Overview
The article examines the mechanics and applications of forced air fan systems, which are essential components of HVAC configurations, facilitating effective heating, cooling, and ventilation in diverse environments. It emphasizes the critical nature of regular maintenance and the pivotal role of key components—such as blowers, ductwork, and filters—in optimizing system efficiency and ensuring reliable performance. This underscores the necessity of comprehending these systems for both residential and industrial applications.
Introduction
Forced air fan systems are pivotal in ensuring optimal climate control across various environments, from homes to industrial facilities. These systems not only facilitate effective heating and cooling but also play a crucial role in maintaining air quality and protecting sensitive electronic components. However, their complexity presents challenges in ensuring peak performance and troubleshooting common issues.
What strategies can be employed to master the mechanics of these systems, enhance their efficiency, and extend their lifespan?
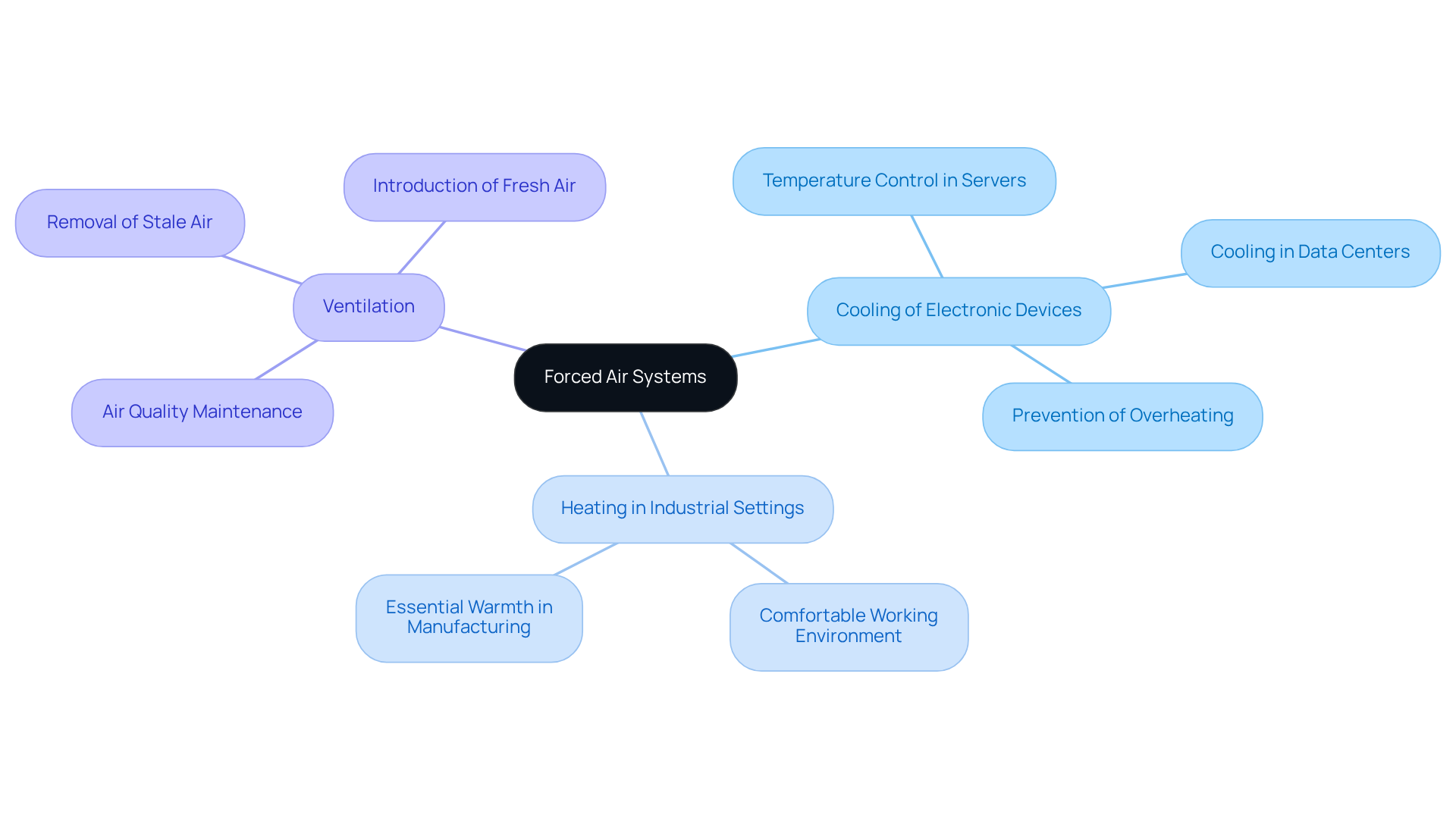
Define Forced Air Systems and Their Applications
The represent a crucial component of HVAC (Heating, , and Air Conditioning) configurations, utilizing a fan or blower to circulate air throughout a space. These systems are widely adopted in both residential and commercial environments for effective heating and cooling. In the electronics sector, the use of a forced air fan is particularly vital for cooling electronic components, ensuring . The applications of :
- : These systems maintain temperature control in servers and data centers, where forced air solutions can reduce surface temperatures by 15-30% compared to natural convection alone, significantly .
- : Forced air fans provide essential warmth in manufacturing facilities, ensuring a comfortable working environment.
- Ventilation: The forced air fan systems play a key role in ensuring air quality in enclosed spaces by removing stale air and introducing fresh air, which is crucial for .
Understanding these applications is essential for recognizing the in sustaining efficiency and performance across diverse settings. every 3-6 months, is vital for ensuring peak performance in these setups.
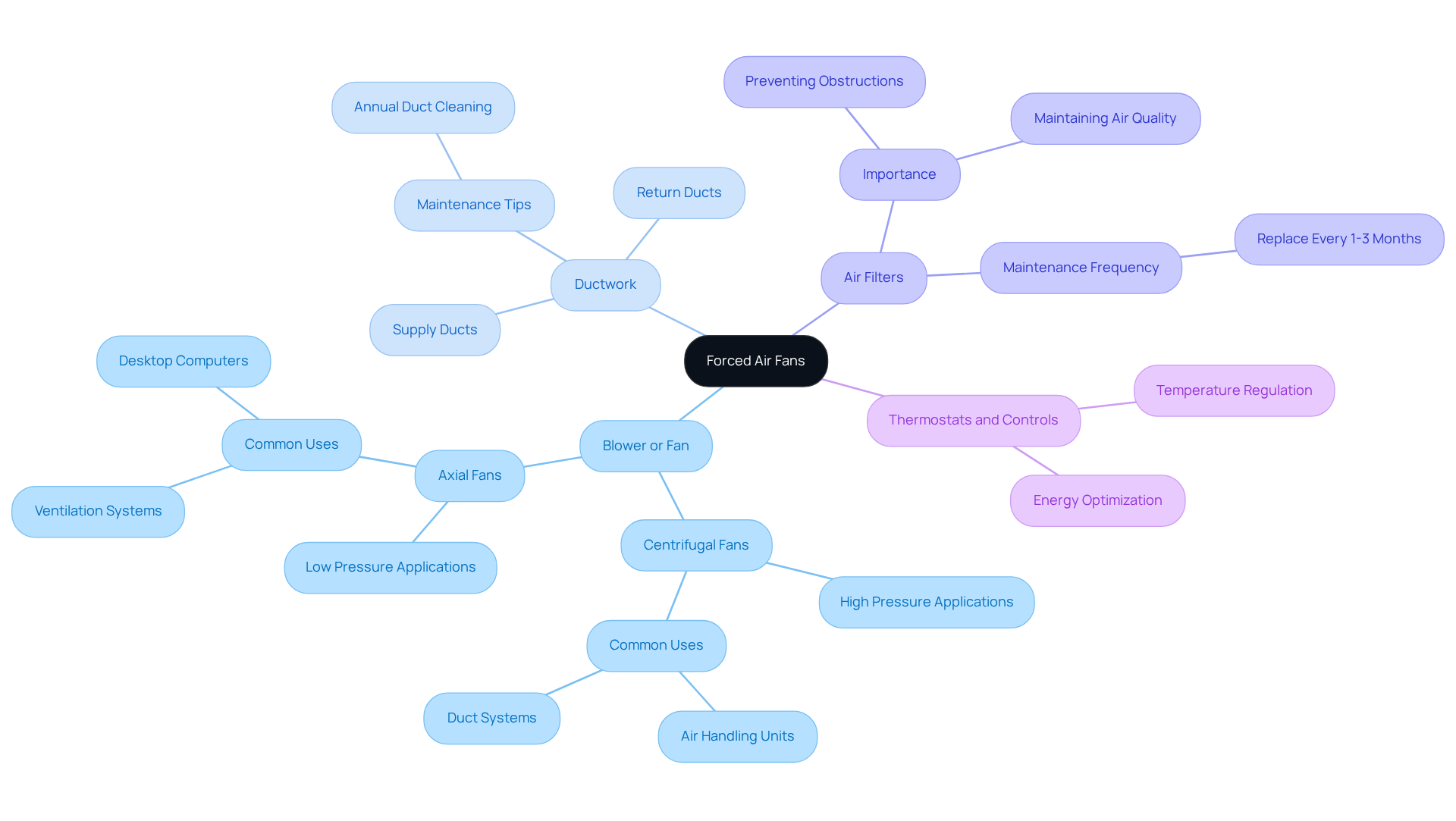
Explain the Mechanics of Forced Air Fans
The forced air fan is an indispensable component of , functioning by drawing air into the apparatus and channeling it through a network of ducts or vents. The primary components include:
- Blower or Fan: Serving as the heart of the system, this component is responsible for air movement. , known for generating high pressure, excel at moving air through resistance in ducting, making them ideal for applications that demand powerful air movement. Conversely, are particularly effective in scenarios requiring high air movement at low pressure, such as in desktop computers and ventilation systems. By 2025, axial flow fan applications are expected to encompass HVAC, cooling, ventilation, and safety across various industries, attributed to their efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Ductwork: A meticulously designed is vital for directing airflow to different areas within a building. Proper ductwork not only enhances efficiency but also improves indoor air quality, ensuring that heated or cooled air reaches its intended destination with minimal losses.
- : These components are critical for maintaining air quality, as they capture dust and debris before air circulates throughout the network. Regular maintenance, such as replacing air filters every 1-3 months, is essential to prevent obstructions and sustain optimal performance.
- Thermostats and Controls: These devices regulate temperature and airflow, ensuring the system operates efficiently. They are instrumental in maintaining comfort levels and optimizing energy consumption.
Understanding the interplay among these elements is essential for enhancing the . For instance, the typical lifespan of in HVAC setups generally ranges from 10 to 15 years, contingent upon usage and maintenance. On average, homeowners invest approximately $4,670 to install a forced air fan heating unit, providing a financial perspective regarding the lifespan of the fans. Engineers emphasize that selecting the appropriate fan type—whether centrifugal or axial—can significantly influence efficiency and comfort. Recent studies indicate that the decision between these fan types should be informed by specific airflow and pressure requirements to achieve optimal results in forced air fan applications. Moreover, integrating variable frequency drives (VFDs) into HVAC systems can substantially enhance , allowing for variable speed control and minimizing energy waste.
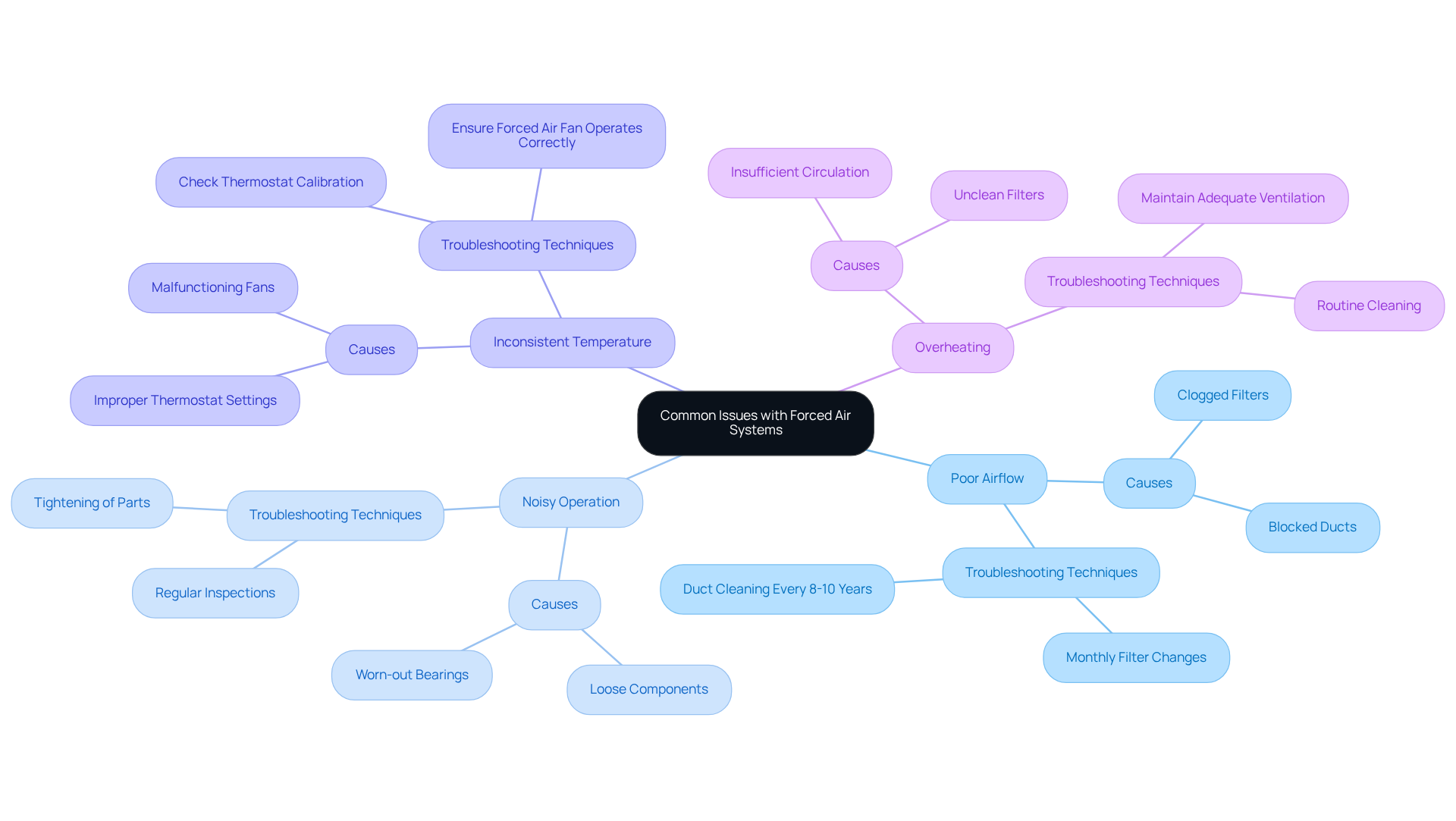
Identify Common Issues and Troubleshooting Techniques
often stem from several key factors:
- : Frequently caused by clogged filters or blocked ducts, poor airflow can significantly impact system efficiency. Statistics indicate that 76% of homeowners reported their HVAC units were over 10 years old, underscoring the . Monthly filter changes and duct cleaning every 8-10 years are essential practices to prevent this issue.
- : Unusual sounds, such as banging or whistling, may signal loose components or worn-out bearings. that “strange noises from the heater suggest mechanical problems that require professional assessment to avoid costly repairs.” Regular inspections and tightening of parts can help mitigate these noises, ensuring a quieter operation.
- : Fluctuations in temperature can arise from improper thermostat settings or malfunctioning fans. It is crucial to check the thermostat calibration and ensure that the forced air fan operates correctly to maintain consistent heating or cooling.
- Overheating: Often a consequence of insufficient circulation or unclean filters, to the unit. Maintaining adequate ventilation and performing .
For effective troubleshooting, begin by examining the air filters and ductwork for any blockages that may impact the operation of the forced air fan. If problems persist, inspect the fan and motor for signs of wear or malfunction. can prevent cooled air from escaping, improving comfort and reducing energy costs. HVAC technicians often highlight that resolving these common issues quickly can prolong the lifespan of the equipment and improve overall efficiency.
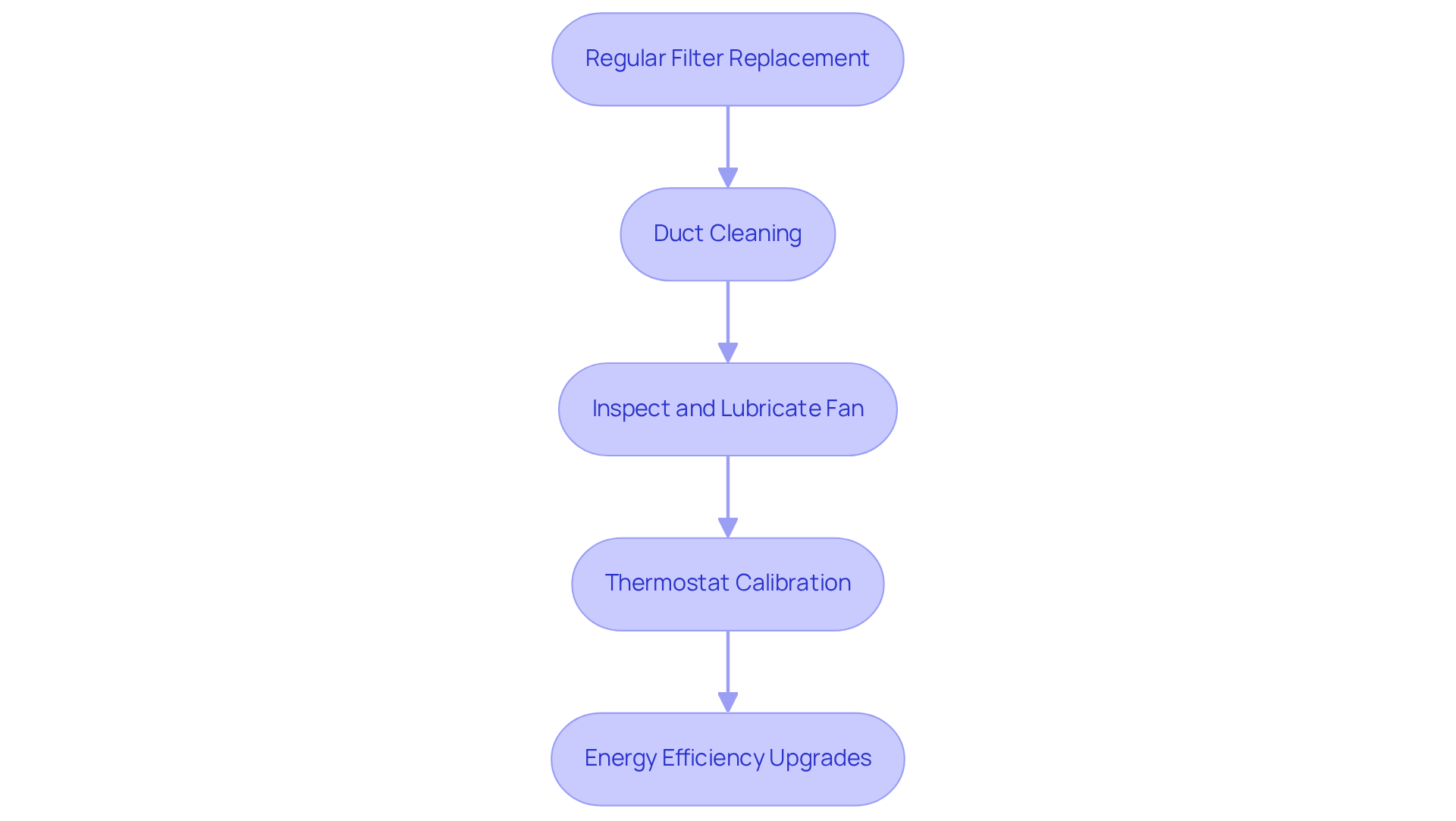
Discuss Maintenance Practices and Efficiency Optimization
To optimize the efficiency of forced air systems, it is essential to implement the following maintenance practices:
- : Changing air filters every 1 to 3 months is crucial for maintaining proper airflow and air quality. While some households may opt to , this practice should not be neglected. Dirty filters can lead to higher energy usage, as they restrict circulation, causing HVAC units to operate more vigorously.
- : Scheduling professional duct cleaning every 3 to 5 years is necessary to eliminate dust and debris that obstruct airflow. Homes with pets, allergies, or those located in dusty areas should consider more frequent cleaning. Clean ducts not only enhance efficiency but also contribute to , potentially decreasing respiratory issues by up to 50%.
- : Regular inspection of the fan motors and bearings for wear is vital. Lubricating these components reduces friction and noise, ensuring smoother operation and prolonging the lifespan of the mechanism.
- : It is important to ensure that thermostats are precisely calibrated to maintain desired temperatures without overstressing the equipment. Proper calibration can prevent unnecessary cycling, which can lead to increased energy costs.
- : Upgrading to and motors should be considered. Although there may be initial investments in duct maintenance, these upgrades can significantly reduce energy consumption and lower utility bills, leading to a more sustainable operation.
By adopting these practices, not only is system efficiency enhanced, but a healthier indoor environment is also fostered, ultimately resulting in and improved comfort.
Conclusion
Mastering the mechanics of forced air fan systems is essential for ensuring optimal performance across diverse applications, ranging from HVAC configurations to electronic cooling solutions. These systems deliver effective air circulation that enhances comfort and efficiency in both residential and commercial environments. Understanding the intricacies of forced air systems not only highlights their importance but also underscores the necessity for regular maintenance to sustain their functionality.
This article has explored key aspects such as:
- The definition and applications of forced air systems
- The mechanics of their operation
- Common issues and troubleshooting techniques
- Essential maintenance practices
The significance of components like blowers, ductwork, air filters, and thermostats has been emphasized, alongside the necessity of addressing common problems to prolong system life and efficiency. Moreover, maintenance practices such as regular filter changes and duct cleaning have been identified as critical for optimizing performance and ensuring a healthy indoor environment.
In a landscape where energy efficiency and comfort are paramount, adopting best practices for forced air systems is not merely beneficial but essential. By prioritizing maintenance and understanding the mechanics behind these systems, users can enhance their HVAC performance, reduce energy costs, and foster a healthier living or working space. Embracing these insights will lead to informed decisions that contribute to the longevity and effectiveness of forced air fan systems, ultimately supporting a more sustainable future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are forced air systems?
Forced air systems are HVAC configurations that use a fan or blower to circulate air throughout a space, providing effective heating and cooling.
Where are forced air systems commonly used?
They are widely adopted in both residential and commercial environments for heating, cooling, and ventilation purposes.
How do forced air systems benefit the electronics sector?
In the electronics sector, forced air fans are vital for cooling electronic components, helping to maintain optimal performance and prevent overheating, particularly in servers and data centers.
What is the impact of forced air cooling on electronic devices?
Forced air solutions can reduce surface temperatures in electronic devices by 15-30% compared to natural convection alone, significantly extending the lifespan of critical components.
How do forced air fans contribute to heating in industrial settings?
Forced air fans provide essential warmth in manufacturing facilities, ensuring a comfortable working environment for employees.
What role do forced air systems play in ventilation?
Forced air fan systems help ensure air quality in enclosed spaces by removing stale air and introducing fresh air, which is crucial for maintaining a healthy atmosphere.
Why is maintenance important for forced air systems?
Regular maintenance, including filter cleaning every 3-6 months, is vital for ensuring peak performance and efficiency in forced air systems.

