Introduction
The emergence of energy efficiency in electronic systems has catalyzed a notable transformation in fan technology, positioning Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) fans at the forefront. These advanced devices not only improve cooling performance but also deliver significant advantages, including reduced noise levels and lower power consumption. As electronics engineers increasingly integrate PWM fans into their designs, one must consider: what makes these fans indispensable in contemporary thermal management?
Delving into the essential characteristics, benefits, and advancing technology of PWM fans underscores their pivotal role in optimizing device performance and promoting sustainability within the demanding realm of electronics. By understanding these elements, engineers can make informed decisions that enhance both functionality and efficiency in their projects.
Define PWM Fan: Key Characteristics and Functionality
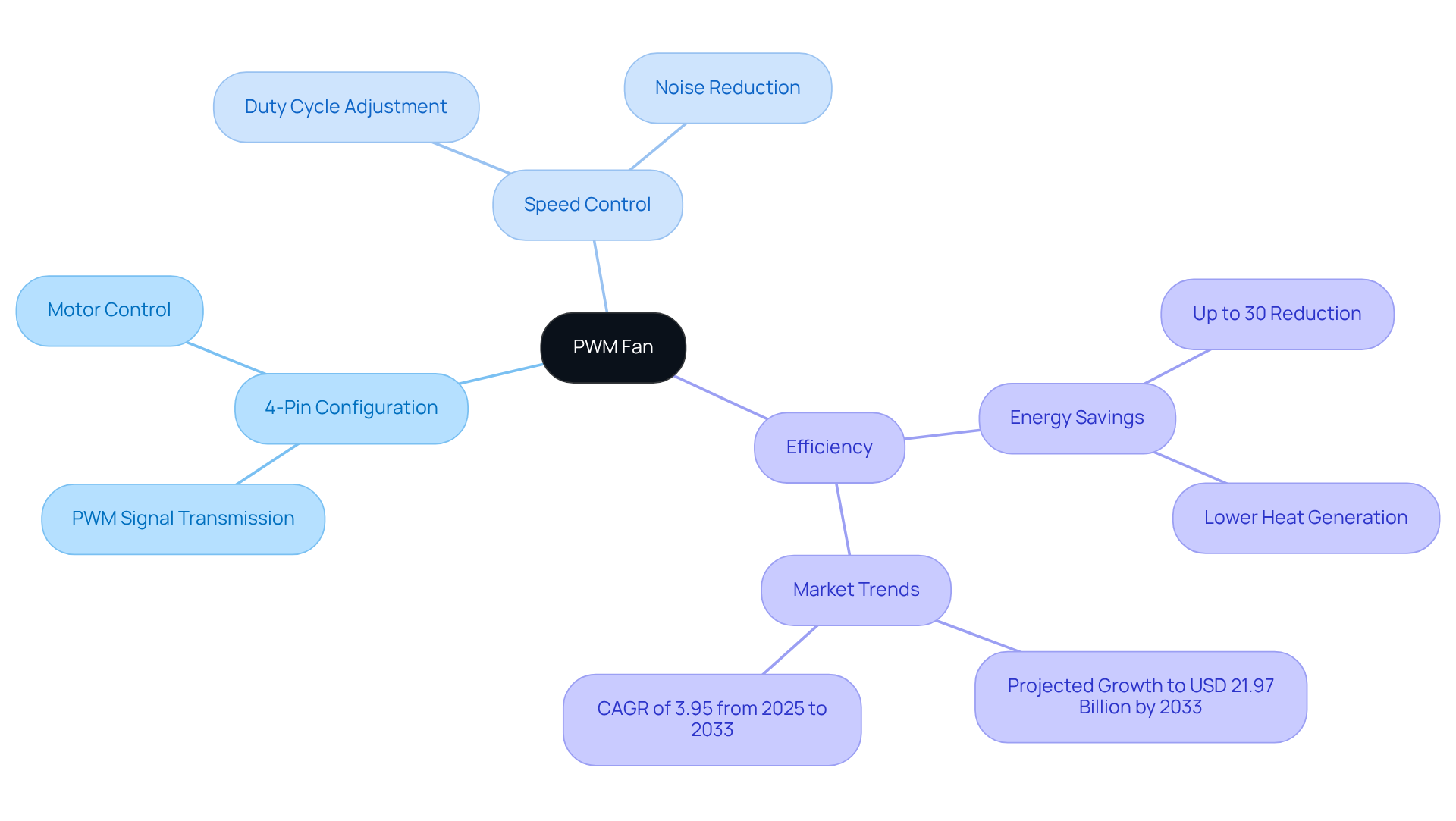
To understand what’s PWM fan, it’s important to know that PWM, or Pulse Width Modulation, is a pivotal technique in controlling fan speeds by adjusting the width of electrical pulses sent to the motor. This dynamic capability allows PWM devices to operate with greater efficiency compared to traditional fans, which run at a constant speed. Key characteristics of PWM fans include:
- 4-Pin Configuration: Typically, PWM fans feature a four-wire design, with the fourth wire transmitting a PWM signal that precisely regulates fan speed.
What’s PWM fan speed control? By altering the duty cycle of the PWM signal, engineers can finely adjust the fan speed, leading to quieter operation and improved energy efficiency.
What’s PWM fan is a crucial aspect of enhanced cooling performance, as PWM devices can adapt their speed in response to temperature fluctuations, ensuring optimal cooling during high-demand scenarios while minimizing noise during low-load conditions.
The adoption of PWM systems is on the rise, with over 70% of electronics engineers incorporating PWM units into their designs. This trend underscores a growing commitment to efficient temperature control. Gagner-Toomey Associates is leading this innovation, offering high-quality PWM fan solutions tailored to meet the rigorous demands of the electronics industry. Their extensive portfolio includes both standard and custom air-movers, such as DC input Tube Axial devices ranging from 15 to 280mm and Centrifugal Blowers from 15 to 225mm, all optimized for performance and efficiency. Recent advancements in temperature regulation methods highlight what’s PWM fan and its critical role in achieving effective thermal control, with potential energy savings of up to 30% compared to conventional DC fans. As the market for PWM fan technology continues to grow, driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions, Gagner-Toomey remains dedicated to delivering cutting-edge products that enhance performance and reliability in electronic systems.
Contextualize PWM Fans: Importance in Electronics Engineering
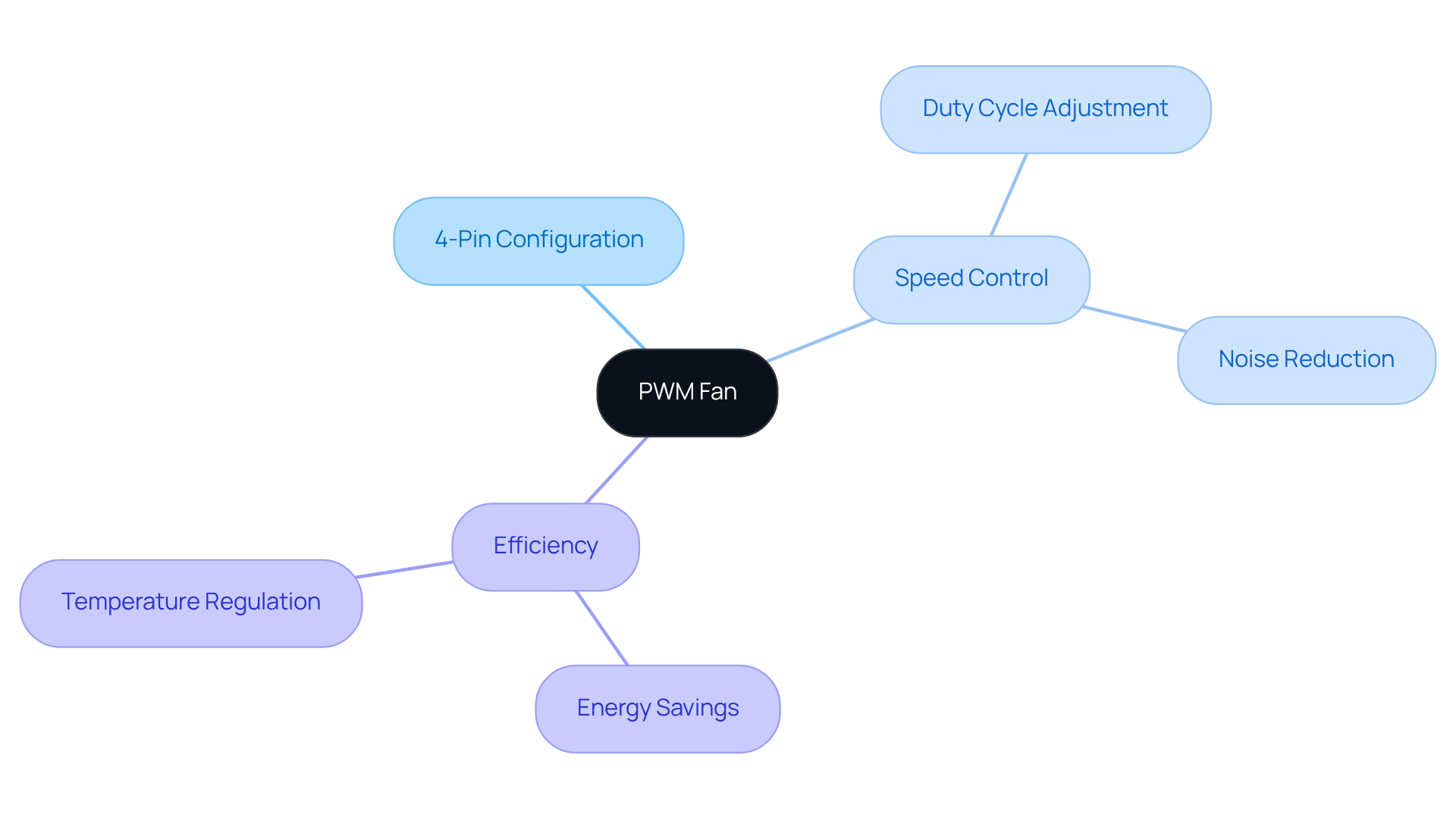
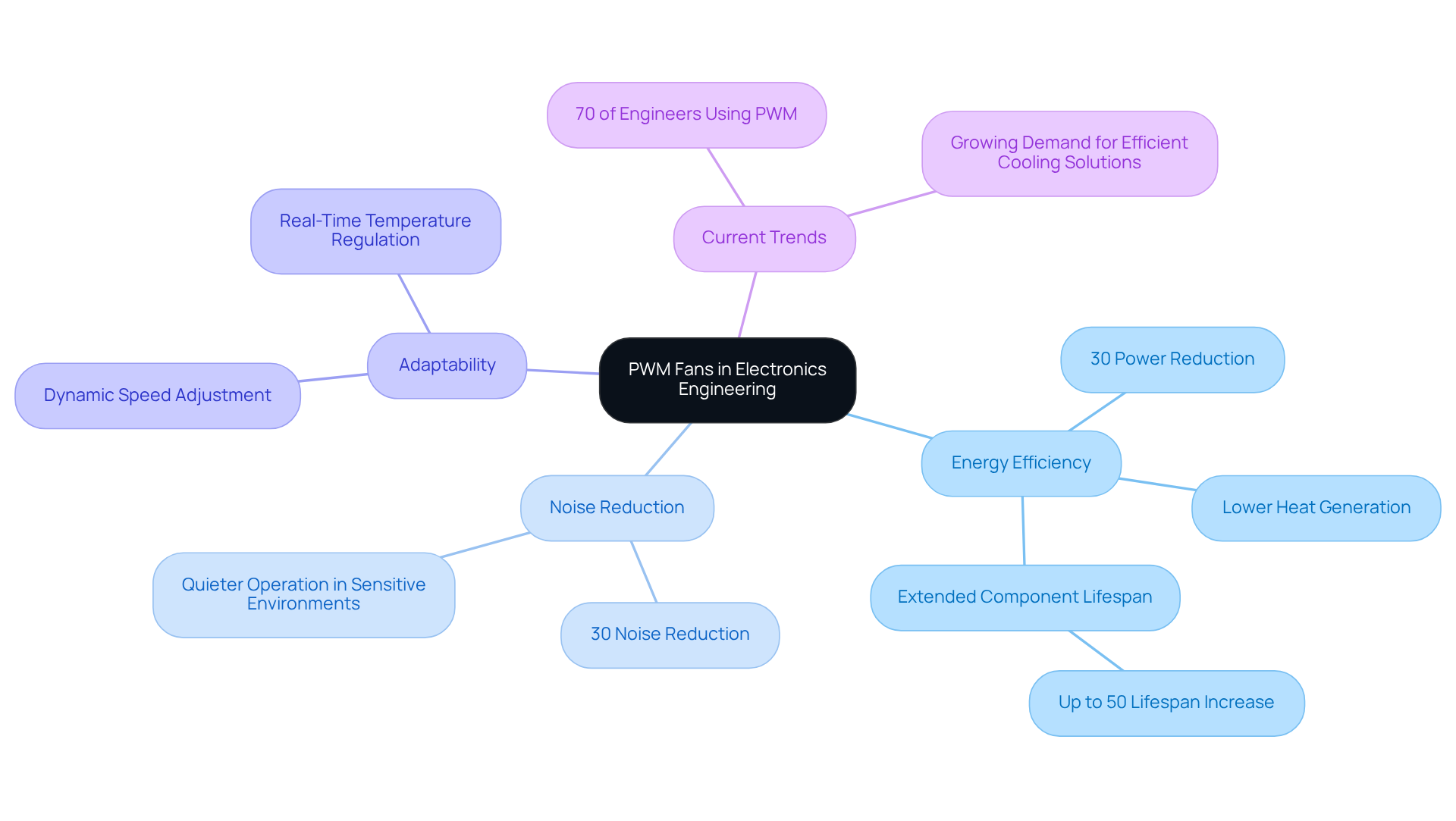
In electronics engineering, it’s crucial to understand what’s a PWM fan, as PWM systems play a vital role in improving thermal management in devices like computers, servers, and industrial equipment. The advantages of PWM fans are compelling:
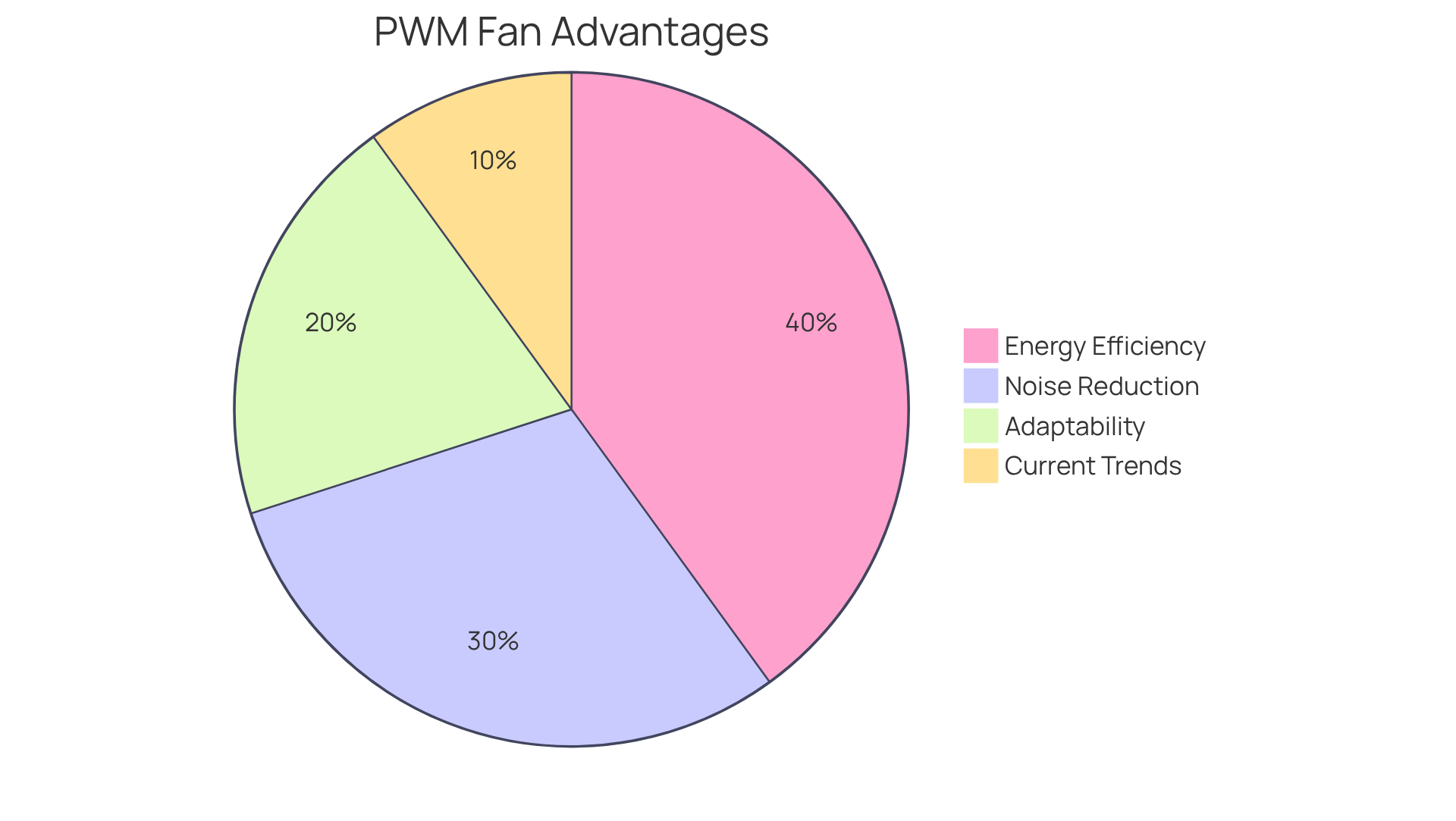
- Energy Efficiency: PWM fans can reduce power consumption by up to 30% compared to traditional direct current devices, all while effectively managing temperatures. This efficiency not only benefits the environment but also represents a financially savvy choice for engineers.
- Noise Reduction: Operating at lower speeds when full temperature control isn’t necessary allows PWM devices to significantly decrease noise levels. This feature is particularly advantageous in sound-sensitive environments, such as offices and home theaters, with some systems achieving noise reductions of up to 30%.
- Adaptability: These devices dynamically adjust their speeds based on real-time temperature readings, ensuring that temperature regulation occurs only when needed. This adaptability not only enhances energy efficiency but also extends the lifespan of electronic components, with estimates suggesting a lifespan increase of up to 50%.
- Current Trends: The rising reliance on PWM methods underscores their significance in modern electronics. Over 70% of electronics engineers are now incorporating PWM temperature control devices into their designs, highlighting a shift towards more efficient temperature regulation solutions. As advancements continue, understanding what’s a PWM fan will be essential, as the demand for them is expected to rise, further solidifying their role in effective thermal management.
Trace the Evolution: The Development of PWM Technology
To understand PWM fan innovation, it’s crucial to recognize its profound impact on electronic temperature regulation systems. This advancement is marked by several key milestones:
- Early Innovations: PWM technology emerged in the 1960s, initially used for regulating electric motor speeds before its adaptation for fan control.
- Integration into Consumer Electronics: By the 1990s, many began to ask what’s pwm fan, as they became a standard feature in computer cooling systems, significantly enhancing thermal management in PCs and servers.
- Advancements in Control Algorithms: Recent innovations have introduced sophisticated algorithms that optimize PWM signals, allowing cooling devices to respond more accurately to varying thermal demands.
- Noise Reduction Benefits: PWM devices can achieve an average noise level reduction of up to 30%, making them ideal for noise-sensitive environments. This capability is crucial in applications such as data centers and residential spaces, where maintaining a quiet atmosphere is essential.
- Energy Conservation: Compared to conventional DC motors, PWM devices demonstrate enhanced energy conservation, with potential power usage decreases of up to 30%. This efficiency not only lowers operational costs but also supports sustainability goals in electronic design, specifically in what’s pwm fan.
- Real-World Examples: Case studies have shown that systems utilizing PWM motors can maintain optimal temperatures while significantly reducing noise levels, thereby improving user experience and system reliability.
These milestones underscore the essential role of PWM systems in contemporary cooling solutions, reflecting a clear trend towards more efficient and quieter operation in electronic applications.
Explore Variations: Types and Components of PWM Fans
PWM blowers come in various configurations, each designed for specific applications, making them essential in today’s technological landscape. For engineers looking to boost performance and energy efficiency in their designs, understanding these variations is paramount.
What’s PWM fan and how does it work?
What’s PWM fan is the most prevalent type, featuring a dedicated PWM control wire that allows for precise speed adjustments based on thermal demands. This adaptability is crucial in environments where maintaining optimal temperatures is vital, such as data centers and high-performance computing. As Matt Safford points out, “The accuracy of PWM devices enables engineers to enhance temperature management strategies efficiently, a factor that is crucial in high-performance settings.”
DC Brushless Fans
Many PWM fans utilize brushless DC motors, which offer superior performance and longer lifespans compared to traditional brushed motors. This reliability is particularly advantageous in telecommunications equipment, where performance is critical. Research indicates that data centers employing PWM technology have seen significant improvements, with a reduction in Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) from 1.55 to 1.42.
Specialized Units
Certain PWM devices are specifically engineered for unique applications, such as high static pressure models for radiator use or low-noise variants suited for silent computing environments. These specialized designs empower engineers to select the most appropriate fan for their project needs.
With over 70% of electronics engineers incorporating PWM fans into their projects, this trend underscores the growing emphasis on energy efficiency and performance. The significance of these advanced cooling solutions cannot be overstated, as they play a pivotal role in optimizing system functionality.
Conclusion
The significance of PWM fans in electronics engineering is profound, representing a pivotal approach to thermal management. By utilizing Pulse Width Modulation technology, these fans empower engineers to precisely control fan speeds, thereby enhancing efficiency and performance while minimizing noise levels. This adaptability is essential across various applications, from data centers to consumer electronics, where maintaining optimal temperatures is critical for system reliability.
Key insights into PWM fans underscore their advantages:
- Energy efficiency
- Noise reduction
- Real-time adaptability to temperature fluctuations
The evolution of PWM technology illustrates its historical development and the milestones that have shaped its current capabilities. With over 70% of electronics engineers now incorporating PWM fans into their designs, the trend toward energy-efficient solutions is unmistakable. These advancements not only promise significant energy savings but also improve the overall user experience by fostering quieter and more reliable systems.
Looking ahead, the ongoing growth and innovation in PWM fan technology will be instrumental in shaping the future of electronics engineering. Engineers are urged to embrace these advanced cooling solutions to optimize performance and sustainability in their projects. As the demand for efficient thermal management solutions escalates, understanding and implementing PWM fans will be crucial for achieving success in the dynamic landscape of electronic design.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a PWM fan?
A PWM fan, or Pulse Width Modulation fan, is a type of fan that uses a technique to control its speed by adjusting the width of electrical pulses sent to the motor, allowing for greater efficiency compared to traditional fans that run at a constant speed.
What are the key characteristics of PWM fans?
Key characteristics of PWM fans include a 4-pin configuration, where the fourth wire transmits a PWM signal to regulate fan speed, and the ability to adjust speed dynamically based on temperature fluctuations, leading to quieter operation and improved energy efficiency.
How does PWM fan speed control work?
PWM fan speed control works by altering the duty cycle of the PWM signal, allowing engineers to finely adjust the fan speed for optimal performance.
Why is PWM technology important for cooling performance?
PWM technology is important for cooling performance because it enables fans to adapt their speed in response to temperature changes, ensuring effective cooling during high-demand scenarios while minimizing noise during low-load conditions.
What percentage of electronics engineers are adopting PWM systems?
Over 70% of electronics engineers are incorporating PWM units into their designs, indicating a growing commitment to efficient temperature control.
Who is leading the innovation in PWM fan solutions?
Gagner-Toomey Associates is leading the innovation in PWM fan solutions, offering high-quality products tailored for the electronics industry.
What types of PWM fans does Gagner-Toomey offer?
Gagner-Toomey offers both standard and custom air-movers, including DC input Tube Axial devices ranging from 15 to 280mm and Centrifugal Blowers from 15 to 225mm, all optimized for performance and efficiency.
What are the potential energy savings of using PWM fans compared to conventional DC fans?
PWM fans can achieve potential energy savings of up to 30% compared to conventional DC fans, making them a more efficient choice for cooling solutions.
How is the market for PWM fan technology evolving?
The market for PWM fan technology is growing, driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions, and Gagner-Toomey is committed to delivering cutting-edge products that enhance performance and reliability in electronic systems.

