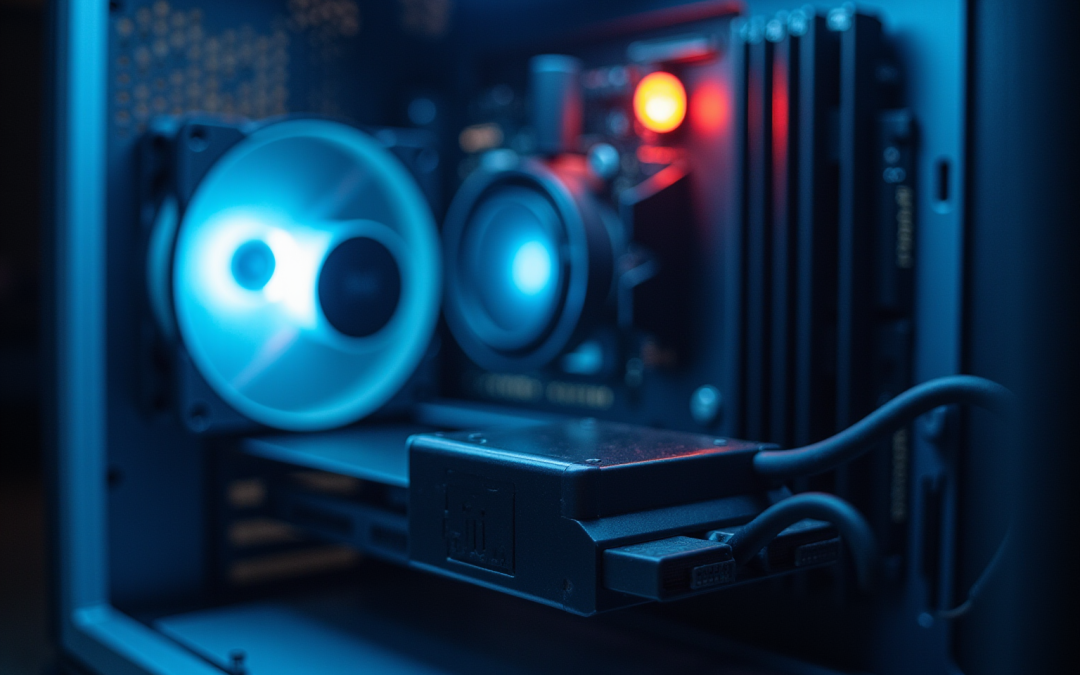
Overview
PWM case fans, or Pulse Width Modulation case fans, represent cutting-edge cooling solutions that dynamically adjust their speed according to temperature demands. This adaptability significantly enhances thermal efficiency while concurrently reducing noise levels. The functionality of these fans is underscored by a 4-pin connector that facilitates precise control, leading to both energy savings and quieter operation. Consequently, PWM case fans have become indispensable in modern electronic applications, particularly within high-performance computing environments.
Introduction
PWM case fans signify a pivotal advancement in thermal management, revolutionizing how electronic devices sustain optimal operating temperatures. By employing Pulse Width Modulation technology, these fans adeptly adjust their speed in response to real-time temperature demands, providing users with enhanced energy efficiency and reduced noise levels. Yet, as the dependence on these advanced cooling solutions escalates, it prompts a critical inquiry: what challenges and considerations must engineers contemplate when integrating PWM technology into their designs?
Define PWM Case Fans and Their Functionality
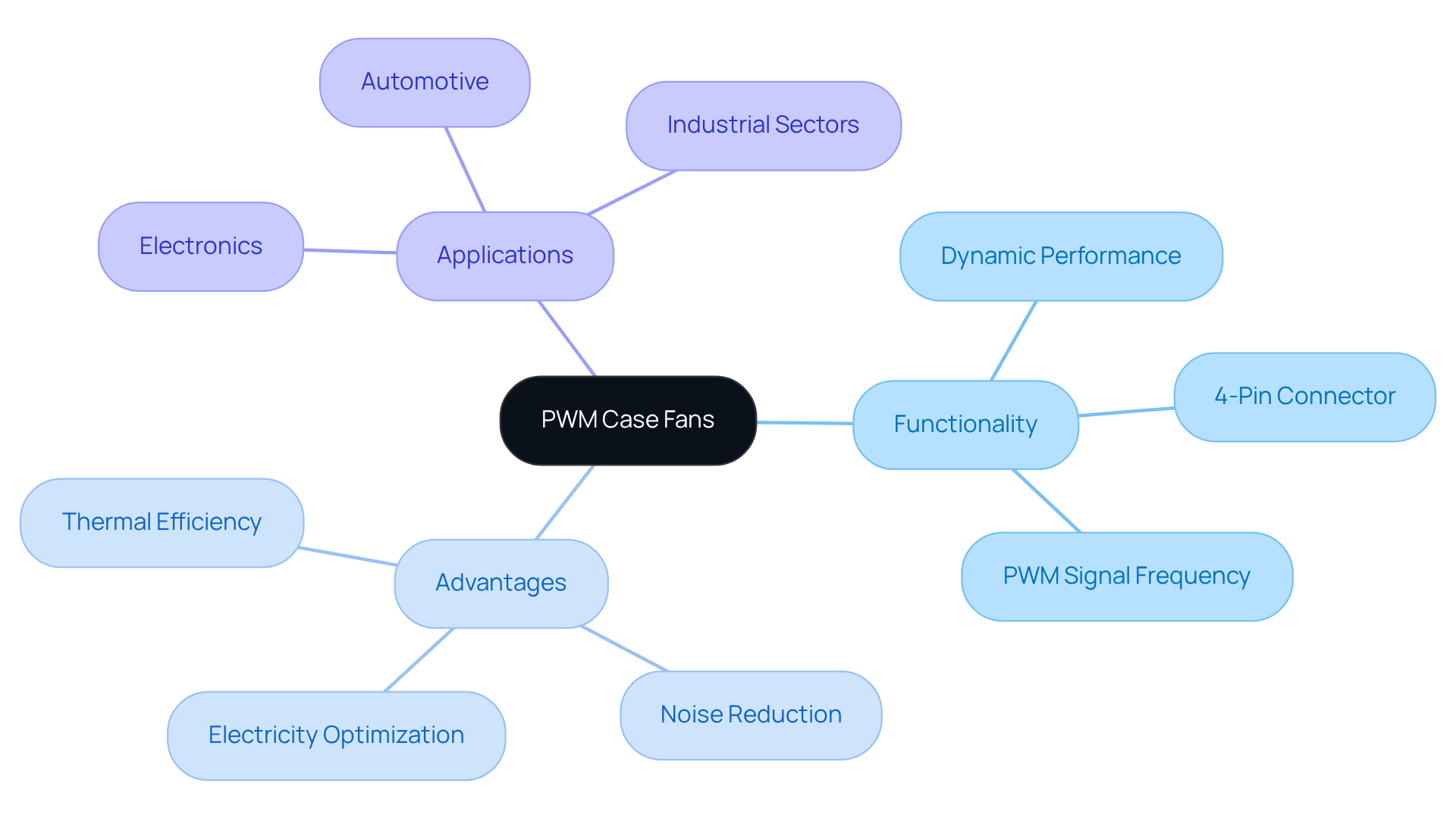
, also known as Pulse Width Modulation case fans, are advanced primarily utilized in electronic devices, particularly computers. Unlike traditional cooling devices that operate at a constant rate, PWM case units adapt their performance dynamically to meet varying temperature demands. This adaptability is facilitated by a , where an additional pin transmits a to the fan, allowing for precise control over its operation. Operating at a frequency of 25kHz or higher, the PWM signal enables rapid adjustments in response to real-time temperature requirements.
This capability not only —permitting fans to reduce their speed by up to 40% when temperature demands are low—but also significantly lowers noise levels, as the device can operate quietly at reduced RPMs. Indeed, below 20% of their rated capacity, making them particularly suitable for environments where noise reduction is essential. Furthermore, their ability to optimize electricity consumption based on immediate cooling needs enhances their attractiveness, especially in where is crucial for system stability and longevity.
As the world’s largest producer of standard and custom air-movers, offers a comprehensive portfolio that includes PWM case fans. This includes various sizes and specifications tailored for diverse applications across electronics, automotive, and industrial sectors, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
Explain PWM Technology and Its Benefits in Cooling
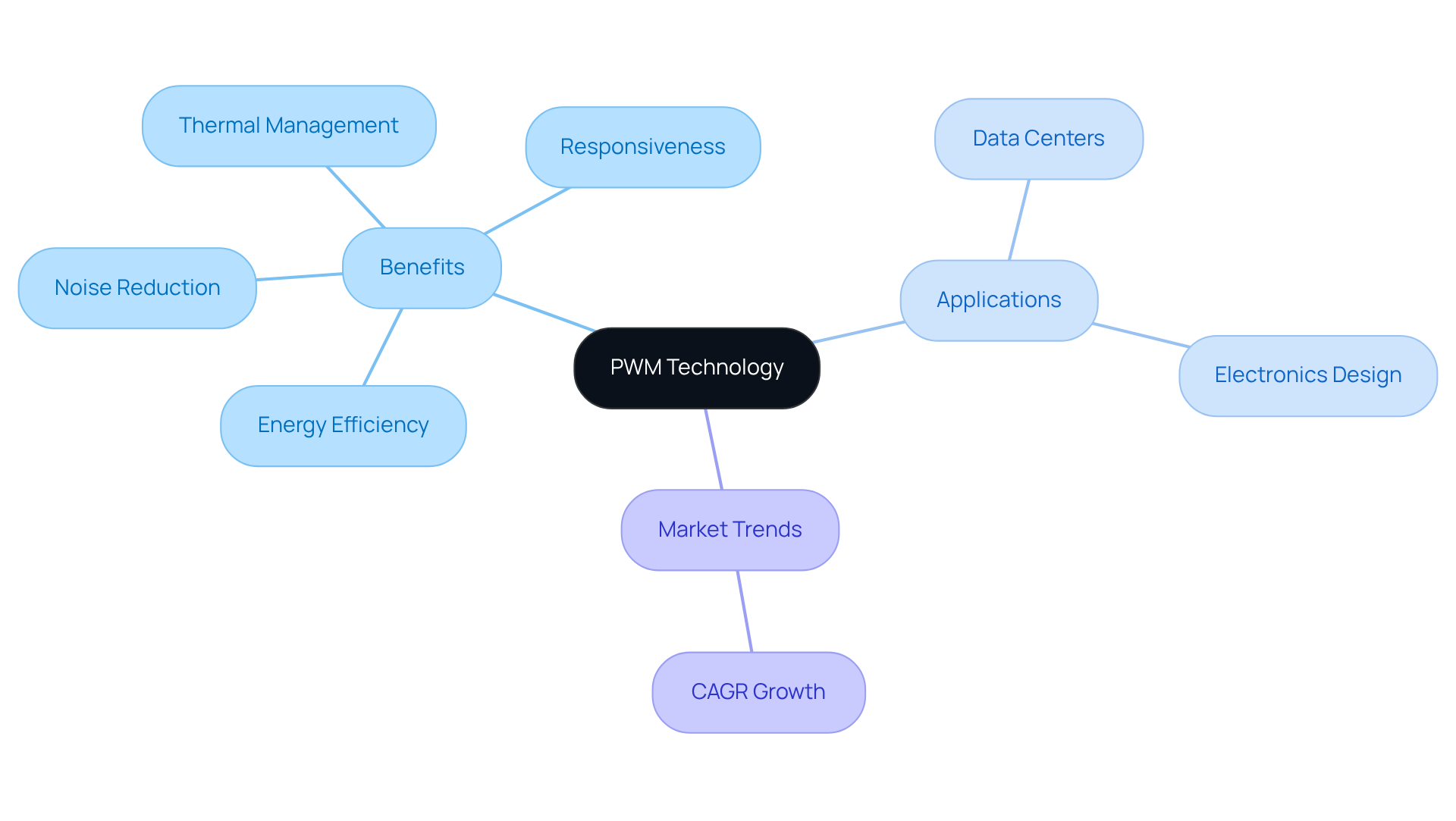
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) represents a sophisticated technique that governs the operation of electronic devices through the modulation of pulse width in a signal. Specifically, in the context of , this approach allows for , enabling precise rotational control without necessitating voltage adjustments. The benefits of in temperature regulation systems are substantial. For instance, PWM ventilators can operate at lower speeds when temperature control demands are minimal, leading to enhanced . This advantage is particularly pronounced in expansive systems or data centers, where energy savings can be considerable.
Moreover, PWM units are designed to operate quietly under low-load conditions, thereby minimizing noise levels that could disrupt sensitive environments such as offices and data centers. Their swift responsiveness to temperature variations ensures optimal thermal management for critical electronic components, significantly mitigating the risk of thermal failures. Real-world applications illustrate that data centers employing PWM technology have realized up to a 30% improvement in efficiency, which correspondingly lowers operational costs.
As engineers increasingly integrate into their designs—over 70% of electronics engineers are now adopting PWM case fan technology—they acknowledge its superior capabilities in speed regulation, noise reduction, and overall temperature management. Furthermore, the market is anticipated to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.9% from 2024 to 2031, underscoring the escalating significance of PWM technology within the industry. , characterized by their four-pin configuration as opposed to the three-pin design of conventional DC units, offer a technical advantage that further enhances their appeal. This positions PWM case fans as a vital component in modern , serving as a compelling alternative to traditional DC devices.
Trace the Evolution of PWM Case Fans in Electronics
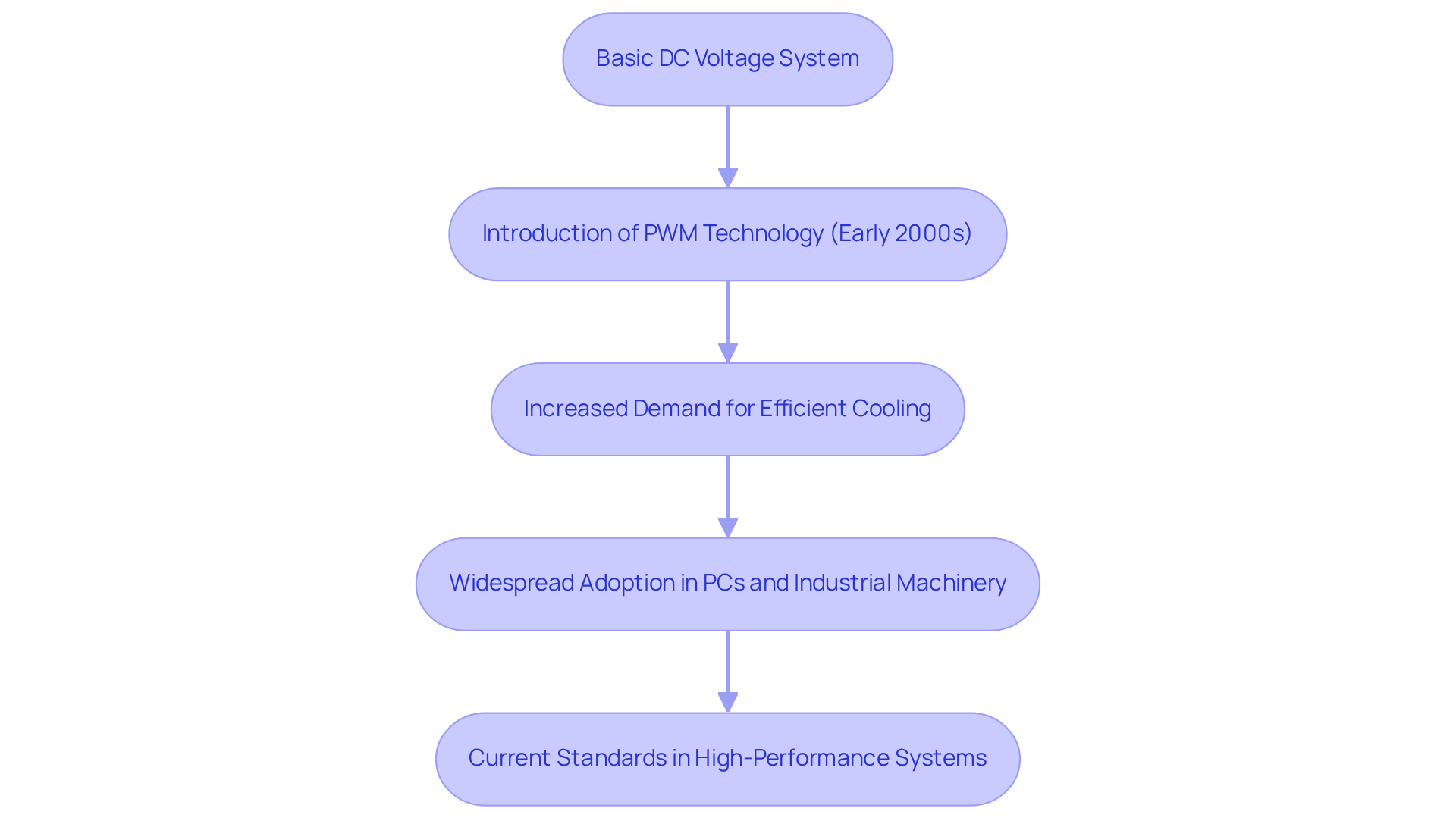
The development of is intricately linked to the escalating demand for in electronic devices. Initially, supporters relied on a basic DC voltage system, which constrained their ability to dynamically adjust rates. The advent of in the early 2000s marked a significant breakthrough, facilitating more precise control over fan speeds.
As electronic components became increasingly powerful and compact, the necessity for efficient intensified, resulting in the widespread adoption of PWM case fans across various applications, including personal computers and industrial machinery. Today, PWM case fans are standard in , highlighting their critical role in sustaining optimal operating temperatures.
Recent studies indicate that systems utilizing PWM fans can achieve up to a 30% reduction in noise levels and power consumption compared to traditional methods, thereby enhancing . Furthermore, case studies demonstrate that data centers employing PWM technology have realized substantial improvements in efficiency, resulting in lower operational costs and enhanced reliability.
However, it is essential to acknowledge that PWM control can occasionally lead to erroneous tach signal readings, posing a challenge for accurate speed feedback. As Mary Burke, an expert in the field, articulates, “From the standpoints of acoustic noise, reliability, and power efficiency, the most preferable method of fan control is the use of high-frequency (>20 kHz) PWM drive.”
This evolution mirrors a broader trend in , where the integration of is vital for addressing the challenges posed by contemporary electronic devices.
Identify Key Features and Characteristics of PWM Case Fans
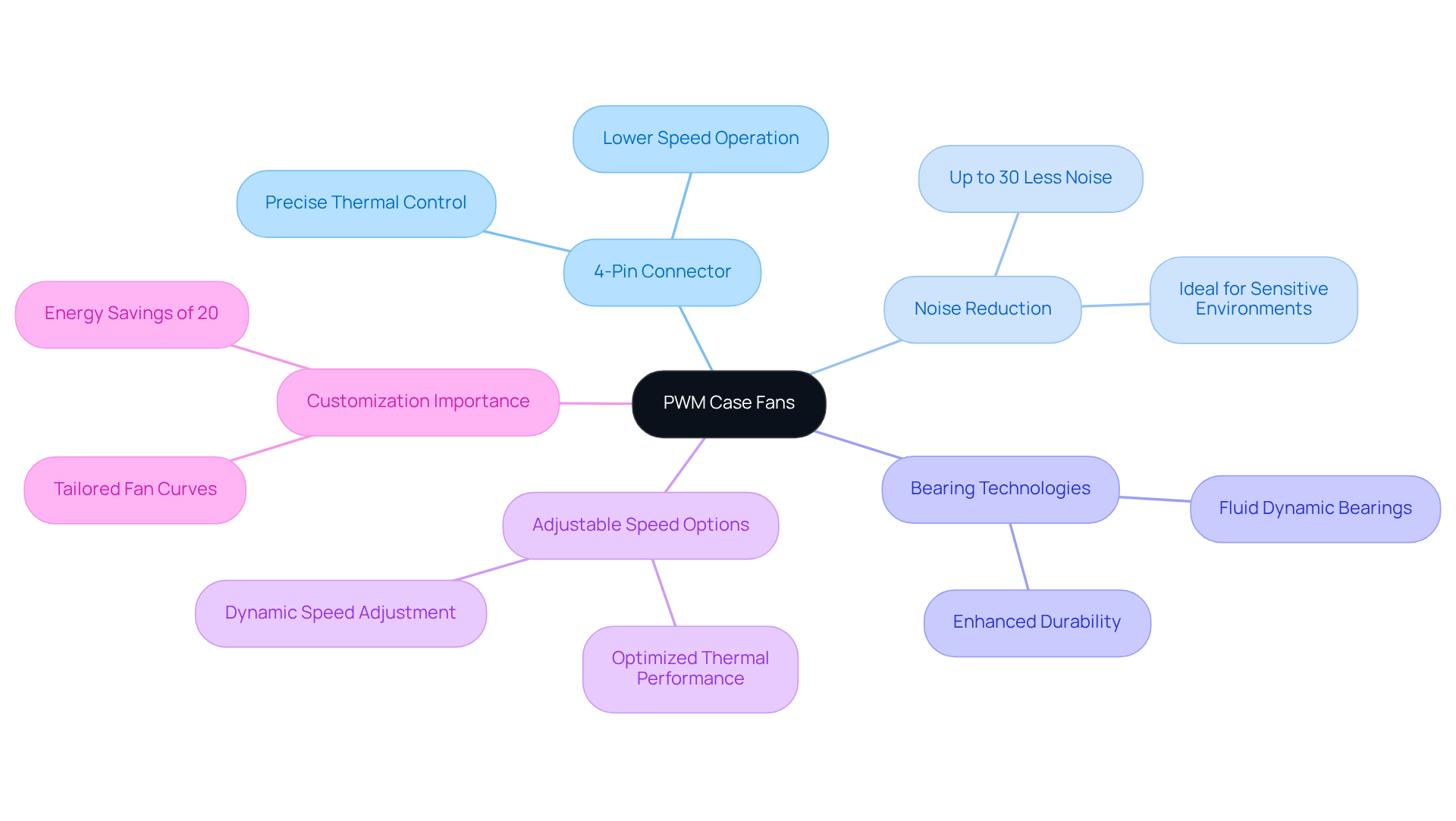
s are distinguished by several critical characteristics that set them apart from conventional models. Primarily, they employ a 4-pin connector for the PWM case fan, which features an extra pin assigned to the PWM signal, allowing for precise control that adjusts to thermal requirements. This capability enables a PWM case fan to function more quietly than its DC equivalents, as it can lower speeds when cooling is less essential, leading to a —up to 30% compared to traditional systems.
Moreover, many PWM case fans are equipped with , such as fluid dynamic bearings, which not only enhance durability but also contribute to quieter operation. These innovations result in extended lifespans for the devices, making them a dependable option for various applications in the electronics sector.
Furthermore, a PWM case fan provides adjustable speed options, enabling engineers to optimize thermal performance based on specific needs. This flexibility is essential in enhancing in various settings, from data centers to consumer electronics, where effective temperature regulation is vital. , as the world’s largest producer of standard and custom air-movers, offers an extensive range of DC input Tube Axial devices and Centrifugal Blowers, available in sizes varying from 15 to 280mm and 15 to 225mm respectively, ensuring that engineers have access to innovative cooling solutions customized to their requirements.
Customizing PWM case fan curves is of utmost importance, as it significantly enhances airflow and efficiency while reducing energy consumption. The integration of PWM case fans is projected to grow, driven by the increasing demand for , with studies indicating that transitioning to PWM technology can yield an estimated 20% reduction in overall energy usage.
Conclusion
PWM case fans signify a pivotal advancement in thermal management technology, delivering dynamic performance adjustments that traditional cooling solutions cannot match. By leveraging Pulse Width Modulation, these fans enhance energy efficiency, minimize noise levels, and optimize cooling in response to real-time temperature demands. Their adaptability to varying conditions positions them as an essential element in modern electronic systems, particularly within high-performance environments.
Key insights regarding the functionality and benefits of PWM case fans have been highlighted throughout the article. Their superior speed regulation capabilities facilitate quieter operation and reduced power consumption, while playing a critical role in maintaining optimal temperatures across diverse applications, from personal computers to data centers. Furthermore, the evolution of PWM technology underscores a growing trend toward its adoption, propelled by the increasing demand for efficient cooling solutions in compact electronic devices.
The significance of PWM case fans transcends mere functionality; they represent a shift toward smarter, more efficient thermal management in electronics. As engineers and designers increasingly embrace this technology, the imperative is clear: prioritize the integration of PWM case fans in future designs to ensure enhanced performance, reliability, and sustainability in electronic systems. Adopting PWM technology not only addresses current cooling challenges but also lays the groundwork for advancements in energy efficiency and noise reduction across the industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are PWM case fans?
PWM case fans, or Pulse Width Modulation case fans, are advanced cooling solutions used primarily in electronic devices, especially computers, that dynamically adjust their performance based on temperature demands.
How do PWM case fans work?
PWM case fans use a 4-pin connector, where one pin transmits a PWM signal to the fan. This signal allows for precise control, enabling the fan to adjust its speed rapidly in response to real-time temperature requirements.
What are the benefits of using PWM case fans?
The benefits include improved thermal efficiency, reduced noise levels (as fans can operate quietly at lower speeds), and optimized electricity consumption based on cooling needs, which is crucial for high-performance computing applications.
How much can PWM case fans reduce their speed?
PWM case fans can reduce their speed by up to 40% when temperature demands are low, and they can achieve minimum speeds below 20% of their rated capacity.
Why are PWM case fans suitable for noise-sensitive environments?
PWM case fans are suitable for noise-sensitive environments because they can operate at reduced RPMs, significantly lowering noise levels during low-temperature conditions.
Who is a major manufacturer of PWM case fans?
Gagner-Toomey Associates is the world’s largest producer of standard and custom air-movers, offering a comprehensive portfolio of PWM case fans tailored for various applications across electronics, automotive, and industrial sectors.

