Introduction
Choosing the right high CFM centrifugal blower can indeed be a challenging endeavor. With a wide array of applications and performance metrics to consider, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamentals of how these blowers function and their specific airflow requirements. This understanding is vital for optimizing efficiency and effectiveness in any project. Yet, with so many options available, how can one pinpoint the blower that best aligns with their unique needs? This guide explores the essential factors that influence blower selection, equipping readers with the knowledge to make informed decisions that significantly enhance operational performance.
Understand Centrifugal Blower Basics
Centrifugal fans, also known as centrifugal devices, operate by harnessing centrifugal force to efficiently transport air or gases. These devices draw air in through the center and expel it at a right angle through the outlet, making them highly effective for a range of applications. The primary components include the impeller, which spins to create air movement, and the housing that directs the airflow. A solid grasp of these elements and their functions is crucial for selecting the right fan to meet your specific needs.
Key terms to familiarize yourself with include:
- CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute), a measure of airflow
- Static pressure
- Efficiency ratings
These metrics are vital for assessing performance and will be referenced throughout the selection process. Notably, the centrifugal fan market is projected to grow significantly, with an expected valuation of approximately USD 3.81 billion by 2030, reflecting the rising demand for energy-efficient solutions across various industries.
Case studies underscore the importance of understanding centrifugal fan technology. For instance, Howden’s use of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) software to optimize impeller designs has resulted in improved energy recovery and reduced consumption. Similarly, Siemens’ SirioVent SSi series integrates Variable Speed Drive (VSD) technologies, enabling precise airflow control and enhanced energy efficiency, highlighting the industry’s commitment to innovation.
Industry leaders emphasize the necessity of mastering the fundamentals of centrifugal fans. As noted, ‘Energy-efficient technologies, including high cfm centrifugal blowers, can lower industrial consumption by as much as 20%,’ underscoring their importance in modern manufacturing operations. By grasping these fundamentals, you can make informed decisions that align with your project’s requirements and contribute to overall operational efficiency.
Evaluate Airflow Requirements and Applications
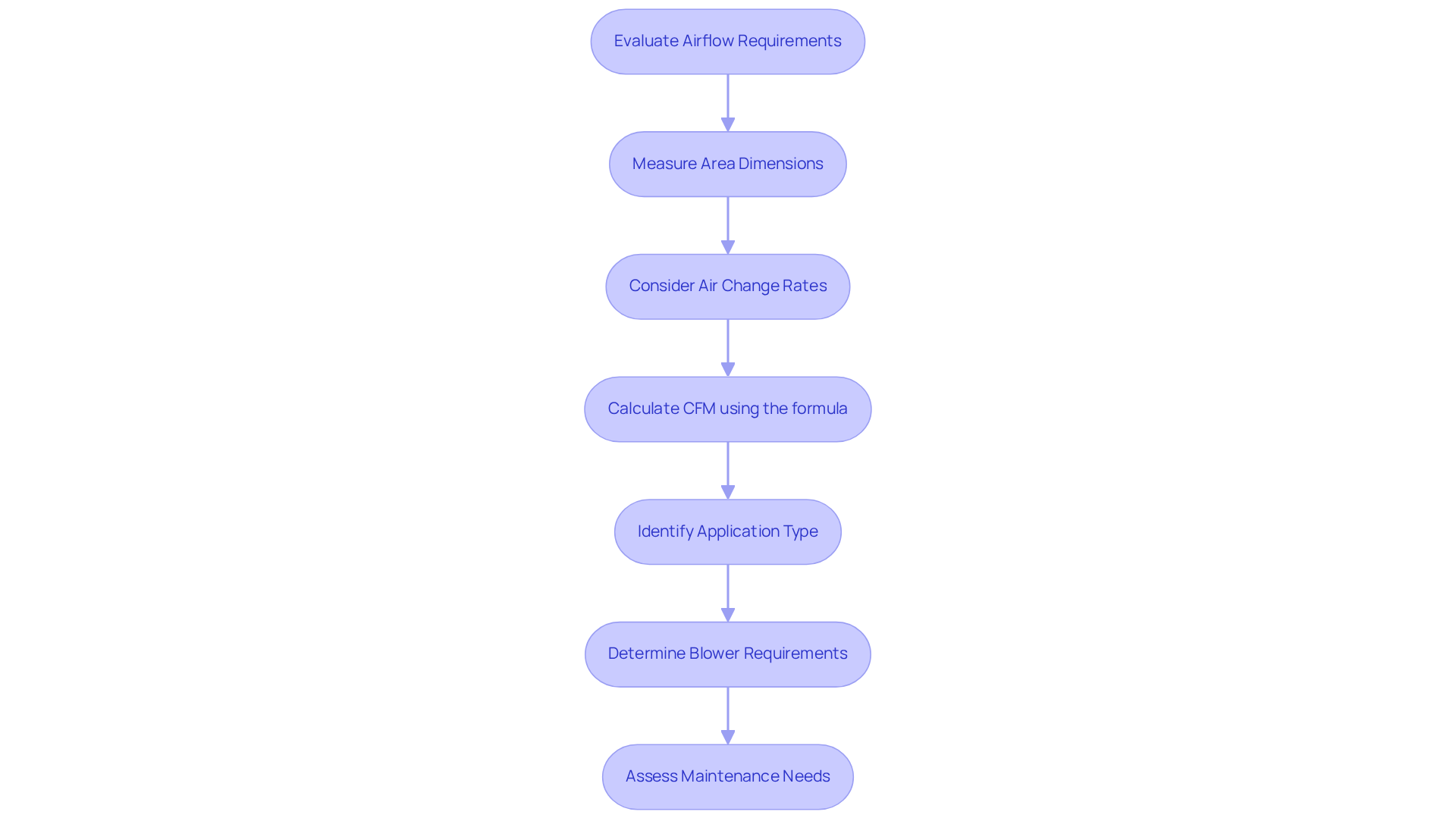
To determine the ventilation requirements for your application, start by measuring the dimensions of the area and considering factors like air change rates and specific process needs. For example, manufacturing facilities typically require a high cfm centrifugal blower for effective ventilation compared to residential settings. The formula to calculate the necessary airflow is:
CFM = (Volume of Space (cubic feet) × Air Changes per Hour) / 60
This calculation establishes a baseline for the minimum airflow required. Additionally, the type of application – whether for cooling, drying, or dust collection – will significantly influence the blower’s design and performance characteristics.
In industrial contexts, understanding the requirements for a high cfm centrifugal blower is essential. For instance, a ½” drill needs 30 CFM, while a grinder requires 60 CFM, totaling 90 CFM when both tools are used simultaneously. This highlights the importance of merging CFM requirements with a high cfm centrifugal blower to ensure adequate ventilation for various tools. Moreover, maintaining optimal air change rates with a high cfm centrifugal blower is critical for manufacturing facilities, as insufficient ventilation can compromise product quality and worker safety. Regular assessments and adjustments based on specific operational needs will enhance efficiency and performance.
Routine maintenance tasks such as cleaning, lubrication, and inspecting components are vital for sustaining system performance. Furthermore, consider the benefits of improving ventilation; for example, an industrial HVAC system achieved a 30% reduction in energy usage after replacing old fans with energy-efficient models. Understanding the role of air receiver tanks is also crucial for effectively managing CFM needs, particularly for certain types of air compressors. Lastly, remember that spray painting necessitates a compressor capable of delivering consistent air at a relatively low pressure.
Explore Different Types of Centrifugal Blowers
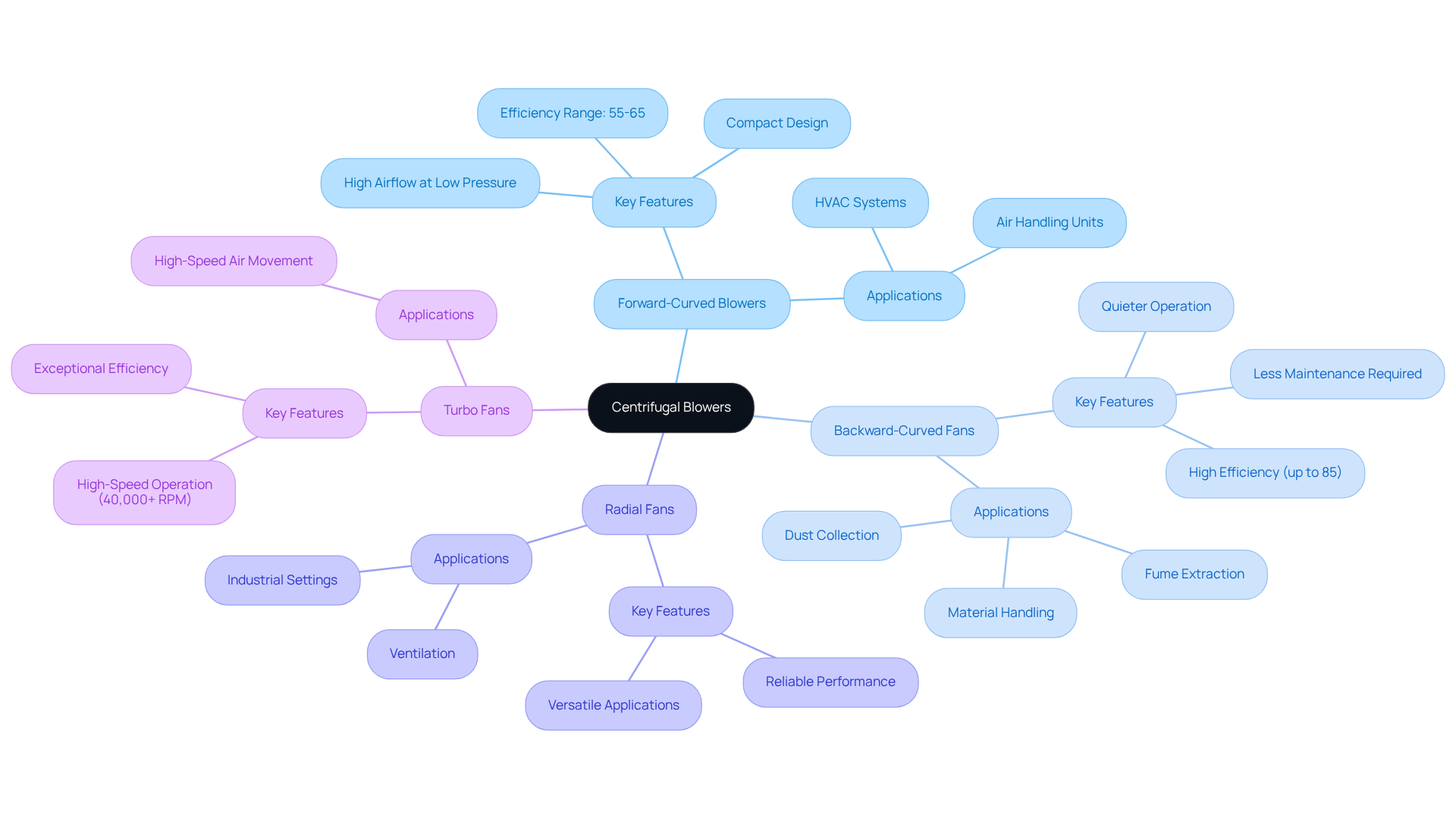
Centrifugal blowers come in various types, each designed for specific applications:
-
Forward-Curved Blowers: These blowers are adept at delivering high airflow at low pressure, making them a favored option in HVAC systems. Their compact design facilitates effective air movement in confined spaces, although their performance typically ranges from 55% to 65% efficiency.
-
Backward-Curved Fans: Known for their efficiency in high-pressure scenarios, backward-curved fans excel in dust collection and material handling. As Daniel VanderPyl notes, “These devices are commonly utilized in material handling, fume extraction, and other industrial processes involving dirty or abrasive airflows.” They can achieve static efficiencies of up to 85%, making them ideal for environments that demand robust performance against significant resistance. Furthermore, they operate more quietly and require less maintenance than their forward-curved counterparts, primarily due to reduced turbulence from their blade design.
-
Radial Fans: These versatile devices find application across numerous industrial settings, striking a balance between air movement and pressure. They are particularly effective in environments that require reliable performance under varying conditions.
-
Turbo Fans: Engineered for high-speed applications, turbo fans deliver exceptional efficiency within a compact footprint. Capable of operating at speeds exceeding 40,000 RPM, they are well-suited for applications that necessitate rapid air movement.
Understanding these categories empowers you to select a fan that aligns with your specific airflow and pressure requirements, ensuring optimal performance in your projects.
Assess Performance Metrics and Energy Efficiency
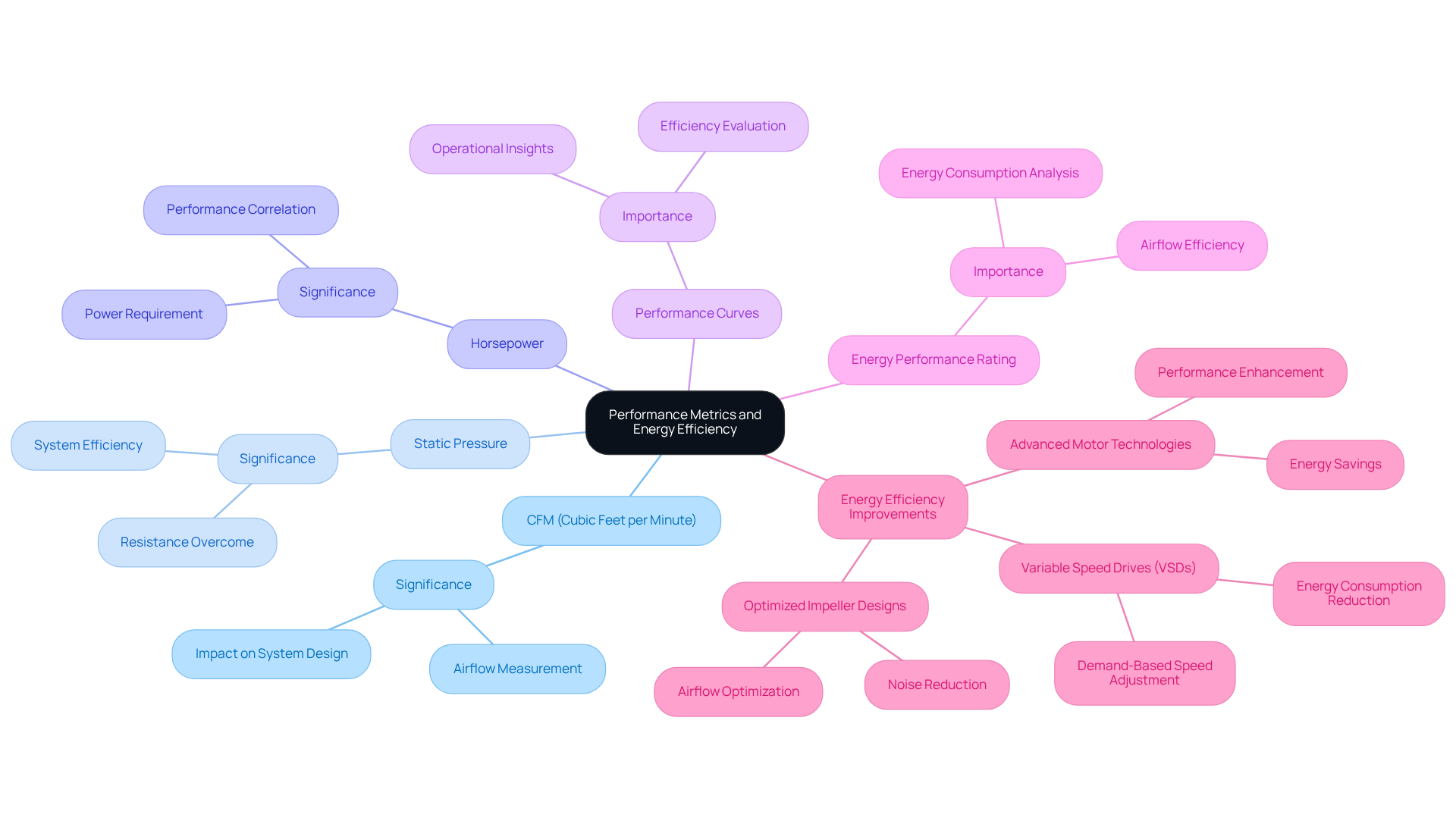
When selecting a centrifugal fan, understanding performance metrics is crucial. Key metrics include CFM, static pressure, and horsepower. Performance curves are essential as they illustrate how the fan operates under different conditions, providing insight into its efficiency. Additionally, consider the fan’s energy performance rating, which indicates the energy consumption relative to the airflow produced.
To boost energy efficiency, opt for fans equipped with advanced motor technologies and optimized impeller designs. For example, variable speed drives allow the fan’s speed to adjust based on demand, significantly reducing energy consumption. Always compare the blower’s specifications with your calculated requirements to ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion
Selecting the right high CFM centrifugal blower is a pivotal decision that can greatly influence the efficiency and effectiveness of various industrial applications. Understanding the fundamental principles of centrifugal blowers-encompassing their components and operational mechanics-sets the stage for making an informed choice tailored to your specific project needs.
In this article, we provided key insights into:
- Evaluating airflow requirements
- Exploring different types of centrifugal blowers
- Assessing performance metrics and energy efficiency
By calculating the necessary CFM based on the unique dimensions and requirements of your space, and familiarizing yourself with the characteristics of forward-curved, backward-curved, radial, and turbo fans, you can ensure optimal airflow and pressure for any application. Moreover, the emphasis on energy-efficient technologies and regular maintenance underscores the importance of sustainability in blower selection.
Ultimately, choosing the right high CFM centrifugal blower not only enhances operational performance but also contributes to energy savings and improved air quality. By adopting a thoughtful approach to selection and maintenance, you can reap significant benefits, reinforcing the importance of this decision in achieving your project goals. Taking the time to understand your specific needs and the capabilities of various blowers will empower you to make choices that drive efficiency and effectiveness in your operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are centrifugal blowers and how do they operate?
Centrifugal blowers, also known as centrifugal fans, operate by harnessing centrifugal force to transport air or gases efficiently. They draw air in through the center and expel it at a right angle through the outlet.
What are the primary components of a centrifugal blower?
The primary components of a centrifugal blower include the impeller, which spins to create air movement, and the housing that directs the airflow.
What key terms should I understand when dealing with centrifugal blowers?
Key terms to familiarize yourself with include CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute), which measures airflow, static pressure, and efficiency ratings, all of which are vital for assessing performance.
What is the projected market growth for centrifugal fans?
The centrifugal fan market is projected to grow significantly, with an expected valuation of approximately USD 3.81 billion by 2030, reflecting the rising demand for energy-efficient solutions across various industries.
How has technology impacted the design and efficiency of centrifugal fans?
Technology has significantly impacted centrifugal fans, as seen in Howden’s use of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) software to optimize impeller designs for improved energy recovery and reduced consumption. Additionally, Siemens’ SirioVent SSi series incorporates Variable Speed Drive (VSD) technologies for precise airflow control and enhanced energy efficiency.
Why is it important to understand the fundamentals of centrifugal fans?
Understanding the fundamentals of centrifugal fans is crucial for making informed decisions that align with project requirements and contribute to overall operational efficiency. Energy-efficient technologies, including high CFM centrifugal blowers, can lower industrial consumption by as much as 20%.

