Introduction
In the realm of electronics, the decision between PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) and DC (Direct Current) fans is pivotal, influencing performance, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Engineers are increasingly gravitating towards PWM technology due to its remarkable capability to dynamically adjust fan speeds, resulting in significant energy savings and reduced noise levels. Yet, the simplicity and reliability of DC fans continue to attract interest for various applications.
As the landscape of cooling solutions evolves, engineers must consider several critical factors when navigating the complexities of PWM versus DC fans:
- Performance
- Efficiency
- Cost-effectiveness
- Energy savings
- Noise levels
- Application suitability
Understanding these distinctions is essential for making informed decisions that align with specific project requirements.
Define PWM and DC Fans: Core Concepts and Mechanisms
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) units utilize a control signal to adjust motor speed by varying the width of electrical pulses sent to the motor. This capability allows for precise velocity control, enabling fans to operate at lower speeds without stalling – an essential feature for applications requiring variable cooling. Notably, reducing a blower’s rotation by 20% can decrease power consumption by nearly 50%, underscoring the efficiency of PWM technology.
In contrast, DC (Direct Current) devices function by modifying the voltage supplied to the motor, typically resulting in a constant speed unless connected to a controller. PWM units generally come with a four-pin connector, where the additional pin is designated for the PWM signal, while DC units usually have a three-pin connector. This fundamental design difference between fan PWM vs DC leads to distinct performance characteristics regarding efficiency and control.
Gagner-Toomey Associates offers an extensive range of DC input Tube Axial units, from 15 to 280mm, alongside a comprehensive selection of DC input Centrifugal Blowers, ranging from 15 to 225mm. This positions them as a leading supplier of cooling solutions for diverse applications.
PWM cooling devices are particularly suited for high-performance computing systems, such as gaming PCs and workstations, as they can dynamically adjust their speed based on system demands. This adaptability not only enhances energy efficiency but also reduces operational costs. Research indicates that PWM technology can achieve power consumption reductions of up to 30%.
Moreover, a standard DC fan operating at full speed may produce noise levels around 45 dBA, whereas a PWM fan at a 50% duty cycle can operate as quietly as 22 dBA. This comparison highlights the significant noise reduction potential of PWM fans.
Case studies further illustrate the effectiveness of PWM units in various settings, including data centers, where they contribute to lower noise levels and improved thermal management. Conversely, DC motors are commonly employed in automotive and medical equipment due to their reliability and quieter operation.
Understanding these distinctions is vital for engineers when selecting the appropriate fan technology, especially in the context of fan PWM vs DC for specific temperature regulation needs. Gagner-Toomey’s innovative temperature control solutions provide the necessary options to meet these demands.
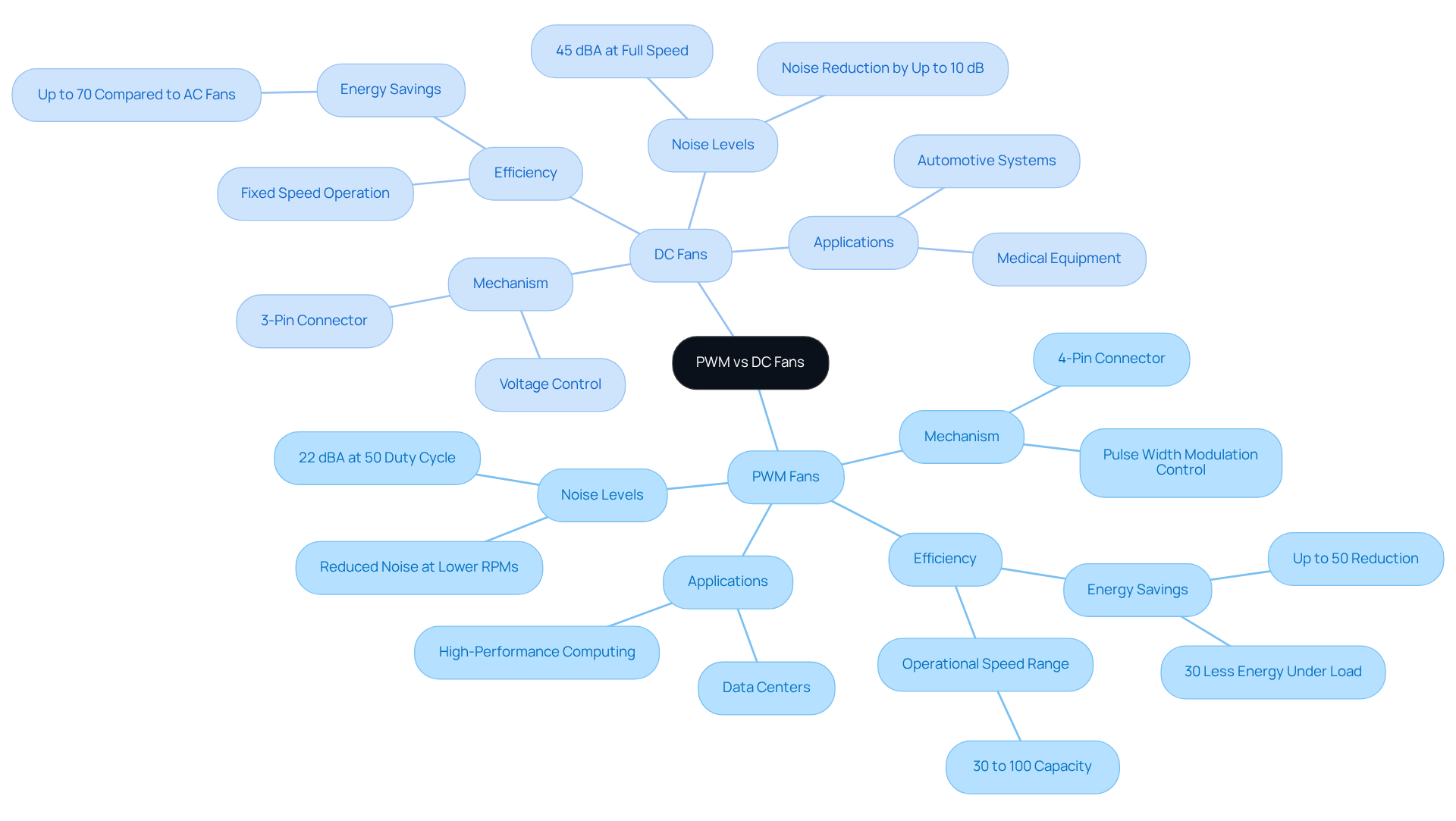
Compare Performance Efficiency: PWM vs. DC Fans in Cooling Applications
PWM devices significantly enhance performance efficiency in dynamic temperature control applications by adjusting their operational rates based on thermal requirements. This adaptability allows them to achieve lower minimum RPMs, often operating as low as 20% of their maximum speed, which notably reduces noise levels during low-load conditions. In contrast, when evaluating fan PWM vs DC, traditional DC fans typically maintain a constant speed, resulting in higher RPM floors that lead to increased noise and energy consumption, even when cooling demands are minimal.
For example, systems utilizing PWM technology can achieve noise reductions of up to 30% compared to conventional DC models, making them ideal for environments where acoustic comfort is paramount. Furthermore, PWM devices can decrease energy usage by as much as 50%, enhancing their effectiveness across various applications. Notably, the Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) can improve from 1.55 to 1.42 during control periods with PWM technology, highlighting the practical benefits of this fan type in data centers.
Consequently, in scenarios with fluctuating thermal loads, the comparison of fan PWM vs DC devices shows that PWM devices are generally more efficient and quieter than their DC counterparts, presenting an appealing option for engineers focused on optimizing thermal management. However, it is crucial to consider potential compatibility issues with motherboards when selecting PWM units, as well as their tendency to wear out less than DC fans due to their ability to spin down easily.
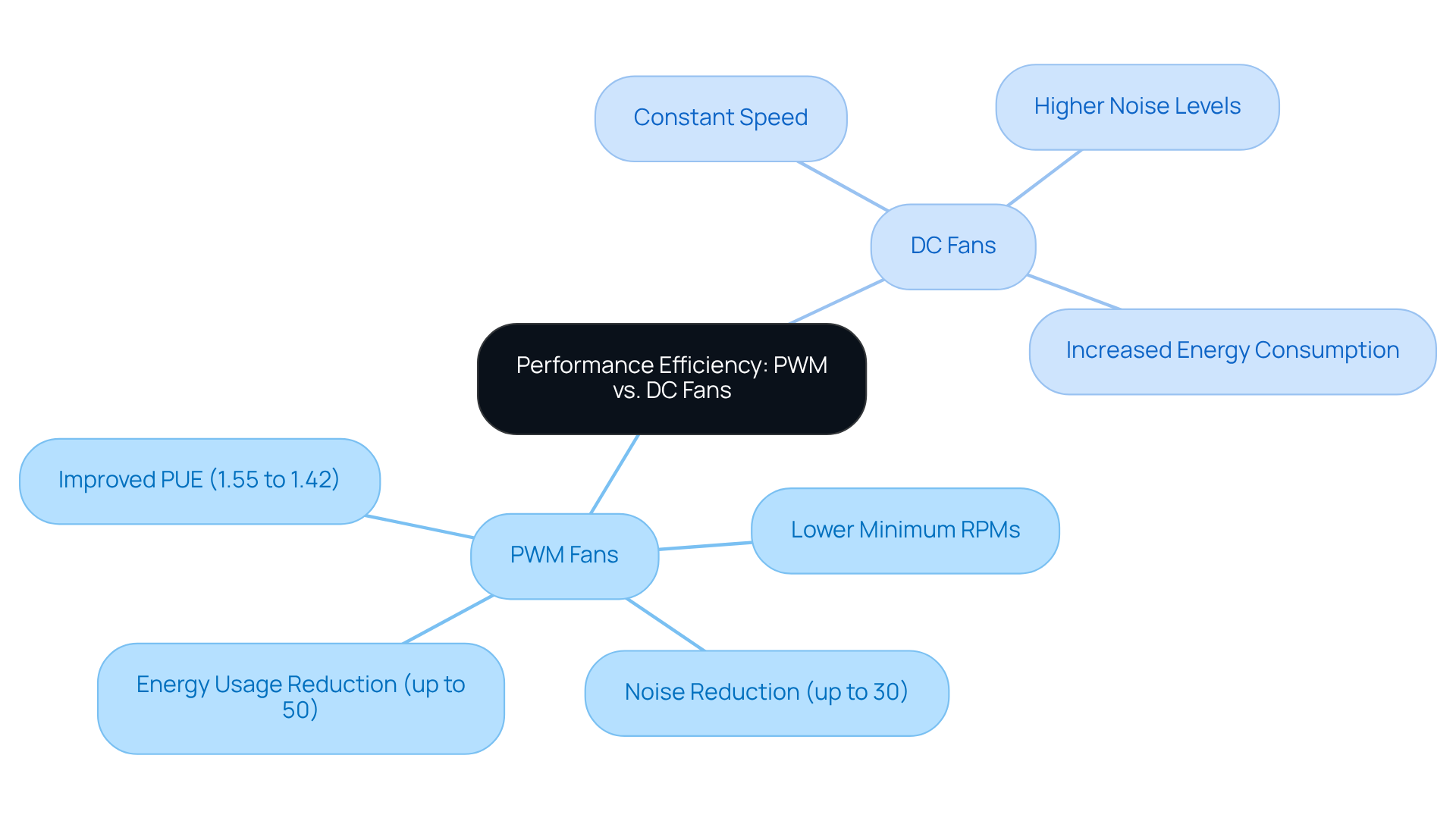
Evaluate Energy Consumption: Efficiency and Cost Implications of PWM and DC Fans
When discussing energy usage, the comparison of fan PWM vs DC devices reveals that PWM devices stand out for their superior efficiency compared to traditional DC models. PWM technology allows devices to operate at lower rates without sacrificing performance, leading to energy savings of up to 30%. For instance, consider a scenario in the fan PWM vs DC context where a PWM fan runs at 50% load; it consumes significantly less power than a DC fan that operates at a constant speed. This efficiency not only translates into lower electricity bills but also reduces heat generation, ultimately enhancing the lifespan of electronic components.
Moreover, PWM devices are highly adaptable to varying thermal requirements, making them particularly suitable for dynamic environments. It’s essential to recognize that PWM devices typically feature a 4-pin connector, whereas DC units utilize a 3-pin connector. This distinction is crucial for ensuring compatibility with modern systems.
On the other hand, while DC devices may appear less expensive initially, the analysis of fan PWM vs DC shows that they often lead to higher operational costs over time due to their less efficient power usage. For engineers focused on long-term cost efficiency and sustainability, PWM devices frequently present a more economical choice, especially in high-performance settings where precise temperature regulation and noise reduction are paramount.
In summary, choosing PWM technology not only enhances operational efficiency but also contributes to significant cost savings and improved reliability in electronic applications.
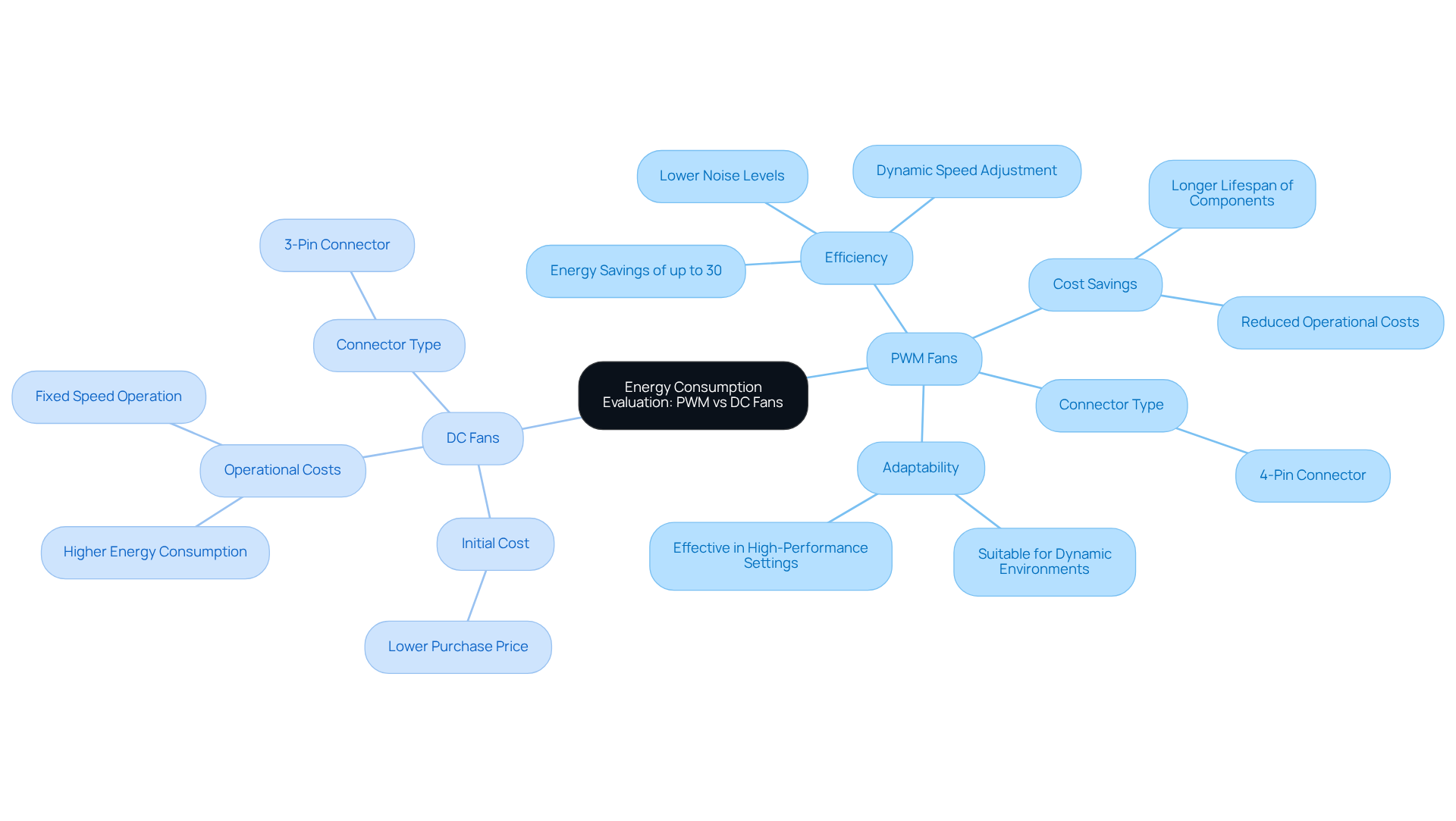
Assess Application Suitability: Choosing Between PWM and DC Fans for Engineering Needs
Choosing between fan PWM vs DC devices necessitates careful consideration of application-specific needs. PWM motors shine in environments with varying cooling demands, such as gaming PCs and servers, where minimizing noise and maximizing energy efficiency are paramount. Their capacity to dynamically adjust speed enables precise thermal management, making them ideal for high-performance applications. For instance, data centers employing PWM technology have reported efficiency improvements in temperature management of up to 30%, underscoring their effectiveness in demanding environments. Furthermore, PWM units necessitate four pins for connection, while DC variants typically require three – an essential factor for engineers assessing compatibility with their systems.
Conversely, DC devices are often more suitable for simpler systems or budget-conscious projects where a constant speed suffices. They deliver reliable performance in older hardware configurations or basic thermal management applications without the added complexity of PWM control. Indeed, many pre-assembled PCs still rely on DC blowers due to their lower cost and sufficient temperature control for standard tasks. However, it’s crucial to recognize that DC devices can generate electrical noise when operating below 12 volts, which may pose challenges in noise-sensitive environments.
Ultimately, the decision between fan PWM vs DC units should be informed by specific cooling requirements, budget constraints, and desired operational characteristics for the project. Engineers must evaluate factors such as noise levels, energy efficiency, and the necessity for precise control to identify the most appropriate fan type for their applications. As Friedrich Stiemer aptly noted, “PWM fans usually last longer than DC variants,” a significant consideration for long-term reliability.
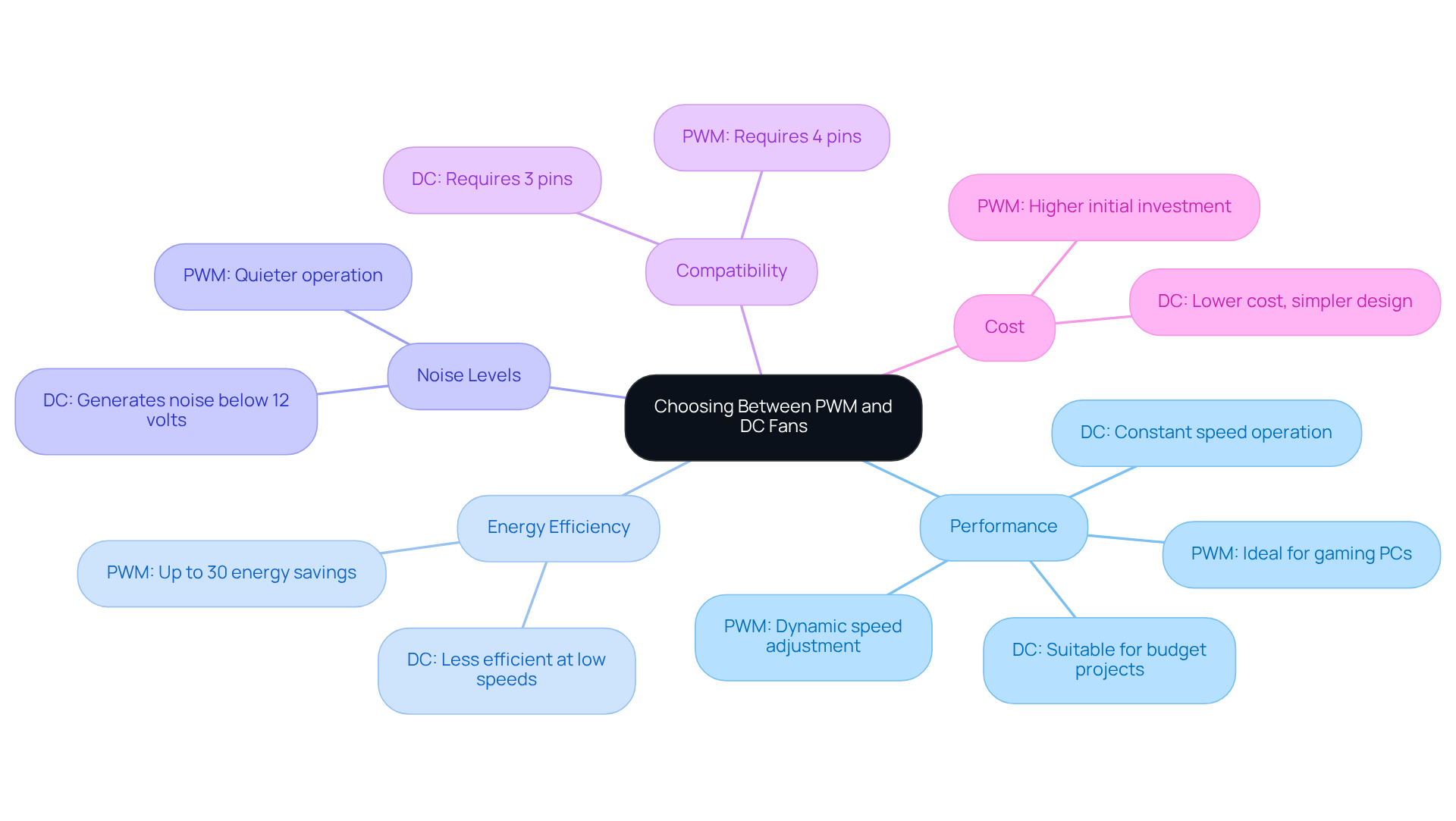
Conclusion
In conclusion, the comparison between PWM and DC fans reveals a fundamental distinction in their operational mechanisms and performance characteristics. PWM fans, with their ability to dynamically adjust speed based on thermal demands, offer significant advantages in energy efficiency and noise reduction. This adaptability makes them particularly suited for high-performance applications, where precise temperature control is essential.
Key insights throughout this discussion highlight how PWM fans can reduce power consumption by up to 50% and achieve noise levels as low as 22 dBA, in stark contrast to the higher operational noise of traditional DC fans. While DC fans may present a more cost-effective option initially, the long-term operational costs often favor PWM technology due to its superior efficiency and longevity. Engineers must carefully consider these factors when selecting the appropriate fan technology for their specific applications.
Ultimately, the choice between PWM and DC fans hinges on the unique requirements of each project. For environments demanding high efficiency, low noise, and adaptable cooling solutions, PWM fans emerge as the clear winner. Conversely, DC fans may suffice for simpler, budget-friendly applications. By understanding the nuances of PWM versus DC fans, engineers can make informed decisions that enhance performance, reduce costs, and ensure reliability in their cooling systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is PWM in the context of fans?
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) is a technology that uses a control signal to adjust the motor speed of fans by varying the width of electrical pulses sent to the motor, allowing for precise speed control.
How does PWM technology benefit fan operation?
PWM technology enables fans to operate at lower speeds without stalling, which is essential for applications requiring variable cooling. Reducing a blower’s rotation by 20% can decrease power consumption by nearly 50%.
What is the difference between PWM and DC fans?
PWM fans typically have a four-pin connector that includes a pin for the PWM signal, allowing for speed control, while DC fans usually have a three-pin connector and modify voltage to control speed, resulting in constant speeds unless a controller is used.
What types of fans does Gagner-Toomey Associates offer?
Gagner-Toomey Associates offers a wide range of DC input Tube Axial units from 15 to 280mm and DC input Centrifugal Blowers from 15 to 225mm, making them a leading supplier of cooling solutions.
In what applications are PWM cooling devices particularly effective?
PWM cooling devices are especially suited for high-performance computing systems, such as gaming PCs and workstations, as they can dynamically adjust their speed based on system demands, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing operational costs.
How does the noise level of PWM fans compare to DC fans?
A standard DC fan operating at full speed may produce noise levels around 45 dBA, while a PWM fan operating at a 50% duty cycle can operate as quietly as 22 dBA, highlighting the noise reduction potential of PWM fans.
What are some advantages of using PWM technology in data centers?
PWM units in data centers contribute to lower noise levels and improved thermal management, making them effective for maintaining optimal operating conditions.
Where are DC motors commonly used?
DC motors are commonly employed in automotive and medical equipment due to their reliability and quieter operation.
Why is it important for engineers to understand the differences between PWM and DC fans?
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for engineers when selecting the appropriate fan technology for specific temperature regulation needs, ensuring optimal performance in their applications.

