Introduction
Understanding the relationship between the pressure at a blower’s inlet and outlet is essential for optimizing airflow and energy efficiency across various applications. This intricate balance of pressures – static, dynamic, and total pressure – holds the key to unlocking significant performance improvements and effectively troubleshooting common issues within blower systems. However, the challenge lies in balancing these pressures to prevent inefficiencies and ensure optimal operation.
What strategies can be employed to enhance blower performance while navigating the complexities of pressure dynamics? By delving into these key concepts, engineers can not only improve system efficiency but also drive innovation in their applications. It’s time to explore actionable insights that can lead to enhanced blower performance.
Define Key Pressure Concepts: Static, Dynamic, and Total Pressure
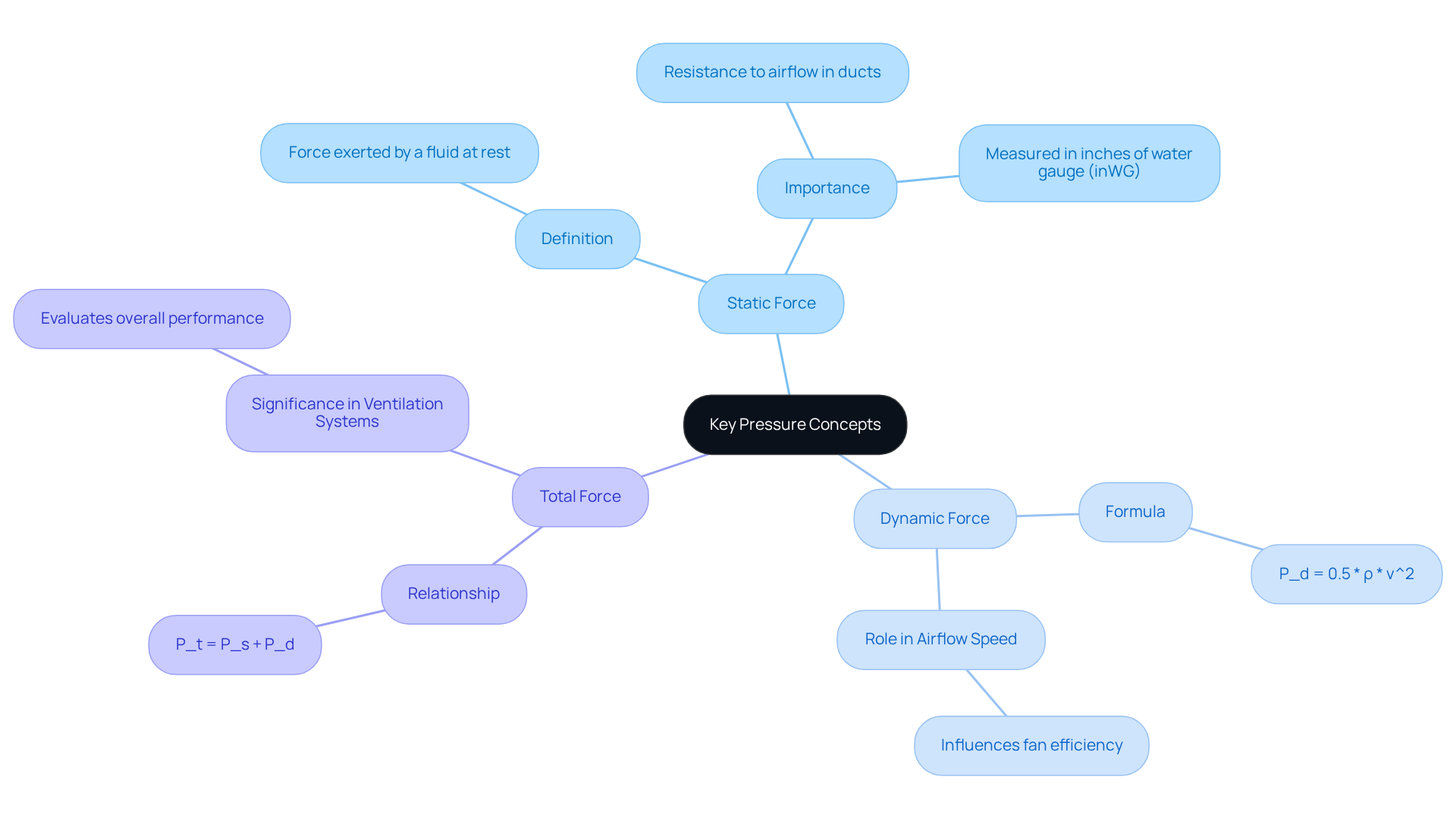
Static Force
Static force refers to the force exerted by a fluid at rest. This concept is vital in blower configurations, as it indicates the resistance to airflow within ducts and components by measuring the pressure difference between the blower inlet and outlet. Typically measured in inches of water gauge (inWG), static force is essential for ensuring that the system can effectively transport air through various barriers, such as filters and bends in ductwork. Regular assessments of static force are crucial for maintaining and improving performance, as they help identify issues related to the pressure difference between the blower inlet and outlet that may arise from clogged filters or improper duct configurations. Implementing remedial actions, including replacing blocked filters, optimizing duct layouts, and adjusting fan controls, can significantly enhance the pressure difference between the blower inlet and outlet, thereby improving static force management and overall efficiency.
Dynamic Force
Dynamic force is associated with the movement of the fluid and is calculated based on the fluid’s velocity. This force plays a critical role in understanding airflow speed within the system. The formula for dynamic force is:
P_d = 0.5 * ρ * v^2
where ρ represents fluid density and v denotes velocity. This calculation is essential for improving fan efficiency, as it directly influences how effectively air is moved through the system.
Total Force
Total force is the cumulative effect of static and dynamic forces, representing the total energy per unit volume of the fluid. It is crucial for evaluating the overall performance of ventilation units. The relationship can be expressed as:
P_t = P_s + P_d
where P_t is total pressure, P_s is static pressure, and P_d is dynamic pressure. Understanding these forces is vital for designing effective ventilation systems that meet specific operational requirements, ensuring optimal air movement and energy efficiency. Moreover, managing static force is key to minimizing system noise and prolonging equipment lifespan.
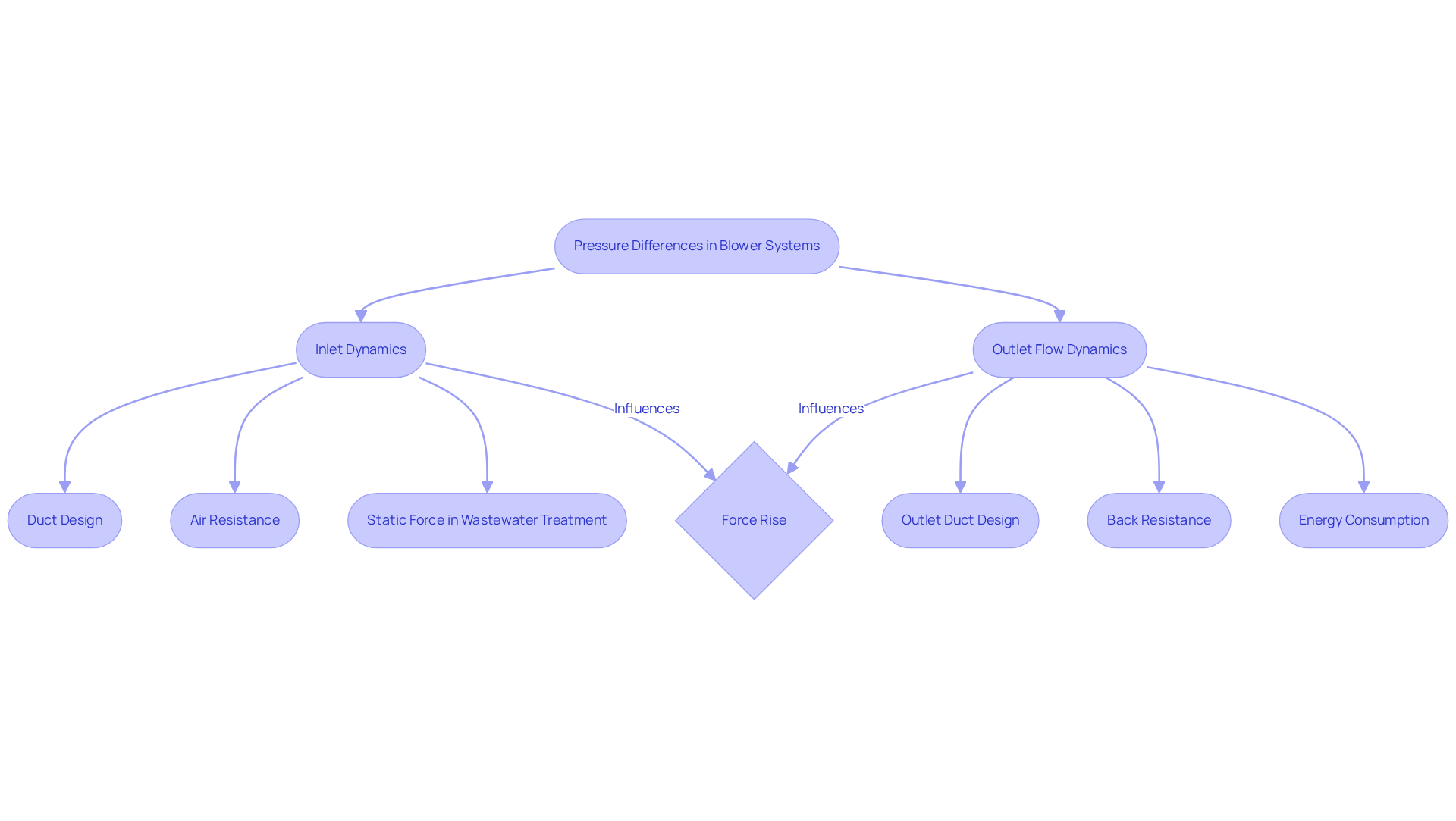
Explain Pressure Differences in Blower Systems: Inlet vs. Outlet Dynamics
-
Inlet Dynamics: The force at the blower entrance is critically influenced by duct design, air resistance, and surrounding conditions. A well-crafted inlet minimizes turbulence and enhances airflow, leading to optimal static force. In wastewater treatment applications, static force arises from the submergence of aeration diffusers in wastewater or sludge, which is vital for sustaining effective aeration in systems like Sequencing Batch Reactors (SBRs) that must accommodate variable water levels.
-
Outlet Flow Dynamics: The design of the outlet duct and any downstream components significantly impact outlet flow. A poorly constructed outlet can create back resistance, diminishing the fan’s efficiency and increasing energy consumption. In practical applications, such as wastewater treatment, maintaining appropriate outlet force is essential to prevent septicity and ensure effective mixing.
-
The variation in forces, known as the ‘force rise,’ is crucial for assessing fan performance, particularly when considering the pressure difference between the blower inlet and outlet. This differential serves as a key specification when selecting a fan for specific applications. Engineers must ensure that the fan can overcome the total loss of force in the setup, which encompasses both static and dynamic forces. For instance, in variable depth processes, fluctuations in water level can significantly affect the required ventilation rate, making it essential to consider the pressure difference between the blower inlet and outlet. Advances in technology have enabled centrifugal blowers to be effectively utilized in variable level processes, as illustrated in the case study on control performance.
-
Practical Implications: A comprehensive understanding of these dynamics empowers engineers to design systems that optimize airflow and energy efficiency. Widening the outlet size can effectively reduce back resistance, while ensuring that the inlet remains unobstructed enhances overall performance. Current trends indicate a shift towards variable frequency drives (VFDs) for improved modulation of fan operations. As Tom Jenkins, President of JenTech Inc., stated, “By utilizing VFDs for regulating flow and force, both PD and centrifugal fans can offer adaptability and high efficiency,” underscoring the importance of these technologies in modern fan setups.
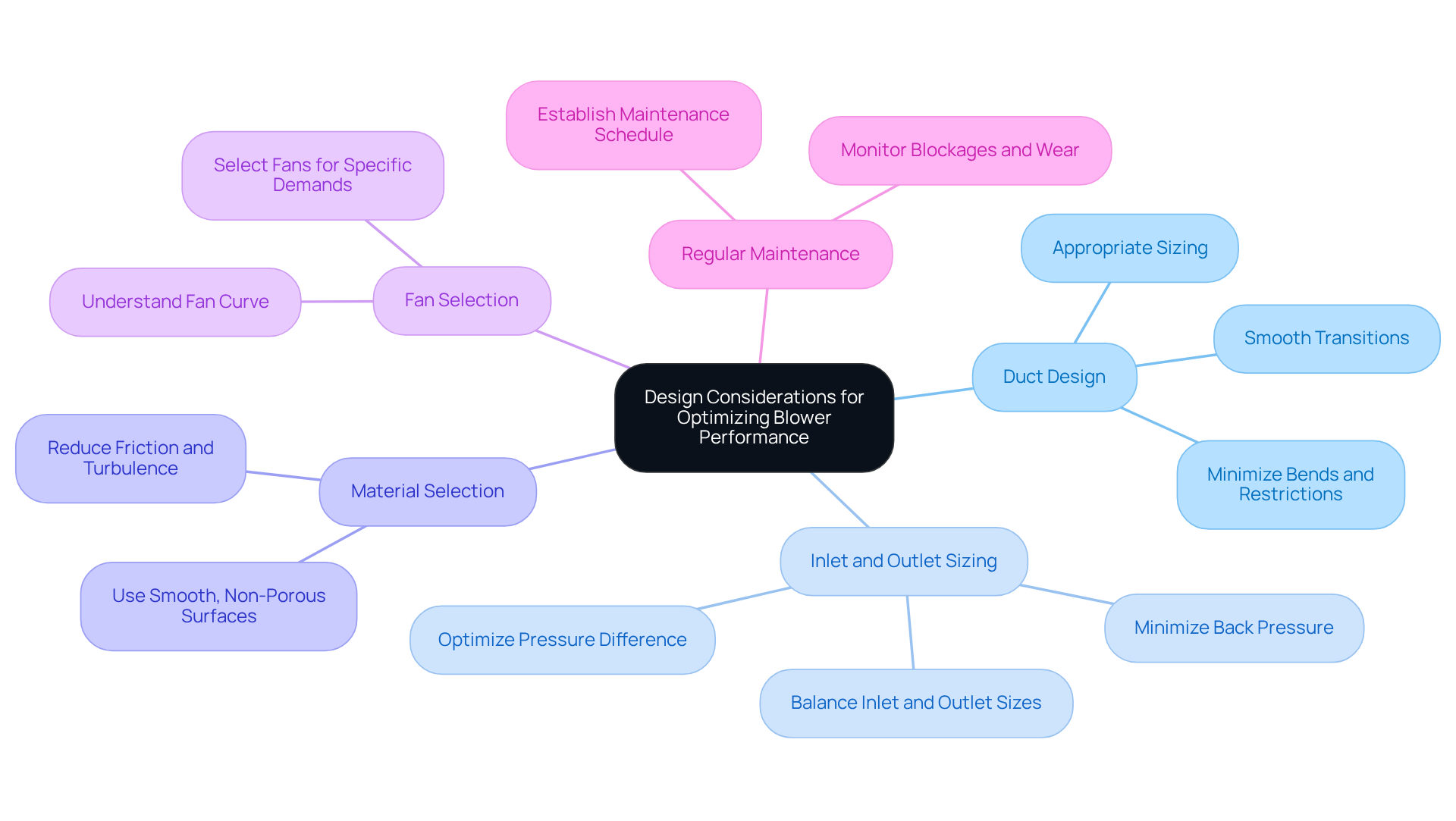
Apply Knowledge: Design Considerations for Optimizing Blower Performance
-
Duct Design: Effective ductwork design is crucial for minimizing bends and restrictions. Smooth transitions and appropriate sizing significantly reduce static losses, thereby enhancing overall system efficiency. By prioritizing these elements, you can ensure that your ductwork operates at its best.
-
Inlet and Outlet Sizing: Proper sizing of the inlet and outlet is essential for optimal blower performance, as it directly affects the pressure difference between the blower inlet and outlet. An oversized inlet may lead to decreased static pressure, while an undersized outlet can create excessive back pressure, thereby impacting the pressure difference between the blower inlet and outlet and hindering air movement. Striking a balance is vital to optimize ventilation and minimize resistance, ensuring effective performance throughout the system.
-
Material Selection: Choosing materials that reduce friction and turbulence within the ductwork is paramount. Utilizing smooth, non-porous surfaces aids in maintaining circulation and minimizing energy losses, ultimately enhancing the blower setup’s overall effectiveness. This careful selection can lead to significant improvements in system performance.
-
Fan Selection: Selecting the right fans to meet the specific demands of your setup is critical. A thorough understanding of the fan curve is essential; ensure that the chosen fan operates efficiently within the desired airflow and pressure range to achieve optimal performance. This knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions that enhance system reliability.
-
Regular Maintenance: Establishing a maintenance schedule is vital for monitoring blockages and wear in the blower system. Regular inspections are key to maintaining optimal performance and preventing unexpected failures, ensuring longevity and reliability in operation. By committing to a proactive maintenance approach, you safeguard your investment and enhance operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Understanding the pressure difference between the blower inlet and outlet is crucial for optimizing blower performance and ensuring efficient airflow across various applications. This article has delved into the essential concepts of static, dynamic, and total pressure, illustrating how these elements interact to influence the overall effectiveness of blower systems. By mastering these foundational principles, engineers and system designers can make informed decisions that significantly enhance operational efficiency and longevity.
Key insights discussed include:
- The importance of duct design
- The sizing of inlet and outlet components
- The selection of appropriate materials and fans
Each of these factors plays a vital role in managing pressure differences, which ultimately dictate the performance of ventilation systems. Regular maintenance and proactive monitoring are also critical, ensuring that any issues related to pressure loss are promptly addressed, thereby safeguarding system integrity.
In conclusion, prioritizing these design considerations is paramount for anyone involved in blower system optimization. A commitment to understanding and applying these principles will not only improve blower efficiency but also lead to energy savings and reduced operational costs. As the industry evolves, staying informed about best practices and emerging technologies will be essential for maximizing performance and adapting to changing demands.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is static force in fluid dynamics?
Static force refers to the force exerted by a fluid at rest, indicating the resistance to airflow within ducts and components. It is measured in inches of water gauge (inWG) and is essential for effective air transport through barriers like filters and ductwork.
Why is it important to assess static force regularly?
Regular assessments of static force are crucial for maintaining and improving system performance, as they help identify issues related to pressure differences caused by clogged filters or improper duct configurations.
What actions can improve static force management?
To improve static force management, one can replace blocked filters, optimize duct layouts, and adjust fan controls, which can enhance the pressure difference between the blower inlet and outlet.
What is dynamic force and how is it calculated?
Dynamic force is associated with the movement of fluid and is calculated based on the fluid’s velocity using the formula: P_d = 0.5 * ρ * v^2, where ρ is fluid density and v is velocity.
How does dynamic force influence fan efficiency?
Dynamic force directly influences how effectively air is moved through the system, making its calculation essential for improving fan efficiency.
What is total force in fluid dynamics?
Total force is the cumulative effect of static and dynamic forces, representing the total energy per unit volume of the fluid.
How is total pressure related to static and dynamic pressure?
Total pressure (P_t) is the sum of static pressure (P_s) and dynamic pressure (P_d), expressed as: P_t = P_s + P_d.
Why is understanding these pressure concepts important for ventilation systems?
Understanding static, dynamic, and total pressures is vital for designing effective ventilation systems that ensure optimal air movement, energy efficiency, minimize system noise, and prolong equipment lifespan.