.

