Introduction
The design of heat pipes is crucial in modern electronics, acting as vital components for effective thermal management. By utilizing the principles of phase change, these devices enable swift heat transfer, ensuring that high-performance gadgets stay cool even under demanding conditions. As technology evolves and devices shrink in size, the challenge becomes optimizing heat pipe performance across diverse operational scenarios.
Key factors influencing their effectiveness include:
- Material selection
- Geometry
- Working fluid properties
Engineers must harness this knowledge to enhance device reliability and performance, ensuring that innovations continue to thrive in an increasingly compact landscape.
Define Heat Pipes and Their Role in Electronics
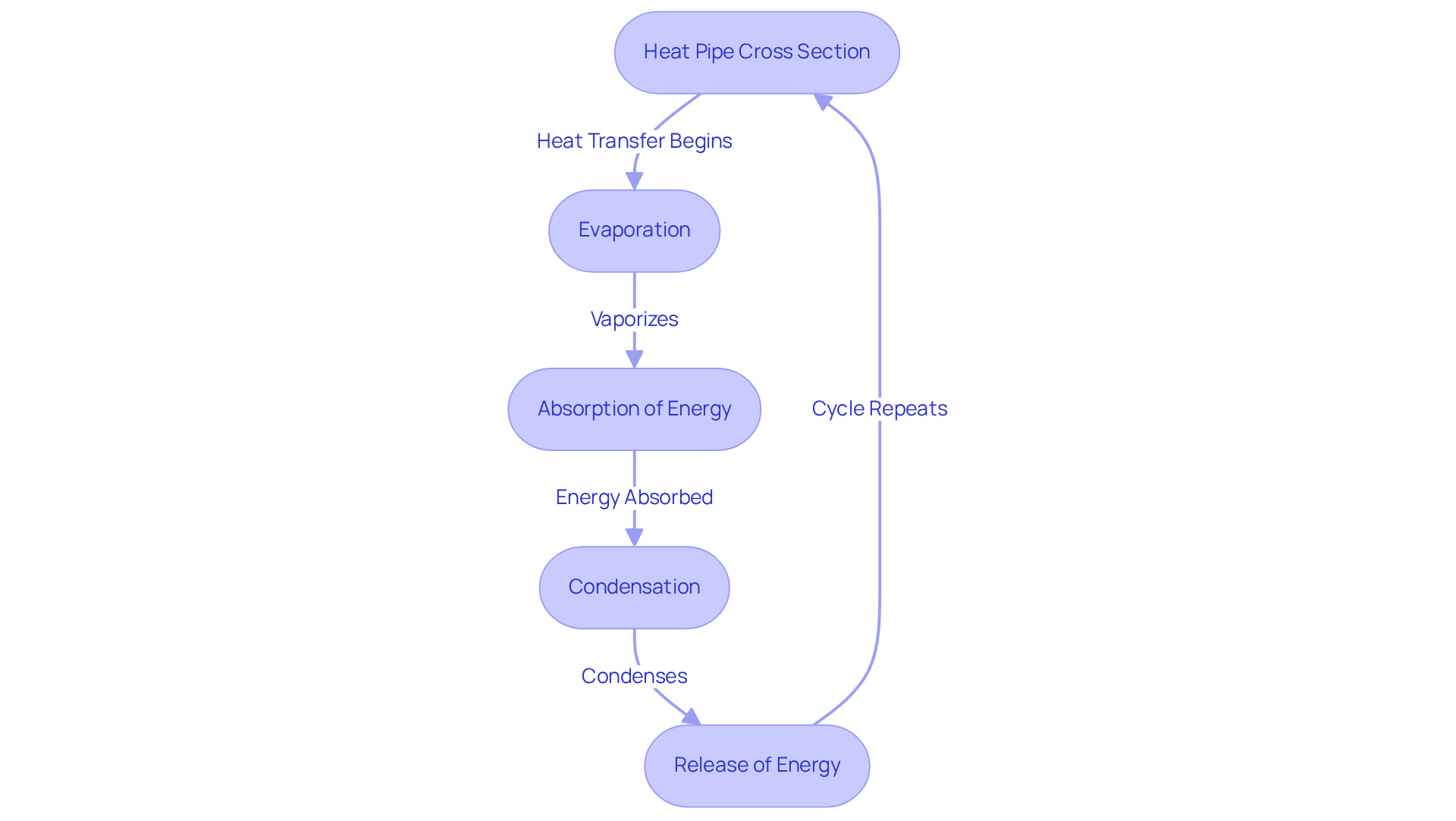
Heat transfer tubes, as shown in a heat pipe cross section, are advanced tools for temperature regulation that utilize phase change to efficiently transfer heat from one location to another. The heat pipe cross section consists of a sealed vessel filled with a working fluid that evaporates at the hot end, absorbs energy, and then condenses at the cooler end, releasing that energy. This mechanism allows the heat pipe cross section to serve as thermal conduits that transfer significant amounts of thermal energy with minimal temperature fluctuations, making them ideal for applications in electronics where effective heat dissipation is crucial.
In the electronics industry, the heat pipe cross section is commonly found in laptops, servers, and other high-performance devices, helping to prevent overheating and ensure optimal performance. The thermal channel market is projected to grow from approximately $1.1 billion in 2025 to over $2.5 billion by 2028, reflecting their increasing adoption across various sectors. Industry experts emphasize the critical role of the heat pipe cross section in modern thermal management solutions. Dr. Lisa Zhang, a Thermal Systems Engineer, notes that the choice between thermal conduits and vapor chambers depends on the specific thermal challenges faced, emphasizing the versatility of thermal conduits as illustrated in the heat pipe cross section for diverse applications.
Recent advancements in thermal transfer technology, particularly in the heat pipe cross section, have further enhanced their effectiveness in electronics. As consumer electronics continue to shrink and the demand for efficient cooling solutions rises, the heat pipe cross section is becoming indispensable for maintaining the performance and reliability of electronic devices. Their passive operation, which eliminates the need for mechanical components, enhances their reliability and efficiency compared to active cooling solutions.
Explain How Heat Pipes Work: Principles and Mechanisms
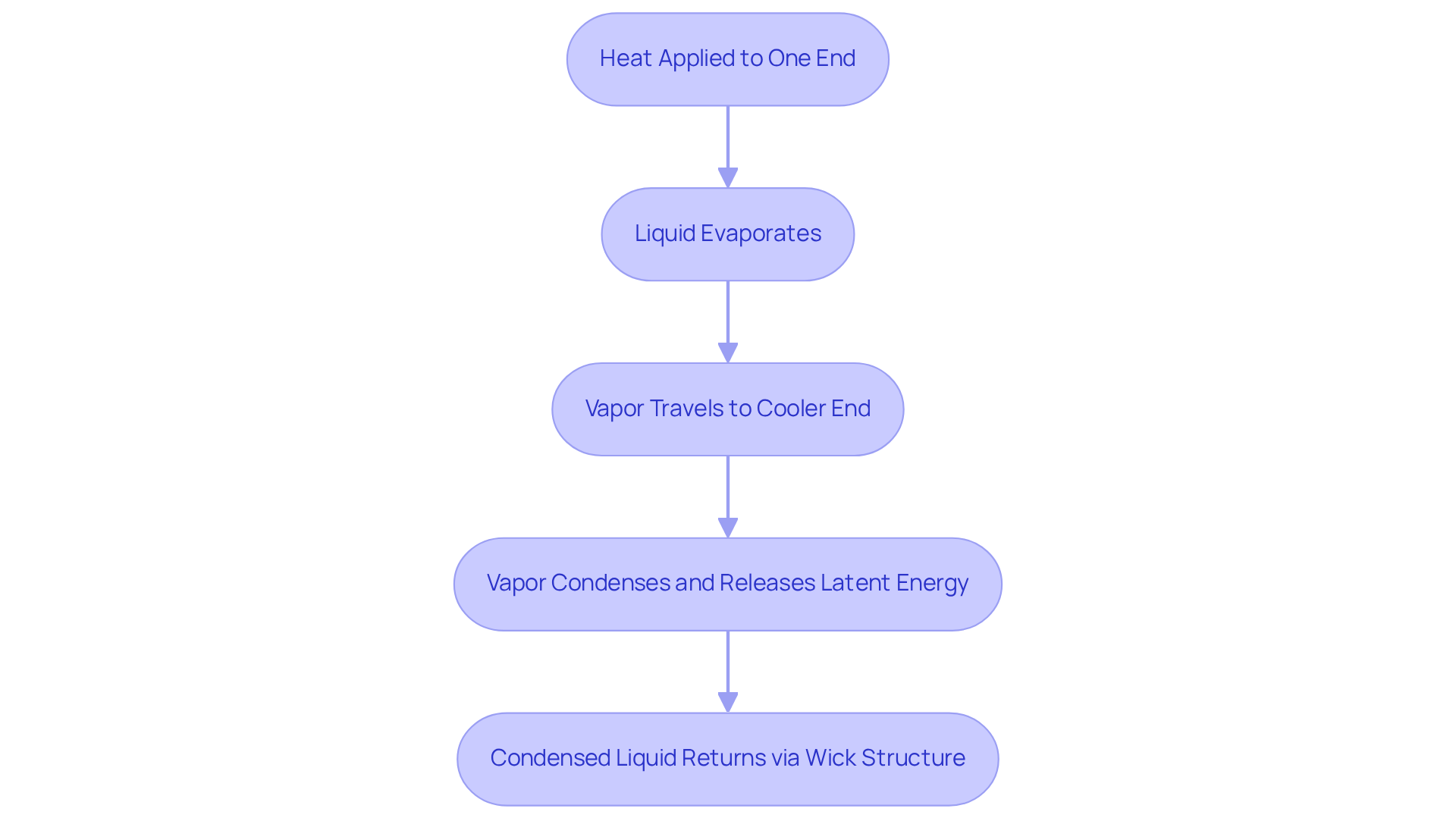
Heat conductors operate based on thermodynamic principles, particularly the phase change of the working fluid. When heat is applied to one end of the thermal conduit, the liquid inside evaporates, creating vapor that travels to the cooler end. As this vapor condenses, it releases latent energy, which dissipates into the surrounding environment. This cycle continues as the condensed liquid returns to the hot end through a wick structure, utilizing capillary action to facilitate fluid movement. Such an ongoing cycle allows the heat pipe cross section to maintain a consistent temperature along its length, making it highly efficient in managing energy loads in electronic devices.
The thermal conductivity range of the heat pipe cross section impressively spans from 1,500 to 60,000 W/(mK), significantly surpassing solid metals like copper, which has a thermal conductivity of about 400 W/(mK). This efficiency is crucial in applications such as laptops and gaming consoles, where effective temperature control is vital for optimal performance and reliability.
Recent research underscores the importance of optimizing wick designs and fluid selection to enhance performance, particularly in high-density environments like gaming consoles and high-performance computing systems. For instance, the choice of wick type can greatly influence the thermal element’s efficiency, as evidenced by case studies that highlight the advantages of sintered wicks in anti-gravity applications.
Moreover, understanding the limitations of thermal conduits, including the capillary limit and the impact of orientation on performance, is essential for engineers. These factors can significantly affect the operational effectiveness of thermal conduits, particularly the heat pipe cross section, ensuring they remain a critical component of modern temperature regulation solutions. As emphasized by temperature regulation specialists, selecting the appropriate working fluid and wick type is vital for optimizing the performance of thermal transfer devices.
Assess Advantages and Limitations of Heat Pipes in Applications
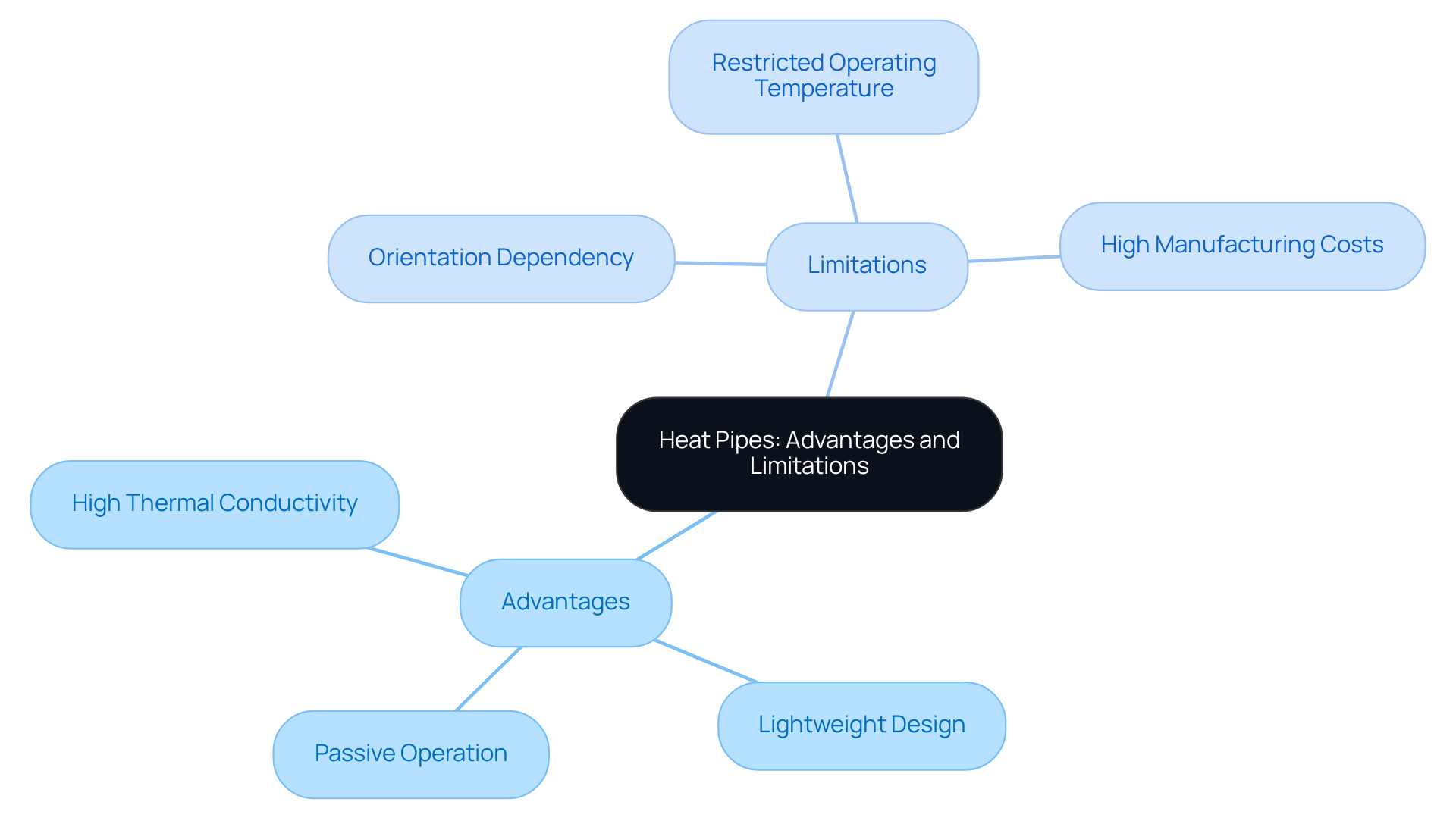
Heat conduits offer significant advantages, including high thermal conductivity, a lightweight design, and passive operation that requires no external power source. These features enable efficient energy transfer over long distances while maintaining uniform temperature profiles, making them particularly suitable for compact electronic devices.
However, it is essential to recognize the limitations of heat pipes. Their performance can be influenced by orientation, as certain designs depend on gravity for fluid movement. Furthermore, they may have a restricted operating temperature range and can incur high manufacturing costs, especially for specialized applications.
Understanding these factors is crucial for engineers when selecting solutions that involve the heat pipe cross section for effective heat management. By weighing the benefits against the limitations, professionals can make informed decisions that optimize performance in their specific applications.
Measure Effective Thermal Conductivity of Heat Pipes
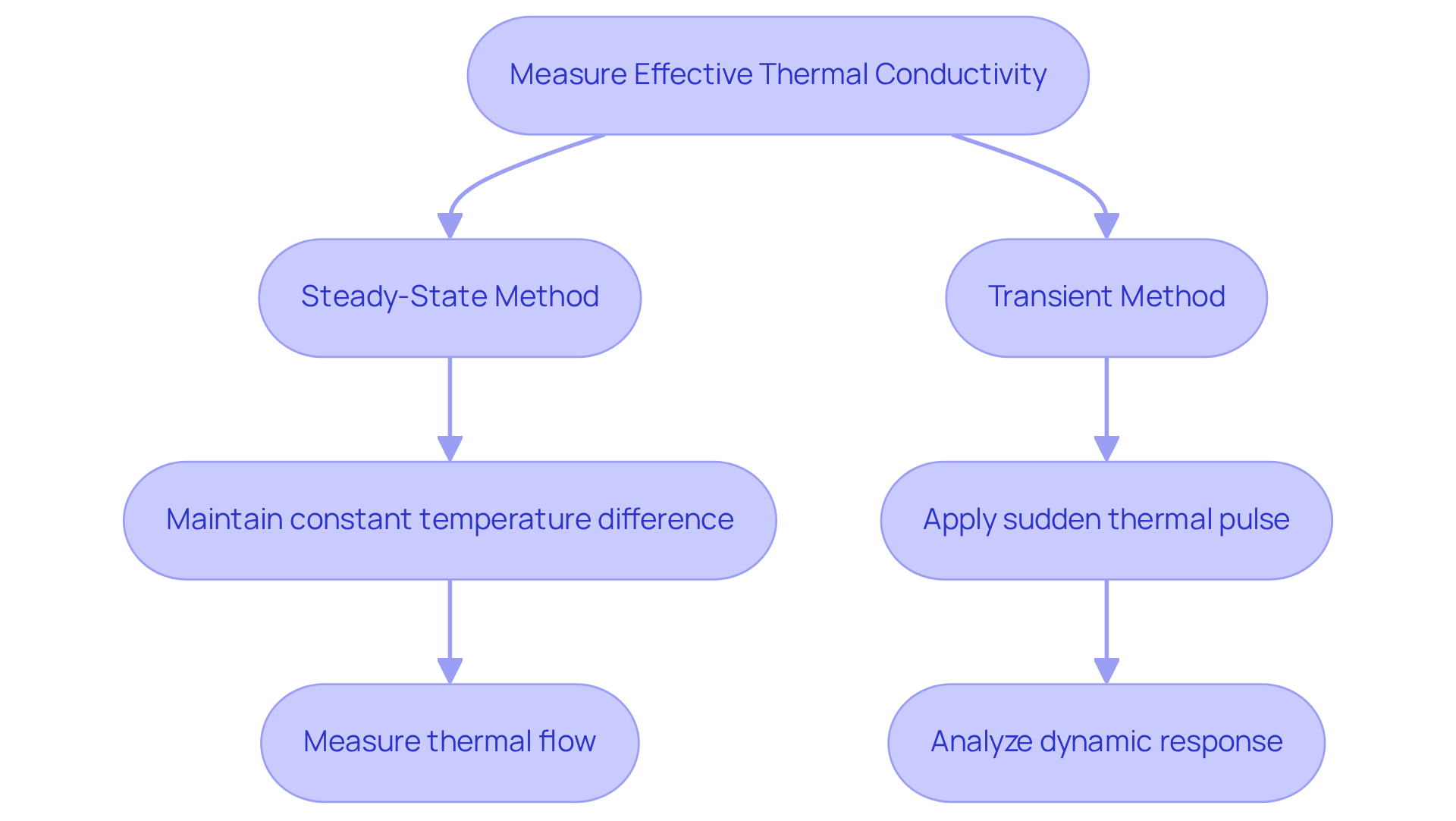
Assessing the effective conductivity of thermal channels is crucial for optimizing heat pipe performance in various applications. To achieve this, several methods can be employed, notably steady-state and transient techniques.
The steady-state approach involves maintaining a constant temperature difference across the thermal conduit while measuring the thermal flow. This method provides a reliable means of determining thermal conductivity under stable conditions. Conversely, the transient method focuses on how the thermal conduit reacts to a sudden thermal pulse, offering insights into its dynamic response.
To quantify the efficient conductive capability (K_eff), we utilize the equation:
K_eff = Q / (ΔT * L)
Here, Q represents the power transferred, ΔT denotes the temperature difference, and L is the effective length of the conduit. This equation is fundamental in evaluating the thermal performance of the heat pipe cross section.
Accurate measurement of thermal conductivity is not just a technical requirement; it is essential for ensuring that the performance demands of specific applications are met by the heat pipe cross section. By employing these methods, engineers can ensure that their designs are both effective and reliable.
Conclusion
The heat pipe cross section stands as a crucial advancement in thermal management, especially within the electronics sector. By harnessing the principles of phase change and thermodynamics, heat pipes deliver an efficient heat transfer mechanism essential for sustaining optimal performance across a range of electronic devices. Their capacity to maintain temperature stability with minimal fluctuations not only boosts device reliability but also aligns with the growing trend towards more compact and powerful electronics.
This article has explored key insights into the functionality and applications of heat pipes. The operational principles, such as the phase change of the working fluid and the importance of wick design, illustrate how these thermal conduits surpass traditional cooling methods. Additionally, the benefits – like high thermal conductivity and passive operation – are weighed against challenges such as orientation sensitivity and manufacturing costs, offering a well-rounded perspective on their role in contemporary engineering.
As the demand for efficient cooling solutions escalates, grasping the nuances of heat pipe technology becomes increasingly vital. Engineers and designers must consider the unique advantages and limitations of heat pipes in their projects. By fine-tuning the selection of working fluids and wick structures, they can fully leverage the potential of heat pipe technology, ensuring that electronic devices function reliably and efficiently in a swiftly evolving technological landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are heat pipes and how do they work?
Heat pipes are advanced tools used for temperature regulation that transfer heat through phase change. They consist of a sealed vessel filled with a working fluid that evaporates at the hot end, absorbs energy, and then condenses at the cooler end, releasing that energy.
What is the significance of heat pipes in electronics?
Heat pipes are crucial in electronics as they help prevent overheating and ensure optimal performance in devices like laptops and servers by efficiently dissipating heat.
What is the projected market growth for thermal channels, including heat pipes?
The thermal channel market is projected to grow from approximately $1.1 billion in 2025 to over $2.5 billion by 2028, indicating an increasing adoption of heat pipes across various sectors.
How do heat pipes compare to vapor chambers in thermal management?
The choice between heat pipes and vapor chambers depends on specific thermal challenges. Heat pipes are versatile thermal conduits suitable for diverse applications, as noted by industry experts.
What advancements have been made in heat pipe technology recently?
Recent advancements have enhanced the effectiveness of heat pipes in electronics, making them indispensable for maintaining performance and reliability in increasingly compact consumer electronics.
What are the advantages of heat pipes over active cooling solutions?
Heat pipes operate passively, eliminating the need for mechanical components, which enhances their reliability and efficiency compared to active cooling solutions.

