Introduction
Understanding the complexities of fan design is crucial for achieving optimal performance across various applications. Each component, from the motor to the cutting edges, plays a vital role in ensuring efficiency and longevity. This article explores the fundamental elements of fans, examining how they work in concert and outlining best practices for selection and maintenance.
However, what occurs when one component fails? Engineers must be prepared to address the risks associated with such failures. By delving into the intricacies of fan design, we can better understand the importance of each part and how to mitigate potential issues effectively.
Explore the Fundamental Components of Fans
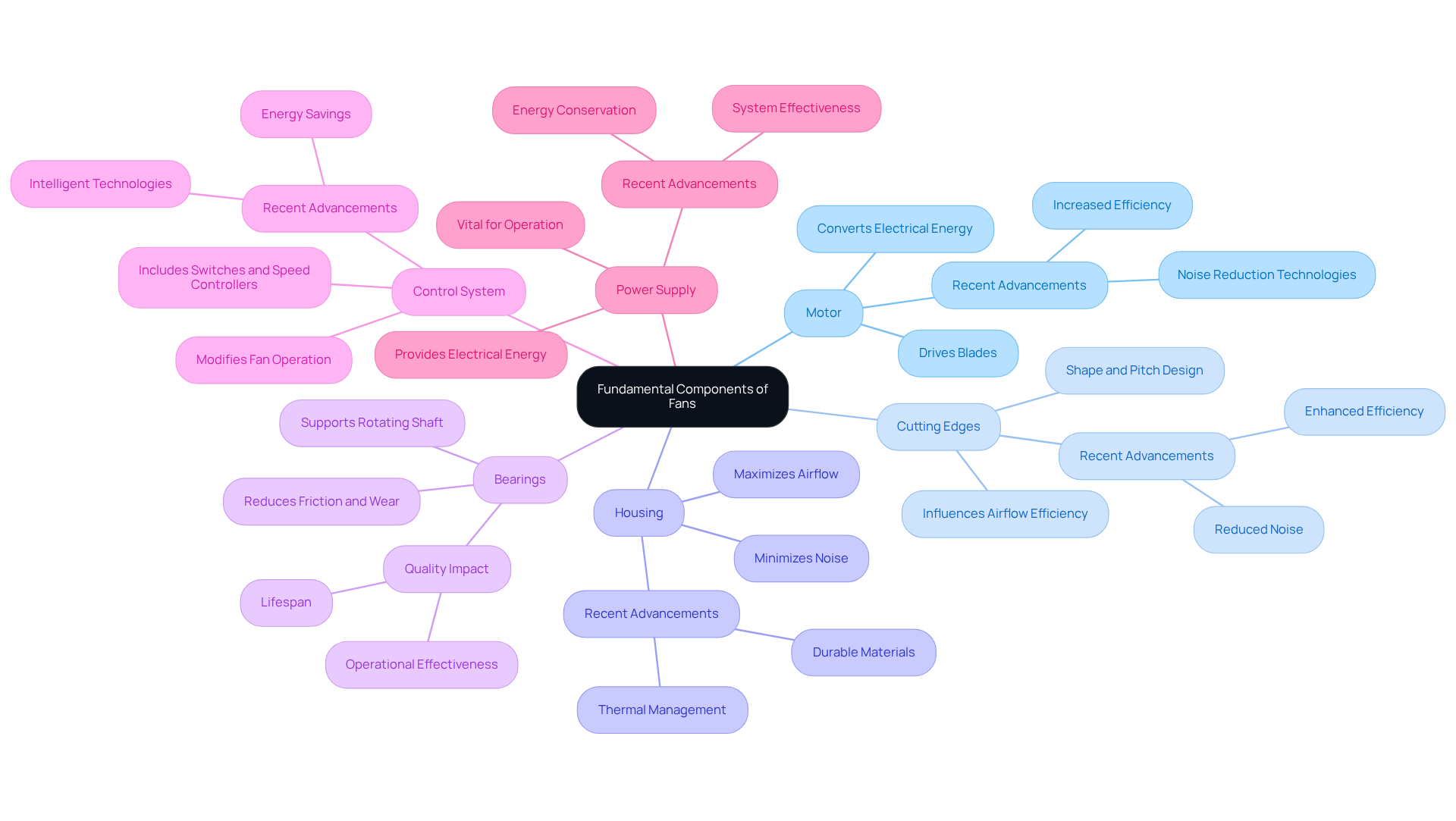
Fans consist of several essential components that work in unison to ensure optimal performance:
- Motor: The heart of the fan, the motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, driving the blades and enabling airflow.
- Cutting Edges: The design of the cutting edges is crucial; their shape and pitch directly influence airflow efficiency. Recent advancements in cutting edge design aim to improve these factors, enhancing efficiency and reducing noise.
- Housing: The outer shell encasing the motor and blades is engineered to minimize noise while maximizing airflow. Advances in housing design increasingly incorporate materials that improve durability and thermal management.
- Bearings: These components support the rotating shaft, reducing friction and wear. The selection of bearings significantly influences the fan’s lifespan and operational effectiveness, with high-quality bearings resulting in quieter and more dependable functionality.
- Control System: This includes switches and speed controllers that allow users to modify the fan’s operation according to specific needs. Contemporary control systems are integrating intelligent technologies for improved user experience and energy savings.
- Power Supply: Providing the necessary electrical energy for the motor, the power supply is vital for the fan’s operation. Advancements in power supply technology focus on energy conservation, enhancing overall system effectiveness.
Understanding the components of a fan is essential for engineers involved in fan selection, maintenance, or troubleshooting, as each component of a fan significantly impacts its effectiveness and performance.
Understand How Fan Components Operate Together
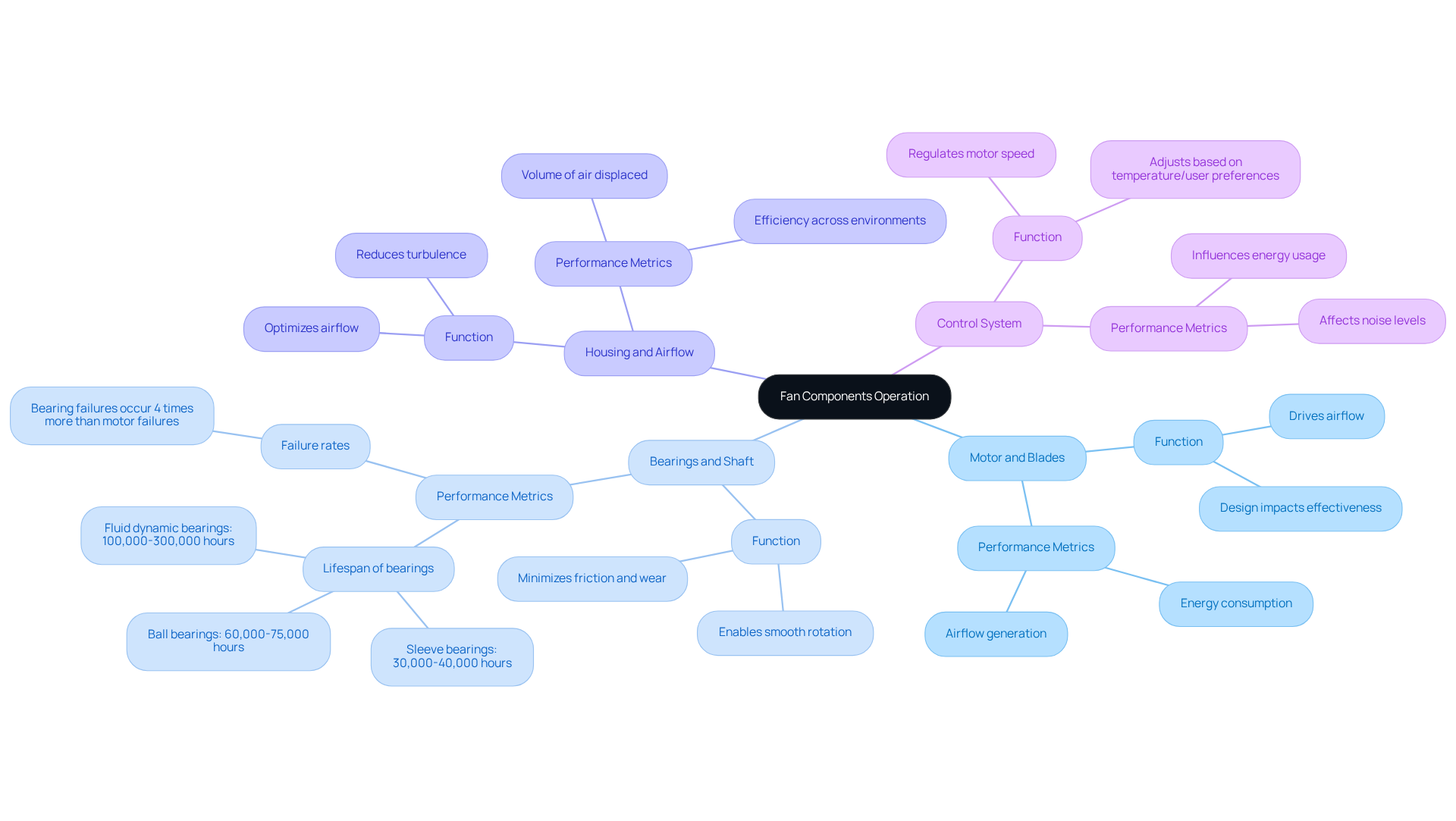
The operation of a fan hinges on the seamless interaction of its components, each playing a vital role in overall performance:
-
Motor and Blades: The motor drives the blades, generating airflow. The design of the propellers, including their angle and shape, significantly impacts airflow effectiveness. High-quality motors paired with well-designed blades can enhance airflow while reducing energy consumption.
-
Bearings and Shaft: Bearings are crucial for enabling the shaft to rotate smoothly, minimizing friction and wear on the motor. This reduction in wear not only extends the fan’s lifespan but also boosts its reliability. For example, ball bearings can outperform sleeve bearings by up to five times under similar conditions, making them the preferred choice for high-speed applications. Fluid dynamic bearings (FDB) can last between 100,000 to 300,000 hours, while ball bearings typically last 60,000 to 75,000 hours, and sleeve bearings range from 30,000 to 40,000 hours. HVAC professionals emphasize that bearing failures occur more frequently than motor insulation breakdown failures at a ratio of 4:1, underscoring the critical role of bearings in fan longevity.
-
Housing and Airflow: The fan housing is engineered to optimize airflow, reducing turbulence and maximizing the volume of air displaced. A well-designed housing can significantly enhance the fan’s efficiency, ensuring effective operation across various environments.
-
Control System and Motor: The control system is essential for regulating the motor’s speed, allowing adjustments based on temperature or user preferences. This regulation directly influences energy usage and noise levels, making it crucial for achieving optimal results.
Understanding these interactions is vital for enhancing the components of a fan and ensuring longevity. Consistent maintenance and observation of the components of a fan can lead to notable improvements in operational effectiveness and lifespan. Additionally, proper lubrication is critical to preventing bearing failures, which can drastically shorten the fan’s lifespan. The Arrhenius relationship indicates that the life of bearings is halved for every 15°C increase in temperature, highlighting the importance of considering environmental factors in fan operation.
Identify Different Types of Fan Components and Their Functions
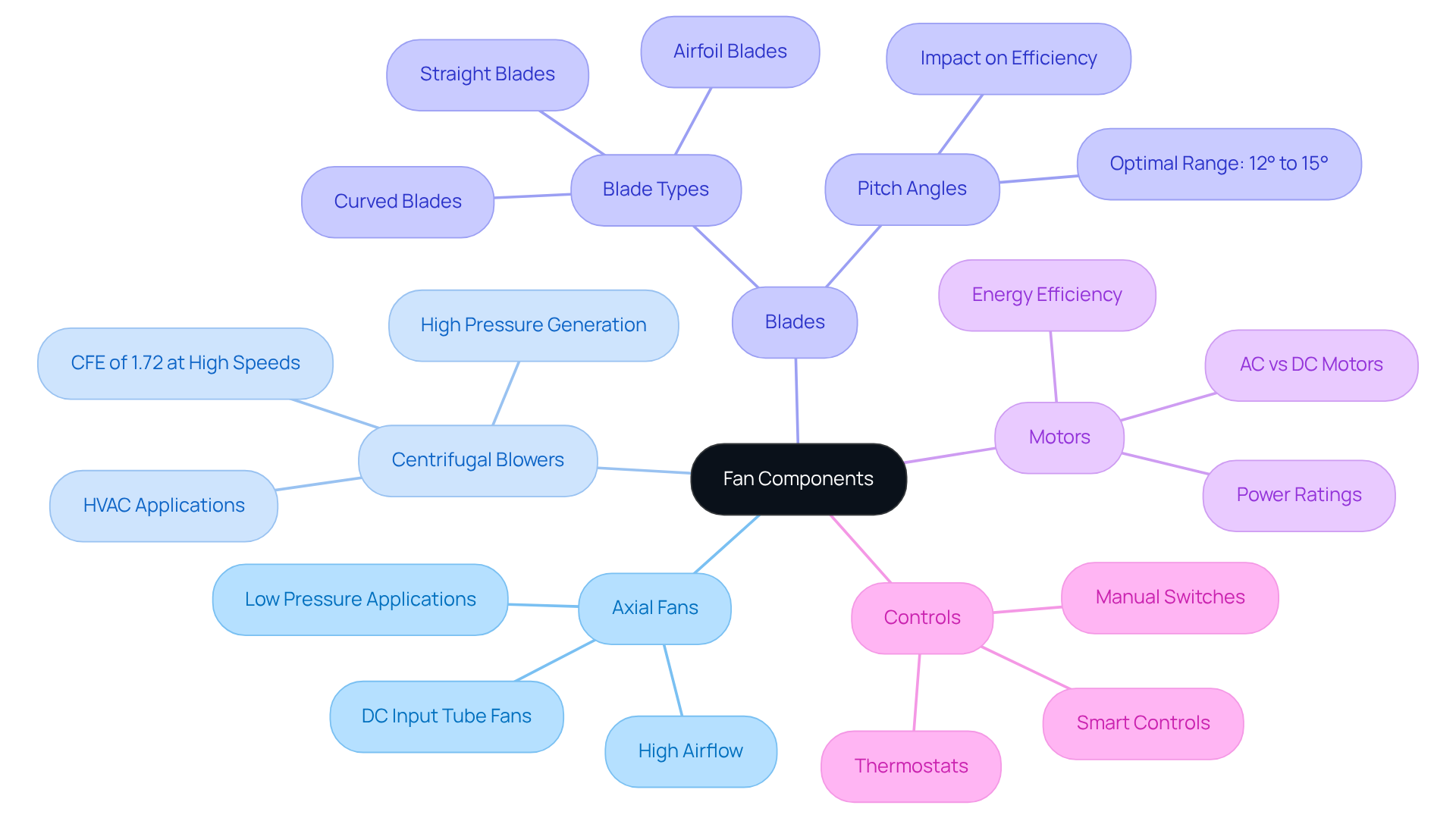
The components of a fan play a pivotal role in determining effectiveness and efficiency in various applications. Understanding the primary types is essential:
-
Axial Fans: Gagner-Toomey Associates provides a comprehensive range of DC input tube axial fans, designed for optimal performance and minimal noise. These fans excel in applications that demand high airflow, such as cooling systems, thanks to their ability to facilitate efficient air movement in low-pressure environments.
-
Centrifugal Blowers: In contrast, Gagner-Toomey’s centrifugal blowers operate by drawing air into the center and expelling it at a right angle, which generates higher pressure. This design is particularly advantageous in HVAC systems, where maintaining consistent airflow against resistance is crucial. Research indicates that efficient fans can achieve a CFE of 1.72 at high speeds, making them well-suited for demanding applications.
-
Blades: The configuration of fan blades-whether straight, curved, or airfoil-significantly impacts airflow dynamics and efficiency. Airfoil-shaped vanes, for example, reduce drag and turbulence, thereby enhancing overall performance. Recent trends highlight the importance of pitch angles, typically ranging from 12° to 15°. An industry expert noted, “I believe ceiling fans function best with a pitch angle of 12 to 15 degrees; any more than this, there will be a negative trade-off regarding energy consumption,” underscoring the critical nature of this design consideration.
-
Motors: Fan motors can be categorized as either AC or DC, each offering distinct power ratings and performance characteristics. Gagner-Toomey’s energy-efficient DC motors are recognized for their ability to lower power consumption compared to traditional AC motors, which contributes to reduced operational costs. Furthermore, the design of energy-efficient fan blades plays a significant role in electricity consumption, further enhancing overall efficiency.
-
Controls: Contemporary fans are equipped with various control mechanisms, including manual switches, thermostats, and smart controls. These features allow for automated adjustments based on environmental conditions, thereby improving efficiency and energy utilization.
Understanding the components of a fan and their respective roles is vital for selecting the right fan for specific applications, which ensures optimal performance and energy conservation.
Select and Maintain Fan Components for Optimal Performance
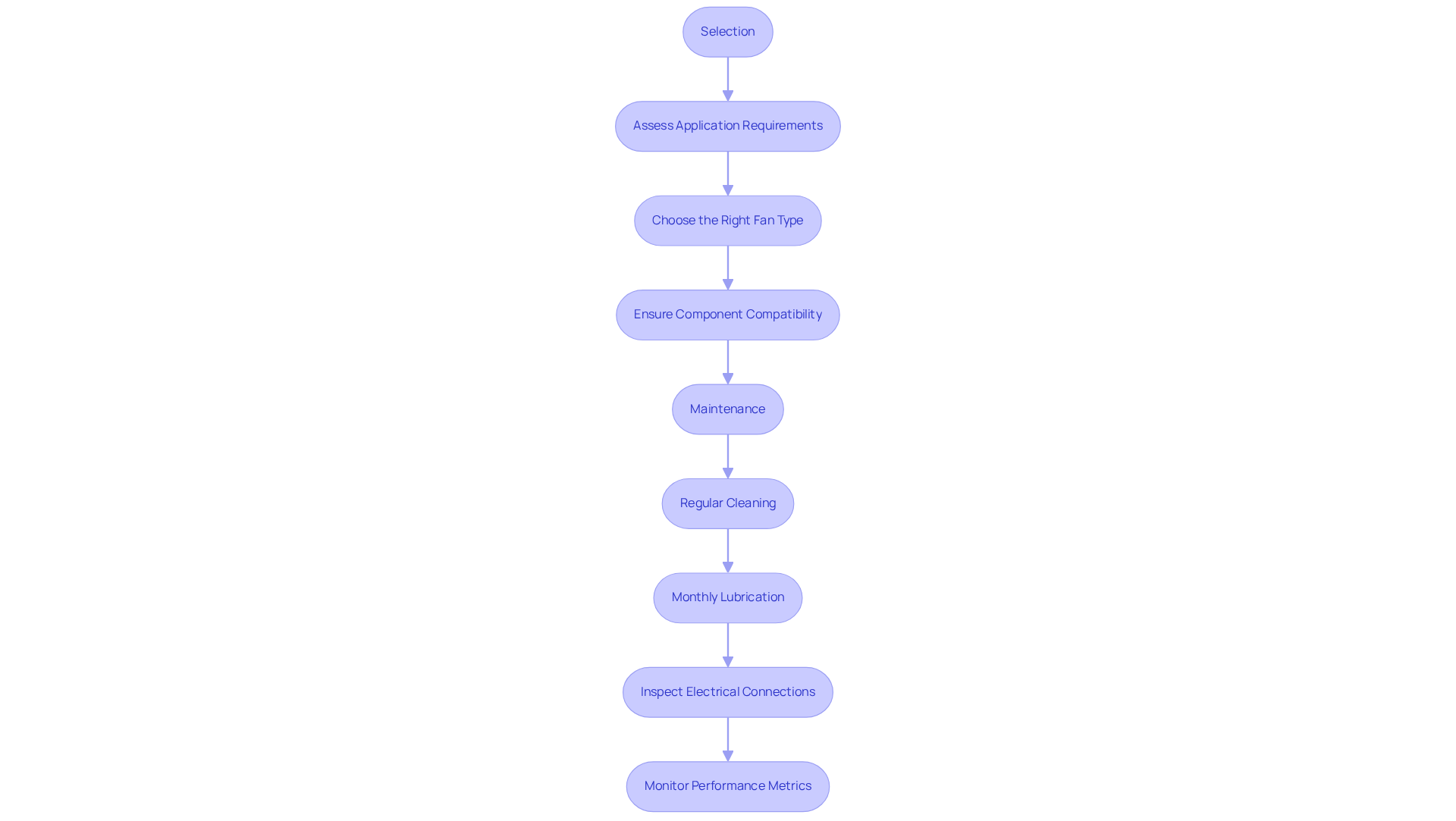
To effectively select and maintain fan components, it’s crucial to follow these guidelines:
Selection:
- Assess Application Requirements: Start by evaluating airflow, pressure, and noise levels to identify the most suitable fan type for your needs.
- Choose the Right Fan Type: Decide between axial and centrifugal fans based on specific operational requirements, as each type presents unique advantages in airflow and pressure capabilities.
- Ensure Component Compatibility: Verify that the components of a fan, including motor power and cutting design, are compatible to enhance overall effectiveness and productivity.
Maintenance:
- Regular Cleaning: Keep blades and housing clean to prevent dust accumulation, which can reduce efficiency by up to 30%.
- Monthly Lubrication: Lubricate bearings monthly to minimize friction and extend the lifespan of the components of a fan, adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended greasing intervals to maintain warranty coverage.
- Inspect Electrical Connections: Regularly check electrical connections and control systems for signs of wear or damage, as neglecting these can lead to critical failures.
- Monitor Performance Metrics: Track performance metrics, including vibration and temperature. For most fans, take vibration readings every 1-4 hours to detect early signs of wear or malfunction, allowing for timely maintenance or replacement.
By adhering to these best practices, engineers can significantly enhance fan efficiency and longevity, ultimately reducing operational costs and downtime. Remember, “Failures are, by nature, unpredictable. They happen at the worst possible times-during a peak production run or in the middle of the night-leading to maximum disruption and lost revenue.” The financial implications of critical fan failures can be substantial, with a total cost of $173,600 and lost production revenue of $160,000 for just 8 hours of downtime.
Conclusion
Mastering the components of a fan is crucial for achieving optimal performance across various applications. Each part, from the motor to the control system, plays a vital role in ensuring that the fan operates efficiently and effectively. Understanding how these components interact not only deepens knowledge but also empowers engineers and users to make informed decisions regarding fan selection, maintenance, and upgrades.
Key insights from this exploration underscore the significance of each component:
- The motor drives airflow
- Cutting edges enhance efficiency
- Housing minimizes noise
- Bearings extend lifespan
- Control systems allow for user customization
Moreover, distinguishing between fan types – axial and centrifugal – illustrates how specific designs cater to unique operational needs. Regular maintenance practices, such as cleaning and lubrication, are essential for prolonging fan life and preventing costly downtime.
Ultimately, the importance of comprehending fan components cannot be overstated. By applying the insights gained from this analysis, individuals can optimize fan performance while ensuring energy efficiency and reliability. Embracing these best practices not only boosts operational effectiveness but also leads to significant cost savings and an improved user experience. Whether for industrial or residential applications, mastering fan components is a key factor in achieving superior airflow management and performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main components of a fan?
The main components of a fan include the motor, cutting edges, housing, bearings, control system, and power supply.
What role does the motor play in a fan?
The motor is the heart of the fan; it converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, driving the blades and enabling airflow.
How do cutting edges affect a fan’s performance?
The design of the cutting edges, including their shape and pitch, directly influences airflow efficiency. Recent advancements aim to enhance these factors, improving efficiency and reducing noise.
What is the purpose of the housing in a fan?
The housing is the outer shell that encases the motor and blades, engineered to minimize noise while maximizing airflow. It increasingly utilizes materials that enhance durability and thermal management.
What function do bearings serve in a fan?
Bearings support the rotating shaft, reducing friction and wear. The selection of bearings significantly affects the fan’s lifespan and operational effectiveness, with high-quality bearings leading to quieter and more reliable functionality.
What is included in a fan’s control system?
The control system includes switches and speed controllers that allow users to modify the fan’s operation according to specific needs. Modern systems are integrating intelligent technologies for improved user experience and energy savings.
Why is the power supply important for a fan?
The power supply provides the necessary electrical energy for the motor, making it vital for the fan’s operation. Recent advancements focus on energy conservation to enhance overall system effectiveness.
Why is it important to understand the components of a fan?
Understanding the components is essential for engineers involved in fan selection, maintenance, or troubleshooting, as each component significantly impacts the fan’s effectiveness and performance.

