Introduction
Understanding the dynamics of static pressure is crucial for engineers navigating the complexities of fluid systems, especially in HVAC and electronic cooling applications. This fundamental concept not only influences airflow but also significantly impacts the efficiency and longevity of engineering setups. But how can a seemingly simple measurement lead to such profound implications for energy consumption and equipment reliability?
Exploring the nuances of static pressure reveals critical insights that can transform engineering practices and enhance system performance. By grasping the intricacies of this measurement, engineers can make informed decisions that optimize their designs and improve overall system reliability.
Incorporating static pressure considerations into engineering practices is not just beneficial; it’s essential for achieving peak performance in fluid systems.
Define Static Pressure in Electronics Engineering
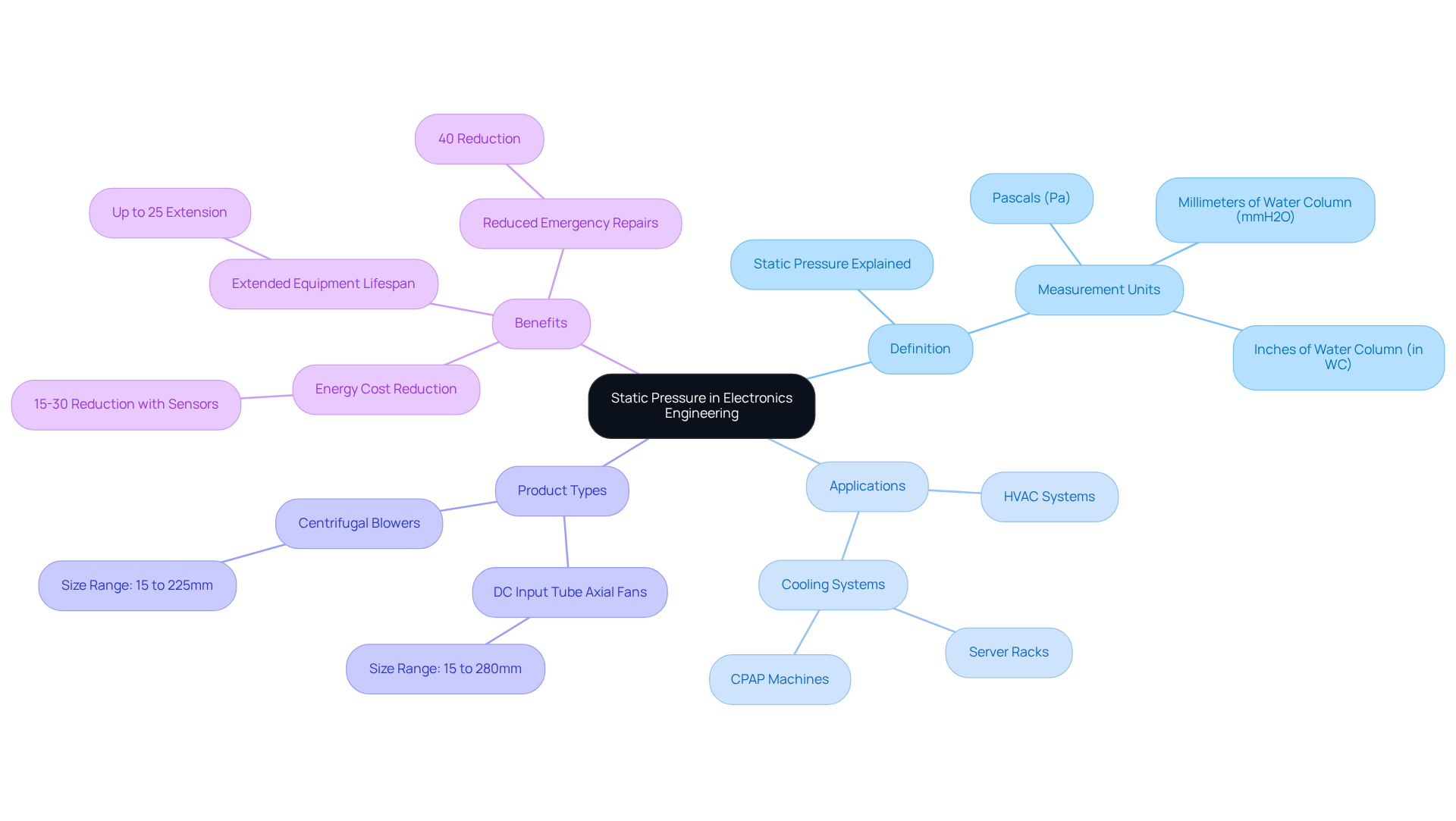
Static force represents the force exerted by a fluid at rest, and it plays a crucial role in the effectiveness of engineering setups, particularly in HVAC and electronic cooling applications. Understanding what’s static pressure is essential in electronics engineering, as it directly influences how air moves through ducts and components, thereby impacting the efficiency of cooling systems. Measured in units such as Pascals (Pa) or inches of water column (in WC), static force ensures that electronic components operate within optimal temperature ranges.
High static airflow fans, like those offered by Gagner-Toomey Associates, excel in applications such as dense server racks and CPAP machines, where airflow resistance is significant. Gagner-Toomey’s extensive product range includes:
- DC input Tube Axial fans ranging from 15 to 280mm
- Centrifugal Blowers from 15 to 225mm
All designed for performance and efficiency. These products can greatly enhance airflow management in electronic cooling setups.
Statistics indicate that the installation of fixed sensors can lead to a 15-30% reduction in energy costs and extend equipment lifespan by up to 25%. Furthermore, real-world examples demonstrate that monitoring what’s static pressure can lead to a reduction of emergency repairs by 40%, highlighting its importance in maintaining reliability and efficiency.
In summary, knowing what’s static pressure is vital for the design and analysis of systems where airflow is critical, such as cooling fans and heat exchangers. By prioritizing the understanding and application of static force, engineers can significantly improve the performance and longevity of their systems.
Explain the Role of Static Pressure in HVAC Systems
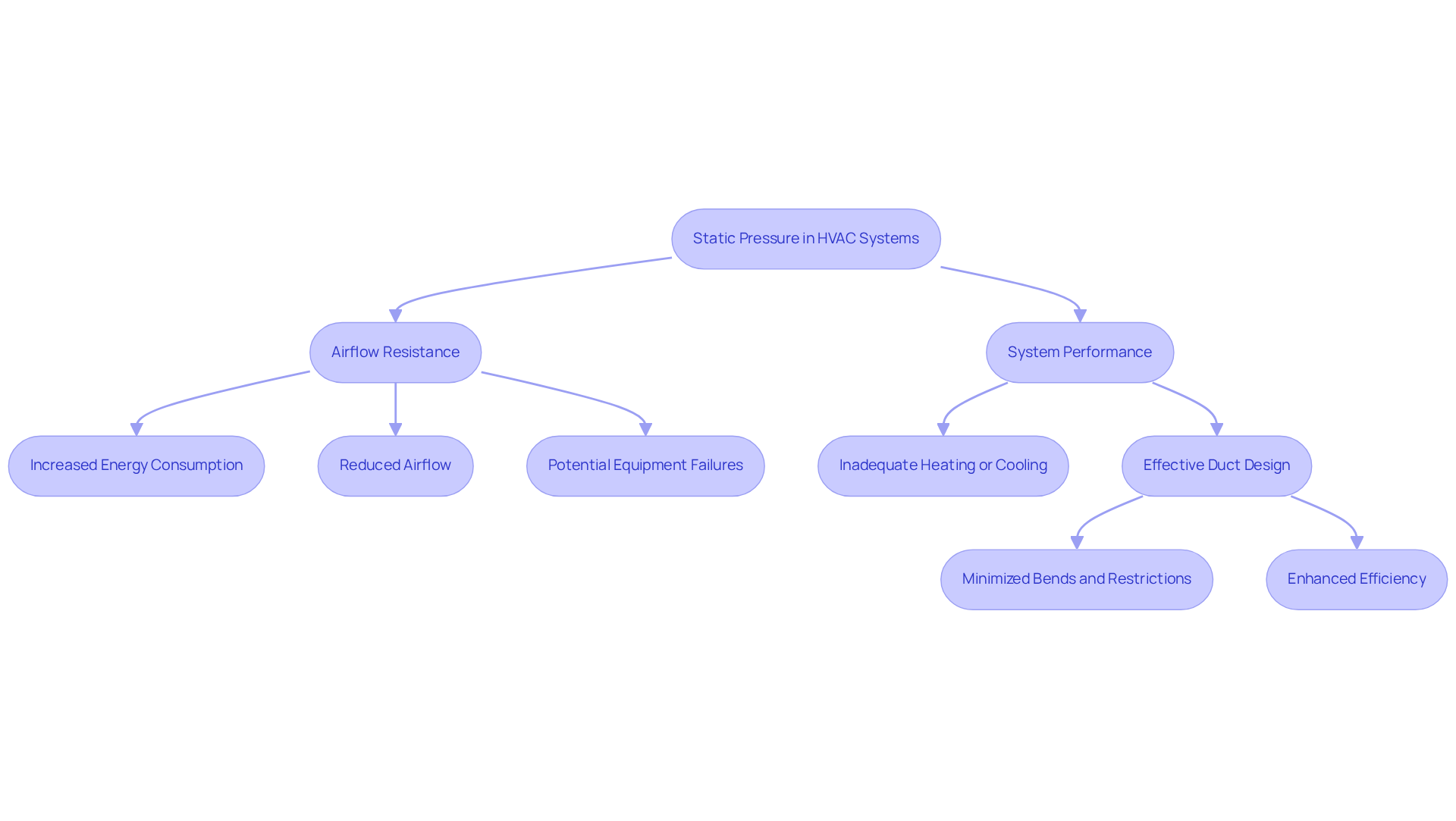
In HVAC setups, fixed force significantly influences airflow resistance within ducting. This force, exerted by air on the walls of ducts and other components when airflow is absent, is critical to system performance. Effective management of fixed force is essential for ensuring that heating and cooling systems operate efficiently.
Elevated air resistance can lead to increased energy consumption, reduced airflow, and potential equipment failures. Conversely, low air resistance may result in inadequate heating or cooling. Engineers must meticulously design duct layouts to achieve a balance of equilibrium force, ensuring optimal airflow and performance. For instance, a well-constructed duct system minimizes bends and restrictions, thereby reducing resistance and enhancing efficiency.
To summarize, addressing fixed force in HVAC systems is not just a technical necessity; it is a fundamental aspect of achieving energy efficiency and reliable performance. By prioritizing effective duct design, engineers can significantly improve system outcomes.
Discuss the Historical Development of Static Pressure Concepts
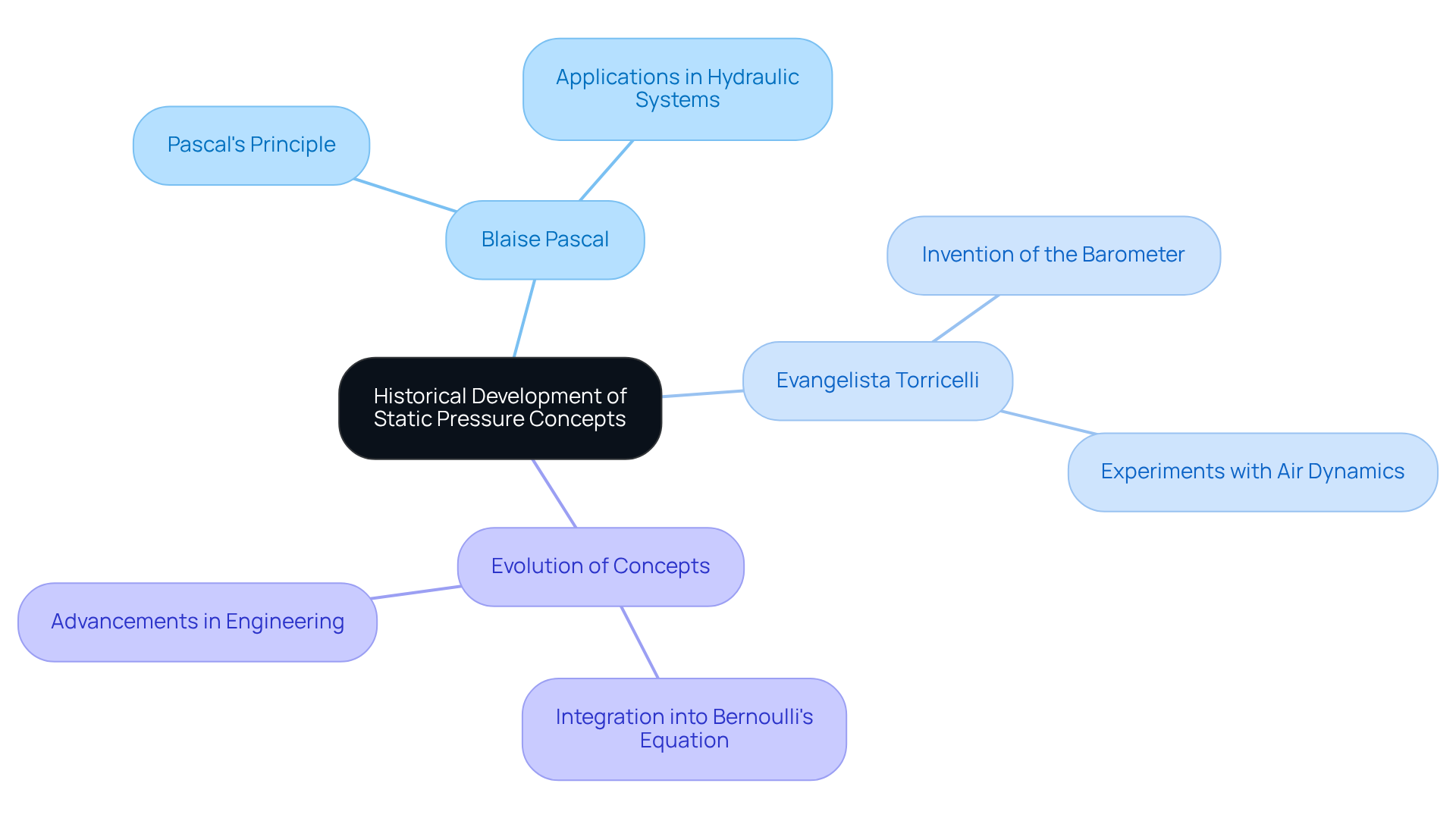
The concept of static force is firmly rooted in liquid mechanics, significantly shaped by the pioneering work of Blaise Pascal and Evangelista Torricelli. Pascal’s principle serves as a cornerstone for understanding the transmission of force through liquids, asserting that any changes in force applied to an enclosed liquid are transmitted undiminished throughout the liquid. This principle is crucial for various applications, including hydraulic systems and force measurement devices.
Torricelli’s groundbreaking experiments with air dynamics led to the invention of the barometer, a device that measures atmospheric pressure and illustrates the relationship between constant force and liquid dynamics. His findings demonstrated that the weight of a column of mercury could be balanced by atmospheric pressure, providing a practical application of static force concepts.
Over the centuries, our understanding of stationary force has evolved, particularly with advancements in engineering and liquid dynamics. The integration of stationary force into Bernoulli’s equation has further underscored its significance in analyzing fluid movement, showcasing the interplay between force, velocity, and height in a fluid context. Today, atmospheric force stands as a fundamental concept across multiple engineering disciplines, including HVAC, aerospace, and mechanical engineering, where it plays a vital role in optimizing system performance and efficiency. This historical overview highlights the enduring importance of static force in both theoretical and practical applications, underscoring its relevance in contemporary engineering.
Identify Key Characteristics and Variations of Static Pressure
Static force is defined as the exertion applied uniformly in all directions within a substance at rest, playing a crucial role in fluid dynamics. Its variations are influenced by several factors, including the fluid’s density, temperature, and the shape of the configuration. In HVAC systems, fixed force is significantly influenced by duct dimensions, configuration, and the presence of filters or barriers. An ideal constant level of force is generally about 0.5 inches of water column, which is essential for effective airflow and energy usage.
Fluctuations in fixed force can lead to various operational scenarios. Positive atmospheric force indicates a potential for airflow, while negative atmospheric force can create suction effects that may hinder performance. Real-world examples show that inadequate management of fixed force can lead to increased energy consumption and operational inefficiencies. Research suggests that monitoring fixed force can reduce energy usage by as much as 30%.
Understanding these characteristics is vital for engineers tasked with designing HVAC systems, especially when considering what static pressure to maintain optimal airflow and efficiency. Consistent measurements of fixed force, taken at various locations within the system, help identify potential issues and ensure compliance with design specifications. Tools like inclined manometers and digital gauges provide accurate and rapid measurements of fluid force, enhancing the reliability of assessments. By addressing fluctuations in fixed airflow, engineers can improve indoor air quality and overall system efficiency.
Moreover, comprehending the specific weight of air at sea level (0.0765 lb/ft) and at 5,000 ft (0.0659 lb/ft) is crucial for understanding what static pressure and how altitude affects static force. As noted by an MEP Academy Instructor, grasping these pressure components is essential for designing, maintaining, and optimizing air conditioning ducts.

Conclusion
Understanding static pressure is crucial for optimizing engineering systems, especially in electronics and HVAC applications. This concept, deeply rooted in fluid dynamics, significantly influences airflow, energy efficiency, and the overall performance of various systems. By comprehending the nuances of static pressure, engineers can design solutions that are not only effective but also sustainable.
The significance of static pressure is evident across multiple contexts. From its definition and role in electronics engineering to its critical function in HVAC systems, managing static pressure is paramount. Key insights reveal its impact on airflow resistance, energy consumption, and equipment longevity. Historical developments further underscore the relevance of static pressure, demonstrating how foundational principles continue to shape modern engineering practices.
In summary, a profound understanding of static pressure enhances system performance and contributes to energy efficiency and reliability. Engineers must prioritize static pressure management in their designs, leveraging measurement techniques and historical insights to foster innovation and improve outcomes. Embracing this knowledge will lead to more efficient systems, reduced operational costs, and ultimately, a more sustainable engineering landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is static pressure in electronics engineering?
Static pressure refers to the force exerted by a fluid at rest, which is crucial for the effectiveness of engineering setups, particularly in HVAC and electronic cooling applications.
Why is understanding static pressure important in electronics engineering?
Understanding static pressure is essential because it directly influences how air moves through ducts and components, impacting the efficiency of cooling systems and ensuring that electronic components operate within optimal temperature ranges.
How is static pressure measured?
Static pressure is measured in units such as Pascals (Pa) or inches of water column (in WC).
What are high static airflow fans and their applications?
High static airflow fans are designed to excel in applications with significant airflow resistance, such as dense server racks and CPAP machines.
What types of fans does Gagner-Toomey Associates offer?
Gagner-Toomey Associates offers DC input Tube Axial fans ranging from 15 to 280mm and Centrifugal Blowers from 15 to 225mm, all designed for performance and efficiency.
What are the benefits of installing fixed sensors related to static pressure?
Installing fixed sensors can lead to a 15-30% reduction in energy costs and extend equipment lifespan by up to 25%.
How does monitoring static pressure impact emergency repairs?
Monitoring static pressure can lead to a reduction of emergency repairs by 40%, highlighting its importance in maintaining reliability and efficiency.
Why is knowledge of static pressure vital for engineers?
Knowledge of static pressure is vital for the design and analysis of systems where airflow is critical, such as cooling fans and heat exchangers, allowing engineers to improve system performance and longevity.

