Introduction
Understanding the intricacies of radiator fan performance hinges on one crucial metric: CFM, or Cubic Feet per Minute. This measurement dictates how effectively a fan can cool components and plays a pivotal role in ensuring the longevity and efficiency of systems reliant on proper ventilation. However, navigating the complexities of CFM calculations can be daunting. How can engineers and enthusiasts alike leverage a radiator fan CFM calculator to optimize their cooling solutions?
This guide unpacks the essential steps and considerations needed to harness this powerful tool effectively. By doing so, you can ensure systems operate at peak performance while avoiding common pitfalls. Let’s delve into the world of CFM and discover how to maximize your radiator fan’s potential.
Understand CFM and Its Importance in Radiator Fans
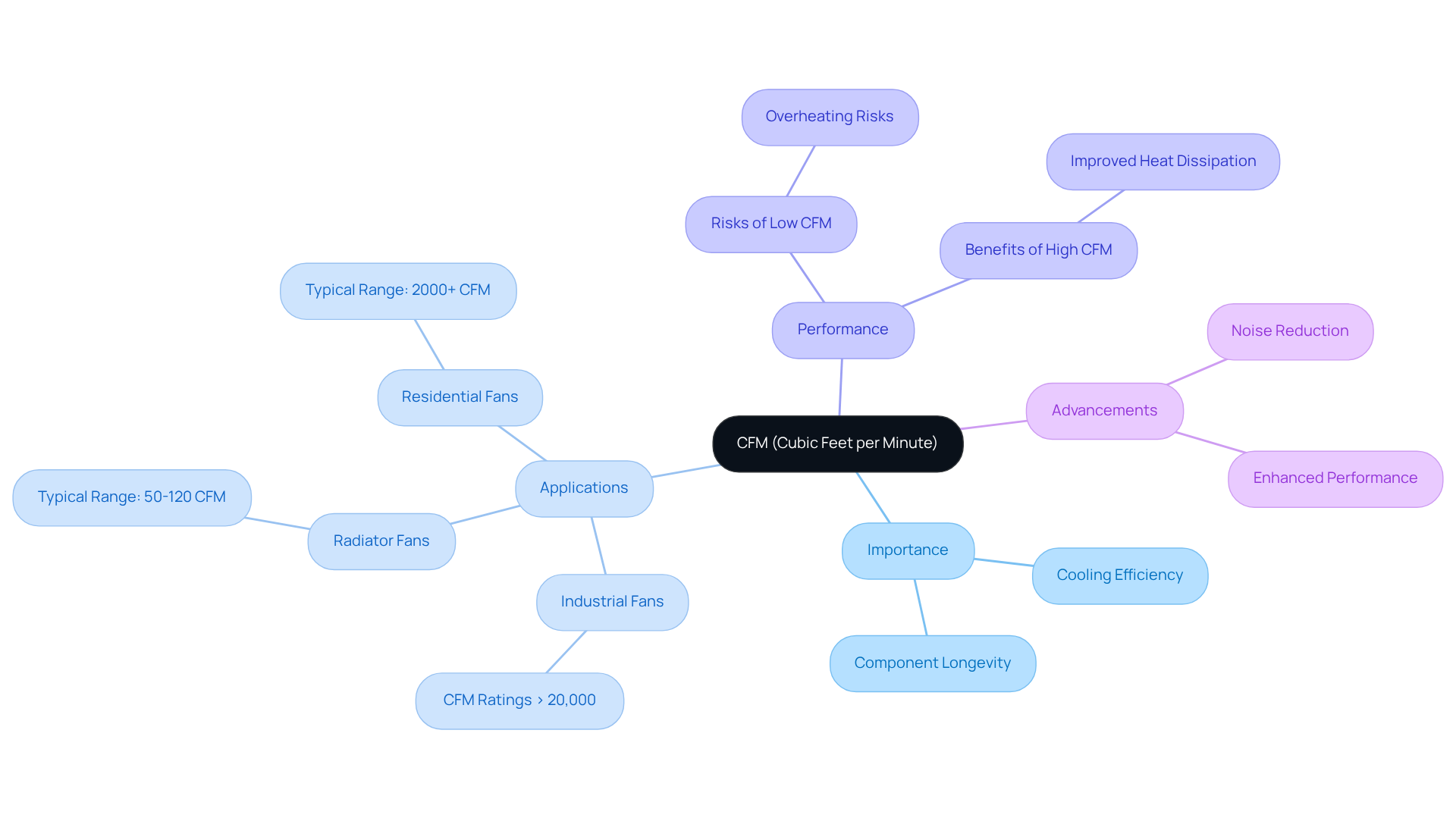
CFM, or Cubic Feet per Minute, is a critical metric that quantifies the volume of air a blower can move in one minute. This measurement is essential for radiator blowers, and using a radiator fan cfm calculator is vital as it directly influences cooling efficiency. Higher CFM ratings facilitate improved heat dissipation from engines or electronic components, making it vital for optimal performance.
For instance, industrial fans from Gagner-Toomey Associates often require CFM ratings exceeding 20,000 to effectively manage ventilation in expansive areas. In contrast, the radiator fan cfm calculator shows that radiator fans typically operate within a range of 50 to 120 CFM for peak performance. A fan that falls short in CFM can lead to overheating, posing a risk to crucial components.
Recent advancements in radiator fan technology have focused on enhancing performance, as indicated by the radiator fan cfm calculator, while simultaneously reducing noise levels. This innovation allows for quieter operation without sacrificing air movement, a significant benefit in many applications. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for engineers who utilize a radiator fan cfm calculator to select the appropriate fan for specific applications, ensuring reliable cooling under varying operational conditions.
As industry experts emphasize, the right CFM not only boosts cooling efficiency but also contributes to the longevity and reliability of electronic systems. By prioritizing CFM in fan selection, engineers can enhance system performance and safeguard critical components.
Identify Key Parameters for CFM Calculation
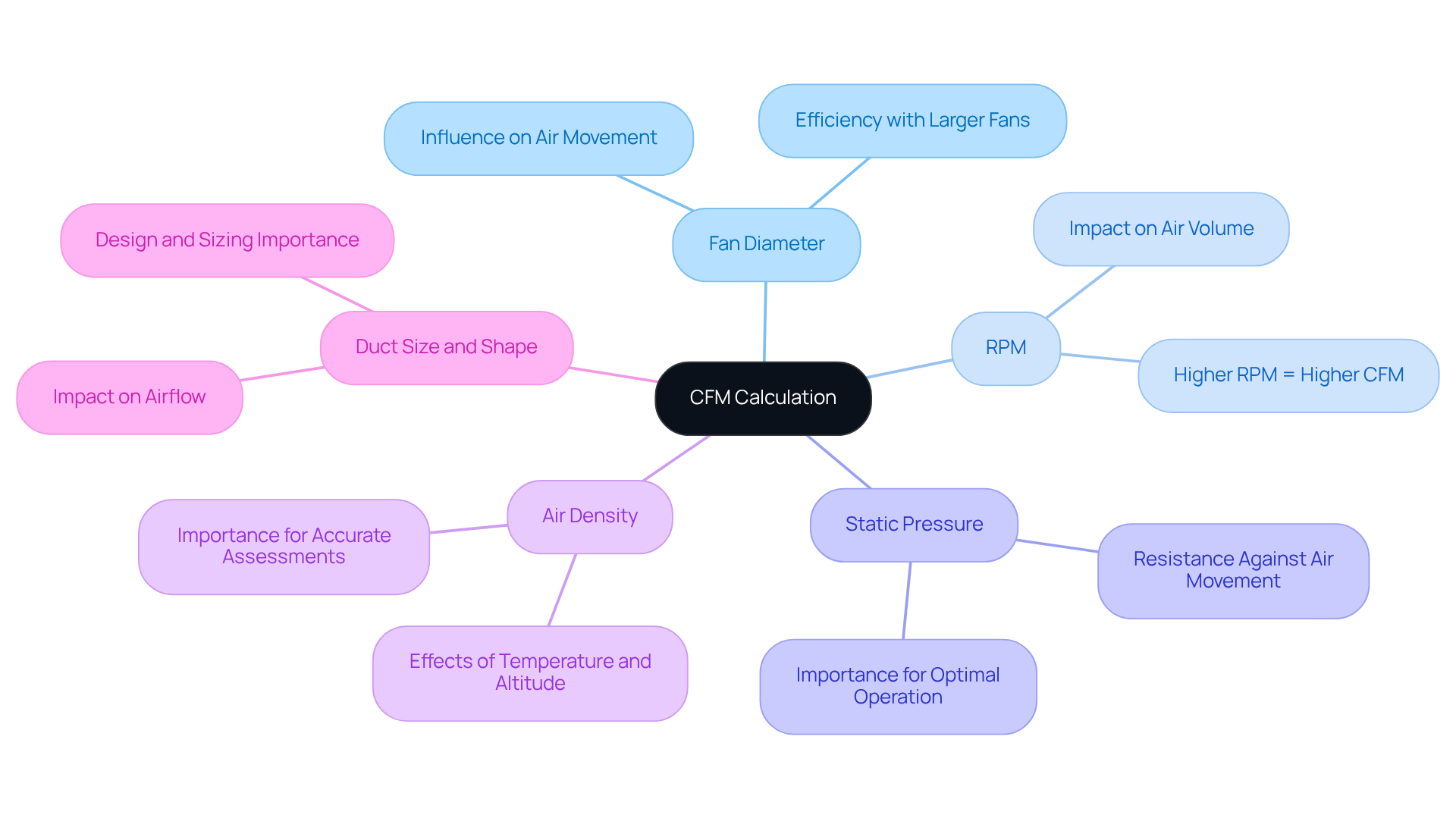
To effectively calculate CFM, it’s essential to identify several key parameters:
- Fan Diameter: The size of the fan blades significantly influences air movement. Larger fans typically move more air, enhancing overall efficiency.
- RPM (Revolutions Per Minute): The speed at which the fan operates directly affects the volume of air moved. Higher RPMs generally result in higher CFM, making this a critical factor in performance.
- Static Pressure: This refers to the resistance against the movement of air within the system. Understanding static pressure is vital for determining how much air the fan can effectively move, ensuring optimal operation.
- Air Density: Variations in temperature and altitude can impact air density, which in turn influences CFM calculations. Recognizing these changes is crucial for accurate assessments.
- Duct Size and Shape: In ducted systems, the size and shape of the ducts can restrict airflow, significantly impacting effective CFM. Proper design and sizing are essential for maximizing performance.
Gathering accurate measurements for these parameters is crucial for using a radiator fan cfm calculator to ensure precise calculations, enabling you to optimize your system’s efficiency.
Use the CFM Calculator: Step-by-Step Instructions
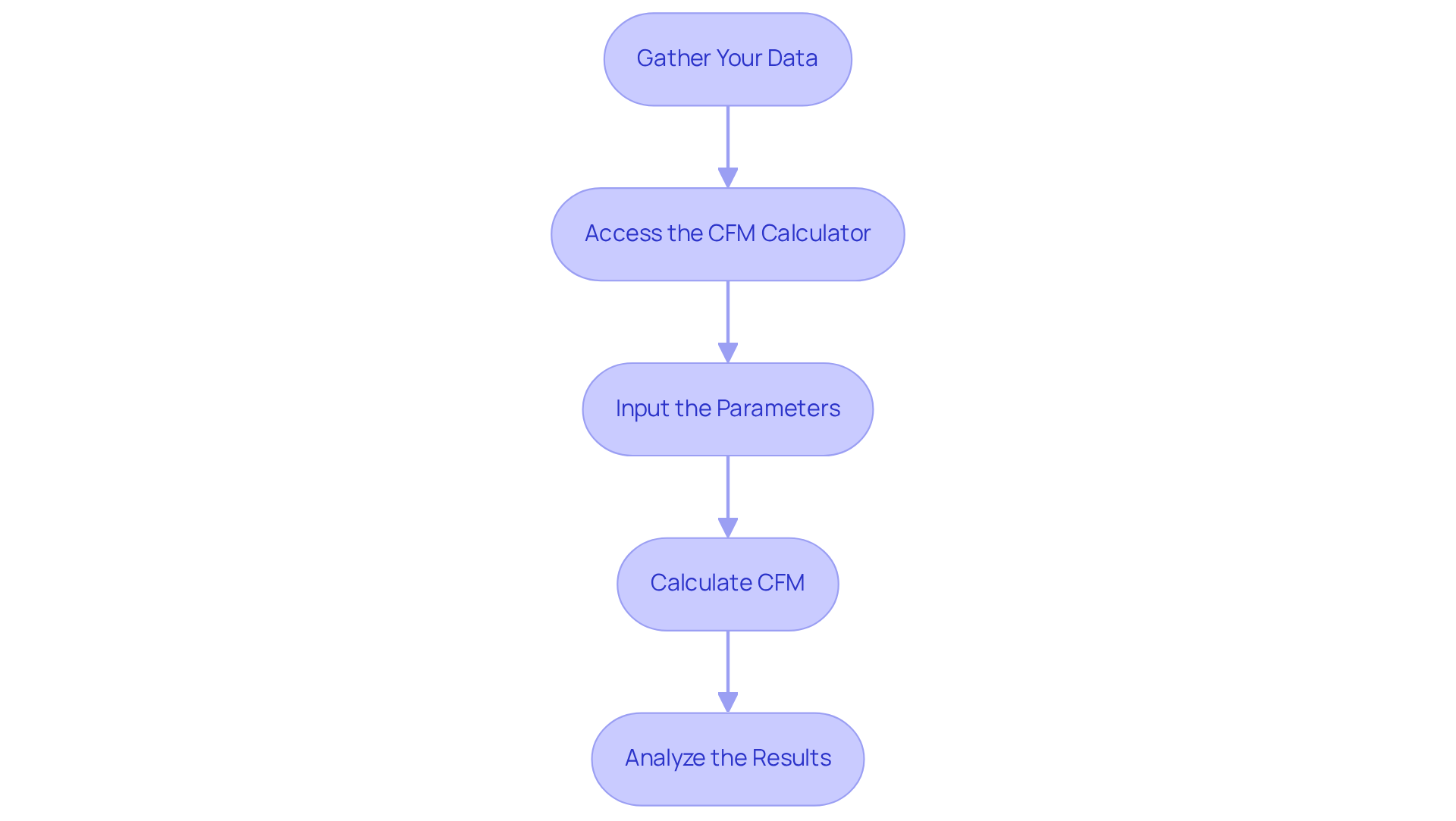
To effectively utilize the CFM calculator, follow these essential steps:
-
Gather Your Data: Start by collecting the necessary parameters identified earlier, such as fan diameter, RPM, and static pressure. This foundational data is crucial for accurate calculations.
-
Access the CFM Calculator: Navigate to an online CFM calculator or a dedicated app. Websites like Omni Calculator offer user-friendly interfaces designed for this purpose, making it easy to input your data.
-
Input the Parameters: Carefully enter the gathered data into the calculator. It’s vital to ensure that all measurements are in the correct units-use inches for diameter and RPM for speed-to avoid any discrepancies in your results.
-
Calculate CFM: Once your data is entered, click the calculate button to obtain the CFM value. Take a moment to review the output, ensuring it aligns with your expectations based on the fan specifications.
-
Analyze the Results: With the calculated CFM in hand, assess whether the fan meets the cooling requirements for your application. If the CFM falls short of what you need, consider adjusting the fan size or speed to achieve optimal performance.
Troubleshoot Common Issues in CFM Calculations
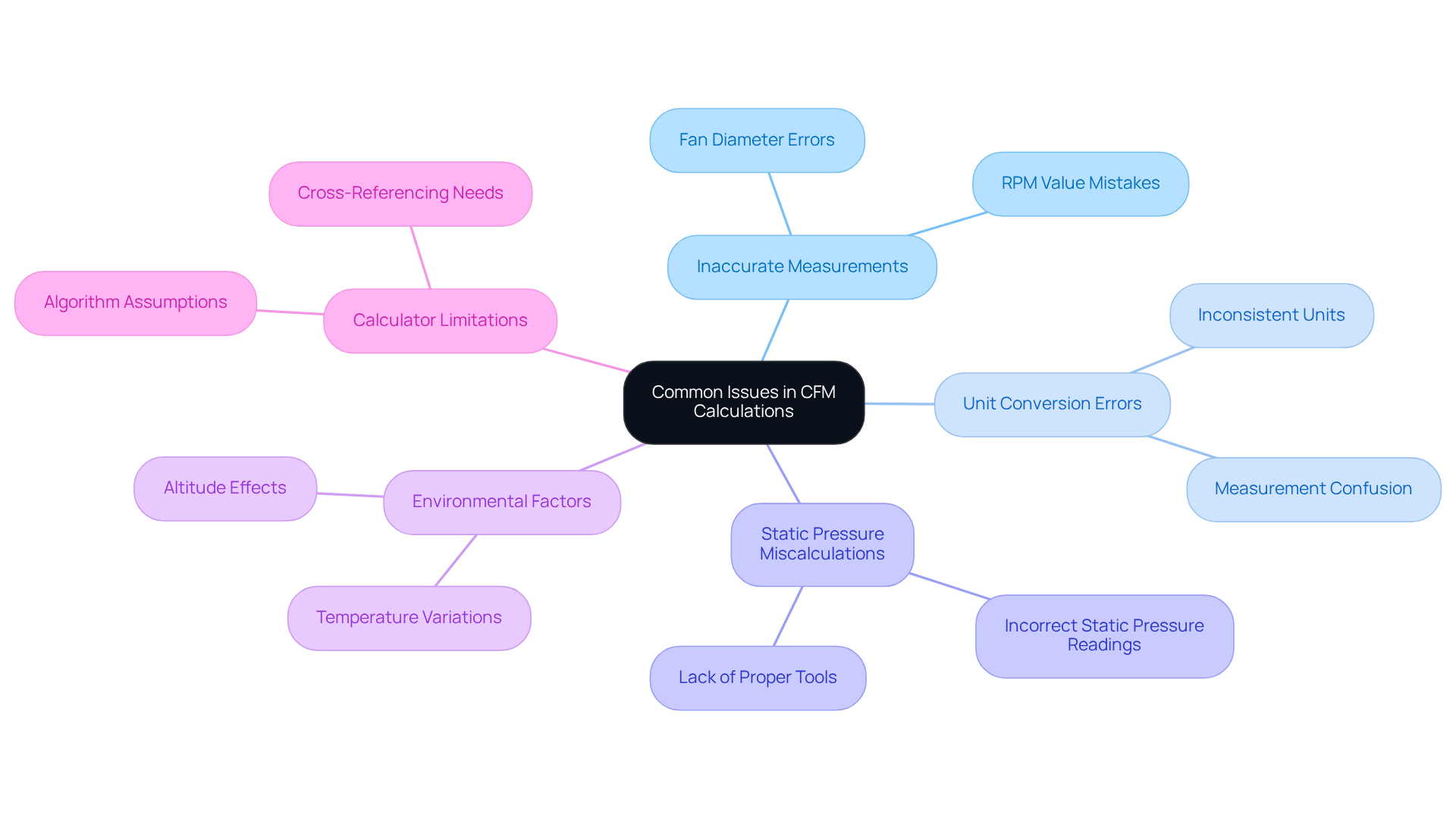
When using a CFM calculator, you may encounter several common issues that can compromise the accuracy of your results:
-
Inaccurate Measurements: It’s crucial to ensure that all parameters are measured accurately. Double-check your fan diameter and RPM values; even small errors can lead to significant discrepancies in CFM calculations.
-
Unit Conversion Errors: Consistency in units is vital. For instance, if the fan diameter is measured in inches, ensure that all other measurements are also in compatible units to avoid confusion.
-
Static Pressure Miscalculations: Incorrect static pressure measurements can lead to erroneous CFM values. Utilize a manometer or consult manufacturer specifications to obtain accurate static pressure readings.
-
Environmental Factors: Be aware that changes in temperature and altitude can affect air density, which in turn impacts CFM calculations. Adjust your calculations based on the current environmental conditions to maintain accuracy.
-
Calculator Limitations: Some online calculators may have inherent limitations or assumptions built into their algorithms. It’s essential to be aware of these factors when interpreting results and consider cross-referencing with other tools or methods for validation.
By addressing these common issues, you can significantly enhance the accuracy and reliability of your CFM calculations.
Conclusion
Effectively utilizing a radiator fan CFM calculator is crucial for optimizing cooling systems. Accurately calculating CFM not only enhances performance but also ensures the reliability of various applications, protecting critical components from overheating. The importance of CFM is foundational in selecting the right fan for specific needs.
This guide has outlined the essential parameters for CFM calculations:
- Fan diameter
- RPM
- Static pressure
- Air density
- Duct size
Each factor plays a vital role in determining air movement efficiency and, consequently, the cooling capacity of the system. Step-by-step instructions have been provided to navigate the CFM calculator effectively, along with troubleshooting tips for common issues that may arise during the process.
Mastering the use of a radiator fan CFM calculator significantly improves cooling efficiency and extends the longevity of electronic systems. Engineers and technicians must prioritize accurate measurements and consider environmental factors when calculating CFM. By doing so, they can ensure optimal performance and reliability in their cooling solutions, safeguarding vital components and contributing to overall system success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does CFM stand for and why is it important in radiator fans?
CFM stands for Cubic Feet per Minute, which quantifies the volume of air a blower can move in one minute. It is important in radiator fans as it directly influences cooling efficiency and heat dissipation from engines or electronic components.
What is the typical CFM range for radiator fans?
Radiator fans typically operate within a range of 50 to 120 CFM for peak performance.
What can happen if a radiator fan has a low CFM rating?
A fan that falls short in CFM can lead to overheating, posing a risk to crucial components.
How do industrial fan CFM requirements compare to radiator fan CFM?
Industrial fans often require CFM ratings exceeding 20,000 to effectively manage ventilation in large areas, whereas radiator fans usually operate within the 50 to 120 CFM range.
What advancements have been made in radiator fan technology?
Recent advancements have focused on enhancing performance while reducing noise levels, allowing for quieter operation without sacrificing air movement.
Why is understanding CFM dynamics crucial for engineers?
Understanding these dynamics is crucial for engineers to select the appropriate fan for specific applications, ensuring reliable cooling under varying operational conditions.
How does prioritizing CFM in fan selection benefit electronic systems?
Prioritizing CFM boosts cooling efficiency and contributes to the longevity and reliability of electronic systems, enhancing overall system performance and safeguarding critical components.

