Introduction
In the dynamic realm of electronic cooling solutions, the choice between PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) and traditional DC fans has gained significant importance. Engineers face the challenge of optimizing performance while balancing energy efficiency, noise levels, and effective thermal management. This article explores the critical differences between PWM and DC fans, emphasizing their unique advantages and limitations.
How do these technologies compare, and which one truly excels in efficiency and effectiveness? The insights provided here may surprise those eager to elevate their cooling systems.
Define PWM and DC Fans: Key Characteristics and Mechanisms
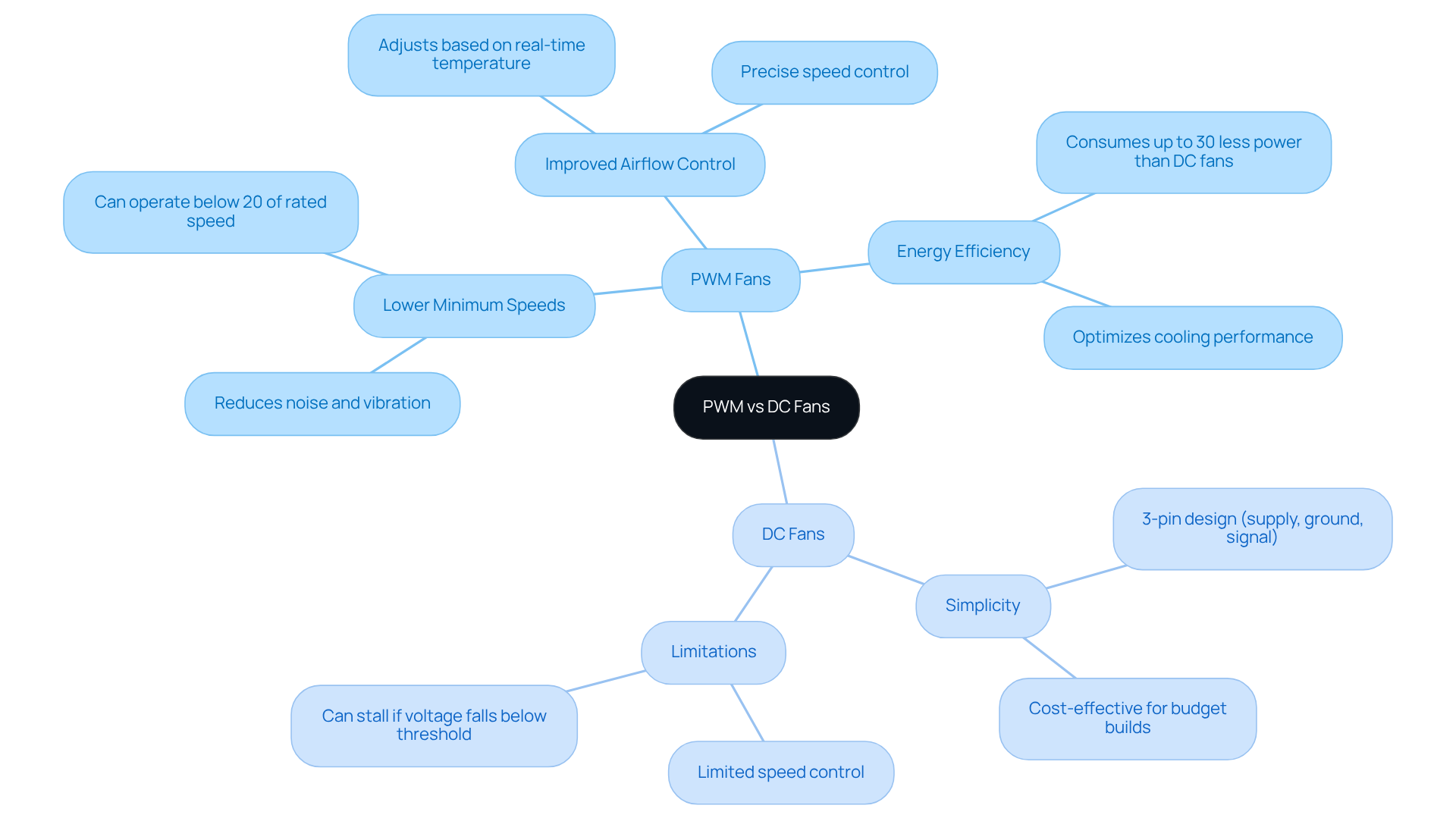
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) motors signify a major advancement in DC technology, particularly when considering the pwm vs dc fans debate, as they utilize a four-pin connector with the fourth pin dedicated to sending a PWM signal for precise rotation control. This innovative design allows PWM units to operate at adjustable rates, enabling them to function at lower levels without the risk of stalling. Such capability is essential for efficient thermal regulation in electronic systems. In contrast, traditional DC motors typically feature a three-pin connector, whereas the performance management differs when comparing pwm vs dc fans by adjusting the voltage supplied. This method often results in a static pace of operation, limiting performance unless additional control mechanisms are employed.
Key characteristics of PWM fans include:
- The ability to achieve lower minimum speeds, enhancing efficiency and reducing noise levels.
- Improved control over airflow, allowing for precise adjustments based on real-time temperature demands.
- Enhanced energy efficiency, with PWM units consuming up to 30% less power than their DC counterparts while delivering comparable temperature regulation.
While DC fans are simpler in design, the discussion of pwm vs dc fans highlights that they often lack the precision and adaptability that PWM fans offer. They may suffice for budget constructions or moderate temperature needs, but they do not provide the same level of performance in environments with fluctuating temperature requirements. Industry specialists emphasize that the transition to PWM technology marks a substantial improvement in temperature control solutions, particularly in high-performance settings such as gaming PCs and data centers, where maintaining optimal temperatures is crucial.
Compare Performance: Efficiency and Effectiveness of PWM vs DC Fans
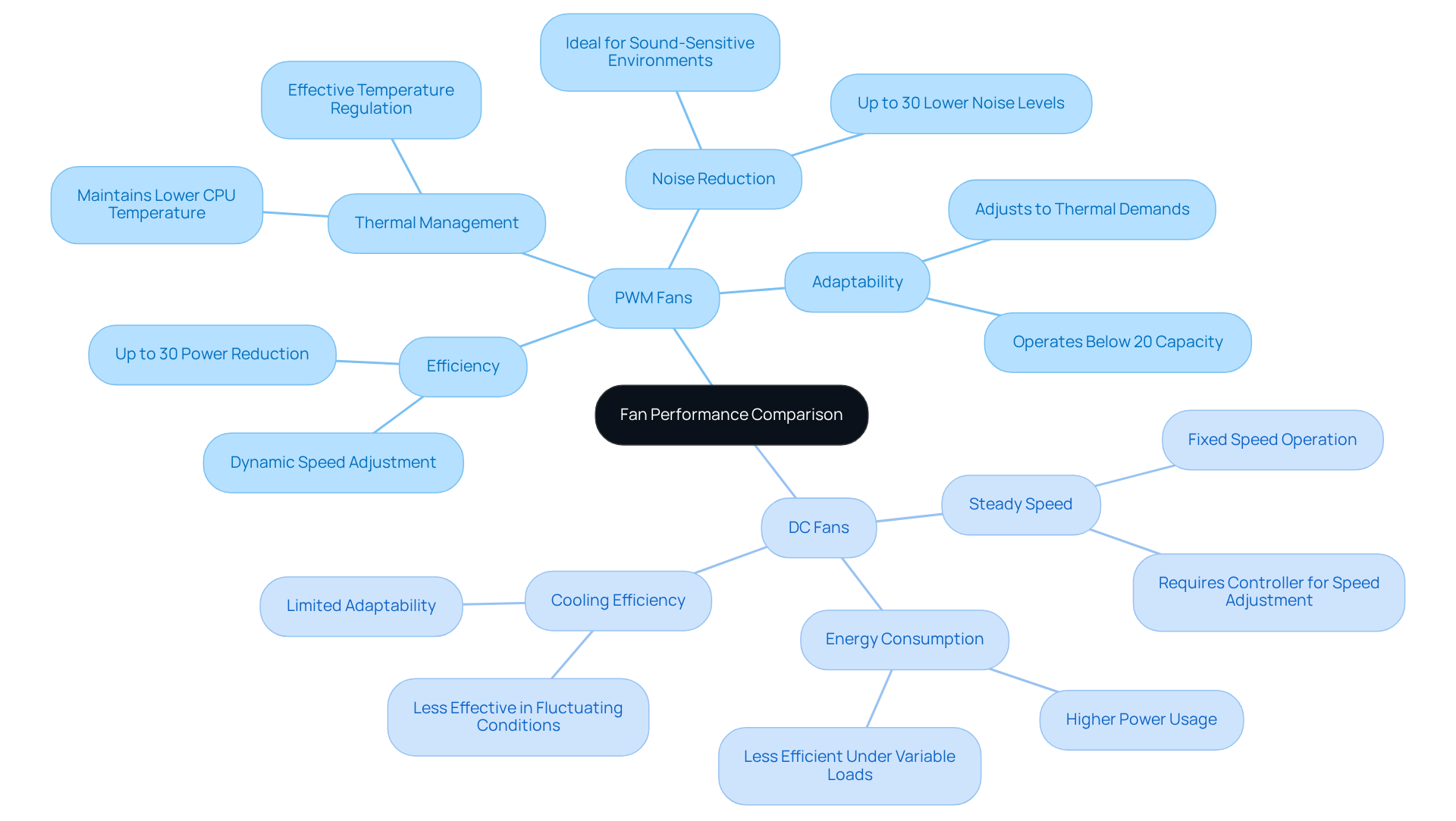
When discussing PWM vs DC fans, PWM models emerge as the clear leaders in efficiency. Their ability to dynamically adjust performance in response to thermal demands sets them apart. This adaptability enables PWM units to significantly reduce power consumption while effectively managing temperature, especially in systems with variable loads.
For example, PWM units can operate at rates as low as 20% of their maximum capacity, with the capability to dip below 20% of their rated velocity. This results in substantial energy savings during idle periods. In contrast, when comparing PWM vs DC fans, DC devices typically maintain a steady speed unless connected to a controller, which can lead to higher energy consumption and diminished cooling efficiency under fluctuating thermal demands.
As a result, discussions about PWM vs DC fans reveal that PWM units are increasingly favored in applications where energy efficiency and precise thermal management are critical. Recent studies from Gagner-Toomey Associates reveal that over 70% of electronics engineers using PWM devices report significant enhancements in thermal management and energy performance. This statistic underscores the growing relevance of PWM technology in contemporary electronic systems.
Moreover, PWM technology can lower noise levels by up to 30%, making it particularly suitable for sound-sensitive applications. The advantages of PWM are clear: improved efficiency, enhanced thermal management, and reduced noise, making them the preferred choice for modern electronic applications.
Evaluate Noise Levels: Impact of PWM and DC Fans on Acoustic Performance
When comparing PWM vs DC fans, PWM devices stand out for their quieter operation compared to DC models, primarily due to their capacity to function at reduced rates without stalling. This capability significantly lowers noise levels during use, making them ideal for noise-sensitive environments. By adjusting their speed in response to thermal requirements, PWM devices can operate at minimal rates when temperature control needs are low. This feature is particularly beneficial in settings like home theaters or quiet office spaces, where excessive noise can be disruptive.
In contrast, when comparing PWM vs DC fans, DC devices typically run at a constant speed, which often leads to increased noise, especially at higher RPMs. This acoustic performance is crucial for applications where maintaining a serene atmosphere is essential. Engineers must carefully evaluate these factors when selecting ventilators to ensure they meet both cooling and acoustic requirements, optimizing performance without compromising the ambient sound environment.
Moreover, when discussing PWM vs DC fans, PWM devices can achieve up to a 30% reduction in power consumption compared to their DC counterparts, enhancing their efficiency and further supporting their application in sensitive environments. Experts note that PWM devices can activate and deactivate several thousand times per second, allowing for precise management of noise levels. Conversely, DC devices operate within a voltage range of 5 to 48 volts, which can lead to elevated noise levels when running at higher speeds.
Understanding these operational characteristics is vital for engineers striving to balance performance and noise in their designs. By leveraging the advantages of PWM technology, they can create solutions that not only meet cooling demands but also maintain a peaceful sound environment.

Assess Energy Efficiency: Power Consumption of PWM vs DC Fans
When comparing PWM vs DC fans, PWM devices offer a significant advantage in energy efficiency over conventional DC models. By utilizing Pulse Width Modulation technology, these devices operate at varying rates, resulting in energy savings of up to 30%. This reduction is particularly evident in systems with fluctuating thermal loads, where PWM devices adjust their operation according to thermal requirements. For instance, during periods of minimal thermal management needs, PWM units run at lower speeds, conserving energy without compromising performance.
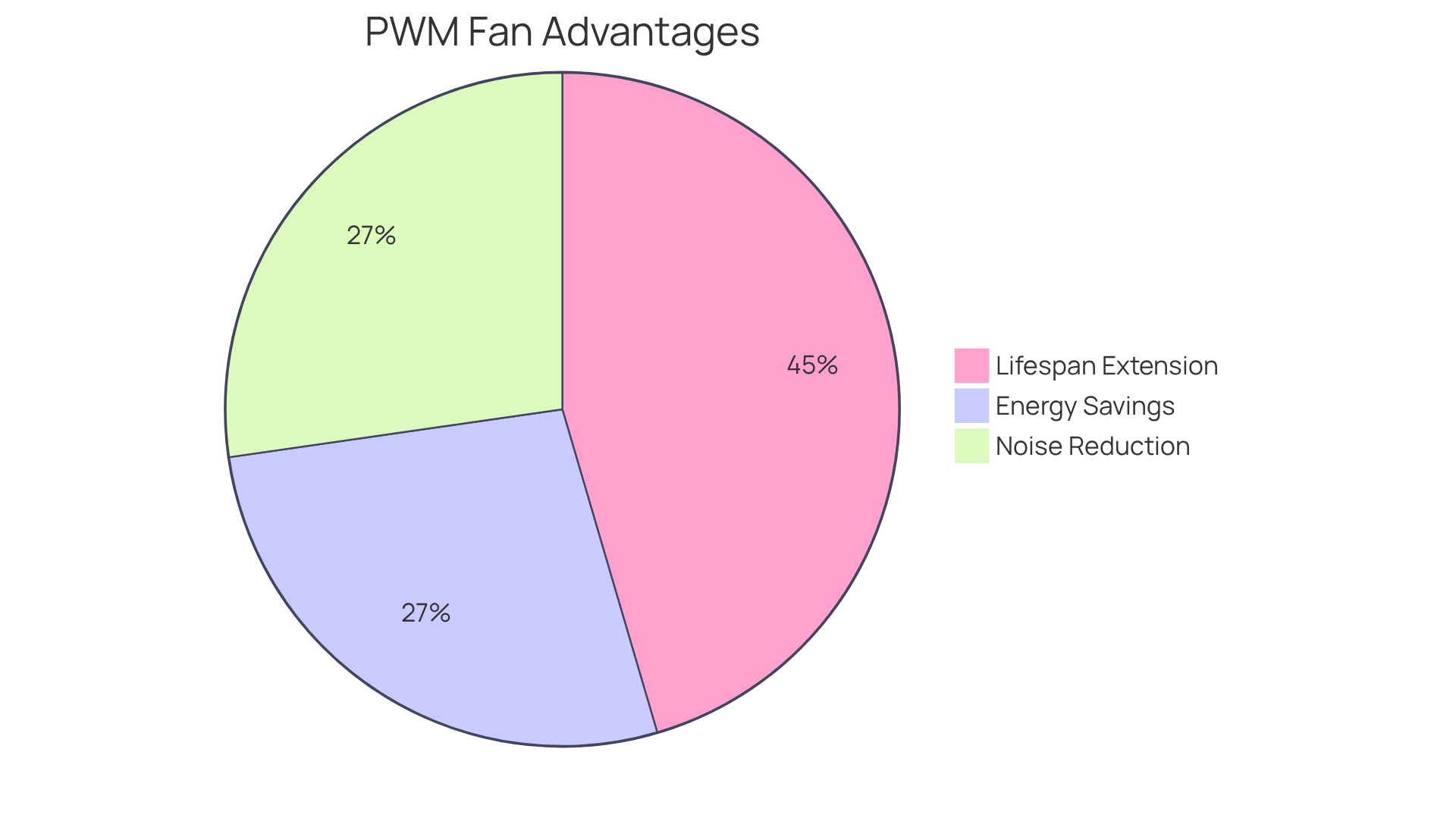
In contrast, traditional DC systems, when evaluated in the context of PWM vs DC fans, consume a constant amount of power regardless of actual cooling demands, leading to unnecessary energy waste. Moreover, PWM devices can achieve noise level reductions of up to 30% in sensitive environments, making them an excellent choice for engineers focused on acoustic comfort. They also extend component lifespan by as much as 50% compared to conventional DC units, enhancing long-term reliability and cost-effectiveness.
Furthermore, integrating PWM technology with smart home systems enhances user control and energy efficiency. Real-world data shows that data centers employing PWM technology experience approximately 20% reductions in overall energy consumption, underscoring the practical efficiency of PWM devices. This distinction positions PWM vs DC fans as the preferred choice for engineers who prioritize sustainability and cost-effectiveness in their cooling solutions.
Conclusion
The comparison between PWM and DC fans reveals critical differences that can significantly influence engineering decisions. PWM fans, leveraging advanced technology, provide dynamic control over speed and energy consumption, making them superior in both efficiency and performance compared to traditional DC fans. This adaptability not only enhances thermal management but also contributes to quieter operation, underscoring the importance of selecting the right fan type for specific applications.
Key points throughout this discussion highlight the benefits of PWM fans:
- Their ability to operate at lower speeds without stalling
- Substantial energy savings
- Reduced noise levels
In contrast, while DC fans are simpler in design, they often lack the precision and adaptability needed for environments with varying thermal demands. The data supporting the efficiency and effectiveness of PWM technology further emphasizes its growing relevance in modern electronic systems.
Ultimately, the choice between PWM and DC fans transcends mere preference; it is a critical decision impacting performance, energy consumption, and noise levels across various applications. Engineers must consider these factors carefully. By leveraging the advantages of PWM technology, they can achieve more efficient and effective cooling solutions, ensuring optimal performance even in the most demanding environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is PWM in relation to fans?
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) refers to a technology used in motors that allows for precise control of rotation speed through a four-pin connector, with one pin dedicated to sending a PWM signal.
How do PWM fans differ from traditional DC fans?
PWM fans utilize a four-pin connector for adjustable speed control, while traditional DC fans typically have a three-pin connector and rely on voltage adjustments for speed management, which can result in a static pace of operation.
What are the key characteristics of PWM fans?
Key characteristics of PWM fans include the ability to achieve lower minimum speeds, improved control over airflow based on real-time temperature demands, and enhanced energy efficiency, consuming up to 30% less power than DC fans while providing comparable temperature regulation.
Why are PWM fans considered more efficient than DC fans?
PWM fans are more efficient because they can operate at lower speeds without stalling, allowing for better thermal regulation, reduced noise levels, and lower power consumption compared to traditional DC fans.
In what environments are PWM fans particularly beneficial?
PWM fans are particularly beneficial in high-performance settings such as gaming PCs and data centers, where maintaining optimal temperatures is crucial due to fluctuating temperature requirements.
Are DC fans suitable for all applications?
While DC fans are simpler and may suffice for budget constructions or moderate temperature needs, they lack the precision and adaptability of PWM fans, making them less ideal for environments with varying temperature demands.

