Overview
A car fan, often referred to as a cooling fan, plays a crucial role in regulating engine temperature. By drawing air through the radiator, it effectively dissipates heat, thereby preventing overheating. This article elucidates the distinction between mechanical and electric car fans, noting that electric fans have gained prevalence due to their superior efficiency.
Furthermore, it underscores the necessity of ensuring proper fan functionality to avert complications such as battery drain and potential engine damage. Understanding these elements is essential for maintaining optimal vehicle performance.
Introduction
In the intricate realm of automotive engineering, the functionality of a car fan stands out as a critical element in sustaining optimal engine performance. Frequently overlooked, this essential component operates relentlessly to regulate engine temperature, thereby preventing overheating and ensuring longevity.
With the emergence of electric vehicles and advanced powertrains, the design and operation of cooling fans have undergone significant evolution, reflecting a shift towards enhanced efficiency and reliability. As vehicles grow increasingly sophisticated, comprehending the factors that influence fan operation—especially post-ignition—becomes imperative for car owners and enthusiasts alike.
This article explores the complexities of car fan functionality, the implications of continuous operation, and practical troubleshooting solutions to guarantee that a vehicle’s cooling system remains in peak condition.
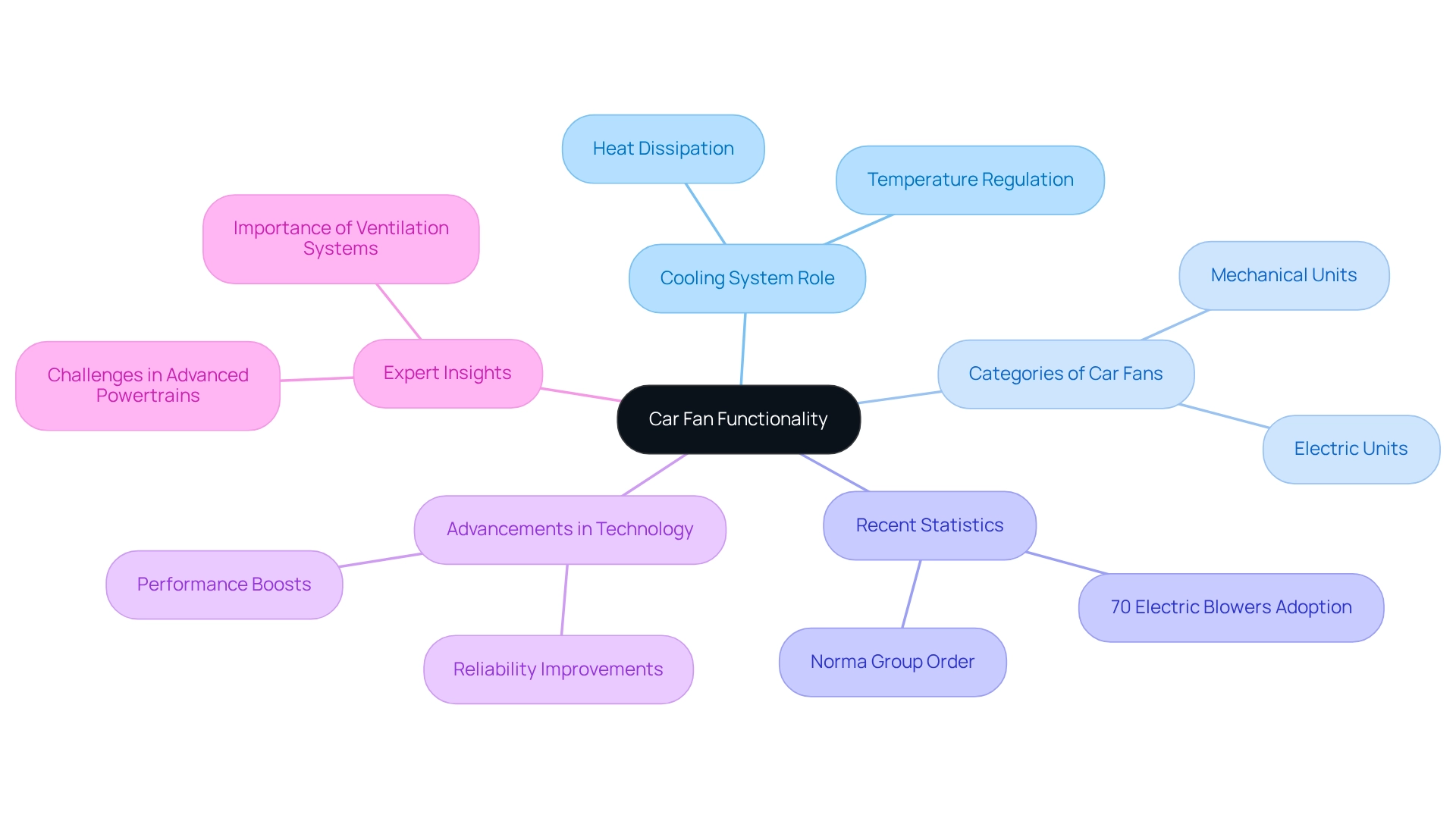
Understanding the Car Fan’s Functionality
A car fan, commonly known as a cooling fan, is a crucial component of an automobile’s cooling system, playing a significant role in temperature regulation. By drawing air through the radiator, the car fan dissipates heat generated by the engine, ensuring optimal operating temperatures. Typically situated between the radiator and the engine, the car fan activates when the engine reaches a designated temperature or when the vehicle is stationary, effectively preventing overheating.
Automotive cooling devices fall into two primary categories:
- Mechanical units, powered by the engine’s belt
- Electric units, governed by the automobile’s electronic control unit (ECU)
The latter has gained traction in modern vehicles due to their enhanced efficiency and ability to operate independently of engine speed. Recent statistics indicate that approximately 70% of automobiles now utilize electric blowers, highlighting a significant shift towards more effective temperature regulation solutions.
In 2025, advancements in car fan design have focused on boosting performance and reliability, particularly in high-performance applications. Manufacturers are developing robust radiator blowers that serve effectively as car fans, adeptly managing increased temperature demands—a critical consideration given the rising thermal control challenges posed by advanced powertrains in electric and hybrid vehicles. This trend is underscored by a recent report showcasing the growing adoption of electric vehicles, which accentuates the importance of efficient temperature regulation systems. Notably, in March 2024, Germany’s Norma Group secured a substantial order from an Indian electric SUV manufacturer, reflecting the surging demand for components that facilitate this transition.
Insights from automotive engineers consistently stress the significance of ventilation systems, such as those employed by car fans, in maintaining engine efficiency and longevity. As highlighted by one expert, the ‘Growing Embrace of Electric and Hybrid Vehicles’ and the ‘Increasing Thermal Management Challenges in Advanced Powertrains’ are pivotal factors driving the evolution of car fan technology. As the automotive industry progresses, the effectiveness of cooling systems remains a focal point for car fans, ensuring vehicles meet the demands of modern engineering and consumer expectations. Furthermore, case studies on emerging trends in high-performance applications illustrate how advancements in machinery technology are influencing the design and functionality of radiator fans, thereby enriching the discourse on performance requirements.
Factors Influencing Fan Operation After Ignition Off
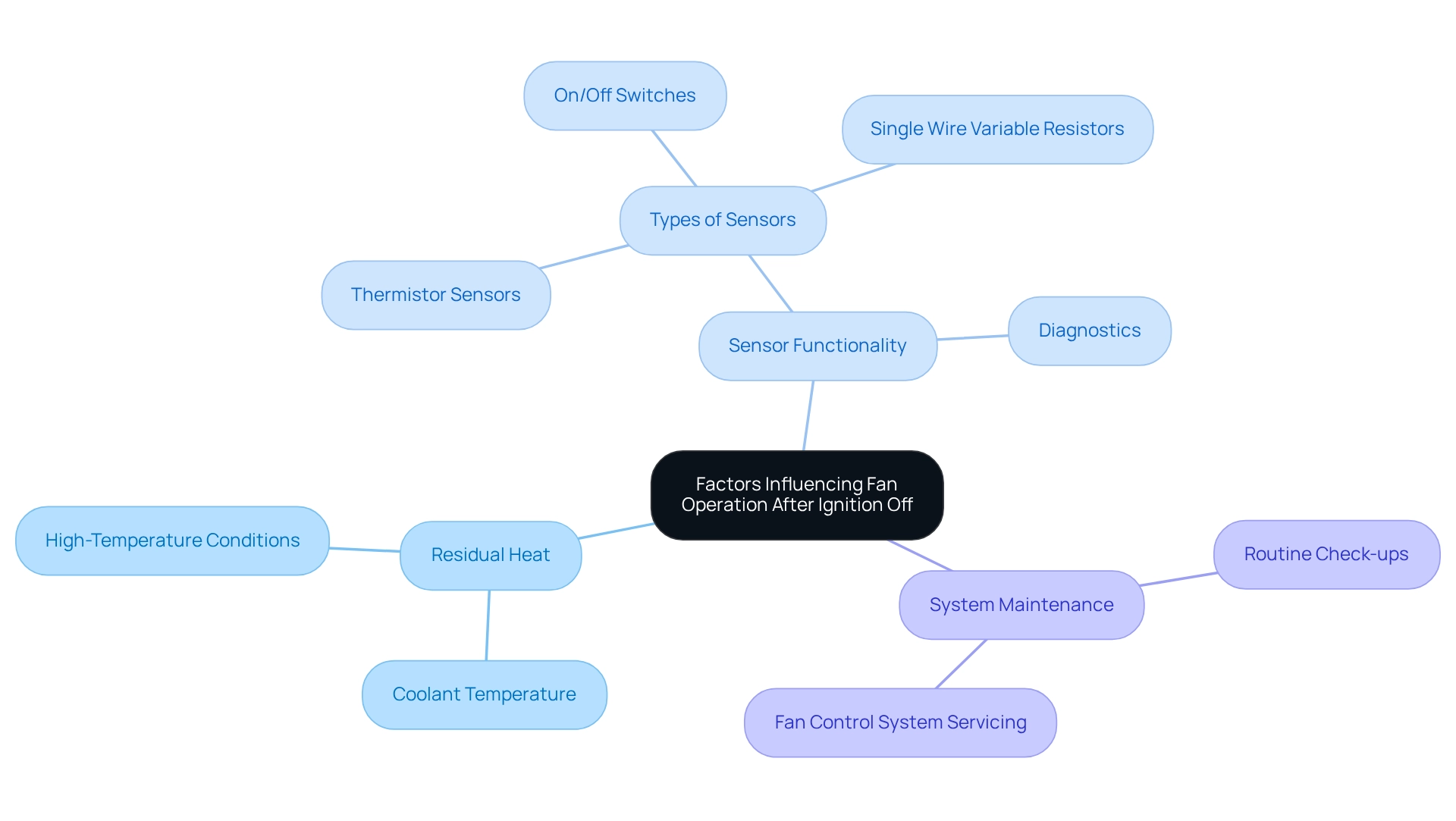
After turning off the ignition, a car fan may continue to operate due to several critical factors. One primary reason is the residual heat present in the motor. Contemporary automobiles are equipped with temperature sensors that consistently monitor coolant temperature, typically located near the thermostat housing in the intake manifold. If the coolant temperature exceeds a predetermined threshold, the control unit may activate the fan to dissipate heat and prevent potential damage to the motor. This is particularly important in vehicles that have been operated under high-temperature conditions or in heavy traffic, where the engine tends to retain more heat.
Furthermore, the effectiveness of the cooling system can be influenced by the condition of the temperature sensors themselves. For example, older vehicles may utilize various types of coolant sensors, such as on/off switches or single wire variable resistors, which function differently compared to modern thermistor sensors. Understanding these distinctions is essential for effective diagnostics and repairs, ensuring that the appropriate sensor type is employed for accurate temperature readings. The case study titled “Older Vehicles and Coolant Sensors” underscores these differences, highlighting the necessity for awareness of the specific sensor technology in use.
Moreover, a malfunctioning temperature sensor or a defective relay can result in the fan operating continuously, even when unnecessary. Statistics indicate that a significant percentage of vehicles rely on temperature sensors to influence fan operation, underscoring the importance of these components in maintaining optimal performance. Routine maintenance of fan control systems is crucial to prevent failures and ensure that the ventilation system operates effectively, as fan control systems require regular servicing to achieve peak performance.
In summary, the interplay of residual heat, sensor functionality, and system maintenance is vital in determining whether a car fan continues to operate after the ignition is turned off. Additionally, the balance of pressure, flow rate, and heat dissipation within the refrigeration system is essential for the motor’s optimal performance. Understanding these factors is critical for diagnosing system issues and extending the motor’s lifespan.
Implications of a Running Fan: Risks and Concerns
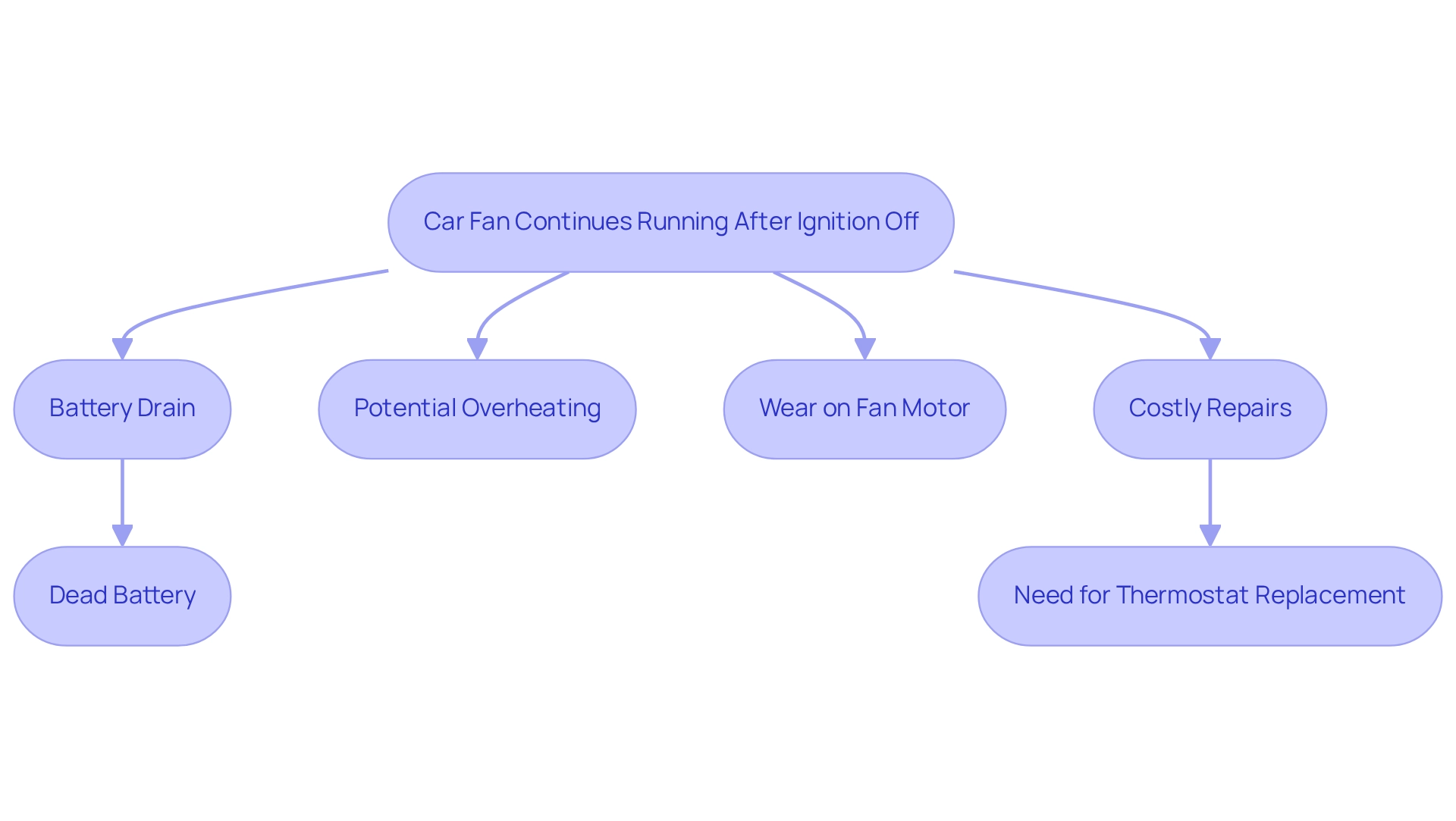
While it is not uncommon for a car fan to continue running after the ignition is turned off, persistent operation can signal underlying issues that require immediate attention. Continuous operation of electric fans can lead to significant battery drain, particularly if they remain active for prolonged periods. This situation often arises from a malfunctioning temperature sensor, which may prevent the fan from shutting off as intended. Over time, such conditions can accelerate wear on the fan motor and related components, potentially resulting in costly repairs. In fact, repair costs associated with faulty temperature sensors can be substantial, making timely intervention crucial.
Furthermore, excessive fan operation may indicate overheating issues, implying that the machinery is not cooling efficiently. This can result in significant damage to the machinery if not addressed quickly. For instance, a case study involving Cadillac CT6 engines revealed that recurring temperature gauge issues were often resolved by replacing the thermostat and temperature sensor, underscoring the importance of these components in maintaining proper fan operation. Comparable problems may occur in other automobile models, reinforcing the need for vigilant monitoring of fan behavior across different makes and types.
Statistics indicate that continuous fan operation can drain a car’s battery significantly, with some estimates suggesting that it can lead to a dead battery within hours. This is particularly concerning given that a community of over 53,443 members has shared experiences regarding automotive issues, including fan operation and battery drain. Automotive professionals emphasize the risks associated with leaving a car fan running after the ignition is off, warning that it can exacerbate battery drain and lead to further electrical issues. Additionally, if the battery is drained, completing emissions monitors can become difficult, affecting performance and compliance. Consequently, attentive observation of fan behavior is crucial for maintaining the overall well-being and durability of the automobile. As one Full Access Member remarked, “This repair is quick and can easily be completed in your garage/driveway within 30 minutes with a few simple hand tools,” emphasizing that tackling these issues is feasible for car owners.
Troubleshooting Solutions for Persistent Fan Operation
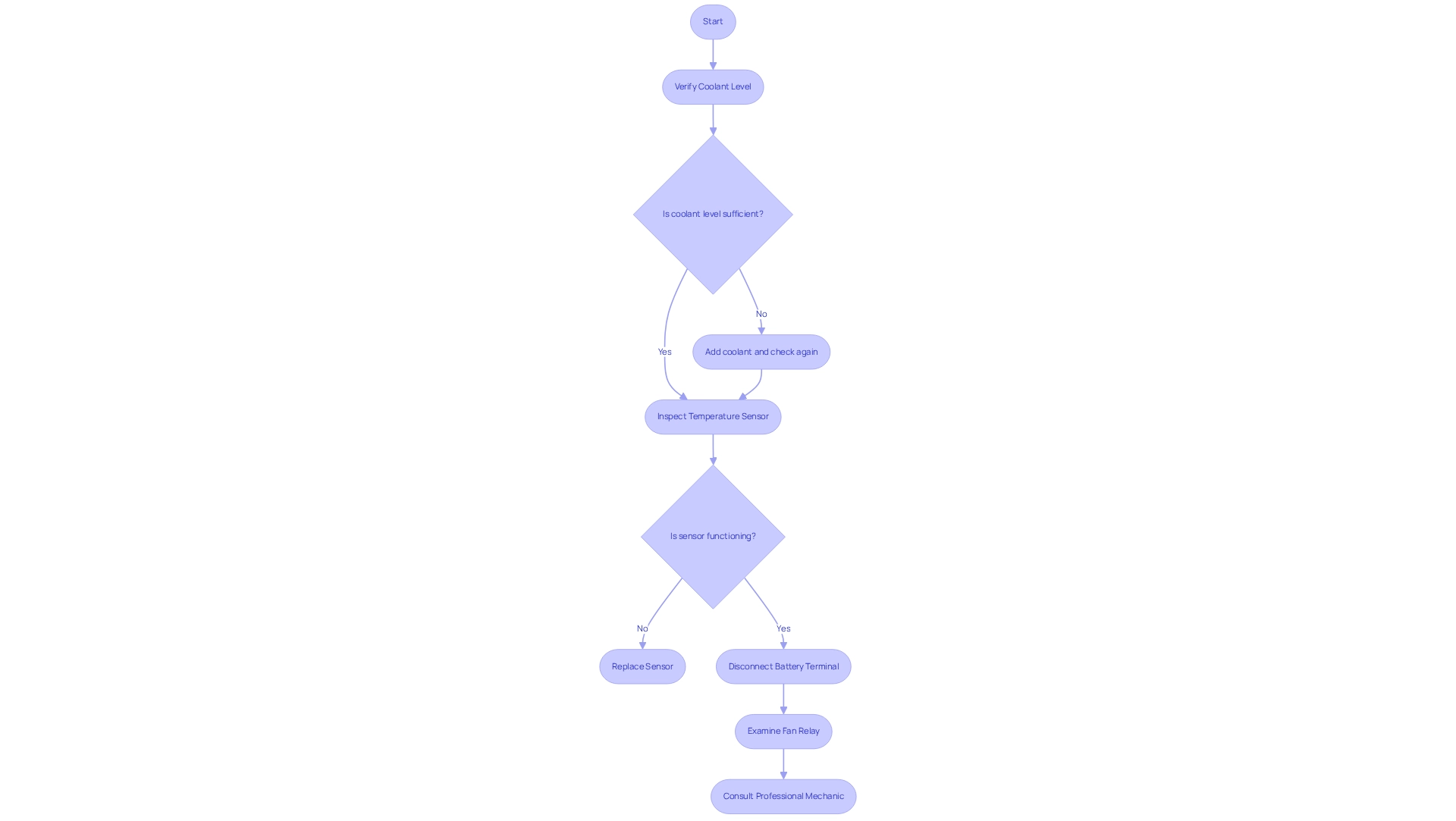
When a car fan continues to run after the ignition is turned off, it is essential to undertake several troubleshooting steps to accurately identify the issue at hand. Begin by verifying the coolant level; insufficient coolant can lead to overheating, which may cause the fan to operate longer than necessary. Statistics reveal that coolant level issues are a prevalent factor in fan operation problems, underscoring the importance of regular checks. It is also crucial to recognize that coolant, radiator fluid, and antifreeze are vital for proper automobile operation, as water is not a suitable substitute.
Next, inspect the temperature sensor for any faults. A malfunctioning sensor may send incorrect signals to the engine control unit (ECU), resulting in the fan remaining active. Data indicates that temperature sensor failures are common in vehicles, making this a critical area for diagnosis. Furthermore, a practical troubleshooting step involves disconnecting the negative terminal of the battery, which has been known to resolve fan running issues in certain instances.
Additionally, examine the fan relay for signs of damage or corrosion. A faulty relay can lead to continuous fan operation, complicating the system’s functionality. If these components appear to be functioning correctly, it may be necessary to consult a professional mechanic for a more thorough diagnosis of the temperature control system.
Regular maintenance is vital in preventing these issues. Adhering to practical maintenance tips, including those found in case studies on radiator fan care, can help keep radiator fans in optimal condition. This encompasses conducting regular inspections and cleaning to ensure all components operate effectively. As one car expert noted, “My 2010 fan is still operating an hour after it was turned off,” highlighting the significance of attentiveness in monitoring automobile performance. By remaining vigilant and addressing any changes in vehicle performance, engineers can significantly reduce the likelihood of persistent fan operation and ensure efficient engine cooling.
Conclusion
The car fan is indispensable for optimal engine performance, particularly as modern vehicles integrate advanced powertrains. With 70% of vehicles now utilizing electric fans, their critical role in regulating engine temperature and preventing overheating cannot be overstated.
Several factors may cause a fan to operate after the ignition is turned off, including:
- Residual heat
- Faulty temperature sensors
- Insufficient maintenance
These issues can result in battery drain and other electrical complications, making regular monitoring essential.
To effectively troubleshoot persistent fan operation, vehicle owners should:
- Check coolant levels
- Inspect temperature sensors
- Examine fan relays
These straightforward steps can help identify issues early, thereby preventing costly repairs and ensuring the cooling system functions efficiently.
In conclusion, understanding and maintaining the car fan is vital for extending engine life and enhancing vehicle performance. By taking a proactive approach and remaining vigilant regarding potential problems, car owners can ensure their cooling systems operate effectively, leading to a more reliable driving experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary function of a car fan?
The primary function of a car fan, also known as a cooling fan, is to regulate the temperature of the engine by drawing air through the radiator to dissipate heat generated by the engine, ensuring optimal operating temperatures.
Where is the car fan typically located in a vehicle?
The car fan is typically situated between the radiator and the engine.
When does the car fan activate?
The car fan activates when the engine reaches a designated temperature or when the vehicle is stationary to prevent overheating.
What are the two main types of automotive cooling devices?
The two main types of automotive cooling devices are mechanical units, which are powered by the engine’s belt, and electric units, which are governed by the automobile’s electronic control unit (ECU).
Why are electric car fans becoming more popular in modern vehicles?
Electric car fans are becoming more popular due to their enhanced efficiency and ability to operate independently of engine speed, with approximately 70% of automobiles now utilizing electric blowers.
What advancements are being made in car fan design by 2025?
Advancements in car fan design by 2025 are focused on boosting performance and reliability, particularly for high-performance applications, with manufacturers developing robust radiator blowers to manage increased temperature demands.
How is the rise of electric and hybrid vehicles influencing car fan technology?
The rise of electric and hybrid vehicles is driving the evolution of car fan technology due to increasing thermal management challenges posed by advanced powertrains, highlighting the importance of efficient temperature regulation systems.
What do automotive engineers emphasize regarding ventilation systems like car fans?
Automotive engineers emphasize the significance of ventilation systems, such as those employed by car fans, in maintaining engine efficiency and longevity.
What recent trends are impacting the design and functionality of radiator fans?
Recent trends impacting the design and functionality of radiator fans include advancements in machinery technology and the growing demand for components that facilitate the transition to electric vehicles.

