Overview
Cold plate manufacturers play a pivotal role in the production of thermal control devices that efficiently dissipate heat from electronic components. This function is essential for ensuring optimal performance and reliability across a variety of applications. The significance of these manufacturers becomes particularly clear when addressing challenges such as thermal interface material issues and cost management. Moreover, the growing demand for efficient cooling solutions in sectors like electric vehicles and data centers underscores their importance in the industry.
As the need for advanced thermal management solutions escalates, cold plate manufacturers are at the forefront of innovation. They tackle complex thermal challenges by developing sophisticated products that meet the stringent requirements of modern electronic systems. This proactive approach not only enhances device performance but also contributes to the overall reliability of electronic components.
In conclusion, the role of cold plate manufacturers is increasingly critical in a landscape where efficient cooling solutions are in high demand. By addressing thermal interface material challenges and managing costs effectively, these manufacturers are well-positioned to support the evolving needs of industries reliant on advanced thermal management technologies.
Introduction
Cold plate manufacturers play a pivotal role in the realm of thermal management, crafting essential devices that dissipate heat from electronic components and ensure optimal performance. As the demand for efficient cooling solutions surges—particularly in high-powered sectors like electric vehicles and data centers—understanding the intricacies of cold plate technology becomes crucial. However, with this growing importance comes a set of challenges, ranging from material costs to manufacturing complexities, that manufacturers must navigate to meet the evolving needs of the electronics industry.
What strategies can these manufacturers employ to overcome these hurdles and continue driving innovation in thermal management? By addressing these challenges head-on, they can not only enhance their product offerings but also solidify their position as leaders in the industry.
Define Cold Plate Manufacturers and Their Functionality
Chilled surface manufacturers concentrate on producing essential thermal control devices, which play a crucial role in dissipating heat from electronic components. Typically crafted from conductive materials such as aluminum or copper, these thermal components feature a flat metallic surface designed for optimal thermal transfer. They are fundamental to cooling systems, absorbing heat from high-temperature parts and transferring it to a circulating coolant, effectively relocating heat away from the source.
The importance of chilled surfaces in electronic cooling cannot be overstated, particularly in high-performance applications such as power electronics, data centers, and electric vehicles. By 2025, the high-powered electronics sector is projected to capture a 40% share of the cold surfaces market, underscoring the growing demand for efficient thermal management solutions.
Chilled surfaces fulfill multiple functions, including:
- Maintaining optimal operating temperatures
- Preventing overheating
- Ensuring the reliability of electronic devices
Their applications range from cooling battery packs in electric vehicles to managing heat within data centers and high-performance computing systems. As the electronics sector continues to evolve, the role of chilled surfaces in enhancing performance and efficiency remains vital, driving innovation and investment in advanced heat management technologies.
Explain the Importance of Cold Plates in Electronics Cooling
Cold surfaces are critical in electronics cooling due to their ability to manage thermal loads effectively. As electronic devices generate heat during operation, excessive temperatures can lead to performance degradation, reduced lifespan, and potentially catastrophic failures. Chilled surfaces provide a reliable solution by ensuring that heat is efficiently dissipated from sensitive components. For instance, in high-power applications such as electric vehicles, thermal surfaces play a vital role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures for batteries and power electronics, thereby enhancing overall system reliability and efficiency.
Moreover, their capacity to support compact designs while delivering exceptional cooling performance renders them indispensable in contemporary electronics. The market for frigid surfaces was valued at over USD 321 million in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 534 million by 2032, underscoring the growing demand for effective heat management solutions.
Furthermore, cold surfaces contribute significantly to environmental sustainability by minimizing energy consumption and electronic waste, establishing them as a crucial element in the pursuit of greener technologies.
Detail Types of Cold Plates and Manufacturing Techniques
Chilled surfaces, produced by cold plate manufacturers, are essential components in temperature control systems, designed to meet specific cooling requirements across various applications. The primary types include:
-
Liquid Cold Plates: These plates circulate a coolant through embedded channels, facilitating efficient heat transfer and maintaining optimal operating temperatures. Cold plate manufacturers produce liquid cold surfaces that hold significant market value, estimated at approximately $473.9 million in 2025, and projected to reach $857.6 million by 2032, capturing around 68% of the market share due to their superior thermal performance compared to air cooling systems.
-
Microchannel Cold Components: Featuring intricate, small channels, these components maximize surface area for thermal exchange, making them particularly effective in high-performance applications such as advanced computing and high-power lasers. They are adept at managing heat dissipation of several kilowatts, which is crucial in high-density computing environments.
-
Brazed Cold Components: Constructed by layering and brazing thin metal sheets, these components deliver excellent heat performance and are suited for high-pressure environments, ensuring reliability in demanding applications. Their design allows for enhanced adaptability in channel arrangement, resulting in improved heat management.
-
Additive Manufactured Cold Components: Leveraging 3D printing technology, these components can be crafted with complex geometries that enhance cooling efficiency, providing tailored solutions for specific heat-related challenges.
Manufacturing methods for cold plate manufacturers vary, with friction stir welding (FSW) and conventional brazing being among the most prevalent. Notably, FSW offers significant advantages, such as reduced heat resistance and increased pressure capacity, making it ideal for high-performance applications. The choice of production technique directly influences heat management, cost, and scalability—critical factors for engineers selecting the appropriate heat exchanger for their projects. As the market for liquid cooling surfaces is projected to grow substantially, cold plate manufacturers will continue to innovate their manufacturing methods, driving advancements in temperature control solutions. Furthermore, operational factors, such as temperature and humidity, play a vital role in selecting a liquid cooling component to ensure compatibility and durability.
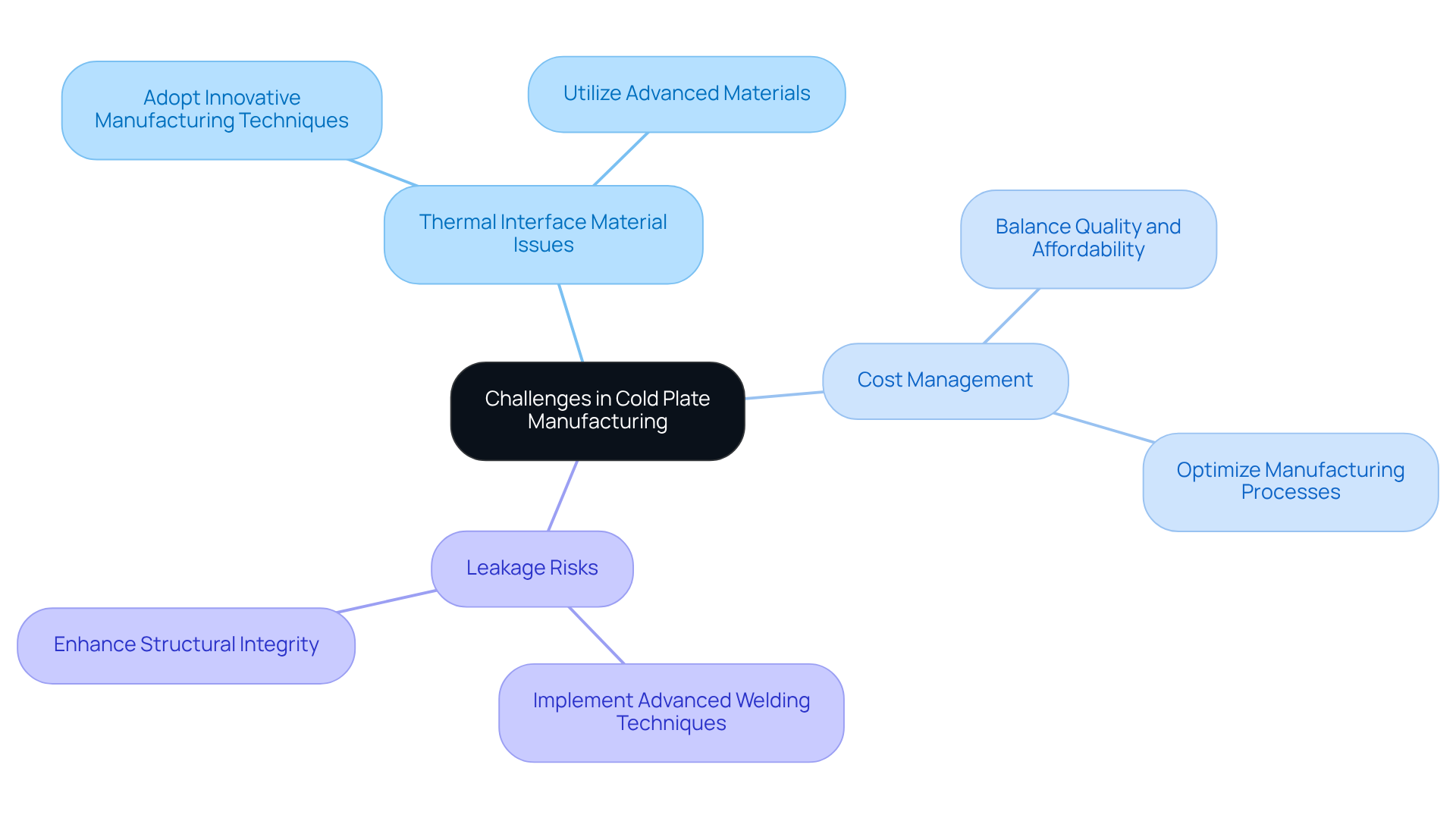
Identify Challenges in Cold Plate Manufacturing and Solutions
Cold plate manufacturers face several significant challenges that must be addressed to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
-
Thermal Interface Material (TIM) Issues: Effective thermal contact between the cold plate and electronic components is critical. Poor TIM can lead to inefficient heat transfer, impacting overall system performance.
-
Cost Management: The use of high-performance materials and complex manufacturing processes can drive up costs. Therefore, it is essential for cold plate manufacturers to find a balance between quality and affordability, ensuring that their products meet performance standards without exceeding budget constraints.
-
Leakage Risks: In liquid cold plates, maintaining structural integrity to prevent coolant leaks is paramount. Advanced welding techniques, such as Friction Stir Welding (FSW), can mitigate these risks, enhancing the reliability of the cold plates.
To overcome these challenges, cold plate manufacturers should consider adopting innovative manufacturing techniques and optimizing their designs for improved thermal performance. Utilizing advanced materials that enhance durability and efficiency is also crucial. Continuous research and development efforts are vital for addressing emerging challenges in the rapidly evolving electronics landscape.
Conclusion
Cold plate manufacturers play a pivotal role in the electronics industry, providing essential thermal management solutions that ensure the reliability and performance of electronic devices. Their ability to efficiently dissipate heat is crucial, particularly as electronic components become increasingly powerful and compact. By leveraging advanced materials and innovative manufacturing techniques, these manufacturers are at the forefront of addressing the growing demand for effective cooling solutions.
The significance of cold plates in various applications cannot be overstated. From electric vehicles to data centers, they maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevent overheating. Different types of cold plates—liquid, microchannel, brazed, and additive manufactured—each cater to specific cooling needs. However, challenges such as thermal interface material issues, cost management, and leakage risks must be navigated, emphasizing the need for continuous innovation and adaptation within the industry.
Ultimately, the importance of cold plate manufacturers is paramount. As the electronics landscape evolves, the necessity for efficient thermal management solutions becomes increasingly critical. Embracing advancements in manufacturing processes and materials will be vital for these manufacturers to overcome challenges and meet the demands of a rapidly changing market. The future of electronics hinges on effective cooling solutions, underscoring the vital role of cold plate manufacturers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are cold plate manufacturers and what do they produce?
Cold plate manufacturers produce thermal control devices known as chilled surfaces, which are essential for dissipating heat from electronic components.
What materials are typically used to create chilled surfaces?
Chilled surfaces are typically crafted from conductive materials such as aluminum or copper.
How do chilled surfaces function in cooling systems?
Chilled surfaces have a flat metallic surface designed for optimal thermal transfer, absorbing heat from high-temperature parts and transferring it to a circulating coolant, effectively relocating heat away from the source.
Why are chilled surfaces important in electronic cooling?
Chilled surfaces are crucial for maintaining optimal operating temperatures, preventing overheating, and ensuring the reliability of electronic devices, especially in high-performance applications.
What are some applications of chilled surfaces?
Chilled surfaces are used in various applications, including cooling battery packs in electric vehicles, managing heat within data centers, and supporting high-performance computing systems.
What is the projected market share for high-powered electronics in the cold surfaces market by 2025?
By 2025, the high-powered electronics sector is projected to capture a 40% share of the cold surfaces market.
How does the evolving electronics sector impact the demand for chilled surfaces?
As the electronics sector continues to evolve, the demand for efficient thermal management solutions, including chilled surfaces, increases, driving innovation and investment in advanced heat management technologies.