Overview
This article provides a comprehensive comparison between mini cooling fans and traditional cooling solutions, addressing a critical issue in thermal management. Mini fans are particularly advantageous for compact spaces and energy efficiency, making them an excellent choice for specific applications. In contrast, traditional cooling methods excel in managing heat for larger systems, showcasing their effectiveness in more extensive setups.
Engineers must weigh the respective advantages and disadvantages of these cooling solutions. Key factors include:
- Size
- Power consumption
- Application suitability
For instance, mini fans often consume less power, which can lead to significant energy savings in smaller designs. However, when dealing with larger systems, traditional cooling methods may offer superior thermal management capabilities.
Ultimately, the choice between mini cooling fans and traditional solutions hinges on the specific requirements of the project at hand. By carefully considering these factors, engineers can select the most appropriate cooling solution, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency in their designs.
Introduction
The rapid evolution of electronic devices has heightened the demand for effective cooling solutions, especially as components shrink and gain power. Enter mini cooling fans—these compact, energy-efficient alternatives are revolutionizing the landscape, challenging traditional cooling methods like heat sinks and large blowers.
But can these miniaturized systems genuinely rival established solutions in performance and reliability? This article explores the advantages and disadvantages of mini cooling fans compared to traditional cooling methods, equipping engineers with essential insights to make informed design decisions.
Comparing Mini Cooling Fans and Traditional Cooling Solutions
Mini cooling fans serve as miniature ventilation devices that efficiently disperse heat from electronic components, making them ideal for applications in restricted spaces. Typically powered by DC voltage, these devices integrate seamlessly into various electronic systems. In contrast, conventional heat dissipation methods, such as heat sinks and larger blowers, often depend on passive or active temperature control techniques that demand more space and power. While small ventilation devices excel in providing effective airflow in tight areas, traditional options generally offer superior thermal control for larger systems.
The market for compact direct current ventilators is projected to expand significantly, driven by technological advancements and an increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions. Currently, small devices account for approximately 25% of the temperature control market within the electronics sector. Engineers have noted that mini cooling fans not only enhance the performance of compact electronic designs but also contribute to energy savings due to their lower power consumption compared to traditional AC models.
Practical applications of small ventilation devices are evident across multiple industries, including automotive, consumer electronics, and HVAC systems. For instance, the Cmyfato Powerful Portable Pivoting Bathroom Device exemplifies how compact appliances can deliver efficient air circulation in limited spaces, featuring three speed options and a 270° pivoting capability.
Engineers have praised the efficiency of small ventilation devices in constrained environments, highlighting their ability to maintain optimal operating temperatures while minimizing noise levels. As the demand for innovative temperature control solutions continues to rise, understanding the distinct advantages of mini cooling fans compared to conventional methods becomes essential for engineers aiming to enhance their designs.
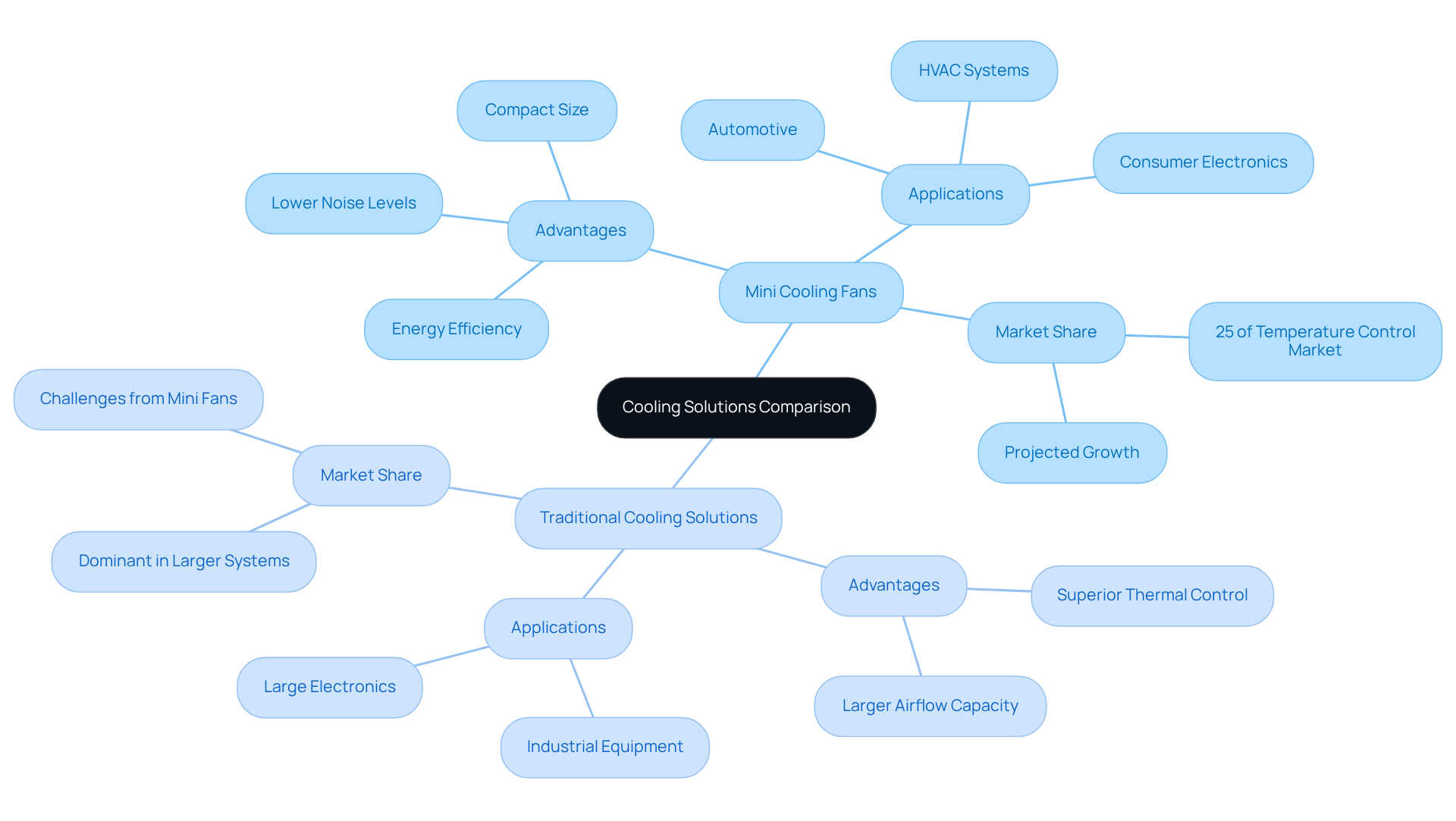
Advantages and Disadvantages of Mini Cooling Fans
Mini cooling fans provide significant advantages, particularly their compact size, making them ideal for applications where space is at a premium. These mini cooling fans are typically straightforward to install and can provide substantial airflow, enhancing the temperature regulation of critical components. However, it is essential to consider their drawbacks. For instance, potential noise generation can pose challenges in sensitive environments. Additionally, their lifespan may be shorter compared to traditional options due to mechanical wear and tear.
Engineers must weigh these factors carefully when assessing whether small ventilation devices are the right choice for their specific applications. By understanding both the benefits and limitations, professionals can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
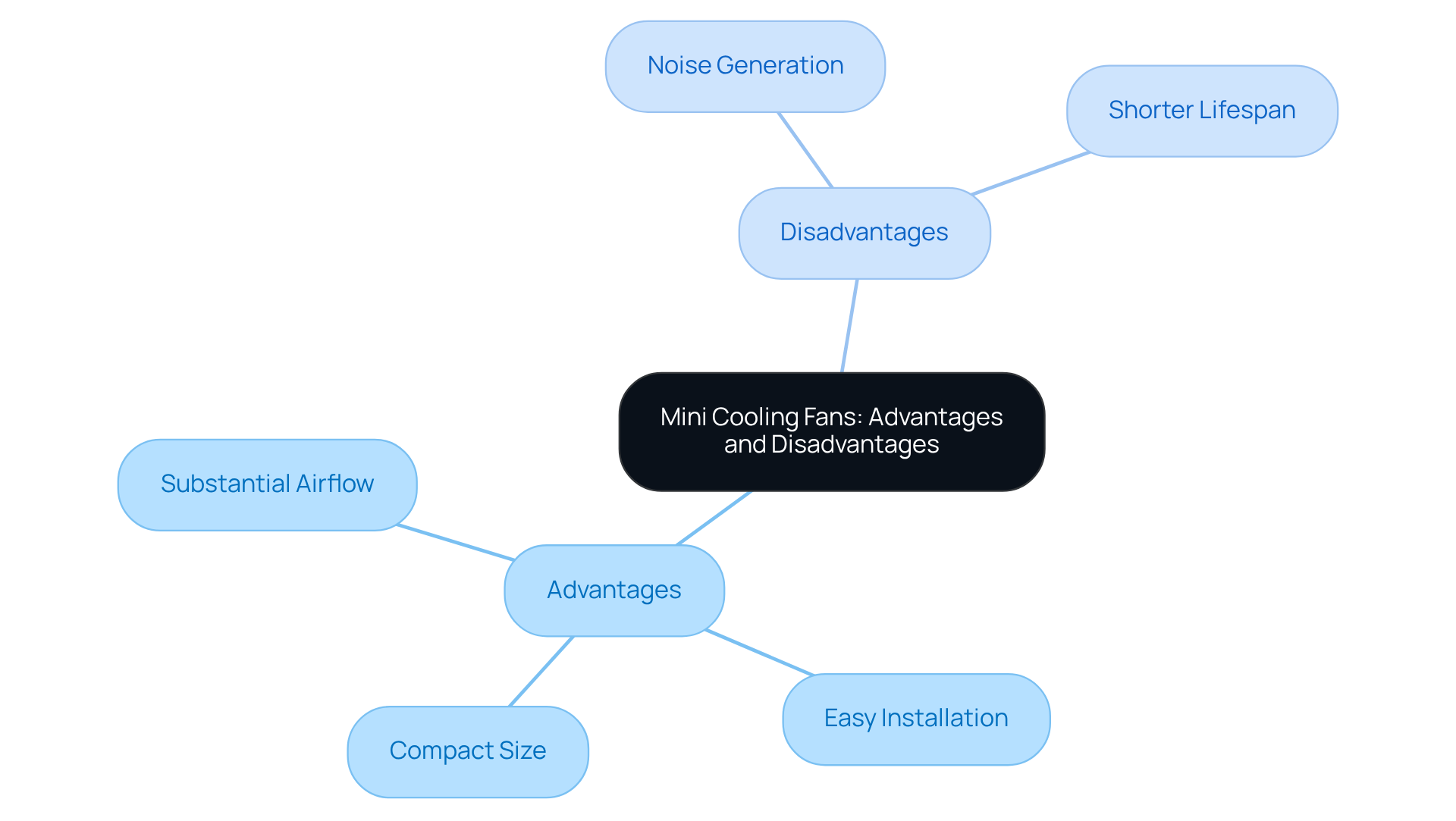
Advantages and Disadvantages of Traditional Cooling Solutions
Conventional cooling methods, such as heat sinks and larger cooling devices, are renowned for their efficient thermal management capabilities, particularly in dissipating heat from high-power components. These systems typically demonstrate superior reliability over extended periods, making them a preferred choice across various applications. However, their bulkiness can present challenges in compact designs, where space is at a premium. Furthermore, the increased power demands of larger units can limit their applicability in energy-sensitive environments, especially considering that energy-efficient systems can reduce energy consumption by 15-30%.
Installation complexity is another critical factor; traditional solutions often require meticulous planning regarding airflow and thermal dynamics to ensure optimal performance. For instance, engineers have noted that while heat sinks provide consistent temperature management, they may not always align with the dynamic responses of small air movers in rapidly changing thermal environments.
Real-world applications highlight these trade-offs. In high-performance computing environments, larger cooling devices have been effectively employed to manage heat in densely packed server racks, demonstrating their efficiency in maintaining operational stability. Conversely, mini cooling fans have gained traction in portable gadgets, where their compact size and lower energy consumption are vital.
As we approach 2025, the reliability of heat sinks remains a focal point for engineers, particularly in applications that demand long-term performance. While mini cooling fans provide flexibility and adaptability, the established reliability of heat sinks continues to offer significant advantages in numerous thermal management scenarios. Ultimately, engineers must carefully evaluate these factors against the specific temperature control requirements of their projects to identify the most suitable solution.
Choosing the Right Cooling Solution for Electronics Engineering
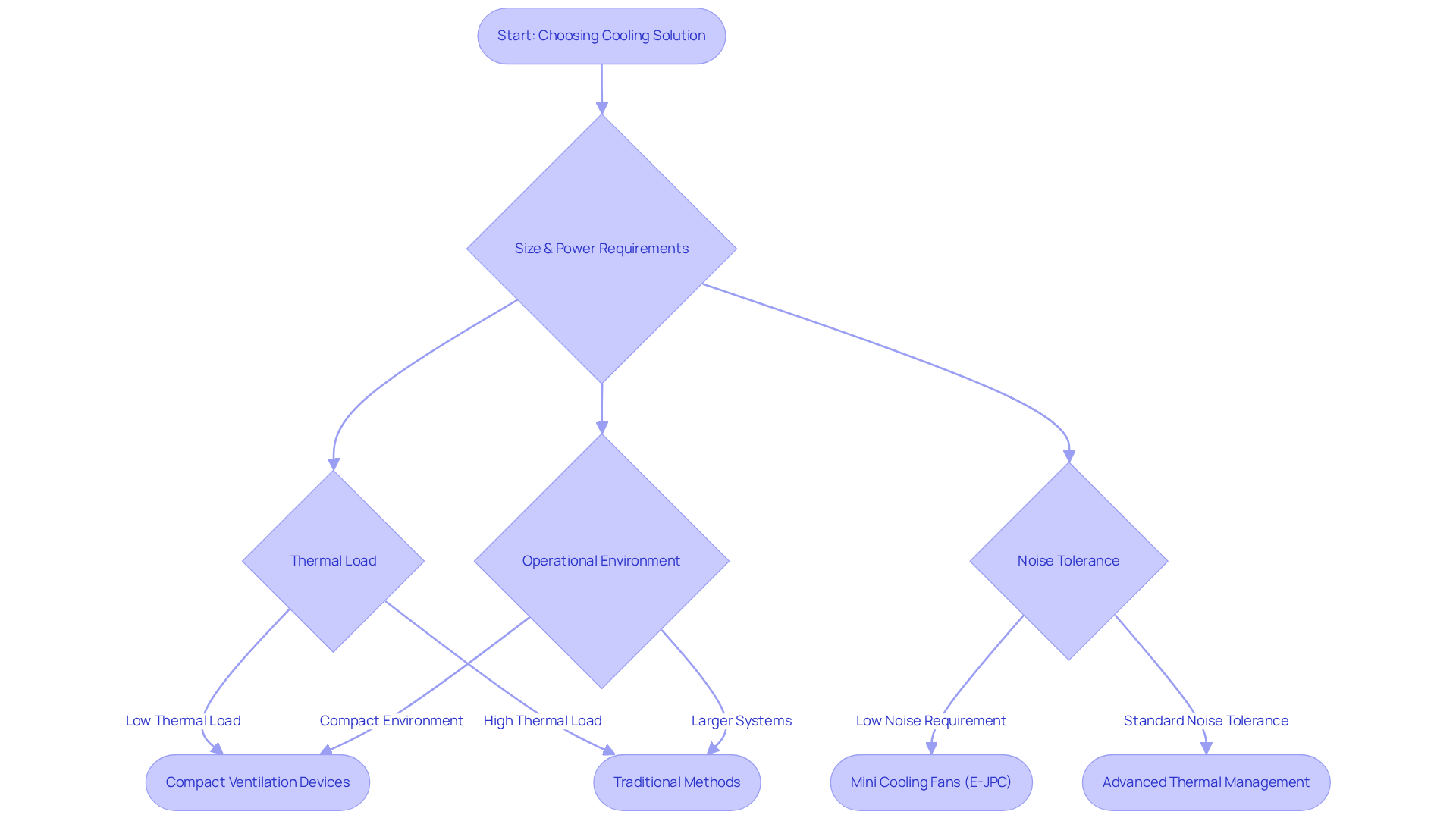
Choosing the right thermal method for electronic components is a complex task that demands careful consideration of several critical factors. Engineers must evaluate the size and power requirements of their devices, the thermal load generated during operation, and the specific operational environment. In scenarios where space is limited, compact ventilation devices often emerge as the optimal choice due to their efficiency and design. Conversely, traditional temperature control methods may be better suited for larger systems that necessitate enhanced thermal management capabilities.
Another vital factor influencing decision-making is noise tolerance. Applications that require low noise levels may prefer mini cooling fans, especially E-JPC fans, which are designed to operate quietly while providing precise temperature regulation. Additionally, integrating power management with thermal design is essential for boosting overall system efficiency, ensuring that temperature control methods work harmoniously with power systems.
Ultimately, the ideal temperature regulation solution relies on a comprehensive evaluation of these criteria, maximizing performance and reliability in the final design. Real-world examples illustrate how engineers assess temperature regulation techniques based on thermal load. For instance, in high-performance applications like medical imaging systems, where over 50% of global CT scan machines utilize advanced ventilation fans, understanding internal heat generation is crucial for selecting the right fan. This assessment aids in calculating the necessary airflow to effectively manage thermal load. Furthermore, data indicates that space constraints significantly impact electronics design, with many engineers reporting challenges in accommodating conventional temperature management methods within compact device structures. Aging effects on thermal performance must also be factored in to ensure the long-term reliability of cooling solutions. By prioritizing these considerations, including material selection for thermal management, engineers can make informed decisions that enhance the thermal management of their electronic systems.
Conclusion
Mini cooling fans and traditional cooling solutions each offer unique advantages tailored to specific engineering needs. As the demand for efficient thermal management continues to rise, understanding the nuances between these two approaches is imperative for engineers aiming to optimize their designs. Mini cooling fans, with their compact size and lower power consumption, present a compelling choice for applications constrained by space. In contrast, traditional methods excel in larger systems where superior thermal control is essential.
Key insights throughout the article highlight the practical applications and performance characteristics of both cooling methods. Mini cooling fans are celebrated for their ability to maintain optimal temperatures in tight environments, providing substantial airflow with minimal noise. Conversely, traditional cooling solutions like heat sinks and larger blowers are recognized for their reliability and effectiveness in managing heat from high-power components. The choice between these options ultimately hinges on factors such as space limitations, noise tolerance, and the specific thermal requirements of the application.
In a rapidly evolving technological landscape, engineers must carefully evaluate their cooling solutions based on the criteria discussed. By weighing the benefits and drawbacks of mini cooling fans versus traditional systems, professionals can make informed decisions that enhance the performance and longevity of their electronic designs. Embracing innovative cooling technologies not only improves efficiency but also contributes to the sustainability of electronic systems, ensuring they meet the demands of the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are mini cooling fans and how do they work?
Mini cooling fans are small ventilation devices that efficiently disperse heat from electronic components, making them suitable for use in restricted spaces. They are typically powered by DC voltage and integrate seamlessly into various electronic systems.
How do mini cooling fans compare to traditional cooling solutions?
Mini cooling fans excel in providing effective airflow in tight areas, while traditional cooling solutions, such as heat sinks and larger blowers, offer superior thermal control for larger systems. Traditional methods often depend on passive or active temperature control techniques that require more space and power.
What is the market trend for mini cooling fans?
The market for compact direct current ventilators is projected to expand significantly due to technological advancements and an increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions. Currently, small devices account for approximately 25% of the temperature control market within the electronics sector.
What are the benefits of using mini cooling fans in electronic designs?
Mini cooling fans enhance the performance of compact electronic designs and contribute to energy savings due to their lower power consumption compared to traditional AC models.
In which industries are mini cooling fans commonly used?
Mini cooling fans are used across multiple industries, including automotive, consumer electronics, and HVAC systems.
Can you provide an example of a mini cooling fan product?
The Cmyfato Powerful Portable Pivoting Bathroom Device is an example of a compact appliance that delivers efficient air circulation in limited spaces, featuring three speed options and a 270° pivoting capability.
What advantages do mini cooling fans offer in constrained environments?
Mini cooling fans maintain optimal operating temperatures while minimizing noise levels, making them efficient for use in constrained environments.
Why is it important for engineers to understand the advantages of mini cooling fans?
Understanding the distinct advantages of mini cooling fans compared to conventional methods is essential for engineers aiming to enhance their designs, especially as the demand for innovative temperature control solutions continues to rise.