Introduction
The landscape of cooling solutions in electronics is evolving at a remarkable pace. Engineers now face a critical decision: should they opt for PWM fans or stick with traditional DC fans? As the demand for energy efficiency and quiet operation grows, grasping the distinct advantages and limitations of these technologies becomes essential.
This article will provide key insights into PWM and DC fans, examining how their operational differences influence performance, cost, and compatibility in modern applications. What factors should engineers weigh when selecting the right fan for their systems? Moreover, how can PWM technology redefine cooling efficiency?
Let’s explore these pressing questions.
Gagner-Toomey Associates: Leading Provider of Cooling Solutions for Electronics
Gagner-Toomey Associates stands out as a premier sales organization, specializing in innovative cooling solutions tailored for the electronics sector. They present a diverse array of manufacturers, ensuring engineers have access to state-of-the-art products that significantly enhance performance in electronic systems. At the core of Gagner-Toomey’s ethos is exceptional customer support, backed by extensive experience and industry knowledge that empower engineers to effectively tackle complex challenges.
Recent research underscores the impressive levels of customer satisfaction in cooling solutions, revealing that over 70% of electronics engineers utilizing PWM fan vs DC devices in their designs report substantial improvements in thermal management and energy performance. This dedication to excellence is further exemplified by their outstanding customer service and technical support, solidifying Gagner-Toomey as a trusted partner for engineers navigating intricate cooling challenges within the electronics industry.
Their focus on cutting-edge technologies, particularly PWM devices, reflects a commitment to providing solutions that not only meet but exceed the evolving demands of modern electronics. Notably, when considering PWM fan vs DC technology, PWM has demonstrated the ability to reduce power consumption by up to 30% compared to traditional direct current devices, all while maintaining effective temperature management. This advancement has also led to a significant reduction in Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE), dropping from 1.55 to 1.42, which highlights its efficiency.
To optimize their sales efforts and maintain industry leadership, Gagner-Toomey Associates leverages IT tools like RPMS for opportunity tracking and sales reporting. This strategic approach ensures they remain at the forefront of the industry, ready to meet the cooling needs of tomorrow.
DC Fans: Understanding Direct Current Cooling Mechanisms
DC enthusiasts thrive on direct current (DC) electricity, which allows them to maintain a consistent operational pace. These devices are typically designed with simplicity in mind, often featuring a brushless motor that efficiently converts electrical energy into mechanical motion. This design not only minimizes wear and tear but also contributes to longer lifespans for the devices.
However, it’s important to note that DC enthusiasts generally operate at a constant speed unless they are connected to a controller. This controller can adjust the voltage, thereby altering the speed of the device. Such simplicity makes DC devices a favored choice across various applications, although when considering pwm fan vs dc, they may not offer the precision found in PWM devices.
In summary, while DC devices provide reliable performance and durability, the discussion of pwm fan vs dc emphasizes their operational limitations, which should be considered when selecting the right technology for specific needs.
PWM Fans: Exploring Pulse Width Modulation Technology
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) devices represent a cutting-edge control method that precisely adjusts the duration of electrical pulses supplied to motors. This capability allows for accurate velocity modifications, enabling fans to operate at varying speeds in response to thermal demands. Typically featuring a four-pin connector, PWM devices include an additional pin dedicated to the PWM signal, which facilitates dynamic control.
The energy efficiency of PWM technology is noteworthy when considering PWM fan vs DC; these units can consume up to 30% less power than traditional DC devices, particularly when operating at lower speeds. Moreover, PWM devices are designed to significantly reduce noise levels, achieving a decrease of up to 30% compared to conventional cooling systems. This makes them particularly advantageous in environments where quiet operation is paramount.
In practical applications, such as data centers and high-performance computing systems, PWM devices not only enhance temperature regulation but also extend the lifespan of electronic components by minimizing wear and tear. Their ability to adapt to fluctuating thermal requirements further boosts their performance.
As the electronics industry increasingly prioritizes energy conservation and noise reduction, the comparison of PWM fan vs DC technology is expected to gain more attention. This trend underscores its vital role in modern cooling solutions, making it an essential consideration for professionals seeking efficient and effective thermal management.
PWM vs. DC Fans: Key Operational Differences Explained
The essential difference when comparing PWM fans vs DC devices lies in their control mechanisms. DC devices typically operate at a steady rate, which can limit their effectiveness, especially under reduced loads. In contrast, PWM devices utilize pulse width modulation to dynamically adjust their speed based on cooling requirements. This capability allows PWM motors to operate at significantly lower minimum speeds, often reaching as low as 20% of their peak RPM without the risk of stalling. As a result, they provide quieter operation during low-load scenarios.
For instance, in high-performance computing environments, PWM units can effectively reduce noise levels by up to 30% while maintaining optimal cooling performance. This translates to energy savings of up to 30% compared to conventional models. Conversely, in the discussion of PWM fans vs DC devices, the latter often struggle to maintain efficiency at lower speeds, typically operating at a fixed percentage of their maximum capacity. This limitation can lead to reduced airflow and increased noise.
The adaptability of PWM devices makes them particularly advantageous for modern electronic applications that require precise temperature control and effective noise management. Furthermore, while DC devices were traditionally less expensive, the price gap in the comparison of PWM fans vs DC models is narrowing, making PWM units a more economical choice for a wide range of applications.
Cost Considerations: Evaluating the Price of DC Fans
When evaluating the cost of DC units, it’s crucial to consider both the initial purchase price and the long-term operational expenses. While enthusiasts of DC typically face a higher upfront cost compared to models in the PWM fan vs DC comparison, the enhanced performance across various loads can lead to significant energy savings over time. For instance, transitioning from older AC motor units to modern DC models can yield energy savings of 50-70%, allowing users to recover their initial investment within just 2-3 years. Moreover, systems that utilize DC motors can maintain optimal cooling efficiency while consuming as little as 30 watts, in contrast to the 60-100 watts required by AC units. This translates to lower electricity bills during the summer months.
Engineers must meticulously assess the overall cost of ownership, which includes not only energy savings but also maintenance and potential durability of the devices. DC devices are designed for durability, often resulting in fewer replacements and repairs, thereby contributing to overall savings. As the demand for energy-efficient solutions continues to grow, pricing trends may evolve, making it essential for engineers to stay informed about the changing market landscape. Ultimately, a comprehensive analysis of both upfront costs and long-term savings will empower engineers to select the most cost-effective cooling solutions, especially when considering PWM fan vs DC for their specific applications.
Advantages of PWM Fans: Efficiency and Performance Benefits
PWM devices present a compelling solution for various applications, offering numerous advantages that set them apart. Their capacity to dynamically adjust pace based on thermal requirements can lead to energy savings of up to 30%, significantly lowering power consumption. Moreover, PWM technology is reported to be seven times more effective than traditional cooling methods, highlighting its superiority in the field.
Looking ahead, it is projected that by 2025, around 70% of electronic devices will incorporate PWM cooling systems, underscoring their growing importance in the industry. Additionally, when comparing PWM fan vs DC units, PWM units operate at lower noise levels, achieving reductions of up to 30% compared to conventional DC models, particularly at reduced speeds, with noise levels reaching as low as 18.3 dBA. This characteristic makes them particularly suitable for noise-sensitive environments.
The precise control over airflow not only enhances system stability but also ensures that electronic components remain within optimal temperature ranges, thereby boosting overall performance. Practical implementations, such as those in data centers, have demonstrated that systems utilizing PWM technology can achieve improvements in temperature regulation of up to 30%. This underscores the critical role these devices play in modern cooling solutions.
As Matt Safford aptly noted, “PWM units are crucial for contemporary electronics, balancing performance and efficiency in a manner that conventional counterparts cannot.” This statement encapsulates the essence of PWM technology’s impact, urging stakeholders to consider its integration into their systems.
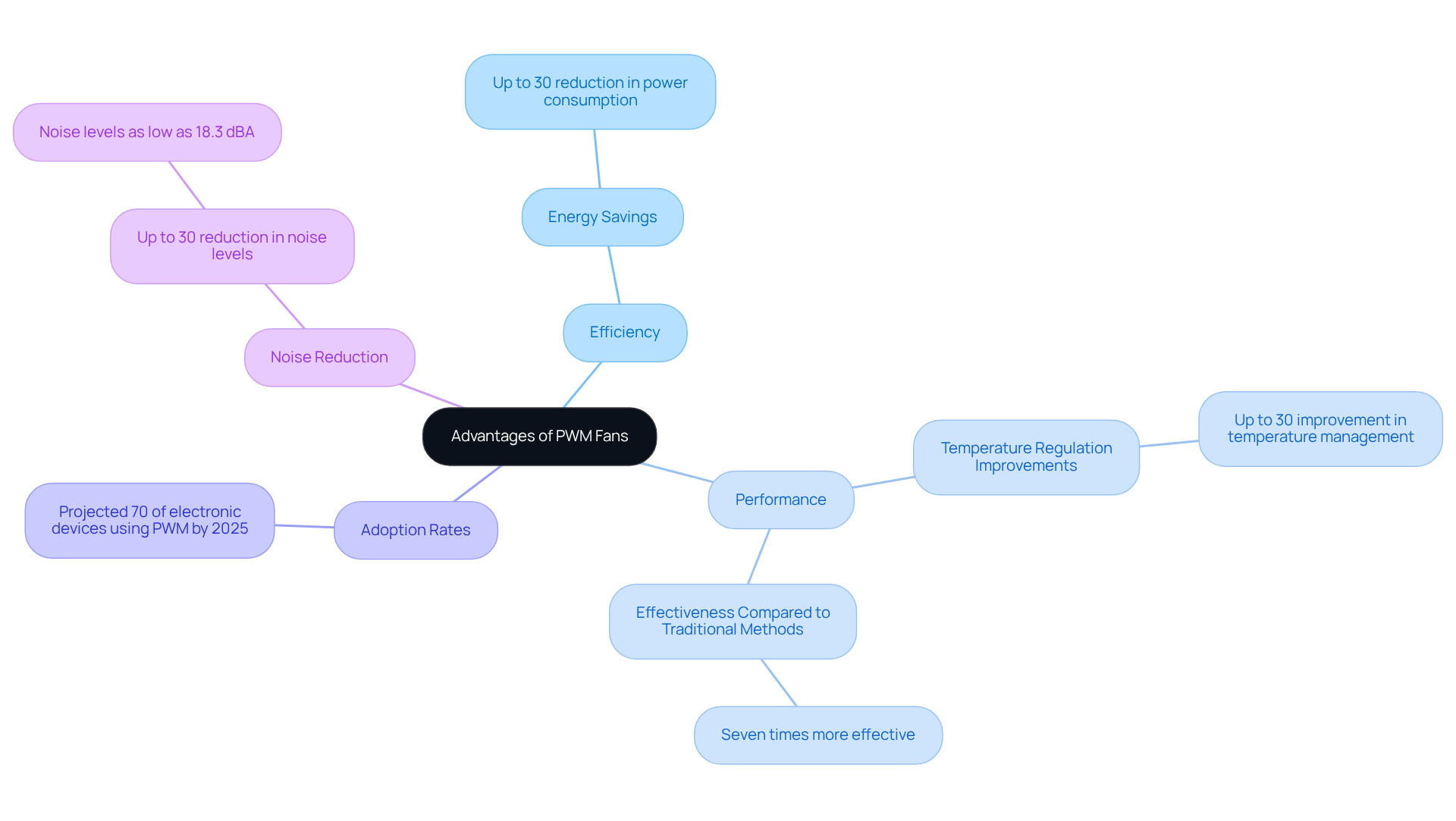
Compatibility Insights: PWM and DC Fans in Modern PC Cases
When selecting cooling devices for modern PC enclosures, compatibility stands as a critical factor. Most contemporary motherboards accommodate both PWM fan vs DC cooling devices, but it’s essential to ensure that the connectors align with the motherboard headers. PWM devices typically feature a four-pin connector, whereas DC units utilize a three-pin connector. Furthermore, certain motherboards offer the flexibility to toggle between PWM and DC control modes within the BIOS, enhancing fan management capabilities.
Engineers must meticulously verify the specifications of both the cooling devices and the motherboard to ensure seamless integration. Notably, when comparing PWM fan vs DC devices, PWM devices can deliver up to a 30% reduction in power consumption, positioning them as a more energy-efficient choice. Additionally, it’s crucial to assess the cooling requirements, including the dimensions of the computer case and the heat output from components, to select the most suitable fan type.
Ultimately, checking motherboard connections is essential to guarantee compatibility with the chosen fan type. By taking these considerations into account, you can optimize your cooling solution effectively.
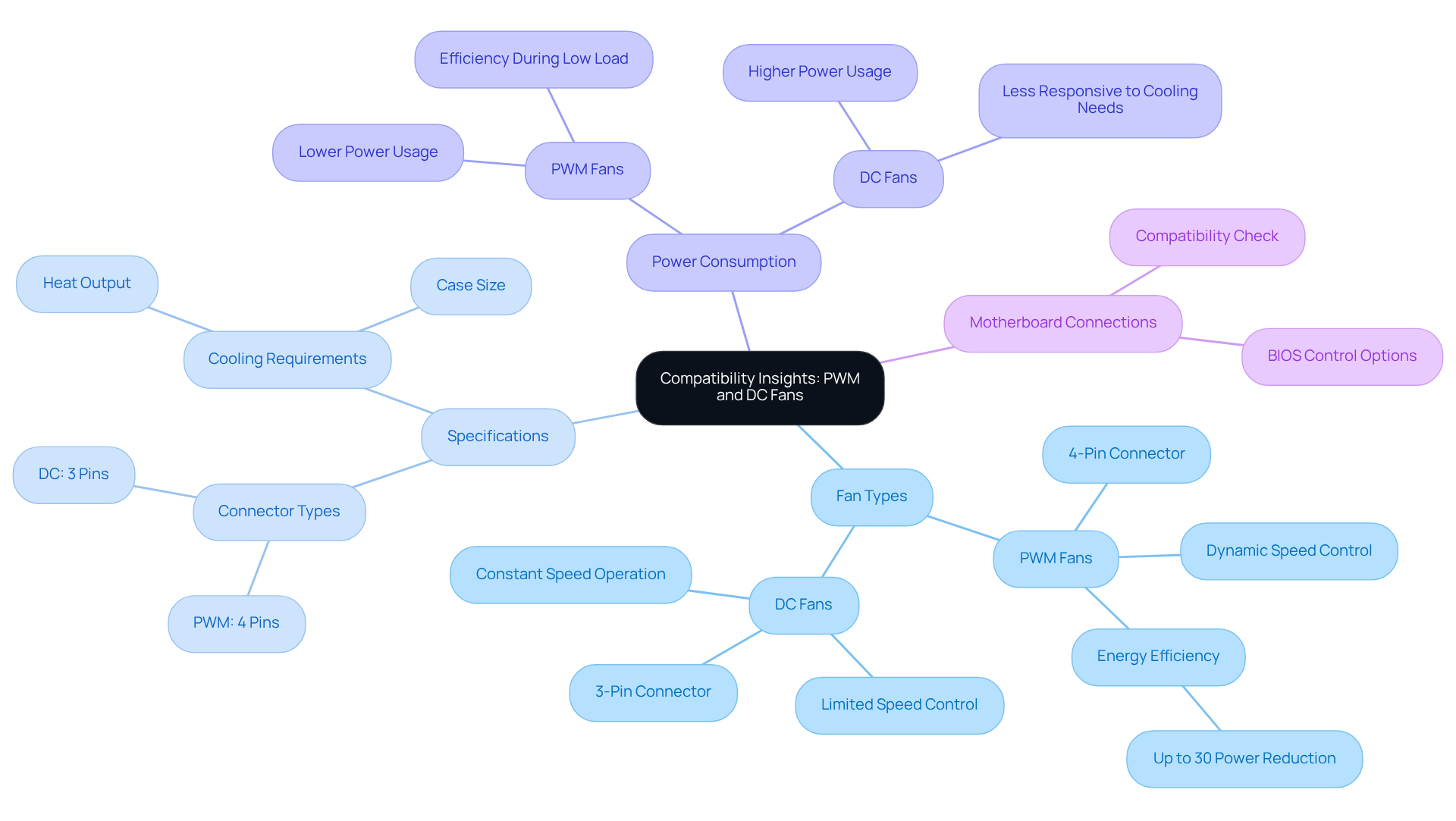
Market Trends: The Rise of PWM Fans in PC Cooling
The cooling solutions market is experiencing a notable transition towards PWM fan vs DC devices, driven mainly by the increasing consumer demand for energy-efficient and quieter performance in PC builds. As gaming and high-performance computing continue to rise, the need for effective thermal management solutions has become increasingly vital. PWM units are emerging as the preferred choice in many new systems, thanks to their capability to deliver precise control over airflow and noise levels.
This trend is expected to endure, with the PWM fan controller market projected to expand at a CAGR of 7.1% from 2025 to 2033. Manufacturers are actively innovating and refining PWM technology, making it more accessible and cost-effective for consumers. Notably, PWM cooling devices can yield energy savings of up to 30% compared to traditional direct current equipment, aligning with the industry’s focus on sustainability and efficiency.
Real-world examples, such as the ARCTIC P14 case cooling device, which boasts a maximum airflow of 72.8 CFM while operating at a low noise level of 11 dBA, underscore the effectiveness of PWM systems in maintaining optimal temperatures with minimal noise. This further cements their position in the market.
Moreover, engineers must consider the compatibility of connector types in the PWM fan vs DC context, as PWM devices typically utilize a 4-pin connector, whereas DC devices employ a 3-pin connector. This distinction is crucial for ensuring proper integration into their systems.
Drawbacks of DC Fans: Limitations to Consider
Despite their widespread use, DC motors present several limitations that engineers must consider. A primary concern is their fixed-velocity operation, which restricts their ability to dynamically adjust speed based on thermal requirements. This limitation can lead to inefficiencies in cooling performance, particularly in applications that demand precise temperature control. Additionally, DC motors often generate higher noise levels at increased speeds, posing challenges in noise-sensitive environments. For instance, at elevated velocities, DC blowers can produce significant noise, which diminishes user comfort and operational effectiveness.
Furthermore, the inability of DC motors to adjust speed can result in increased energy consumption during low-load situations, making them less suitable for modern systems that prioritize adaptive cooling solutions. In contrast, when discussing PWM fan vs DC devices, PWM devices offer superior performance by enabling variable speed control, achieving a minimum speed below 20% of their rated velocity. This capability not only enhances cooling efficiency but also reduces noise levels by up to 30% in the comparison of PWM fan vs DC models. Moreover, in the discussion of PWM fan vs DC devices, PWM devices can consume up to 30% less power than their DC counterparts, further underscoring their efficiency advantages.
As noted by Sam Pelonis, “DC enthusiasts are widely considered the most effective type of supporters,” yet the evolving demands of contemporary applications necessitate a closer examination of the benefits offered by PWM technology. Engineers and decision-makers should consider these insights when evaluating cooling solutions to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
Choosing the Right Fan: A Guide for Engineers
When considering a PWM fan vs DC, selecting the right fan type poses a critical decision for engineers, necessitating a thorough evaluation of application needs, budget constraints, and system compatibility. When considering cooling solutions, the comparison of PWM fan vs DC devices reveals that PWM cooling devices excel in scenarios demanding precise temperature control and minimal noise, making them ideal for high-performance environments. Friedrich Stiemer emphasizes this point, stating, ‘When comparing PWM fan vs DC models, PWM models are quieter,’ which underscores their appropriateness for noise-sensitive applications.
On the other hand, in the discussion of PWM fan vs DC, DC fans can be a more budget-friendly option, particularly for projects with tight financial limits, as they are frequently found in ultra-budget cases priced under $50. Historically, DC fans were the more economical choice, but the narrowing price gap indicates a shift in preference, highlighting the comparison of PWM fan vs DC models, which now present competitive pricing.
Engineers must also take into account airflow requirements, physical dimensions, and pin configurations. When comparing PWM fan vs DC units, it is evident that PWM units typically feature a 4-pin setup, while DC units usually have a 3-pin arrangement. This distinction is crucial for ensuring optimal integration within systems. Ultimately, the decision regarding a PWM fan vs DC rests on a careful balance of performance, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Studies from the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory indicate that PWM fans are increasingly favored for their superior adaptability and energy savings of up to 30%, especially in discussions of PWM fan vs DC.
Conclusion
The exploration of PWM fans versus DC fans highlights critical advancements in cooling technology that are shaping the future of electronics. PWM fans are particularly notable for their energy efficiency, noise reduction, and adaptability to varying thermal demands. These features make them essential for engineers aiming to optimize performance in modern applications. In contrast, while DC fans provide reliability and simplicity, their fixed-speed operation can limit effectiveness in scenarios requiring precise cooling solutions.
Key insights throughout the article underscore the significant advantages of PWM technology. For instance, PWM fans can reduce power consumption by up to 30% and operate at lower noise levels, which is crucial for environments sensitive to sound. The comparative analysis also emphasizes the narrowing cost gap between PWM and DC fans, suggesting a growing trend toward adopting PWM solutions across various electronic systems. Furthermore, the compatibility of these fans with contemporary PC builds and their increasing popularity in the market underscore the shift toward more efficient cooling mechanisms.
As the demand for energy-efficient and high-performance cooling solutions continues to rise, engineers must consider the benefits of PWM fans over traditional DC models. By embracing this technology, they can enhance the reliability and efficiency of electronic systems while contributing to sustainability efforts. The future of cooling in electronics is undoubtedly leaning toward PWM, making it imperative for engineers to stay informed and adapt their designs accordingly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Gagner-Toomey Associates known for?
Gagner-Toomey Associates is a leading sales organization specializing in innovative cooling solutions for the electronics sector, offering a diverse range of manufacturers to enhance performance in electronic systems.
What is the significance of customer satisfaction in cooling solutions?
Recent research shows that over 70% of electronics engineers using PWM fans instead of DC devices report significant improvements in thermal management and energy performance, highlighting high levels of customer satisfaction.
How does PWM technology compare to DC technology in terms of power consumption?
PWM technology can reduce power consumption by up to 30% compared to traditional direct current (DC) devices while maintaining effective temperature management.
What is Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE), and how does it relate to PWM technology?
Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) is a measure of energy efficiency in data centers. PWM technology has been shown to decrease PUE from 1.55 to 1.42, indicating improved efficiency.
What tools does Gagner-Toomey Associates use to optimize their sales efforts?
Gagner-Toomey Associates utilizes IT tools like RPMS for opportunity tracking and sales reporting to maintain their industry leadership and effectively meet cooling needs.
What are the characteristics of DC fans?
DC fans typically feature a brushless motor for efficient energy conversion, operate at a constant speed unless connected to a controller, and are known for their reliability and durability.
What are the operational limitations of DC devices compared to PWM devices?
DC devices generally do not offer the same level of precision in speed control as PWM devices, which can adjust speeds dynamically based on thermal demands.
What advantages do PWM fans offer over DC fans?
PWM fans can consume up to 30% less power, reduce noise levels by up to 30%, and adapt to fluctuating thermal requirements, making them ideal for environments requiring quiet operation and effective temperature regulation.
In what applications are PWM devices particularly beneficial?
PWM devices are especially advantageous in data centers and high-performance computing systems, as they enhance temperature regulation and extend the lifespan of electronic components.
Why is the comparison of PWM fan vs DC technology gaining attention in the electronics industry?
As the industry increasingly prioritizes energy conservation and noise reduction, the efficiency and effectiveness of PWM technology in thermal management are becoming essential considerations for professionals.

