Overview
DC fans operate on a constant voltage and feature a simpler design, making them suitable for basic applications. In contrast, PWM fans utilize a varying voltage signal to dynamically adjust speed, offering greater efficiency and quieter operation. This distinction is critical as PWM fans can achieve significant energy savings, adapt to thermal demands, and reduce noise levels by up to 30%. Such capabilities make them particularly ideal for high-performance and noise-sensitive environments, where operational efficiency and sound levels are paramount.
Introduction
In the realm of cooling technology, the choice between DC (Direct Current) and PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) fans significantly impacts performance and efficiency. While DC fans offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness, PWM fans provide advanced control and energy savings, making them increasingly popular in high-performance applications. However, these benefits raise questions about their suitability for various environments and operational demands. Which fan technology truly reigns supreme in terms of efficiency, noise reduction, and adaptability? This article delves into the nuances of DC and PWM fans, comparing their characteristics and performance metrics to guide informed decisions in cooling solutions.
Define DC and PWM Fans: Key Characteristics
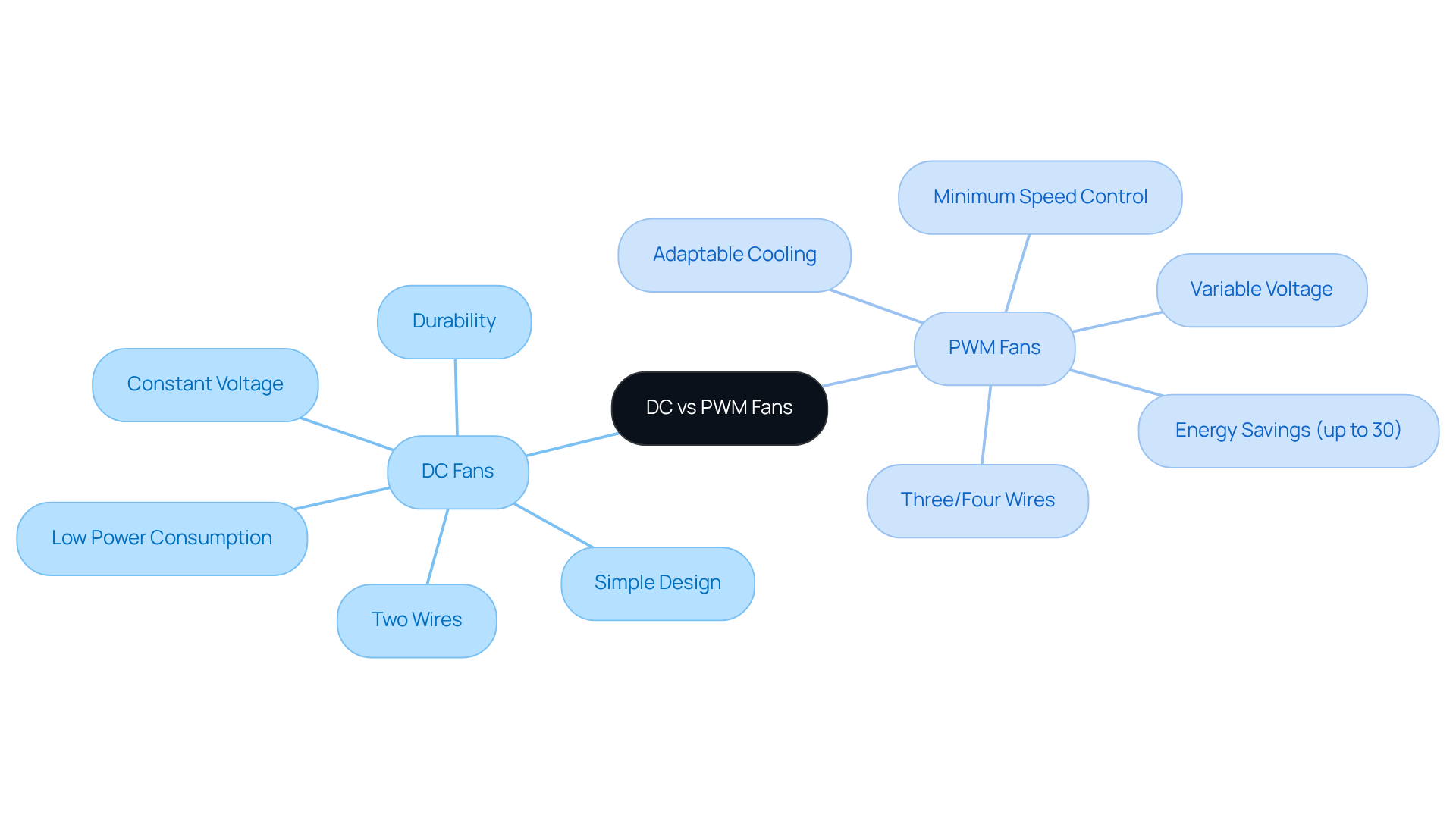
DC (Direct Current) blowers operate on a constant voltage source, enabling them to maintain a steady pace. Their design is straightforward, typically consisting of two wires for electricity and ground. In contrast, PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) devices employ a varying voltage signal to modulate the rotation rate. This modulation is accomplished by rapidly toggling the power on and off, which alters the average voltage supplied to the fan, thus adjusting its speed. PWM units generally feature three or four wires, with the additional wire designated for the PWM signal.
This fundamental operational difference in DC vs PWM results in distinct performance characteristics:
- PWM units can achieve a minimum speed below 20% of their rated velocity, allowing for precise control and significant energy savings—up to 30% compared to DC devices.
- PWM technology enables cooling devices to adapt swiftly to fluctuating thermal demands, making them ideal for high-performance applications where noise reduction and efficiency are paramount.
Examine Operational Mechanisms: How DC and PWM Fans Work
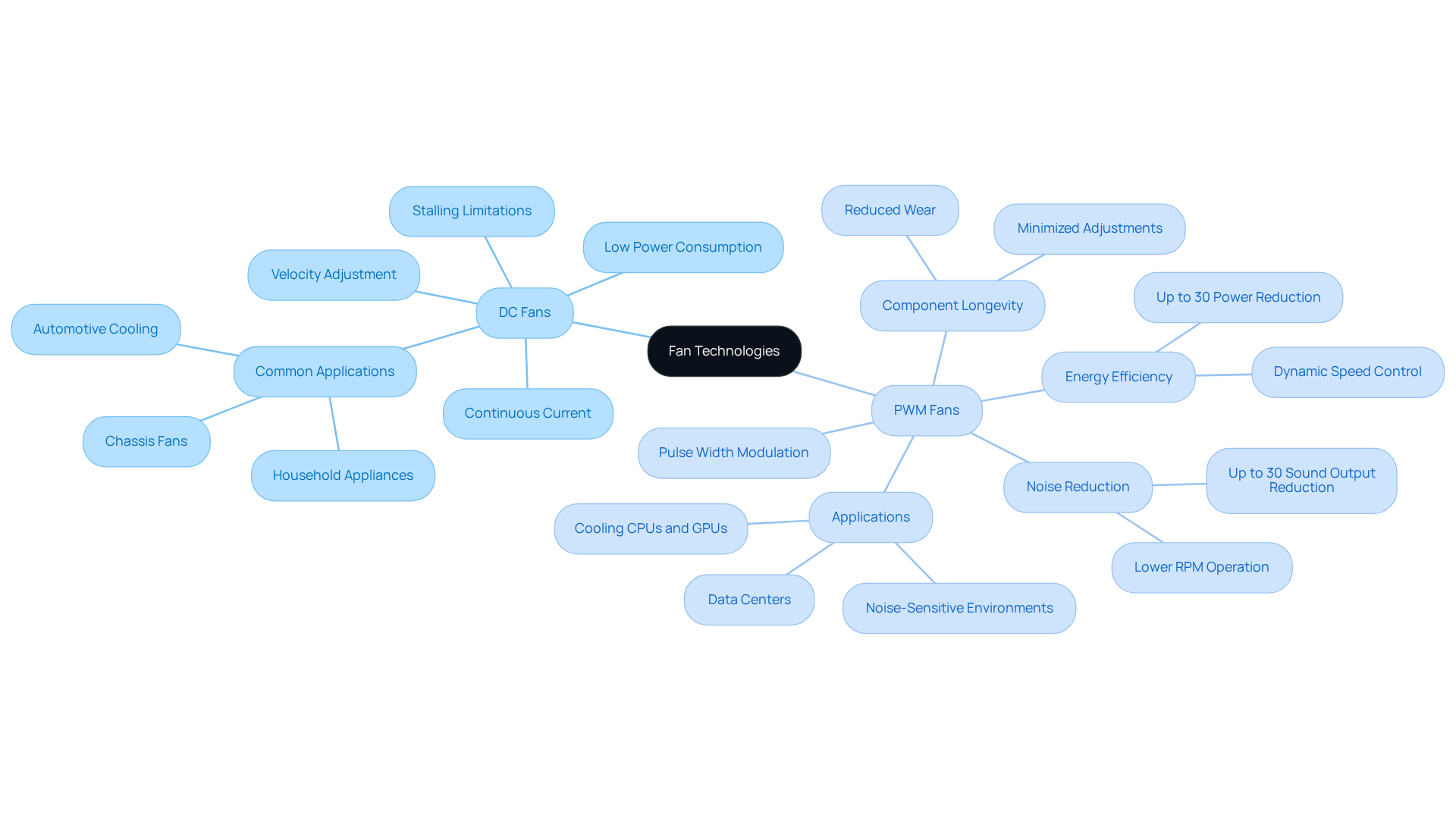
In the discussion of DC vs PWM, DC enthusiasts operate by extracting a continuous current from the source, resulting in a consistent rotational pace. Velocity adjustments occur through modifications to the voltage supplied to the fan; however, this method has limitations, particularly when attempting to decrease pace below a certain threshold, potentially leading to stalling.
In contrast, the technique used by PWM devices in the DC vs PWM comparison adjusts the energy source via a series of on/off pulses. The width of these pulses directly influences the effective voltage supplied to the fan, enabling precise regulation of its pace. This capability allows PWM devices to operate efficiently at lower levels when maximum power is unnecessary, significantly enhancing energy efficiency. Notably, PWM units can reduce their rotation by up to 40% of their rated performance, making them ideal for cooling CPUs, GPUs, and other heat-generating components across various devices.
Furthermore, systems employing PWM technology can achieve up to a 30% reduction in sound output compared to traditional cooling systems, rendering them perfect for noise-sensitive environments. PWM units are also equipped with a fourth wire that transmits a PWM signal to the motor, which is crucial for their operation. Additionally, PWM cooling devices mitigate wear on components by minimizing the need for constant adjustments, thereby extending their lifespan.
As industry expert Matt Safford notes, ‘The accuracy of PWM devices enables engineers to enhance temperature management strategies efficiently, which is crucial in high-performance settings.’
Case studies have demonstrated that data centers utilizing PWM technology have realized efficiency improvements in temperature management of up to 30%, underscoring the operational advantages of PWM devices in modern cooling applications.
Compare Performance Metrics: Efficiency, Noise, and Power Consumption
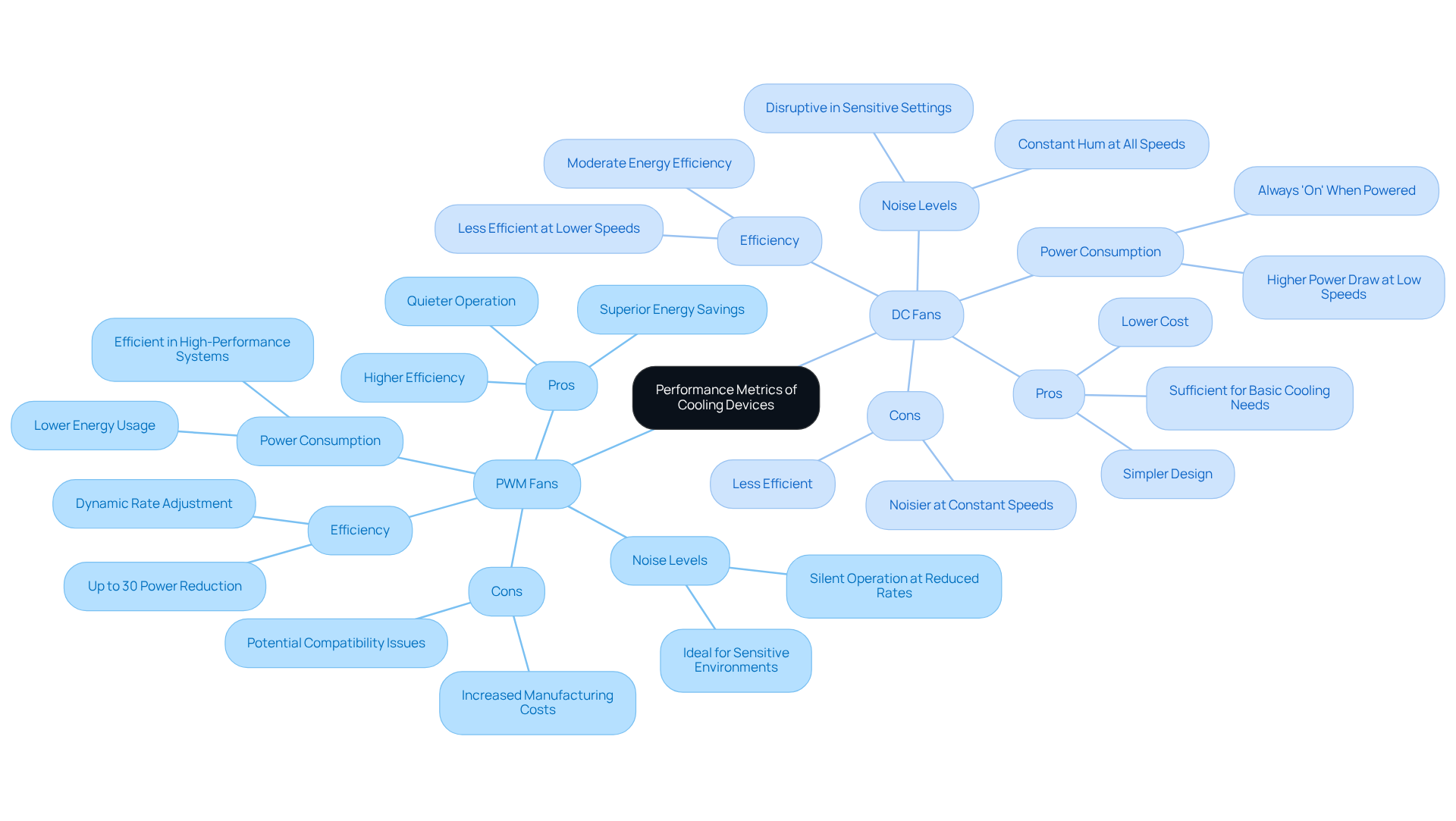
In terms of efficiency, PWM units significantly outperform DC vs PWM units, primarily due to their ability to dynamically adjust rates according to cooling requirements. This capability allows PWM devices to consume less energy during operation, particularly in scenarios where adjustable control is essential. Conversely, when comparing DC vs PWM units, the DC units, while simpler in design, often draw more power than necessary at lower speeds, leading to decreased efficiency.
In terms of noise levels, PWM devices hold a distinct advantage. They operate silently at reduced rates, making them ideal for environments where noise is a concern. In contrast, DC units tend to produce a constant hum, irrespective of their speed settings, which can be disruptive in sensitive settings.
Power consumption represents another critical area where PWM devices excel. Research indicates that PWM devices can achieve up to a 30% reduction in energy consumption compared to their DC vs PWM counterparts while maintaining the same cooling efficiency. This characteristic makes PWM devices particularly suitable for energy-conscious configurations, especially in high-performance systems that generate significant heat. Real-world applications, such as CPU coolers and high-performance gaming rigs, frequently employ PWM devices to optimize both cooling efficiency and noise levels, underscoring their superiority in contemporary cooling solutions.
Key Differences:
- Pin Configuration: PWM fans feature four pins (power, ground, tachometer, PWM signal), whereas DC fans typically have three pins (power, ground, tachometer).
- Operational Mechanics: In the context of dc vs pwm, PWM devices sustain constant voltage and adjust rotation through duty cycles, while DC units modify rotation by altering voltage.
- Expert Insight: Friedrich Stiemer notes, “PWM devices can generally rotate slower than their DC counterparts,” emphasizing their efficiency.
Pros and Cons:
- PWM Fans:
- Pros: Higher efficiency, quieter operation, superior energy savings.
- Cons: Increased manufacturing costs, potential compatibility issues with motherboards.
- DC Fans:
- Pros: Lower cost, simpler design, sufficient for basic cooling needs.
- Cons: Less efficient, noisier at constant speeds.
Case Studies:
- Noise Reduction Benefits of PWM Fans: PWM fans markedly decrease noise levels compared to DC fans, making them suitable for sound-sensitive environments without compromising cooling efficiency.
- Energy Efficiency of PWM Devices: PWM devices optimize energy usage by operating at adjustable rates, leading to reduced power consumption and cost savings, particularly in large systems or data centers.
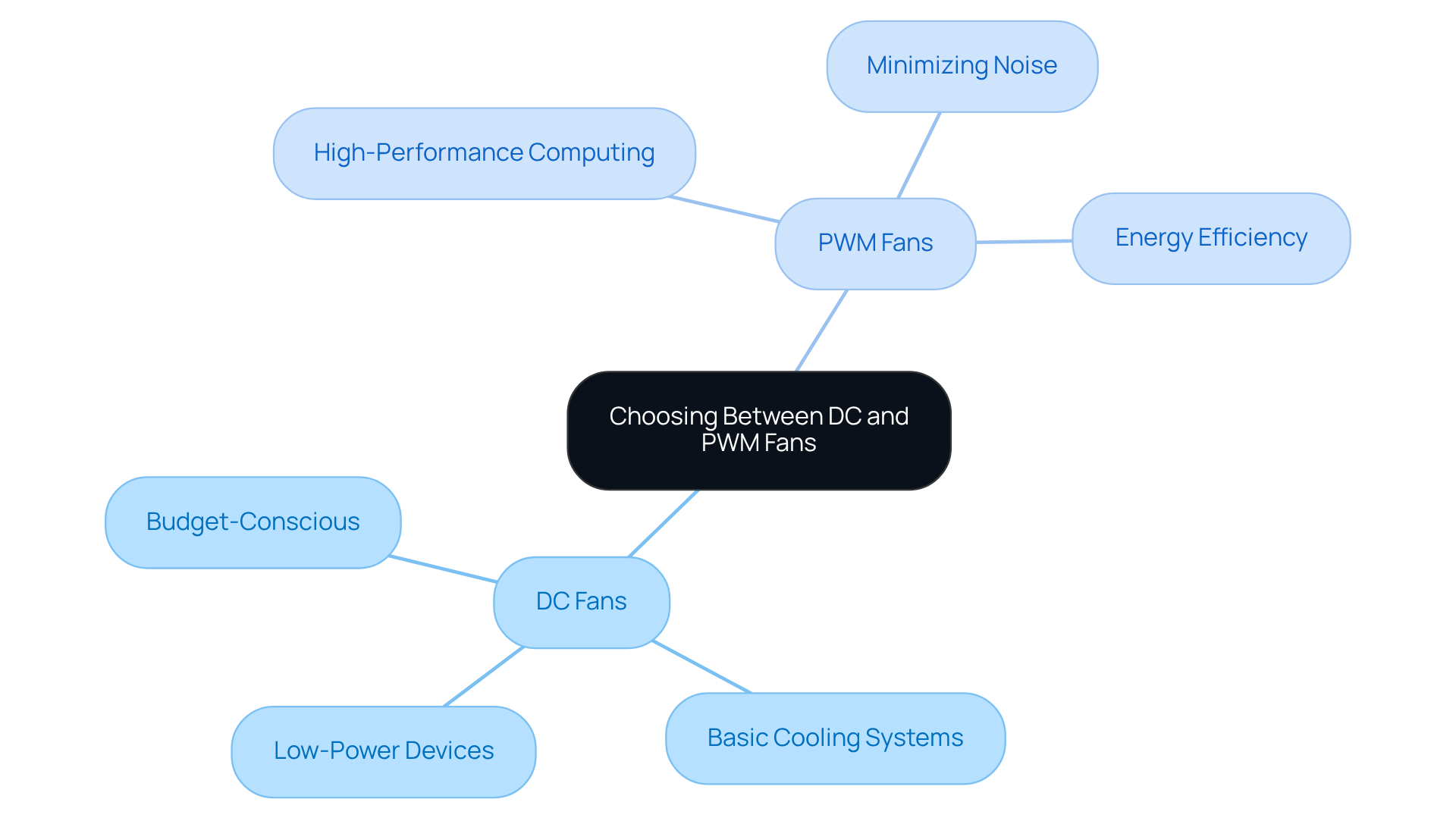
Assess Application Suitability: Choosing Between DC and PWM Fans
When selecting between DC vs PWM units, understanding the application context is paramount. DC units often find favor in straightforward, budget-conscious applications where precise control over velocity is not a priority. They are commonly utilized in basic cooling systems and low-power devices. Conversely, PWM units excel in scenarios that demand accurate control of rotation, such as high-performance computing or environments where minimizing noise is critical. Their capacity to operate efficiently across varying speeds renders them ideal for modern electronic systems that require adaptability and energy efficiency. Ultimately, the decision between DC vs PWM fans should be informed by the specific operational requirements and constraints of the intended application.
Conclusion
The comparison between DC and PWM fans underscores the significant differences in their operational mechanisms, efficiency, and suitability for various applications. DC fans operate on a steady voltage and feature a simpler design, whereas PWM fans employ a sophisticated method of pulse width modulation, allowing for greater control over speed and energy consumption. This distinction positions PWM fans as the superior choice for high-performance environments where adaptability and noise reduction are paramount.
Throughout this article, we have examined key insights into the performance metrics of both fan types. PWM fans not only deliver enhanced energy efficiency—consuming up to 30% less power—but also operate more quietly, making them ideal for sound-sensitive applications. In contrast, while DC fans are cost-effective and straightforward, they often fall short in efficiency and noise reduction, particularly at lower speeds.
Ultimately, the decision to choose between DC and PWM fans should be driven by the specific needs of the application. For environments that demand precise temperature control and minimal noise, PWM fans clearly emerge as the winner. Conversely, for basic cooling requirements where budget constraints are a concern, DC fans may suffice. Understanding these differences is crucial for optimizing performance and energy efficiency in modern electronic systems, ensuring that the appropriate fan technology is employed for the task at hand.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between DC and PWM fans?
The main difference is that DC fans operate on a constant voltage source, maintaining a steady pace, while PWM fans use a varying voltage signal to modulate their rotation rate by rapidly toggling power on and off.
How do DC fans typically connect?
DC fans typically consist of two wires: one for electricity and one for ground.
What is the wiring configuration for PWM fans?
PWM fans generally feature three or four wires, with the additional wire designated for the PWM signal.
What are the speed capabilities of PWM fans compared to DC fans?
PWM fans can achieve a minimum speed below 20% of their rated velocity, allowing for precise control and significant energy savings, while DC fans do not have this capability.
How much energy savings can PWM fans provide compared to DC fans?
PWM fans can provide energy savings of up to 30% compared to DC devices.
In what applications are PWM fans particularly beneficial?
PWM fans are ideal for high-performance applications where noise reduction and efficiency are paramount, as they can adapt swiftly to fluctuating thermal demands.

